Abstract
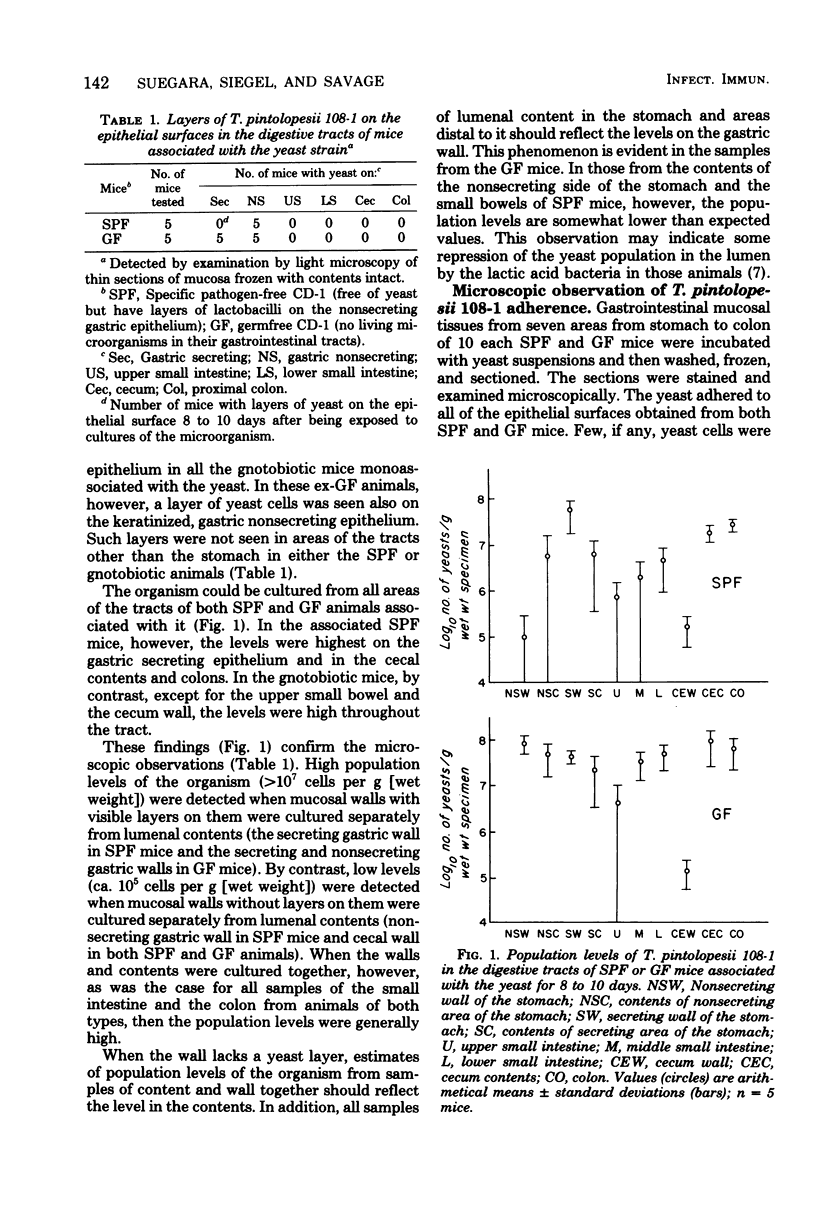
Torulopsis pintolopesii is a yeast indigenous to the gastrointestinal tracts of conventional mice and rats from many colonies. In such natively colonized animals, the organism forms layers on the surface of the epithelium in the secreting portion of the stomach and can be cultured from all areas of the gastrointestinal tract. When given in water or food to germfree mice or specific pathogen-free mice possessing an indigenous microbiota free of yeast, T. pintolopesii also can be cultured from all areas of the tract at population levels ranging from 10(5) to 10(8) cells per g (wet weight). Likewise, as in its native hosts, the organism forms layers on gastric surfaces in the associated animals. The layers form on the secreting surface in both the specific pathogen-free and monoassociated ex-germfree mice. In the latter animal, however, a layer of yeast also forms on the nonsecreting gastric surface. In tests of its capacity to adhere to gastrointestinal surfaces in vitro, the organism adheres to epithelia from all areas of the mouse tract. These findings support an hypothesis that the capacity of T. pintolopesii to adhere to epithelial surfaces may be only one determinant influencing it to form layers on the gastric secreting surface in its native hosts.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Artwohl J. E., Savage D. C. Determinants in microbial colonization of the murine gastrointestinal tract: pH, temperature, and energy-yielding metabolism of Torulopsis pintolopesii. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Apr;37(4):697–703. doi: 10.1128/aem.37.4.697-703.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbons R. J., Houte J. V. Bacterial adherence in oral microbial ecology. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1975;29:19–44. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.29.100175.000315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones G. W., Rutter J. M. Role of the K88 antigen in the pathogenesis of neonatal diarrhea caused by Escherichia coli in piglets. Infect Immun. 1972 Dec;6(6):918–927. doi: 10.1128/iai.6.6.918-927.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savage D. C., Blumershine R. V. Surface-surface associations in microbial communities populating epithelial habitats in the murine gastrointestinal ecosystem: scanning electron microscopy. Infect Immun. 1974 Jul;10(1):240–250. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.1.240-250.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savage D. C., Dubos R. J. Localization of indigenous yeast in the murine stomach. J Bacteriol. 1967 Dec;94(6):1811–1816. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.6.1811-1816.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savage D. C., Dubos R., Schaedler R. W. The gastrointestinal epithelium and its autochthonous bacterial flora. J Exp Med. 1968 Jan 1;127(1):67–76. doi: 10.1084/jem.127.1.67. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savage D. C. Factors involved in colonization of the gut epithelial surface. Am J Clin Nutr. 1978 Oct;31(10 Suppl):S131–S135. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/31.10.S131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savage D. C. Microbial ecology of the gastrointestinal tract. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1977;31:107–133. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.31.100177.000543. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savage D. C. Microbial interference between indigenous yeast and lactobacilli in the rodent stomach. J Bacteriol. 1969 Jun;98(3):1278–1283. doi: 10.1128/jb.98.3.1278-1283.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. Microbial surfaces in relation to pathogenicity. Bacteriol Rev. 1977 Jun;41(2):475–500. doi: 10.1128/br.41.2.475-500.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suegara N., Morotomi M., Watanabe T., Kawal Y., Mutai M. Behavior of microflora in the rat stomach: adhesion of lactobacilli to the keratinized epithelial cells of the rat stomach in vitro. Infect Immun. 1975 Jul;12(1):173–179. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.1.173-179.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



