FIGURE 1.
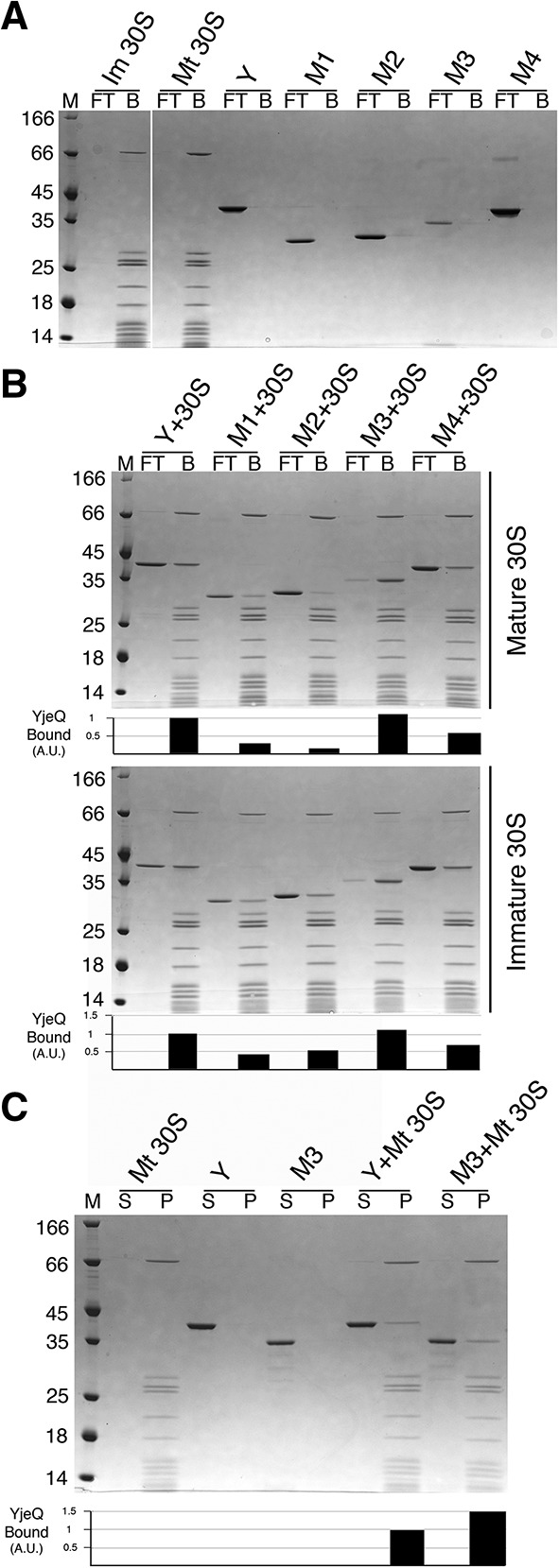
Binding of YjeQ carboxy-terminal variants to the mature and immature 30S subunits. (A,B) Ability of YjeQ (Y) and YjeQ variants (M1, M2, M3, and M4) to bind to the mature (Mt) and immature (Im) 30S subunits analyzed by filtration assays. Coomassie blue stained SDS-PAGE in A contains the controls for the experiment consistent in reactions containing either YjeQ (full-length or variants) or 30S subunits (mature or immature) by themselves. Reactions containing a mixture of YjeQ protein and ribosomal particles contained a fivefold molar excess of protein. Assembly mixtures were incubated for 15 min at 16°C in the presence of 1 mM GMP-PNP. Following incubation, the reactions were passed through a 100 kDa cut-off filter using centrifugation. The unbound protein was captured in the flow-through (FT) and the protein bound to the ribosomal particles (B) was retained by the filter and resuspended by an equal volume of buffer. The molecular weight marker (M) is in kDa. The flow-through and bound portions from these assays were loaded into 4%–12% bis–tris polyacrylamide gels and resolved using SDS-PAGE. (C) Pelleting assay of YjeQ M3 variant with the mature 30S subunit. A fivefold excess of YjeQ M3 was incubated with mature 30S subunits for 15 min at 16°C. Following the incubation, reactions were laid over a sucrose cushion and subjected to ultracentrifugation. Proteins that were unbound were collected in the supernatant (S), while proteins that bound to the 30S particle were found in the pellet (P). The molecular weight (M) is in kDa. The pellet and supernatant were resolved by 4%–12% bis–tris SDS-PAGE and stained with Coomassie blue. The bar diagrams under the gels in B and C indicate the binding of the YjeQ variants to the 30S subunits with respect to wild-type YjeQ (set as 1).
