Abstract
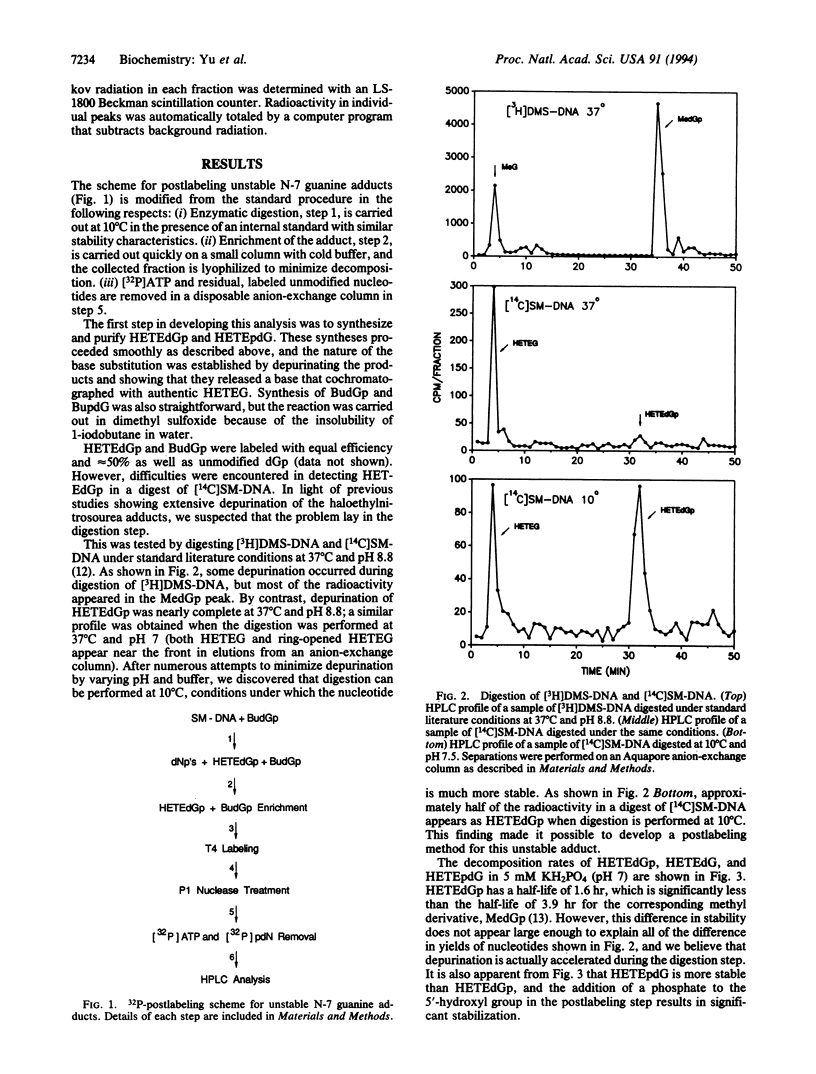
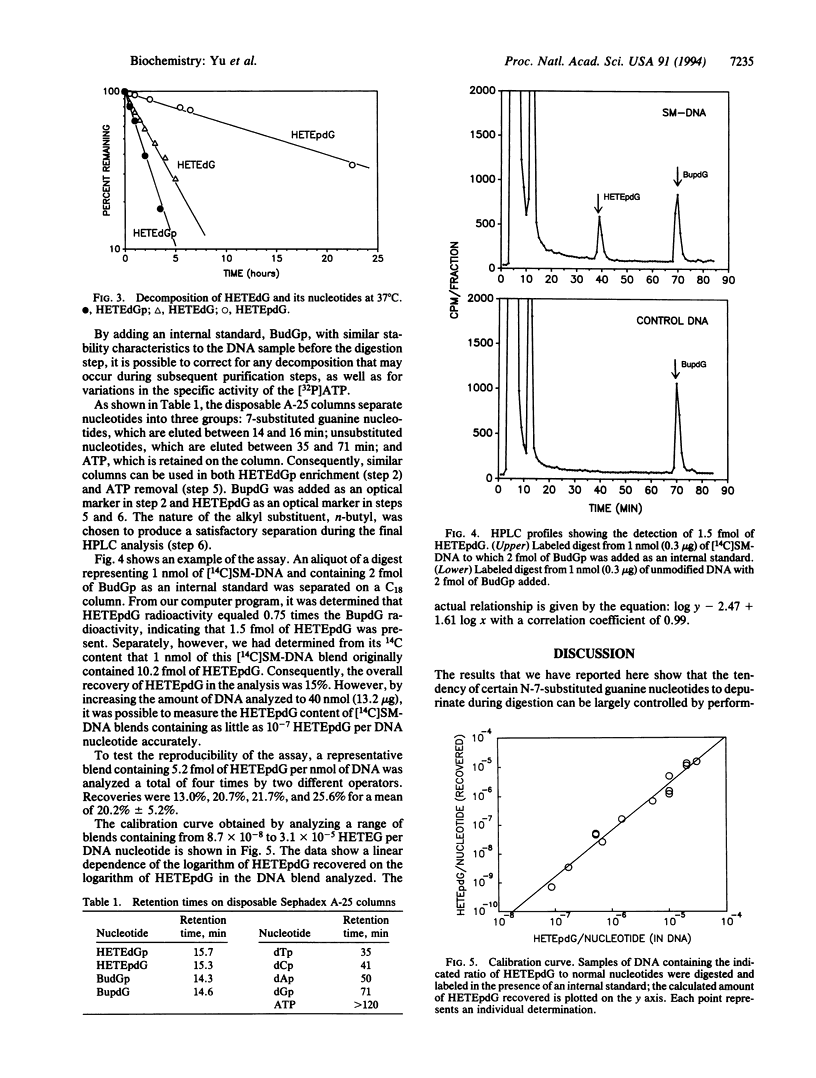
Many antitumor agents, including the mustards, form N-7 deoxyguanosine adducts in DNA that are difficult to quantitate by the 32P-postlabeling procedure because of their instability. We have developed a method that is successful for the analysis of such adducts using, as a prototype mustard, 14C-labeled bis(2-chloroethyl)sulfide. This agent forms the unstable product 7-hydroxyethylthioethyldeoxyguanosine in DNA. By performing enzymatic digestions to 3'-deoxynucleotides at 10 degrees C, including a second N-7-substituted guanine deoxynucleotide as an internal standard, removing most of the unmodified nucleotides and [32P]ATP on disposable anion columns, and measuring the labeled products after separation on a C18 column, we are able to detect 1 unstable N-7 deoxyguanosine adduct in 10(7) normal nucleotides with good precision.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brookes P., Lawley P. D. The reaction of mustard gas with nucleic acids in vitro and in vivo. Biochem J. 1960 Dec;77(3):478–484. doi: 10.1042/bj0770478. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chetsanga C. J., Polidori G., Mainwaring M. Analysis and excision of ring-opened phosphoramide mustard-deoxyguanine adducts in DNA. Cancer Res. 1982 Jul;42(7):2616–2621. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gombar C. T., Tong W. P., Ludlum D. B. Mechanism of action of the nitrosoureas--IV. Reactions of bis-chloroethyl nitrosourea and chloroethyl cyclohexyl nitrosourea with deoxyribonucleic acid. Biochem Pharmacol. 1980 Oct 1;29(19):2639–2643. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(80)90079-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gupta R. C., Reddy M. V., Randerath K. 32P-postlabeling analysis of non-radioactive aromatic carcinogen--DNA adducts. Carcinogenesis. 1982;3(9):1081–1092. doi: 10.1093/carcin/3.9.1081. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris C. C. Chemical and physical carcinogenesis: advances and perspectives for the 1990s. Cancer Res. 1991 Sep 15;51(18 Suppl):5023s–5044s. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemminki K., Alhonen-Raatesalmi A., Koivisto P., Vodicka P. Synthesis and stability of 2'-deoxyguanosine 3'-monophosphate adducts of dimethyl sulfate, ethylene oxide and styrene oxide. Chem Biol Interact. 1990;75(3):281–292. doi: 10.1016/0009-2797(90)90071-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadlubar F. F. Detection of human DNA-carcinogen adducts. Nature. 1992 Nov 12;360(6400):189–189. doi: 10.1038/360189a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kallama S., Hemminki K. Alkylation of guanosine by phosphoramide mustard, chloromethine hydrochloride and chlorambucil. Acta Pharmacol Toxicol (Copenh) 1984 Mar;54(3):214–220. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0773.1984.tb01920.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato S., Petruzzelli S., Bowman E. D., Turteltaub K. W., Blomeke B., Weston A., Shields P. G. 7-Alkyldeoxyguanosine adduct detection by two-step HPLC and the 32P-postlabeling assay. Carcinogenesis. 1993 Apr;14(4):545–550. doi: 10.1093/carcin/14.4.545. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ludlum D. B., Austin-Ritchie P., Hagopian M., Niu T. Q., Yu D. Detection of sulfur mustard-induced DNA modifications. Chem Biol Interact. 1994 Apr;91(1):39–49. doi: 10.1016/0009-2797(94)90005-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matijasevic Z., Bodell W. J., Ludlum D. B. 3-Methyladenine DNA glycosylase activity in a glial cell line sensitive to the haloethylnitrosoureas in comparison with a resistant cell line. Cancer Res. 1991 Mar 1;51(5):1568–1570. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mehta J. R., Przybylski M., Ludlum D. B. Alkylation of guanosine and deoxyguanosine by phosphoramide mustard. Cancer Res. 1980 Nov;40(11):4183–4186. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mustonen R., Försti A., Hietanen P., Hemminki K. Measurement by 32P-postlabelling of 7-methylguanine levels in white blood cell DNA of healthy individuals and cancer patients treated with dacarbazine and procarbazine. Human data and method development for 7-alkylguanines. Carcinogenesis. 1991 Aug;12(8):1423–1431. doi: 10.1093/carcin/12.8.1423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mustonen R., Schoket B., Hemminki K. Smoking-related DNA adducts: 32P-postlabeling analysis of 7-methylguanine in human bronchial and lymphocyte DNA. Carcinogenesis. 1993 Jan;14(1):151–154. doi: 10.1093/carcin/14.1.151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller N., Eisenbrand G. The influence of N7 substituents on the stability of N7-alkylated guanosines. Chem Biol Interact. 1985 Feb-Apr;53(1-2):173–181. doi: 10.1016/s0009-2797(85)80094-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Randerath K., Li D., Nath R., Randerath E. Exogenous and endogenous DNA modifications as monitored by 32P-postlabeling: relationships to cancer and aging. Exp Gerontol. 1992 Sep-Dec;27(5-6):533–549. doi: 10.1016/0531-5565(92)90008-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Randerath K., Reddy M. V., Gupta R. C. 32P-labeling test for DNA damage. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Oct;78(10):6126–6129. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.10.6126. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Routledge M. N., Garner R. C., Kirsch-Volders M. Comparison of 32P-postlabelling and cytogenetic analysis of human blood treated in vitro with melphalan. Mutagenesis. 1992 Sep;7(5):329–333. doi: 10.1093/mutage/7.5.329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shields P. G., Povey A. C., Wilson V. L., Weston A., Harris C. C. Combined high-performance liquid chromatography/32P-postlabeling assay of N7-methyldeoxyguanosine. Cancer Res. 1990 Oct 15;50(20):6580–6584. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shuker D. E. Nucleic acid-carcinogen adducts in human dosimetry. Arch Toxicol Suppl. 1989;13:55–65. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-74117-3_6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wogan G. N., Gorelick N. J. Chemical and biochemical dosimetry of exposure to genotoxic chemicals. Environ Health Perspect. 1985 Oct;62:5–18. doi: 10.1289/ehp.85625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



