Abstract
In the title compound, C13H16N2O2S, the pyrrolidine ring has a twisted conformation on the central –CH2–CH2– bond. Its mean plane is inclined to the 4-methoxybenzoyl ring by 72.79 (15)°. In the crystal, molecules are linked by N—H⋯O and C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds to the same O-atom acceptor, forming chains along [001]. The chains are linked via slipped parallel π–π interactions [inter-centroid distance = 3.7578 (13) Å], forming undulating slabs parallel to (100).
Keywords: crystal structure, benzoylthiourea, pyrrolidine, thiourea, benzamide, hydrogen bonding
Related literature
For thiourea derivatives containing a carbonothioyl R–C(=O)—N(H)—C(=S)—N functional group, where R is an alkyl or aryl group, see: Arslan et al. (2006 ▸). For copper(II) complexes of similar compounds, see: Kulcu et al. (2005 ▸); Tan et al. (2014 ▸). For the biological properties of coordination complexes of such compounds, see: Rodríguez-Fernandez et al. (2005 ▸); Cikla et al. (2010 ▸). For the crystal structures of similar compounds, see: Al-abbasi et al. (2011 ▸, 2012 ▸); Md Nasir et al. (2011 ▸); Hassan et al. (2008 ▸, 2009 ▸).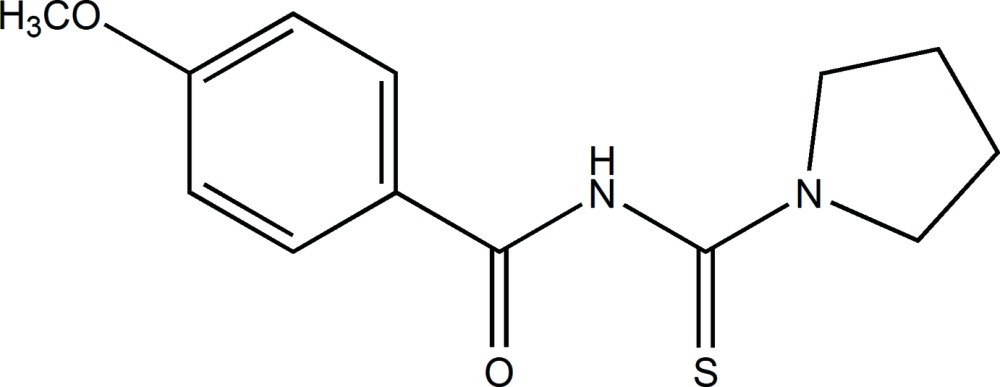
Experimental
Crystal data
C13H16N2O2S
M r = 264.34
Monoclinic,

a = 11.8548 (12) Å
b = 11.4463 (11) Å
c = 9.8317 (9) Å
β = 93.124 (3)°
V = 1332.1 (2) Å3
Z = 4
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.24 mm−1
T = 296 K
0.50 × 0.41 × 0.15 mm
Data collection
Bruker SMART APEX CCD area-detector diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2007 ▸) T min = 0.890, T max = 0.965
17732 measured reflections
2763 independent reflections
2140 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.043
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.049
wR(F 2) = 0.130
S = 1.07
2763 reflections
169 parameters
H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement
Δρmax = 0.26 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.23 e Å−3
Data collection: SMART (Bruker, 2007 ▸); cell refinement: SAINT (Bruker, 2007 ▸); data reduction: SAINT; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▸); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▸); molecular graphics: SHELXTL (Sheldrick, 2008 ▸); software used to prepare material for publication: SHELXTL, PLATON (Spek, 2009 ▸) and publCIF (Westrip, 2010 ▸).
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015003813/su5083sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015003813/su5083Isup2.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015003813/su5083Isup3.cml
. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015003813/su5083fig1.tif
A view of the molecular structure of the title compound, with atom labelling. Displacement ellipsoids are drawn at the 50% probability level.
x . DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015003813/su5083fig2.tif
A view along the x axis of the crystal packing of the title compound. Hydrogen bonds are shown as dashed lines (see Table 1 for details).
CCDC reference: 1051012
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (, ).
| DHA | DH | HA | D A | DHA |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N1H1AO1i | 0.83(3) | 2.11(3) | 2.927(2) | 170(2) |
| C1H1O1i | 0.93 | 2.50 | 3.350(3) | 152 |
Symmetry code: (i)  .
.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the Universiti Kebangsaan Malaysia (UKM) for financial support via research grants DIP-2012-11, DLP-2013-001, DPP-2013-043 and DPP-2014-048, and the Ministry of Education, Malaysia for grant FRGS/1/2014/ST01/UKM/02/2.
supplementary crystallographic information
S1. Synthesis and crystallization
Benzoyl chloride (0.01 mol) was slowly added to ammonium thiocyanate (0.01 mol) in acetone and the mixture was stirred for 30 min at room temperature. A white precipitate of ammonium chloride was filtered off. The filtrate was cooled in an ice bath (278-283 K) for about 15 min. Then, a cold solution (5-10°C) of pyrrolidine (0.01 mol) in acetone was added to the benzoyl isothiocyanate and the mixture was left for 3 h at room temperature. A yellowish solution was formed and the mixture was filtered into a beaker containing some ice cubes. The yellow residue was washed with cold water followed pale-yellow block-like crystals (yield: 85%; m.p. 397-399 K). IR(KBr, cm-1) ν(-NH) 3389; (O—CH3) = 2967; ν(C═Oaliphatic) = 1716, ν(C—Cbenzene) = 1651 and 1424; ν(C═Ostretching) = 1311 and ν(C═S) = 1210 cm-1.
S2. Refinement
Crystal data, data collection and structure refinement details are summarized in Table 3. The NH H atom, H1A, was located in a difference Fourier map and freely refined. The C-bound H atoms were included in calculated positions and treated as riding atoms: C–H = 0.93 – 0.97 Å with Uiso(H) = 1.5Ueq(C) for methyl H atoms and = 1.2Ueq(C) for other H atoms.
S3. Comment
The title compound, is a derivative of a thiourea compound containing a carbonothioyl R–C(═O)—N(H)—C(═S)—N functional group (Arslan et al., 2006), where R can be either alkyl or aryl group. The C═O and C═S groups can serve as coordination sites upon reaction with metal ions. Such complexes have been found to be biologically active, for example anti-bacterial, anti-fungal (Rodríguez-Fernandez et al., 2005), and anti-cancer (Cikla et al., 2010). The title compound is similar to the previously reported derivatives namely 1,1-diethyl-3-(4-methoxybenzoyl)thiourea (Al-abbasi et al., 2011) and 3-(3-methoxybenzoyl)-1,1-diphenylthiourea (Md Nasir et al., 2011).
Reaction of these organic compounds cis-bis[4-chloro-N-(pyrrolidine-1-carbothioyl)-benzamido] with Cu(II) formed a stable complex compound with a 1:2 ratio. The complex was tested for anti-bacterial activity (Kulcu et al., 2005). Similarly, a 1:3 ratio between copper(II)acetate and 1-benzoyl-(3,3-disubstituted)thiourea derivatives gave a series of copper(III) complexes in which the 1-benzoyl-(3,3-disubstituted)thiourea derivatives were deprotonated prior to the complexation reaction. Hence, 1-benzoyl-(3,3-disubstituted)thiourea derivatives behaved as a bidentate chelate through (O,S) coordination to give neutral cobalt(III) complexes (Tan et al., 2014).Herein we report on the crystal structure of the title compound (MPCB), and compare it to previously reported carbonyl thioureas.
In the title compound, Fig. 1, the 4-methoxybenzoyl and pyrrolidine fragments adopting a trans-cis conformation with respect to the thiono S atom across the C8—N1 bond. The pyrolidine ring (N2/C2-C9) has a twisted conformation on the C10-C11 bond. The benzamide fragment (C1-C7/O1/N1) is approximately planar with a maximum deviation for atom O1 [0.045 (2)°], and it is twisted with respect to the thiourea fragment (S1/N1/N2/C8/C12) [maximum deviation of -0.034 (2)° for N2] with a dihedral angle of 61.81 (7)°.
The C═O [1.220 (2) Å] and C=S [1.662 (2) Å] bond lengths are comparable to those reported for propyl 2-(3-benzoylthioureido)acetate [1.220 (3) Å, 1.658 (3) Å, respectively] (Hassan et al., 2008) and methyl 2-(3-benzoylthioureido)acetate [1.223 (5) Å, 1.661 (4) Å, respectively] (Hassan et al., 2009). Other bond lengths and angles in the molecule are comparable those reported for N-(pyrrolidin-1-ylcarbothioyl) benzamide (Al-abbasi et al., 2012).
In the crystal, molecules are linked by bifurcated N-H···O and C-H···O hydrogen bond forming chains along the c-axis direction (Table 1 and Fig. 2). Further stabilization is afforded by slipped parallel π-π stacking interactions involving the (C1-C6) benzene ring [Cg1···Cg1i = 3.7578 (13) Å; inter-planar distance = 3.6228 (9) Å; slippage = 0.998 Å; symmetry code: (i) -x,+2, -y+1, -z], forming undulating slabs parallel to (100).
Figures
Fig. 1.

A view of the molecular structure of the title compound, with atom labelling. Displacement ellipsoids are drawn at the 50% probability level.
Fig. 2.

A view along the x axis of the crystal packing of the title compound. Hydrogen bonds are shown as dashed lines (see Table 1 for details).
Crystal data
| C13H16N2O2S | F(000) = 560 |
| Mr = 264.34 | Dx = 1.318 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/c | Melting point = 397–399 K |
| Hall symbol: -P 2ybc | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| a = 11.8548 (12) Å | θ = 3.2–26.5° |
| b = 11.4463 (11) Å | µ = 0.24 mm−1 |
| c = 9.8317 (9) Å | T = 296 K |
| β = 93.124 (3)° | Block, pale-yellow |
| V = 1332.1 (2) Å3 | 0.50 × 0.41 × 0.15 mm |
| Z = 4 |
Data collection
| Bruker SMART APEX CCD area-detector diffractometer | 2763 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 2140 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Graphite monochromator | Rint = 0.043 |
| ω scan | θmax = 26.5°, θmin = 3.2° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2007) | h = −14→14 |
| Tmin = 0.890, Tmax = 0.965 | k = −14→14 |
| 17732 measured reflections | l = −12→12 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.049 | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| wR(F2) = 0.130 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0485P)2 + 1.055P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| S = 1.07 | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 2763 reflections | Δρmax = 0.26 e Å−3 |
| 169 parameters | Δρmin = −0.23 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Extinction correction: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008), Fc*=kFc[1+0.001xFc2λ3/sin(2θ)]-1/4 |
| Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods | Extinction coefficient: 0.031 (3) |
Special details
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| S1 | 0.72135 (6) | 0.00137 (5) | 0.03914 (6) | 0.0491 (2) | |
| O1 | 0.76464 (14) | 0.29334 (14) | 0.26290 (14) | 0.0456 (4) | |
| O2 | 0.93009 (16) | 0.73574 (15) | −0.05668 (17) | 0.0582 (5) | |
| N1 | 0.71420 (15) | 0.23446 (15) | 0.04921 (17) | 0.0345 (4) | |
| N2 | 0.58223 (15) | 0.13540 (14) | 0.17024 (18) | 0.0383 (4) | |
| C1 | 0.80147 (19) | 0.45074 (19) | −0.0520 (2) | 0.0386 (5) | |
| H1 | 0.7689 | 0.3985 | −0.1151 | 0.046* | |
| C2 | 0.8420 (2) | 0.5562 (2) | −0.0950 (2) | 0.0472 (6) | |
| H2 | 0.8365 | 0.5748 | −0.1872 | 0.057* | |
| C3 | 0.89105 (18) | 0.63501 (18) | −0.0028 (2) | 0.0387 (5) | |
| C4 | 0.89724 (19) | 0.60796 (19) | 0.1342 (2) | 0.0421 (5) | |
| H4 | 0.9283 | 0.6610 | 0.1973 | 0.051* | |
| C5 | 0.85703 (19) | 0.50171 (18) | 0.1772 (2) | 0.0383 (5) | |
| H5 | 0.8623 | 0.4834 | 0.2695 | 0.046* | |
| C6 | 0.80889 (15) | 0.42189 (16) | 0.08530 (18) | 0.0290 (4) | |
| C7 | 0.76284 (16) | 0.31244 (17) | 0.14072 (18) | 0.0310 (4) | |
| C8 | 0.66841 (17) | 0.12705 (17) | 0.09137 (18) | 0.0320 (4) | |
| C9 | 0.5215 (2) | 0.2428 (2) | 0.2040 (3) | 0.0504 (6) | |
| H9A | 0.5074 | 0.2912 | 0.1240 | 0.060* | |
| H9B | 0.5640 | 0.2877 | 0.2731 | 0.060* | |
| C10 | 0.4126 (2) | 0.1985 (3) | 0.2569 (4) | 0.0705 (8) | |
| H10A | 0.3559 | 0.1871 | 0.1832 | 0.085* | |
| H10B | 0.3835 | 0.2521 | 0.3229 | 0.085* | |
| C11 | 0.4468 (3) | 0.0836 (3) | 0.3227 (4) | 0.0747 (9) | |
| H11A | 0.4820 | 0.0959 | 0.4129 | 0.090* | |
| H11B | 0.3819 | 0.0329 | 0.3299 | 0.090* | |
| C12 | 0.5294 (2) | 0.0320 (2) | 0.2289 (3) | 0.0469 (6) | |
| H12A | 0.5851 | −0.0159 | 0.2787 | 0.056* | |
| H12B | 0.4910 | −0.0150 | 0.1585 | 0.056* | |
| C13 | 0.9838 (2) | 0.8187 (2) | 0.0323 (3) | 0.0582 (7) | |
| H13A | 0.9295 | 0.8506 | 0.0911 | 0.087* | |
| H13B | 1.0149 | 0.8804 | −0.0202 | 0.087* | |
| H13C | 1.0433 | 0.7813 | 0.0863 | 0.087* | |
| H1A | 0.734 (2) | 0.234 (2) | −0.030 (3) | 0.048 (7)* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| S1 | 0.0650 (4) | 0.0340 (3) | 0.0487 (4) | 0.0064 (3) | 0.0070 (3) | −0.0051 (2) |
| O1 | 0.0643 (10) | 0.0483 (9) | 0.0242 (7) | −0.0124 (8) | 0.0019 (6) | 0.0034 (6) |
| O2 | 0.0803 (12) | 0.0404 (9) | 0.0530 (10) | −0.0216 (9) | −0.0036 (9) | 0.0101 (7) |
| N1 | 0.0480 (10) | 0.0322 (9) | 0.0237 (8) | −0.0064 (7) | 0.0070 (7) | −0.0009 (7) |
| N2 | 0.0454 (10) | 0.0273 (8) | 0.0427 (10) | −0.0038 (7) | 0.0077 (8) | 0.0025 (7) |
| C1 | 0.0527 (13) | 0.0360 (11) | 0.0267 (10) | −0.0074 (9) | −0.0005 (9) | −0.0014 (8) |
| C2 | 0.0712 (16) | 0.0421 (12) | 0.0279 (10) | −0.0107 (11) | −0.0019 (10) | 0.0062 (9) |
| C3 | 0.0428 (11) | 0.0319 (10) | 0.0415 (12) | −0.0035 (9) | 0.0028 (9) | 0.0038 (9) |
| C4 | 0.0489 (12) | 0.0407 (12) | 0.0360 (11) | −0.0089 (10) | −0.0033 (9) | −0.0059 (9) |
| C5 | 0.0473 (12) | 0.0423 (12) | 0.0250 (9) | −0.0068 (9) | −0.0010 (8) | −0.0006 (8) |
| C6 | 0.0293 (9) | 0.0306 (9) | 0.0271 (9) | 0.0000 (7) | 0.0030 (7) | 0.0001 (7) |
| C7 | 0.0350 (10) | 0.0332 (10) | 0.0251 (9) | 0.0007 (8) | 0.0039 (7) | 0.0004 (7) |
| C8 | 0.0405 (11) | 0.0317 (10) | 0.0236 (9) | −0.0024 (8) | −0.0011 (8) | −0.0005 (7) |
| C9 | 0.0539 (14) | 0.0379 (12) | 0.0614 (15) | 0.0057 (10) | 0.0207 (11) | 0.0027 (11) |
| C10 | 0.0517 (15) | 0.0604 (17) | 0.101 (2) | 0.0007 (13) | 0.0229 (15) | −0.0096 (16) |
| C11 | 0.0720 (19) | 0.0608 (17) | 0.095 (2) | −0.0163 (15) | 0.0387 (17) | 0.0083 (16) |
| C12 | 0.0486 (13) | 0.0379 (11) | 0.0543 (14) | −0.0136 (10) | 0.0037 (11) | 0.0074 (10) |
| C13 | 0.0617 (16) | 0.0372 (13) | 0.0752 (18) | −0.0113 (11) | −0.0010 (13) | −0.0021 (12) |
Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| S1—C8 | 1.662 (2) | C5—C6 | 1.386 (3) |
| O1—C7 | 1.220 (2) | C5—H5 | 0.9300 |
| O2—C3 | 1.361 (2) | C6—C7 | 1.482 (3) |
| O2—C13 | 1.418 (3) | C9—C10 | 1.505 (4) |
| N1—C7 | 1.372 (2) | C9—H9A | 0.9700 |
| N1—C8 | 1.415 (2) | C9—H9B | 0.9700 |
| N1—H1A | 0.83 (3) | C10—C11 | 1.512 (4) |
| N2—C8 | 1.319 (3) | C10—H10A | 0.9700 |
| N2—C12 | 1.471 (3) | C10—H10B | 0.9700 |
| N2—C9 | 1.472 (3) | C11—C12 | 1.502 (4) |
| C1—C2 | 1.375 (3) | C11—H11A | 0.9700 |
| C1—C6 | 1.387 (3) | C11—H11B | 0.9700 |
| C1—H1 | 0.9300 | C12—H12A | 0.9700 |
| C2—C3 | 1.384 (3) | C12—H12B | 0.9700 |
| C2—H2 | 0.9300 | C13—H13A | 0.9600 |
| C3—C4 | 1.380 (3) | C13—H13B | 0.9600 |
| C4—C5 | 1.381 (3) | C13—H13C | 0.9600 |
| C4—H4 | 0.9300 | ||
| C3—O2—C13 | 118.55 (19) | N2—C9—C10 | 103.63 (19) |
| C7—N1—C8 | 121.83 (16) | N2—C9—H9A | 111.0 |
| C7—N1—H1A | 119.3 (18) | C10—C9—H9A | 111.0 |
| C8—N1—H1A | 114.0 (18) | N2—C9—H9B | 111.0 |
| C8—N2—C12 | 122.12 (18) | C10—C9—H9B | 111.0 |
| C8—N2—C9 | 126.67 (17) | H9A—C9—H9B | 109.0 |
| C12—N2—C9 | 111.08 (17) | C9—C10—C11 | 103.0 (2) |
| C2—C1—C6 | 120.23 (19) | C9—C10—H10A | 111.2 |
| C2—C1—H1 | 119.9 | C11—C10—H10A | 111.2 |
| C6—C1—H1 | 119.9 | C9—C10—H10B | 111.2 |
| C1—C2—C3 | 120.82 (19) | C11—C10—H10B | 111.2 |
| C1—C2—H2 | 119.6 | H10A—C10—H10B | 109.1 |
| C3—C2—H2 | 119.6 | C12—C11—C10 | 104.4 (2) |
| O2—C3—C4 | 124.7 (2) | C12—C11—H11A | 110.9 |
| O2—C3—C2 | 115.90 (19) | C10—C11—H11A | 110.9 |
| C4—C3—C2 | 119.41 (19) | C12—C11—H11B | 110.9 |
| C3—C4—C5 | 119.72 (19) | C10—C11—H11B | 110.9 |
| C3—C4—H4 | 120.1 | H11A—C11—H11B | 108.9 |
| C5—C4—H4 | 120.1 | N2—C12—C11 | 103.30 (19) |
| C4—C5—C6 | 121.15 (19) | N2—C12—H12A | 111.1 |
| C4—C5—H5 | 119.4 | C11—C12—H12A | 111.1 |
| C6—C5—H5 | 119.4 | N2—C12—H12B | 111.1 |
| C5—C6—C1 | 118.65 (18) | C11—C12—H12B | 111.1 |
| C5—C6—C7 | 117.66 (17) | H12A—C12—H12B | 109.1 |
| C1—C6—C7 | 123.61 (17) | O2—C13—H13A | 109.5 |
| O1—C7—N1 | 120.88 (18) | O2—C13—H13B | 109.5 |
| O1—C7—C6 | 121.76 (18) | H13A—C13—H13B | 109.5 |
| N1—C7—C6 | 117.32 (16) | O2—C13—H13C | 109.5 |
| N2—C8—N1 | 115.53 (17) | H13A—C13—H13C | 109.5 |
| N2—C8—S1 | 124.18 (15) | H13B—C13—H13C | 109.5 |
| N1—C8—S1 | 120.28 (15) | ||
| C6—C1—C2—C3 | 0.2 (4) | C5—C6—C7—N1 | 179.28 (18) |
| C13—O2—C3—C4 | 1.7 (4) | C1—C6—C7—N1 | 2.5 (3) |
| C13—O2—C3—C2 | −178.4 (2) | C12—N2—C8—N1 | −176.49 (18) |
| C1—C2—C3—O2 | 178.9 (2) | C9—N2—C8—N1 | 8.0 (3) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | −1.2 (4) | C12—N2—C8—S1 | 4.8 (3) |
| O2—C3—C4—C5 | −178.5 (2) | C9—N2—C8—S1 | −170.72 (18) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | 1.5 (3) | C7—N1—C8—N2 | 63.0 (3) |
| C3—C4—C5—C6 | −0.9 (3) | C7—N1—C8—S1 | −118.27 (18) |
| C4—C5—C6—C1 | −0.1 (3) | C8—N2—C9—C10 | 162.6 (2) |
| C4—C5—C6—C7 | −177.08 (19) | C12—N2—C9—C10 | −13.4 (3) |
| C2—C1—C6—C5 | 0.5 (3) | N2—C9—C10—C11 | 31.6 (3) |
| C2—C1—C6—C7 | 177.3 (2) | C9—C10—C11—C12 | −38.8 (3) |
| C8—N1—C7—O1 | −2.6 (3) | C8—N2—C12—C11 | 173.3 (2) |
| C8—N1—C7—C6 | 179.56 (17) | C9—N2—C12—C11 | −10.5 (3) |
| C5—C6—C7—O1 | 1.5 (3) | C10—C11—C12—N2 | 30.2 (3) |
| C1—C6—C7—O1 | −175.3 (2) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| N1—H1A···O1i | 0.83 (3) | 2.11 (3) | 2.927 (2) | 170 (2) |
| C1—H1···O1i | 0.93 | 2.50 | 3.350 (3) | 152 |
Symmetry code: (i) x, −y+1/2, z−1/2.
Footnotes
Supporting information for this paper is available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: SU5083).
References
- Al-abbasi, A. A., Mohamed Tahir, M. I. & Kassim, M. B. (2011). Acta Cryst. E67, o3414. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Al-abbasi, A. A., Mohamed Tahir, M. I. & Kassim, M. B. (2012). Acta Cryst. E68, o201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Arslan, H., Florke, U., Kulcu, N. & Kayhan, E. (2006). Turk. J. Chem. 30, 429–440.
- Bruker (2007). SMART, SAINT and SADABS. Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Cikla, P., Kucukguzel, S. G., Kucukguzel, I., Rollas, S., Clercq, E. D., Pannecouque, C., Andrei, G., Snoeck, R., Sahin, F. & Bayrak, O. F. (2010). Pharm. J. 14, 13–20.
- Hassan, I. N., Yamin, B. M. & Kassim, M. B. (2008). Acta Cryst. E64, o2083. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Hassan, I. N., Yamin, B. M. & Kassim, M. B. (2009). Acta Cryst. E65, o3078. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Kulcu, N., Florke, U. & Arslan, H. (2005). Turk. J. Chem. 29, 1–6.
- Md Nasir, M. F., Hassan, I. N., Yamin, B. M., Daud, W. R. W. & Kassim, M. B. (2011). Acta Cryst. E67, o1947–o1948. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez-Fernández, E., Manzano, J. L., Benito, J. J., Hermosa, R., Monte, E. & Criado, J. J. (2005). J. Inorg. Biochem. 99, 1558–1572. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Spek, A. L. (2009). Acta Cryst. D65, 148–155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Tan, S. S., Al-abbasi, A. A., Mohamed Tahir, M. I. & Kassim, M. B. (2014). Polyhedron, 68, 287–294.
- Westrip, S. P. (2010). J. Appl. Cryst. 43, 920–925.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015003813/su5083sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015003813/su5083Isup2.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015003813/su5083Isup3.cml
. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015003813/su5083fig1.tif
A view of the molecular structure of the title compound, with atom labelling. Displacement ellipsoids are drawn at the 50% probability level.
x . DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015003813/su5083fig2.tif
A view along the x axis of the crystal packing of the title compound. Hydrogen bonds are shown as dashed lines (see Table 1 for details).
CCDC reference: 1051012
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report


