Abstract
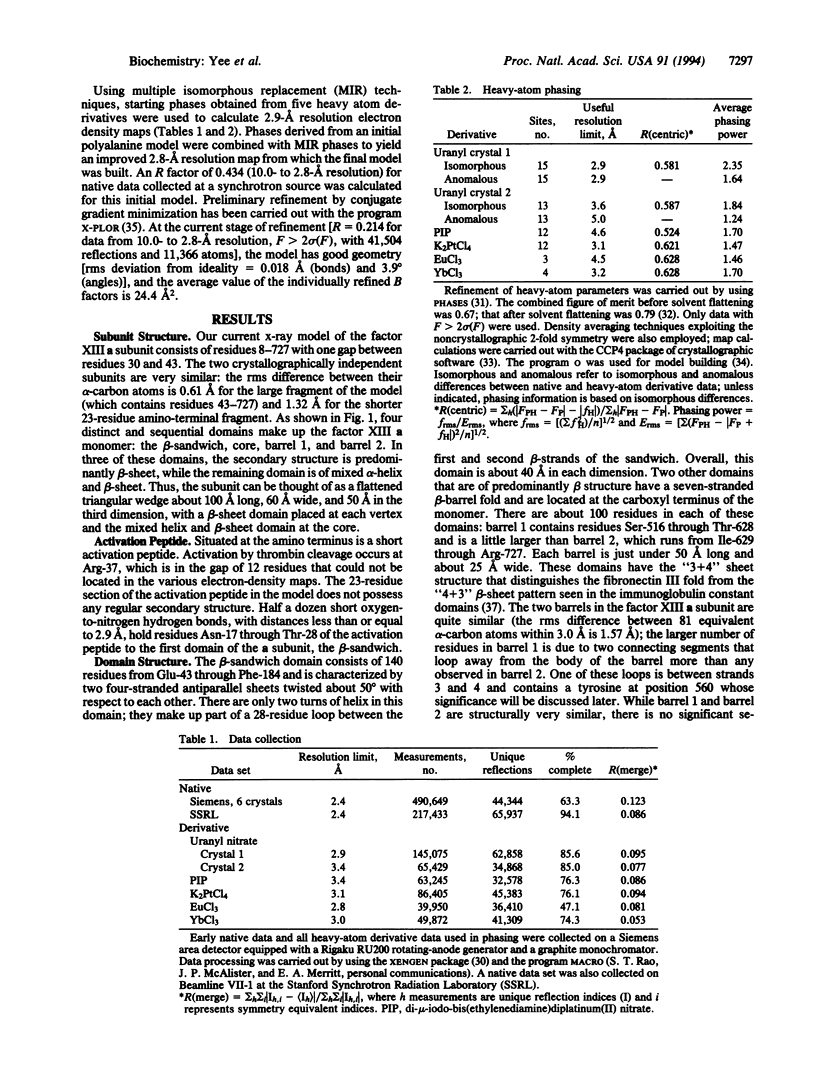
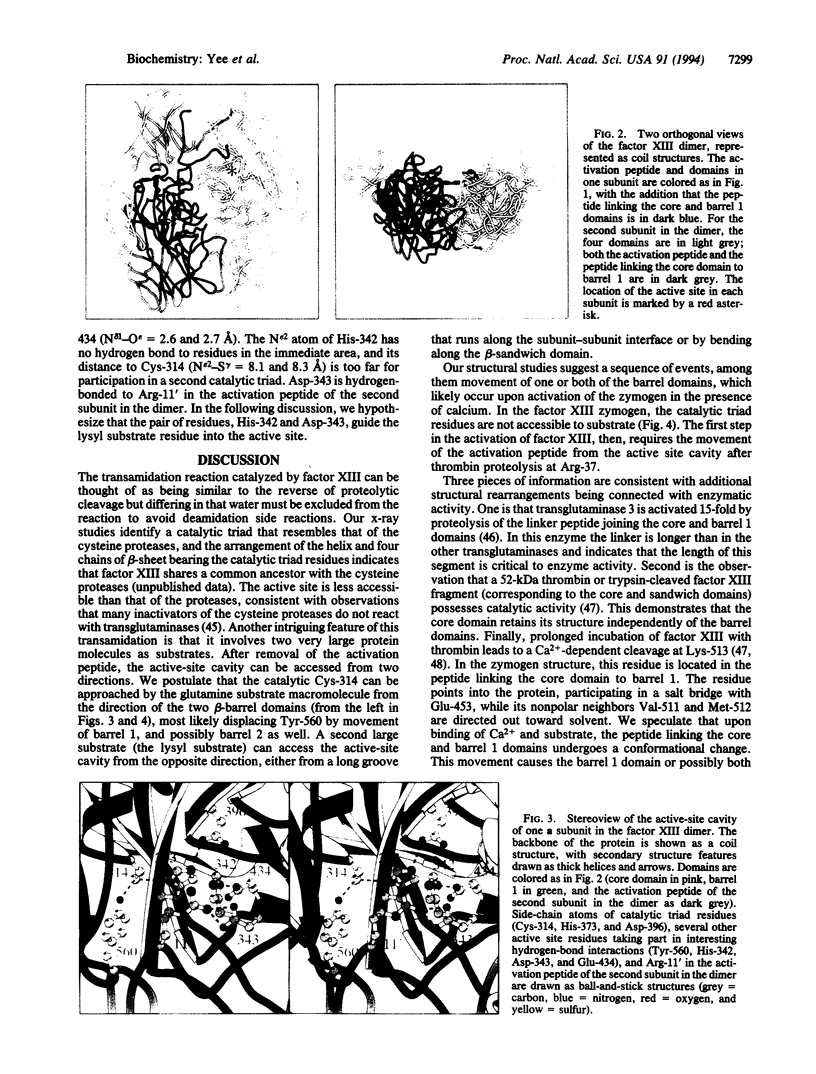
Mechanical stability in many biological materials is provided by the crosslinking of large structural proteins with gamma-glutamyl-epsilon-lysyl amide bonds. The three-dimensional structure of human recombinant factor XIII (EC 2.3.2.13 zymogen; protein-glutamine:amine gamma-glutamyltransferase a chain), a transglutaminase zymogen, has been solved at 2.8-A resolution by x-ray crystallography. This structure shows that each chain of the homodimeric protein is folded into four sequential domains. A catalytic triad reminiscent of that observed in cysteine proteases has been identified in the core domain. The amino-terminal activation peptide of each subunit crosses the dimer interface and partially occludes the opening of the catalytic cavity in the second subunit, preventing substrate binding to the zymogen. A proposal for the mechanism of activation by thrombin and calcium is made that details the structural events leading to active factor XIIIa'.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adány R., Szegedi A., Ablin R. J., Muszbek L. Fibrinolysis resistant fibrin deposits in lymph nodes with Hodgkin's disease. Thromb Haemost. 1988 Oct 31;60(2):293–297. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bale M. D., Mosher D. F. Thrombospondin is a substrate for blood coagulation factor XIIIa. Biochemistry. 1986 Sep 23;25(19):5667–5673. doi: 10.1021/bi00367a048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballerini G., Guerra S., Rodeghiero F., Castaman G. A contribution to the pathology of acquired plasma factor XIII deficiency. Semin Thromb Hemost. 1985 Oct;11(4):357–361. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-1004394. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barry E. L., Mosher D. F. Factor XIIIa-mediated cross-linking of fibronectin in fibroblast cell layers. Cross-linking of cellular and plasma fibronectin and of amino-terminal fibronectin fragments. J Biol Chem. 1989 Mar 5;264(7):4179–4185. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop P. D., Lasser G. W., Le Trong I., Stenkamp R. E., Teller D. C. Human recombinant factor XIII from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Crystallization and preliminary x-ray data. J Biol Chem. 1990 Aug 15;265(23):13888–13889. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop P. D., Teller D. C., Smith R. A., Lasser G. W., Gilbert T., Seale R. L. Expression, purification, and characterization of human factor XIII in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biochemistry. 1990 Feb 20;29(7):1861–1869. doi: 10.1021/bi00459a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borth W., Chang V., Bishop P., Harpel P. C. Lipoprotein (a) is a substrate for factor XIIIa and tissue transglutaminase. J Biol Chem. 1991 Sep 25;266(27):18149–18153. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brünger A. T., Kuriyan J., Karplus M. Crystallographic R factor refinement by molecular dynamics. Science. 1987 Jan 23;235(4787):458–460. doi: 10.1126/science.235.4787.458. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costantini V., Zacharski L. R., Memoli V. A., Kisiel W., Kudryk B. J., Rousseau S. M. Fibrinogen deposition without thrombin generation in primary human breast cancer tissue. Cancer Res. 1991 Jan 1;51(1):349–353. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doyle P. M., Harris C. J., Carter K. R., Simpkin D. S., Bailey-Smith P., Stone D., Russell L., Blackwell G. J. Peptides incorporating electrophilic glutamine analogues as potential transglutaminase inhibitors. Biochem Soc Trans. 1990 Dec;18(6):1318–1320. doi: 10.1042/bst0181318. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folk J. E. Mechanism and basis for specificity of transglutaminase-catalyzed epsilon-(gamma-glutamyl) lysine bond formation. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1983;54:1–56. doi: 10.1002/9780470122990.ch1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francis C. W., Connaghan D. G., Scott W. L., Marder V. J. Increased plasma concentration of cross-linked fibrin polymers in acute myocardial infarction. Circulation. 1987 Jun;75(6):1170–1177. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.75.6.1170. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukui H., Kamitsuji H., Nagao T., Yamada K., Akatsuka J., Inagaki M., Shike S., Kobayashi Y., Yoshioka K., Maki S. Clinical evaluation of a pasteurized factor XIII concentrate administration in Henoch-Schönlein purpura. Japanese Pediatric Group. Thromb Res. 1989 Dec 15;56(6):667–675. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(89)90284-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gladner J. A., Nossal R. Effects of crosslinking on the rigidity and proteolytic susceptibility of human fibrin clots. Thromb Res. 1983 May 1;30(3):273–288. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(83)90081-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg C. S., Birckbichler P. J., Rice R. H. Transglutaminases: multifunctional cross-linking enzymes that stabilize tissues. FASEB J. 1991 Dec;5(15):3071–3077. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.5.15.1683845. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg C. S., Enghild J. J., Mary A., Dobson J. V., Achyuthan K. E. Isolation of a fibrin-binding fragment from blood coagulation factor XIII capable of cross-linking fibrin(ogen). Biochem J. 1988 Dec 15;256(3):1013–1019. doi: 10.1042/bj2561013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gregoret L. M., Rader S. D., Fletterick R. J., Cohen F. E. Hydrogen bonds involving sulfur atoms in proteins. Proteins. 1991;9(2):99–107. doi: 10.1002/prot.340090204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hada M., Kaminski M., Bockenstedt P., McDonagh J. Covalent crosslinking of von Willebrand factor to fibrin. Blood. 1986 Jul;68(1):95–101. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen M. S. Fibronectin and coagulation factor XIII increases blood platelet adhesion to fibrin. Thromb Res. 1984 Jun 15;34(6):551–556. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(84)90259-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ichinose A., Hendrickson L. E., Fujikawa K., Davie E. W. Amino acid sequence of the a subunit of human factor XIII. Biochemistry. 1986 Nov 4;25(22):6900–6906. doi: 10.1021/bi00370a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones T. A., Zou J. Y., Cowan S. W., Kjeldgaard M. Improved methods for building protein models in electron density maps and the location of errors in these models. Acta Crystallogr A. 1991 Mar 1;47(Pt 2):110–119. doi: 10.1107/s0108767390010224. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim I. G., Gorman J. J., Park S. C., Chung S. I., Steinert P. M. The deduced sequence of the novel protransglutaminase E (TGase3) of human and mouse. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jun 15;268(17):12682–12690. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitchens C. S., Newcomb T. F. Factor XIII. Medicine (Baltimore) 1979 Nov;58(6):413–429. doi: 10.1097/00005792-197911000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kram H. B., Nathan R. C., Stafford F. J., Fleming A. W., Shoemaker W. C. Fibrin glue achieves hemostasis in patients with coagulation disorders. Arch Surg. 1989 Mar;124(3):385–387. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1989.01410030135023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kłoczko J., Wojtukiewicz M., Bielawiec M., Zarzycka B., Kinalska I. Plasma factor XIII and some other haemostasis parameters in patients with diabetic angiopathy. Acta Haematol. 1986;76(2-3):81–85. doi: 10.1159/000206026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kłoczko J., Wojtukiewicz M., Bielawiec M., Zuch A. Alterations of haemostasis parameters with special reference to fibrin stabilization, factor XIII and fibronectin in patients with obliterative atherosclerosis. Thromb Res. 1988 Sep 15;51(6):575–581. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(88)90141-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leahy D. J., Hendrickson W. A., Aukhil I., Erickson H. P. Structure of a fibronectin type III domain from tenascin phased by MAD analysis of the selenomethionyl protein. Science. 1992 Nov 6;258(5084):987–991. doi: 10.1126/science.1279805. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorand J. B., Pilkington T. R., Lorand L. Inhibitors of fibrin cross-linking: relevance for thrombolysis. Nature. 1966 Jun 18;210(5042):1273–1274. doi: 10.1038/2101273a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorenz R., Heinmüller M., Classen M., Tornieporth N., Gain T. Substitution of factor XIII: a therapeutic approach to ulcerative colitis. Haemostasis. 1991;21(1):5–9. doi: 10.1159/000216195. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mangani S., Håkansson K. Crystallographic studies of the binding of protonated and unprotonated inhibitors to carbonic anhydrase using hydrogen sulphide and nitrate anions. Eur J Biochem. 1992 Dec 15;210(3):867–871. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1992.tb17490.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paye M., Nusgens B., Lapière C. M. Factor XIII of blood coagulation decreases the susceptibility of collagen precursors to proteolysis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Apr 9;1073(3):437–441. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(91)90212-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penneys N. S., Smith K. J., Nemeth A. J. Factor XIIIa in the hamartomas of tuberous sclerosis. J Dermatol Sci. 1991 Jan;2(1):50–54. doi: 10.1016/0923-1811(91)90042-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sane D. C., Moser T. L., Pippen A. M., Parker C. J., Achyuthan K. E., Greenberg C. S. Vitronectin is a substrate for transglutaminases. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Nov 30;157(1):115–120. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)80020-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen L., Lorand L. Contribution of fibrin stabilization to clot strength. Supplementation of factor XIII-deficient plasma with the purified zymogen. J Clin Invest. 1983 May;71(5):1336–1341. doi: 10.1172/JCI110885. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi N., Takahashi Y., Putnam F. W. Primary structure of blood coagulation factor XIIIa (fibrinoligase, transglutaminase) from human placenta. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(21):8019–8023. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.21.8019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamaki T., Aoki N. Cross-linking of alpha 2-plasmin inhibitor to fibrin catalyzed by activated fibrin-stabilizing factor. J Biol Chem. 1982 Dec 25;257(24):14767–14772. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tulip W. R., Varghese J. N., Laver W. G., Webster R. G., Colman P. M. Refined crystal structure of the influenza virus N9 neuraminidase-NC41 Fab complex. J Mol Biol. 1992 Sep 5;227(1):122–148. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90687-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang B. C. Resolution of phase ambiguity in macromolecular crystallography. Methods Enzymol. 1985;115:90–112. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(85)15009-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang D. L., Annamalai A. E., Ghosh S., Gewirtz A. M., Colman R. W. Human platelet factor V is crosslinked to actin by FXIIIa during platelet activation by thrombin. Thromb Res. 1990 Jan 1;57(1):39–57. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(90)90194-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberg J. B., Pippen A. M., Greenberg C. S. Extravascular fibrin formation and dissolution in synovial tissue of patients with osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1991 Aug;34(8):996–1005. doi: 10.1002/art.1780340809. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weller M., Bresgen M., Heimann K., Wiedemann P. Blood coagulation factor XIII contributes to the development of traction retinal detachment. Acta Ophthalmol (Copenh) 1990 Jun;68(3):246–252. doi: 10.1111/j.1755-3768.1990.tb01917.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]