Abstract
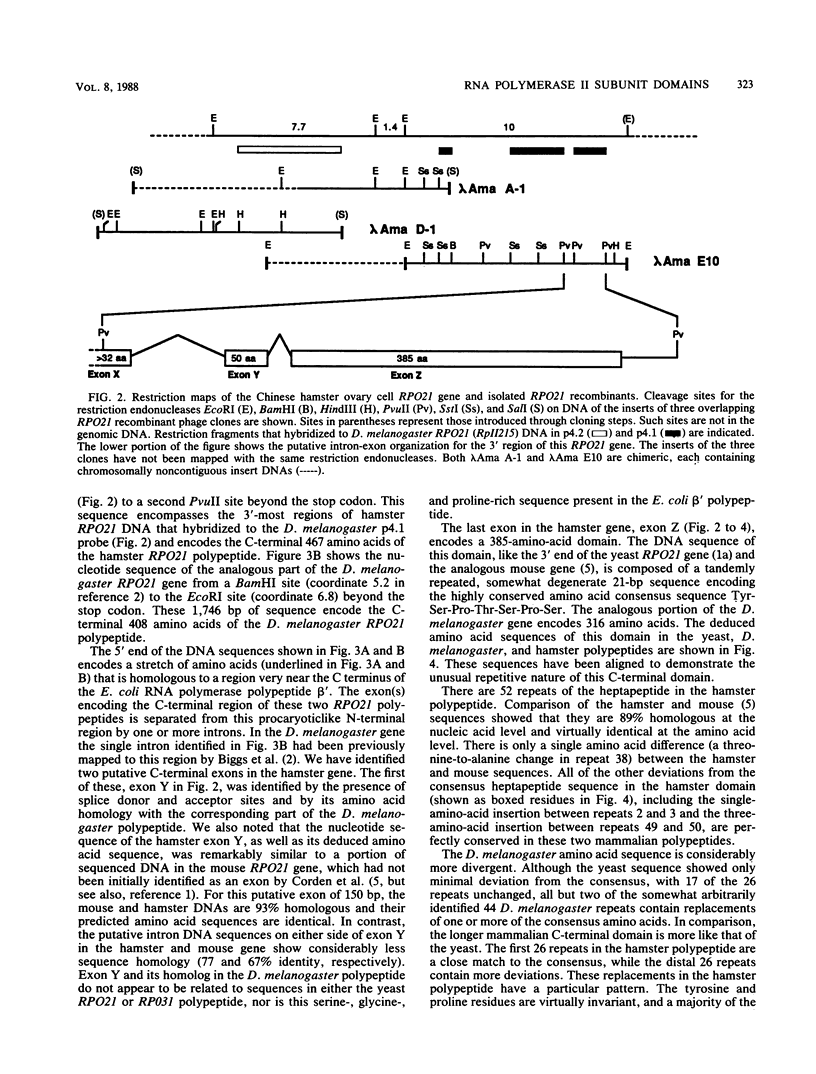
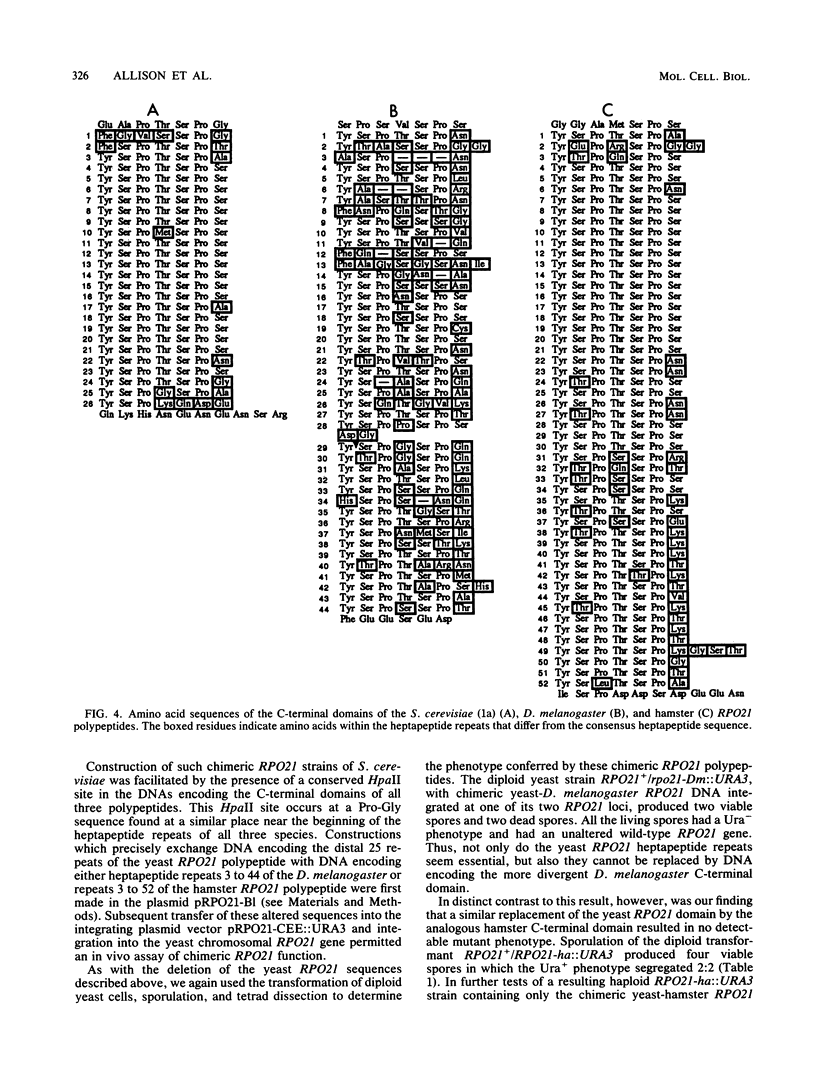
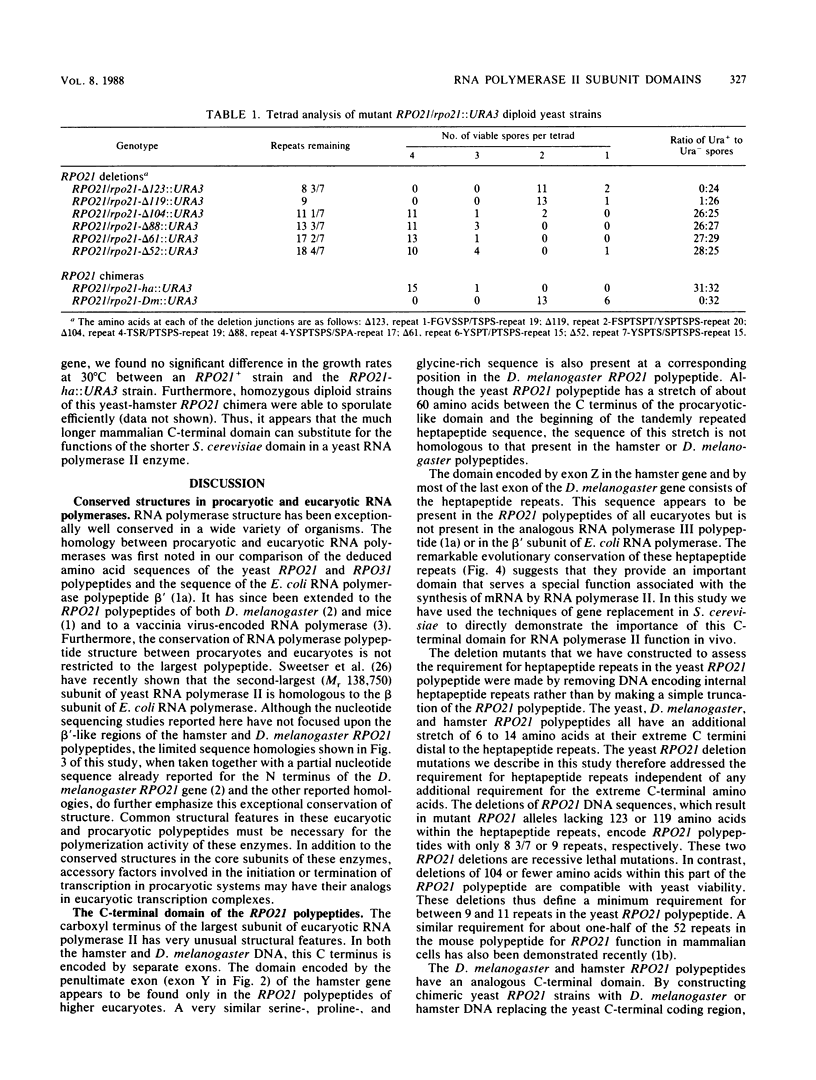
Using DNA encoding the largest subunit of Drosophila melanogaster RNA polymerase II, we isolated the homologous hamster RPO21 gene. Nucleotide sequencing of both the hamster and D. melanogaster RPO21 DNAs confirmed that the RPO21 polypeptides of these two species, like the Saccharomyces cerevisiae RPO21 polypeptide, contain both an N-terminal region homologous to the Escherichia coli RNA polymerase subunit beta' and a unique polymerase II-specific C-terminal domain. This C-terminal domain, encoded by separate exons in the D. melanogaster and hamster genes, consists of a tandemly repeated heptapeptide sequence. By constructing a series of deletions in DNA encoding the 26 heptapeptide repeats normally present in the S. cerevisiae RPO21 polypeptide, we have established that a minimum of between 9 and 11 repeats is necessary for RPO21 function in yeast cells. Replacement of the yeast RPO21 heptapeptide repeats by the longer hamster repetitive domain resulted in viable yeast cells with no detectable mutant phenotype, while a similar replacement of the yeast repeats by the more divergent D. melanogaster repeats was a recessive lethal mutation. We suggest that this novel repetitive domain is essential for proper initiation of transcription by RNA polymerase II and that it may mediate the functions of TATA boxes, upstream activating sequences, and enhancers.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahearn J. M., Jr, Bartolomei M. S., West M. L., Cisek L. J., Corden J. L. Cloning and sequence analysis of the mouse genomic locus encoding the largest subunit of RNA polymerase II. J Biol Chem. 1987 Aug 5;262(22):10695–10705. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allison L. A., Moyle M., Shales M., Ingles C. J. Extensive homology among the largest subunits of eukaryotic and prokaryotic RNA polymerases. Cell. 1985 Sep;42(2):599–610. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90117-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartolomei M. S., Halden N. F., Cullen C. R., Corden J. L. Genetic analysis of the repetitive carboxyl-terminal domain of the largest subunit of mouse RNA polymerase II. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jan;8(1):330–339. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.1.330. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biggs J., Searles L. L., Greenleaf A. L. Structure of the eukaryotic transcription apparatus: features of the gene for the largest subunit of Drosophila RNA polymerase II. Cell. 1985 Sep;42(2):611–621. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90118-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broyles S. S., Moss B. Homology between RNA polymerases of poxviruses, prokaryotes, and eukaryotes: nucleotide sequence and transcriptional analysis of vaccinia virus genes encoding 147-kDa and 22-kDa subunits. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(10):3141–3145. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.10.3141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cho K. W., Khalili K., Zandomeni R., Weinmann R. The gene encoding the large subunit of human RNA polymerase II. J Biol Chem. 1985 Dec 5;260(28):15204–15210. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corden J. L., Cadena D. L., Ahearn J. M., Jr, Dahmus M. E. A unique structure at the carboxyl terminus of the largest subunit of eukaryotic RNA polymerase II. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(23):7934–7938. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.23.7934. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahmus M. E., Kedinger C. Transcription of adenovirus-2 major late promoter inhibited by monoclonal antibody directed against RNA polymerases IIO and IIA. J Biol Chem. 1983 Feb 25;258(4):2303–2307. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dente L., Cesareni G., Cortese R. pEMBL: a new family of single stranded plasmids. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 25;11(6):1645–1655. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.6.1645. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frischauf A. M., Lehrach H., Poustka A., Murray N. Lambda replacement vectors carrying polylinker sequences. J Mol Biol. 1983 Nov 15;170(4):827–842. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80190-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fristensky B., Lis J., Wu R. Portable microcomputer software for nucleotide sequence analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Oct 25;10(20):6451–6463. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.20.6451. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenleaf A. L. Amanitin-resistant RNA polymerase II mutations are in the enzyme's largest subunit. J Biol Chem. 1983 Nov 25;258(22):13403–13406. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenleaf A. L., Weeks J. R., Voelker R. A., Ohnishi S., Dickson B. Genetic and biochemical characterization of mutants at an RNA polymerase II locus in D. melanogaster. Cell. 1980 Oct;21(3):785–792. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90441-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henikoff S. Unidirectional digestion with exonuclease III creates targeted breakpoints for DNA sequencing. Gene. 1984 Jun;28(3):351–359. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90153-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Himmelfarb H. J., Simpson E. M., Friesen J. D. Isolation and characterization of temperature-sensitive RNA polymerase II mutants of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jun;7(6):2155–2164. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.6.2155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hope I. A., Struhl K. Functional dissection of a eukaryotic transcriptional activator protein, GCN4 of yeast. Cell. 1986 Sep 12;46(6):885–894. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90070-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingles C. J., Biggs J., Wong J. K., Weeks J. R., Greenleaf A. L. Identification of a structural gene for a RNA polymerase II polypeptide in Drosophila melanogaster and mammalian species. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(11):3396–3400. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.11.3396. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingles C. J., Himmelfarb H. J., Shales M., Greenleaf A. L., Friesen J. D. Identification, molecular cloning, and mutagenesis of Saccharomyces cerevisiae RNA polymerase genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):2157–2161. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.2157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingles C. J. Temperature-sensitive RNA polymerase II mutations in Chinese hamster ovary cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jan;75(1):405–409. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.1.405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ma J., Ptashne M. Deletion analysis of GAL4 defines two transcriptional activating segments. Cell. 1987 Mar 13;48(5):847–853. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90081-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mortin M. A., Lefevre G., Jr An RNA polymerase II mutation in Drosophila melanogaster that mimics ultrabithorax. Chromosoma. 1981;82(2):237–247. doi: 10.1007/BF00286108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moyle M., Hofmann T., Ingles C. J. The RPO31 gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae encodes the largest subunit of RNA polymerase III. Biochem Cell Biol. 1986 Aug;64(8):717–721. doi: 10.1139/o86-098. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nonet M., Sweetser D., Young R. A. Functional redundancy and structural polymorphism in the large subunit of RNA polymerase II. Cell. 1987 Sep 11;50(6):909–915. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90517-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orr-Weaver T. L., Szostak J. W., Rothstein R. J. Yeast transformation: a model system for the study of recombination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Oct;78(10):6354–6358. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.10.6354. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petko L., Lindquist S. Hsp26 is not required for growth at high temperatures, nor for thermotolerance, spore development, or germination. Cell. 1986 Jun 20;45(6):885–894. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90563-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Searles L. L., Jokerst R. S., Bingham P. M., Voelker R. A., Greenleaf A. L. Molecular cloning of sequences from a Drosophila RNA polymerase II locus by P element transposon tagging. Cell. 1982 Dec;31(3 Pt 2):585–592. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90314-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sweetser D., Nonet M., Young R. A. Prokaryotic and eukaryotic RNA polymerases have homologous core subunits. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Mar;84(5):1192–1196. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.5.1192. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



