Abstract
Background
Neuroinflammation and dysfunctional glial glutamate transporters (GTs) in the spinal dorsal horn (SDH) are implicated in the genesis of neuropathic pain. We determined if adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase (AMPK) in the SDH regulates these processes in rodents with neuropathic pain.
Methods
Hind paw withdrawal responses to radiant heat and mechanical stimuli were used to assess nociceptive behaviors. Spinal markers related to neuroinflammation and glial GTs were determined by Western blotting. AMPK activities were manipulated pharmacologically and genetically. Regulation of glial GTs was determined by measuring protein expression and activities of glial GTs.
Results
AMPK activities were reduced in the SDH of rats (n = 5) with thermal hyperalgesia induced by nerve injury, which were accompanied with the activation of astrocytes, increased production of interleukin-1beta and activities of glycogen synthase kinase 3β, and suppressed protein expression of glial glutamate transporter-1. Thermal hyperalgesia was reversed by spinal activation of AMPK in neuropathic rats (n = 10), and induced by inhibiting spinal AMPK in naïve rats (n = 7 to 8). Spinal AMPKα knockdown (n = 6) and AMPKα1 conditional knockout (n = 6) induced thermal hyperalgesia and mechanical allodynia. These genetic alterations mimicked the changes of molecular markers induced by nerve injury. Pharmacological activation of AMPK enhanced glial GT activity in mice with neuropathic pain (n = 8) and attenuated glial glutamate transporter-1 internalization induced by interleukin-1β (n = 4).
Conclusion
These findings suggest enhancing spinal AMPK activities could be an effective approach for the treatment of neuropathic pain.
Introduction
Adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase (AMPK) is a serine/threonine kinase originally identified as a metabolic stress-sensing protein. 1,2 Activation of AMPK generally promotes catabolic pathways such as glucose uptake and glycolysis which generate adenosine triphosphate (ATP) while inhibiting anabolic pathways that consume ATP such as fatty acid and glycogen synthesis. 1,3 Emerging studies suggest that AMPK also plays an important role in neuroinflammation 4,5 and the genesis of pathologic pain. 6,7
AMPK is widely expressed in different cell types, including neurons, astrocytes, microglia, and macrophages. 4,8,9 In primary rat astrocytes, microglia, and peritoneal macrophages, AMPK activation suppresses the production of interleukin (IL)-1β, IL-6, and tumor necrosis factor α (TNF-α) induced by lipopolysaccharide. 4 Similarly, the enhanced gene expression induced by interferon-γ on chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 2, C-X-C motif chemokine 10, and inducible nitric oxide synthase in primary murine astrocytes are suppressed by AMPK activation. 8 The role of AMPK in pathological pain has recently been reported. 10 AMPK activators attenuate mechanical allodynia in animals with neuropathic pain 7 or surgical incision pain 6 through acting at peripheral sensory neurons. Inflammatory pain induced by subcutaneous injection of formalin or zymosan is attenuated by the systemic administration of AMPK activators. 11 Currently, the molecular and synaptic mechanisms by which AMPK regulates spinal nociceptive processing remain elusive.
One predominant synaptic mechanism leading to excessive neuronal activation in the spinal dorsal horn (SDH) is the increased activation of glutamate receptors. Three factors determine the activation of glutamate receptors, including the amount of glutamate released from presynaptic terminals, the function and number of the post-synaptic glutamate receptors, and the rate at which glutamate is cleared from the synaptic cleft. 12 We and others have demonstrated that the downregulation of astrocytic glutamate transporter (GT) protein expression and functions in the SDH is associated with allodynia induced by chronic nerve injury. 13–15 Selectively increasing the protein expression of glial GTs by ceftriaxone treatment 16 or gene transfer 17 can effectively prevent the development of pathological pain induced by nerve injury. It remains unknown whether the protein expression and activities of glial GTs are regulated by AMPK activities in the SDH.
AMPK is a heterotrimeric protein complex consisting of α, β, and γ subunits where all subunits are necessary for kinase activity. 18 The α subunit possesses the catalytic kinase domain while the β subunit functions as a scaffold molecule, and the γ subunit detects the cellular energy state by binding adenosine monophosphate, adenosine diphosphate, and ATP. The α subunit consists of two isoforms, AMPKα1 and AMPKα2. 19,20 The specific roles of each AMPKα isoform in the pain signaling pathway are not fully understood.
In this study, we demonstrated that suppression of AMPK activities in the SDH causes hypersensitivity in rodents through inducing spinal neuroinflammation and suppressing glial GT activities. Furthermore, we also identified the AMPKα1 isoform as the key isoform implicated in these processes.
Material and Methods
Animals
Adult male Sprague-Dawley rats (weight range 225–300 g, Harlan Laboratories, Indianapolis, IN) or male mice (weight range 25–35 g) were used. FVB-Tg(GFAP-cre)25Mes/J, 21 Prkaa1tm1.1Sjm/J, 22 and GFP-GFAP 23 mice were purchased from Jackson Laboratories (Bar Harbor, MN). All experiments were approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee at the University of Georgia (Athens, Georgia) and were fully compliant with the National Institutes of Health Guidelines for the Use and Care of Laboratory Animals.
Partial sciatic nerve ligation
Animals were randomly divided into partial sciatic nerve ligation (pSNL) or sham-operated groups. The pSNL model is a well-established neuropathic pain model which has been shown to produce mechanical allodynia and thermal hyperalgesia. 24,25 Briefly, under isoflurane-induced (2–3%) anesthesia, the left sciatic nerve at the upper thigh was exposed and ligated approximately two-thirds the thickness of the sciatic nerve with a 5-0 silk suture as previously described. 24 Following surgery, the wound was closed with skin stables. In sham-operated rats, the left sciatic nerve was exposed but not ligated.
Behavior tests
Measurement of thermal thresholds of hind paws withdrawal responses
For behavioral tests, the animals were placed on a glass surface at 30°C while loosely restrained under a Plexiglass cage (12 × 20 × 15 cm), and allowed to acclimate for at least 30 min for rats and 1 h and 30 min for mice. To test the thermal sensitivity in the animals, a radiant heat beam was directed from below to the midplantar surface of the left hind paw for mice and rats receiving pSNL surgery and the left and right hind paw for AMPKα knockdown rats and AMPKα1 knockout mice and littermates to evoke a withdrawal response. The latency of paw withdrawal responses, i.e., the time between the stimulus onset and paw withdrawal responses, was recorded. 26 A cutoff time of 20 s was used to avoid damage to the skin. Each hind paw was stimulated three times with an interval of at least 2 min and the three latencies obtained from each paw were averaged. The sample size used in experiments was based on our previous studies. 14,25,27–29
Measurement of mechanical thresholds of hind paws withdrawal responses
To test possible changes in mechanical sensitivity in AMPKα1 knockout mice compared to their littermates, mice were placed on a wire mesh, loosely restrained under a plexiglass cage (12 × 20 × 15 cm3) and allowed to acclimate for at least 1 h and 30 min. A series of von Frey monofilaments (bending force ranging from 0.07 to 2.00 g) were tested in ascending order to generate response-frequency functions for each animal. Each von Frey filament was applied five times to the midplantar area of each hind paw from beneath for about 1 s. The response-frequency [(number of withdrawal responses of both hind paws/10) × 100%] for each von Frey filament was determined. Withdrawal response mechanical threshold was defined as the lowest force filament that evoked a 50% or greater response-frequency. This value was later averaged across all animals in each group to yield the group response threshold. 30,31
Intrathecal catheter implantation and drug administration
The AMPK activator or inhibitor was applied to the spinal lumbar enlargement through a pre-implanted intrathecal catheter. 32 Briefly, rats were anesthetized under isoflurane (2–3%) and the atlanto-occipital membrane was exposed by dissection. A polyethylene 10 catheter was carefully advanced through an opening in the atlanto-occipital membrane to the lumbar enlargement. The wound was then closed in layers. The animals were allowed to recover for 7 days prior to behavioral tests. The AMPK activator (5-Aminoimidazole-4-carboxamide ribonucleotide, AICAR) and the AMPK inhibitor (Compound C) each were respectively prepared in saline and injected onto the spinal lumbar enlargement through the pre-implanted catheter in a volume of 10 μl, followed by 20 μl of saline to flush. Vehicle (saline, 10 μl) was also injected in the same fashion in control groups. The experimenter who conducted the behavioral tests was blind to the treatments given to the rats. Following behavior experiments, rats were intrathecally injected with 50 μL of 2% lidocaine and if hind paw paralysis did not ensue; rats were omitted from the experiment. Two rats were omitted from experiments due to minimal paralysis following lidocaine administration.
Administration of AMPKα siRNA
AMPKα small interfering RNA (siRNA) and scrambled siRNA (for controls) were intrathecally administered to the rats through a pre-implanted intrathecal catheter as described above. AMPKα siRNA and scrambled siRNA were prepared immediately prior to the intrathecal administration by mixing the RNA solution (100 μM) with the transfection reagent (iFect), in a ratio of 1:5 (w:v) as described in the iFect siRNA transfection kit. 33 AMPKα siRNA (2 μg) and an equal amount of scrambled siRNA in a volume of 10 μl were intrathecally injected at 9:30 AM and 9:30 PM for two consecutive days. The hind paw withdrawal latency to thermal stimuli was measured prior to the initial intrathecal injection and 12 h following the last intrathecal injection. The dorsal lumbar of the spinal cord at the L4–5 region was removed after the behavioral tests for Western Blotting.
Generation of AMPKα1 gene knockout mice and genotyping
Mice with AMPKα1 gene knockout were generated through Cre-LoxP mediated recombination by mating mice carrying the homozygous floxed AMPKα1 allele (flanking exon 3 of the kinase 22) with mice expressing the Cre recombinase under the control of the glial fibrillary acid protein promoter (GFAP). 21 Male offspring which carried the Cre-GFAP recombinase and were heterozygous for the AMPKα1 LoxP flanked allele were crossed with homozygous floxed AMPKα1 female mice to generate GFAP-AMPKα1 conditional knockout mice. The genotype of GFAP-AMPKα1 conditional knockout mice was confirmed through polymerase chain reaction. This was performed on genomic DNA extracted from mouse ear clips. Genomic DNA was extracted by proteinase K digestion (proteinase K 0.5 mg/mL, 5 mM EDTA, 200 mM sodium chloride (NaCl), 100 mM tris(hydroxymethyl)aminomethane (pH = 8.5), and 0.2% sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS)) as described previously 34 followed by ethanol precipitation. Genotyping was conducted using the primers described by Jackson Laboratories for the sense strand 5′-CCC ACC ATC ACT CCA TCT-3′ and for the anti-sense strand 5′-AGC CTG CTT GGC ACA CTT AT-3′ to detect the AMPKα1 floxed allele and for the sense strand 5′-ACT CCT TCA TAA AGC CCT-3′ and for anti-sense strand 5′-ATC ACT CGT TGC ATC GAC CG-3′ to detect the GFAP-Cre transgene. 21 Littermates were used in all experiments to control for genetic background effects.
Western blot experiments
Animals were deeply anesthetized with urethane (1.3–1.5 g/kg, intraperitoneal). The L4 to L5 spinal segment was exposed by surgery and removed from the animals. The dorsal quadrant of the spinal L4 to L5 segment ipsilateral to the operated side was isolated from animals with pSNL or sham operation. In the siRNA and the Cre-loxP experiments, the dorsal half of the spinal cord at the L4 to L5 segment was removed. The spinal tissue was quickly frozen in liquid nitrogen and stored at −80°C for later use. Following tissue isolation the animals were euthanized. Frozen tissues were homogenized with a hand-held pellet in lysis buffer (50 mM tris(hydroxymethyl)aminomethane, 150 mM NaCl, 1 mM EDTA, 0.1% SDS, 1% deoxycholic acid, 2 mM orthovanadate, 100 mM sodium fluoride, 1% Triton X-100, 0.5 mM phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride, 20 μM leupeptin, 100 IU mL−1 aprotinin, pH = 7.5) and placed for 30 min at 37°C. The samples were then centrifuged for 20 min at 12,000 g at 4°C and the supernatants containing proteins were collected. For measuring protein expression in the plasma membrane and cytosol in rat spinal slices, spinal slices of the spinal L4 to L5 segment were obtained as previously described. 14 Spinal slices were incubated with plain artificial cerebrospinal fluid (aCSF), aCSF plus IL-1β (10 ng/mL), or aCSF plus IL-1β (10 ng/mL) and AICAR (10 μM) bubbled with 95% O2 and 5% CO2 at 35°C for 15 min. The dorsal halves of the spinal slices were quickly frozen in liquid nitrogen and stored at −80°C. The tissue was fractionated into cytosolic and membrane compartment using the cytoplasmic, nuclear and membrane compartmental protein extraction kit (Biochain Institute, Newark, CA). Protein concentrations were quantified with the Pierce BCA method (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Suwanee, GA). Protein samples were electrophoresed in 10% SDS polyacrylamide gels and transferred to a polyvinylidene difluoride membrane (Millipore, Bedford, MA). The membranes were blocked with 5% milk and incubated overnight at 4°C with a rabbit anti-IL-1β (1:1,000, Millipore), mouse anti-GFAP (1:2,000, Cell Signaling, Danvers, MA), rabbit anti-phosphorylated AMPKα (1:1,000, Cell Signaling), rabbit anti-AMPKα (1:1000, Cell Signaling), guinea pig anti-glial glutamate transporter 1 (GLT-1, 1:2,000, Millipore), rabbit anti-glycogen synthase kinase 3 beta (GSK3β, 1:1,000, Cell Signaling), rabbit anti-GSK3β phospho S9 (1:1,000, Abcam, Cambridge, MA) antibody, or a monoclonal mouse anti-beta-Actin (β-Actin, 1:2,000, Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO) primary antibody as a loading control. To determine cytosolic and membrane fraction specificity, anti-α-tubulin (1:200, Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Dallas, TX) or anti-epidermal growth factor receptor (1:200, Santa Cruz Biotechnology) were used. The blots were then incubated for 1 h at room temperature with the corresponding horseradish peroxidase-conjugated secondary antibody (1:5,000; Santa Cruz Biotechnology), visualized in enhanced chemiluminescence solution (SuperSignal West Chemiluminescent Substrate, Pierce, Rockford, IL), and exposed on the FluorChem HD2 System. The intensity of immunoreactive bands was quantified using ImageJ 1.46 software (National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, MD). Results are expressed as the ratio of each marker over β-Actin control unless otherwise indicated.
Recording and analysis of glial glutamate transporter currents (GTCs) from astrocytes
GTCs were recorded from adult male GFAP-GFP (Green Fluorescent Protein) transgenic mice as described previously. 14 Astrocytes in these mice were labeled by the green fluorescent protein which is under the control of the astrocyte-specific GFAP promoter. 23 Transverse spinal cord slices (400 μm thick) of the L4 to L5 segment were prepared 14,35 and pre-incubated in Krebs solution oxygenated with 95% O2 and 5% CO2 at 35°C. The Krebs solution contained (mM): 117.0 NaCl, 3.6 potassium chloride, 1.2 magnesium chloride, 2.5 calcium chloride, 1.2 monosodium phosphate, 11.0 glucose, and 25.0 sodium bicarbonate at 35°C. To record GTCs, the spinal slice was placed in a recording chamber perfused with Krebs solution. Visualized whole-Cell patch clamp recordings were obtained from the SDH laminae I and II astrocytes identified by GFP under the fluorescent microscope. Borosilicate glass recording electrodes (resistance = 4–6 MΩ) were filled with an intracellular solution (290–300 mOsm) which contained (mM): 145 K gluconate, 5 NaCl, 1 magnesium chloride, 0.2 EGTA, 10 HEPES, 2 Mg-ATP, and 0.1 Na-GTP. GTCs were recorded at a holding potential of −80 mV in voltage clamp mode in the presence of blockers of γ-Aminobutyric acid A (GABAA) receptor (10 μM bicuculline), glycine receptor (5 μM strychnine), α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid (AMPA) receptor/kainate receptors (10 μM DNQX), N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor (25 μM D-AP5), and tetrodotoxin (1 μM) at 35°C. 14,36 GTCs were evoked by puffing 50 μM L-glutamate onto the recorded astrocyte through a glass pipette connected to a Picospritzer controlled by a computer. Access resistance within the range of 10–20 MΩ was monitored continuously throughout the experiments. Recordings were abandoned when the access resistance changed >20%. All the drugs were applied through bath-perfusion unless otherwise indicated. Data were recorded using Axopatch 700B amplifiers, digitized at 10 kHz, and analyzed off-line. Four sweeps of GTCs were averaged and the mean amplitude and charge transfer of GTCs were measured. 14,37 The commercial computer software Clampfit (Molecular Device, Sunnyvale, CA) was used for data analysis.
Materials
AICAR was purchased from LC Laboratories (Woburn, MA) and Compound C was purchased from EMD Millipore. AMPKα siRNA and scrambled siRNA were obtained from Santa Cruz Biotechnology. The siRNA vehicle, i-Fect, in the siRNA experiments was obtained from Neuromics (Edina, MN).
Statistical Analysis
All data are presented as the mean ± SEM. One or two way analysis of variance (ANOVA) with repeated measures was used to detect differences on nociceptive behaviors between rodents receiving different treatments. A Bonferroni post-hoc test was performed to determine sources of the differences. Whenever applicable, Student’s t-tests were used to make comparison between groups (nonpaired) or within the same group (paired). Comparisons were run as two-tailed tests. A p value less than 0.05 was considered statistically significant. Statistical analysis was performed using GraphPad Prism 5 (GraphPad Software Inc., La Jolla, CA).
Results
Nerve Injury Induced Allodynia
In this study, pSNL was performed to produce neuropathic pain in animals. The rodents receiving the surgery exhibited thermal hyperalgesia prior to undergoing the molecular and electrophysiological studies. The latency of hind paw withdrawal responses to radiant heat stimuli in the pSNL side decreased from 11.68 ± 0.36 s at baseline (before nerve ligation) to 7.52 ± 0.39 s (p < 0.001, n = 24) in rats with pSNL, and from 11.26 ± 0.51 s at baseline to 5.23 ± 0.26 s in GFP-GFAP mice with pSNL (p < 0.001, n = 5) 10 days postinjury. In contrast, the latency of withdrawal responses to the heat stimuli did not show significant changes in animals receiving the sham operation [12.71 ± 0.44 s at baseline and 12.10 ± 0.56 s 10 days after the sham surgery for rats (n = 15); 11.57 ± 0.44 s at baseline and 10.98 ± 0.60 s 10 days after the sham surgery in mice (n = 4)].
AMPK signaling activities in the SDH are repressed whereas astrocytes are activated, IL-1β expression is increased, and GLT-1 is decreased 10 days following partial sciatic nerve injury
To identify the relationship between altered nociceptive behaviors following pSNL and AMPKα activities within the SDH, levels of phosphorylated AMPKα (pAMPKα) and total AMPKα (tAMPKα) in the SDH were analyzed in rats 10 days following pSNL or sham surgery. The protein levels of tAMPKα on day 10 (n = 5) following pSNL surgery were comparable to those of the sham-operated rats (n = 5) (data not shown). However, ratios of pAMPKα protein expression over tAMPKα protein expression (pAMPKα/tAMPKα) in the pSNL rats (n = 5) 10 days after pSNL were significantly (p < 0.05) lower than in sham-operated rats (n = 5) (fig. 1), indicating decreased AMPKα activity in the SDH 10 days following pSNL. The decreased AMPK activity in pSNL rats was accompanied with the significant increased expression of GFAP (the marker for astrocytes, p < 0.01, n = 5), the increased protein expression of IL-1β (p < 0.05, n = 5), and the decreased protein expression of GLT-1 (p < 0.05, n = 5). These data indicate that suppressed AMPKα activity in the SDH of rats with neuropathic pain is associated with astrocytic activation, increased production of IL-1β, and decreased GLT-1 expression in the SDH.
Figure 1.
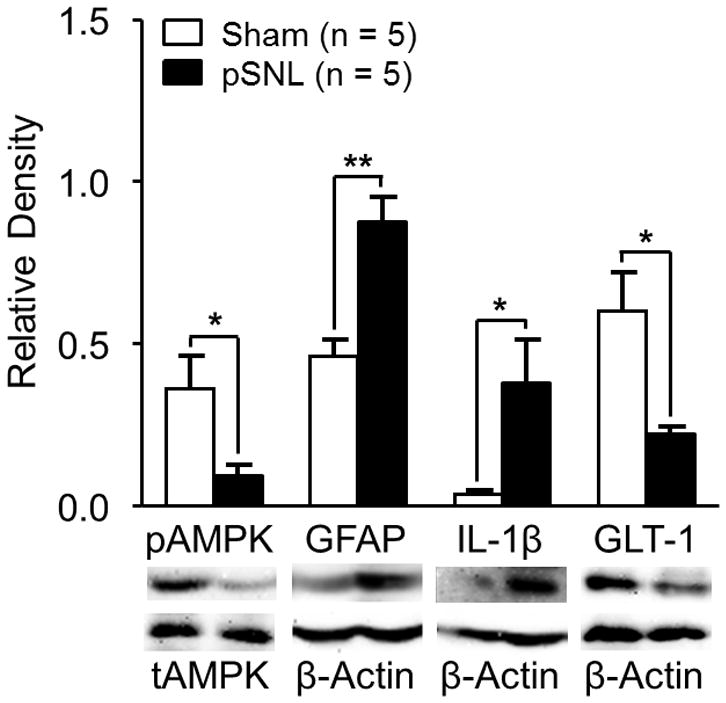
Ten days after nerve injury, protein expressions of phosphorylated adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase α (pAMPK) and glial glutamate transporter 1 (GLT-1) in the spinal dorsal horn ipsilateral to the injury site are suppressed whereas glial fibrillary acid protein promoter (GFAP) and interleukin-1beta (IL-1β) are increased. Bar graphs show the mean (+ SEM) ratio of pAMPKα/total AMPKα (tAMPK) as well as the mean (+ SEM) relative density of GFAP, IL-1β, and GLT-1 to β-Actin in the spinal dorsal horn of partial sciatic nerve ligation (pSNL) and Sham-operated rats. * p < 0.05; ** p < 0.01.
Pharmacological activation of AMPK activities attenuated preexisting thermal hyperalgesia induced by pSNL
To determine whether reduced AMPK activity in the SDH contributes to thermal hyperalgesia in rats with neuropathic pain, three groups of rats preimplanted with intrathecal catheters were used: sham + vehicle group, pSNL + AMPK activator group, and pSNL + vehicle group. After taking baseline hind paw withdrawal response latencies to radiant heat stimuli, we performed either pSNL or sham surgery on the rats. Hind paw withdrawal response latencies to heat stimuli were recorded 10 days postsurgery. We then topically applied an allosteric AMPK activator, AICAR, (10 μl at a concentration of 30 μM) onto the spinal lumbar enlargement through the implanted intrathecal catheter in the pSNL + AMPK activator group. AICAR acts as a cellular mimetic of adenosine monophosphate and is widely used to activate AMPK 38,39 in animals. 40,41 Furthermore, 30 μM of AICAR has previously been shown to increase AMPK phosphorylation in primary mouse cell cultures. 39 The pSNL + vehicle group and the sham + vehicle group received intrathecal injections of 10 μl saline (vehicle) in the same fashion. As shown in figure 2, in comparison with their readings at 10 days postsurgery prior to administration of AICAR, withdrawal response latencies to heat stimuli in the pSNL rats receiving AICAR were increased within 15 min after AICAR injection, which was statistically significant (p < 0.01, n = 10) (fig. 2). Further, withdrawal response latencies to heat stimuli were significantly longer at 15 min (p < 0.05) in the pSNL + AMPK activator group compared to the pSNL + vehicle group (n = 9). Additionally, animals receiving AMPK activators did not display changes in their motor behaviors, which included grooming, postures, and gaits. These results indicate that activation of AMPK in the spinal cord attenuates the thermal hyperalgesia induced by nerve injury.
Figure 2.
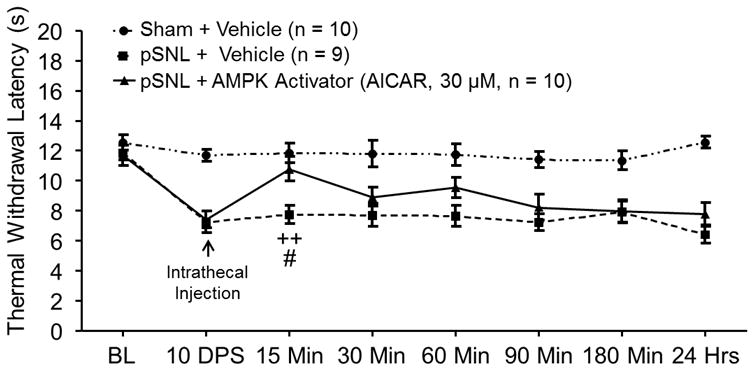
Pharmacological activation of adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase (AMPK) in the spinal cord attenuated preexisting thermal hyperalgesia induced by partial sciatic nerve ligation (pSNL). Line plots show measurements of the hind paw withdrawal response latency (± SEM) to thermal stimuli collected at baseline (BL, day 0), 10 days postsurgery (10 DPS), and then 15, 30, 60, 90, 180 min, and 24 h after the intrathecal administration of the tested agent. Baseline (day 0) indicates the baseline measurement before animals received surgery. Comparisons between data collected on 10 DPS and at each time point are indicated with a + for the pSNL + AMPK Activator group. Comparisons between the pSNL + Vehicle group and the pSNL + AMPK Activator group are labeled with #. One symbol: p < 0.05, Two symbols: p < 0.01.
Pharmacological inhibition of AMPK activity induced thermal hyperalgesia in naïve rats
To simulate low AMPK activities in neuropathic rats, we assessed the effects of the AMPK inhibitor (Compound C) on naïve (no pSNL or sham surgery) rats in the spinal cord. Two groups of rats preimplanted with intrathecal catheters were used: naïve + vehicle group and naïve + AMPK inhibitor group. After obtaining the hind paw withdrawal response latency to heat stimuli, rats received an intrathecal injection of either Compound C (10 μl at a concentration of 100 μM or 500 μM ) for the naïve + AMPK inhibitor group or saline (10 μL) for the naïve + vehicle group. As shown in figure 3, spinal inhibition of AMPK with Compound C induced thermal hyperalgesia in a dose dependent manner. In comparison with their baseline measurements, the withdrawal response latencies to heat stimuli in naïve rats receiving Compound C (100 μM) were significantly decreased at 15 min (p < 0.01, n = 7) following drug treatment. Intrathecal injection of Compound C at 500 μM significantly reduced the withdrawal response latencies at 15 min (p < 0.01, n = 8) and 30 min (p < 0.001). Moreover, in comparison with the naïve + vehicle group, withdrawal response latencies to heat stimuli in the naïve + AMPK inhibitor group were significantly decreased at 15 min in rats receiving 100 μM Compound C (p < 0.001), and at 15 min (p < 0.05) and 30 min (p < 0.01) in rats receiving 500 μM Compound C. These results indicate that suppression of AMPK activities in the spinal cord induces thermal hyperalgesia in naïve rats. Taken together with the data from figure 2, we conclude that suppressed AMPK activities contribute to thermal hypersensitivity induced by nerve injury.
Figure 3.
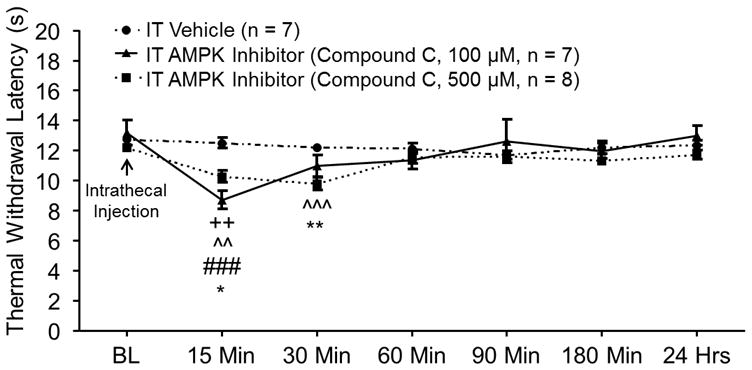
Pharmacological inhibition of adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase (AMPK) activities in the spinal cord induced thermal hyperalgesia in naïve rats. Line plots show measurements of the hind paw withdrawal response latency (± SEM) to thermal stimuli collected at baseline (BL) and then 15, 30, 60, 90, 180 min, and 24 h after the intrathecal administration of the tested agent. Baseline indicates the measurement before animals received intrathecal drug treatment. Comparisons between data collected at baseline and each time point are indicated with + for the AMPK Inhibitor group (100 μM) and ^ for the AMPK Inhibitor group (500 μM). Comparisons between the Naïve Vehicle group and the AMPK Inhibitor group (100 μM) are labeled with #. Comparisons between the Naïve Vehicle group and the AMPK Inhibitor group (500 μM) are labeled with *. One symbol: p <0.05, Two symbols: p < 0.01, Three symbols: p < 0.001.
Genetic knockdown of AMPKα enhanced thermal hyperalgesia in naïve rats
We then genetically knocked down AMPKα in the lumbar region of the spinal cord using siRNA and examined the effects on nociceptive behaviors in naïve rats. Three groups of rats implanted with intrathecal catheters were used: AMPKα siRNA group, scrambled siRNA group, and iFect vehicle group. After baseline withdrawal response latencies to thermal stimuli were obtained, the rats received intrathecal injections of either AMPKα siRNA (2 μg in 10 μL per intrathecal injection 33), scrambled siRNA (2 μg in 10 μL per intrathecal injection), or iFect vehicle (10 μL) at two times (morning and evening) on day 1 and day 2. The withdrawal response latency to thermal stimuli was examined in the rats in the morning of day 3 (12 h after the last injection). We did not observe significant changes in the withdrawal response latency to thermal stimuli in either the scrambled siRNA group or iFect vehicle group (fig. 4A). In contrast, in the AMPKα siRNA group, the withdrawal response latency to thermal stimuli was significantly reduced in comparison with their own baseline (p < 0.001, n = 6) and to rats receiving either scrambled siRNA (p < 0.01, n = 4) or the iFect vehicle (p < 0.01, n = 4) (fig. 4A). Immediately after behavioral data were collected on day 3, the spinal dorsal L4–5 segment was removed from rats and protein expression of AMPKα in the SDH was analyzed using Western blot. As shown in figure 4B, the protein expression of AMPKα in the AMPKα siRNA group (n = 6) was significantly reduced compared to the scrambled siRNA group (p < 0.01, n = 4) and the iFect Vehicle group (p < 0.05, n = 4). These results indicate that the reduction of AMPKα protein expression in the SDH can initiate the development of thermal hyperalgesia.
Figure 4.
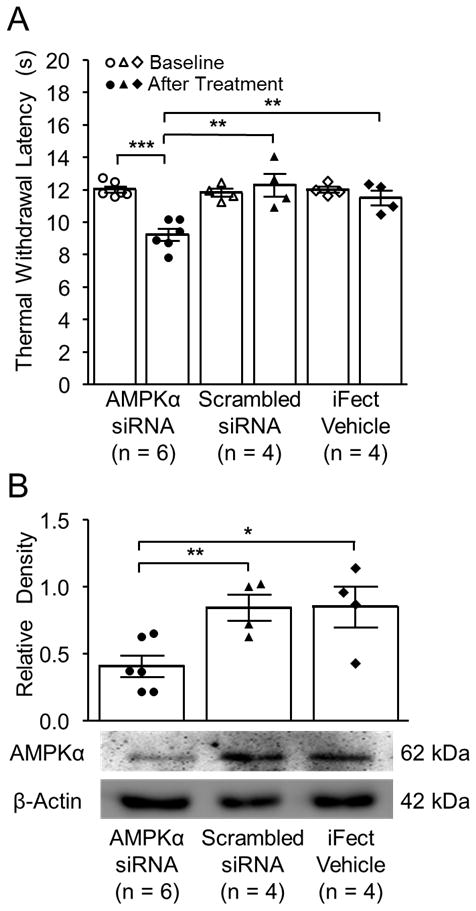
Adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase α (AMPKα) genetic knockdown through intrathecal small interfering RNA (siRNA) induced thermal hyperalgesia in naïve rats. (A) Bar graphs show the mean (± SEM) of the thermal withdrawal latency at baseline and after two days of intrathecal treatment (After treatment) in rats treated with AMPKα siRNA, Scrambled siRNA, or the iFect Vehicle. Data obtained from individual animals are shown in scatter plots. (B) Bar graphs show the mean (± SEM) relative density of AMPKα to β-Actin in the spinal dorsal horn of rats treated with AMPKα siRNA, Scrambled siRNA, or the iFect Vehicle. Data obtained from individual animals are shown in the scatter plots. Samples of each molecule protein expression in each group are shown. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, and *** p < 0.001.
Genetic knockdown of AMPKα increased protein expressions of GFAP and IL-1β, and GSK3β activity, as well as decreased GLT-1 protein expression in the SDH
To understand the spinal molecular mechanisms underlying the changes of nociceptive behaviors induced by AMPKα gene knockdown, the rats from the above three groups that completed the behavioral tests were used for Western blot experiments. We found that expressions of GFAP and IL-1β were significantly higher in the AMPKα siRNA group (n = 6) than those in the scrambled siRNA group (p < 0.05, n = 4) and the iFect vehicle group (p < 0.05, n = 4) (fig. 5). At the same time, GLT-1 protein expression in the AMPKα siRNA group was significantly reduced compared to the scrambled siRNA group (p < 0.05, n = 4) and the iFect vehicle group (p < 0.05, n = 4). The suppression of GLT-1 protein expression, and enhanced expression of IL-1β and GFAP in neuropathic rats with pSNL were recently reported by us to be related to increased GSK3β activities. 25 Decreased phosphorylated GSK3β (pGSK3β) denotes an increase in GSK3β activity. 42–44 Thus, protein expressions of total GSK3β (tGSK3β) and pGSK3β were analyzed. Expressions of total GSK3β among the AMPKα siRNA group, scrambled siRNA group, and iFect vehicle group were similar (data not shown). In contrast, the ratio of pGSK3β to tGSK3β (pGSK3β/tGSK3β) in the AMPKα siRNA group were significantly reduced in comparison with those in the scrambled siRNA group (p < 0.05, n = 4), and the iFect vehicle group (p < 0.05, n = 4) (fig. 5), indicating an increase of GSK3β activity in the SDH. These results suggest that glial activation, over-production of IL-1β, increased activities of GSK3β, and suppression of glial GT functions may underlie mechanisms by which dysfunctional AMPK induces thermal hypersensitivity in rats.
Figure 5.
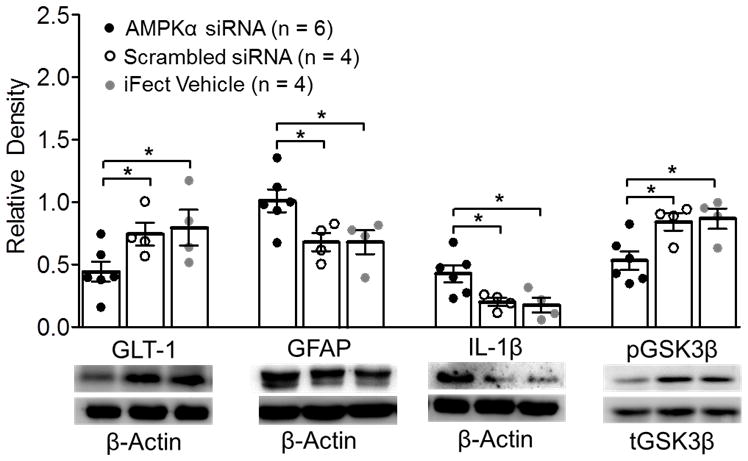
Spinal genetic knockdown of adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase α (AMPKα) decreased glial glutamate transporter 1 (GLT-1) protein expression and increased glial fibrillary acid protein promoter (GFAP) and interleukin-1beta (IL-1β) protein expression, and glycogen synthase kinase 3 beta (GSK3β) activity in naïve rats. Bar graphs show the mean (± SEM) relative density of GLT-1, GFAP, and IL-1β to β-Actin and phosphorylated GSK3β (pGSK3β) to tGSK3β in the spinal dorsal horn of AMPKα small interfering RNA (siRNA), Scrambled siRNA, or the iFect Vehicle treated rats. Data obtained from individual animals are shown in the scatter plot. Samples of each molecule protein expression in each group are shown. * p < 0.05
Selective AMPKα1 deletion induced thermal hyperalgesia and mechanical allodynia
To further narrow down the specific AMPKα isoform implicated in spinal nociceptive processing, the AMPKα1 isoform was selectively deleted from mice expressing the Cre recombinase under the control of GFAP 21 using the well-characterized Cre-loxP recombination system for conditional gene knockout in mice. 45–47 When hind paw withdrawal response latencies to heat stimuli were measured in AMPKα1 knockout mice (n = 6) and control littermates (n = 5), we found that AMPKα1 knockout mice had a significantly shorter latency of withdrawal responses to heat stimuli (p < 0.01, fig. 6A). Additionally, the 50% withdrawal threshold was measured in AMPKα1 knockout mice and littermates. We found that AMPKα1 knockout mice had a significantly (p < 0.01, n = 6) decreased mechanical withdrawal threshold compared to littermates (n = 5, fig. 6B). Furthermore, we also analyzed protein expressions of GFAP, IL-1β, GSK3β, and GLT-1 in the SDH in AMPKα1 knockout mice and control littermates. In comparison with the littermates (n = 5), AMPKα1 knockout mice (n = 6) had significantly increased expressions of GFAP (p < 0.05) and IL-1β (p < 0.01), significantly decreased ratio of pGSK3β/tGSK3β (p < 0.05) and protein expression of GLT-1 (p < 0.05, fig. 6C). These data are consistent with the changes induced by the genetic knockdown of AMPKα induced by siRNA in rats and further indicate that: a) AMPKα regulates spinal nociceptive processing in both mice and rats; b) reduced AMPKα1 activities in the central nervous system (CNS) results in the development of thermal hyperalgesia and mechanical allodynia through increasing astrocytic activation, production of IL-1β, and activities of GSK3β, as well as reducing GLT-1 protein expression in the SDH.
Figure 6.
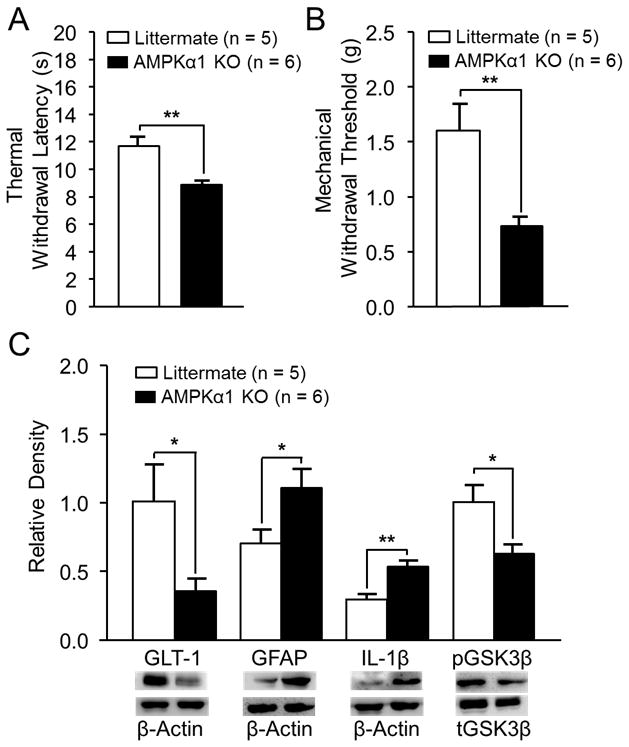
Selective adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase α1 genetic deletion (AMPKα1 KO) induced thermal hyperalgesia and mechanical allodynia, which is associated with decreased glial glutamate transporter 1 (GLT-1) expression, and increased glial fibrillary acid protein promoter (GFAP) and interleukin-1beta (IL-1β) protein expression and glycogen synthase kinase 3 beta (GSK3β) activity. (A) Bar graphs show summaries (+ SEM) of the withdrawal latency to heat stimuli in the AMPKα1 KO and littermate mice. (B) Bar graphs show summaries (+ SEM) of the 50% mechanical withdrawal threshold in the AMPKα1 KO and littermate mice. (C) Bar graphs show the mean (+ SEM) relative density of GLT-1, GFAP, and IL-1β to β-Actin and pGSK3β to tGSK3β in the spinal cord of AMPKα1 knockout mice and littermates. Samples of each molecule protein expression in each group are shown. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01
AMPK activation enhanced glial glutamate transporter activities in astrocytes in the SDH of mice following nerve injury
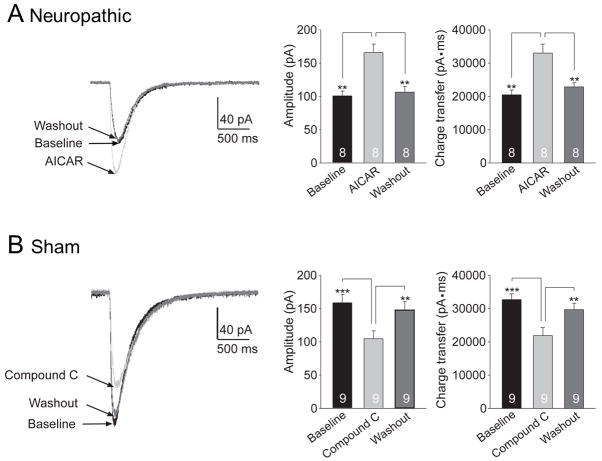
We next determined whether glial GT activities are regulated by AMPK. Glial GT activities were directly monitored by recording glutamate transporter currents (GTCs) from astrocytes in the SDH of GFP-GFAP transgenic mice with neuropathic pain 10 days following pSNL. The transport of glutamate by glial GTs is accompanied by the cotransport of two or three Na+ with one H+ and the counter transport of one K+.48,49 Because of the translocation of a net positive charge during each transport cycle, the transport of glutamate generates a current called GTC. The size of GTCs reflects the amount of transported glutamate, which has been widely used as an effective tool to study the function of glial GTs. 14,36,50 We recently reported that mice with pSNL had lower amplitudes of GTCs. 14 After recording baseline GTCs in spinal slices taken from neuropathic GFP-GFAP mice, we perfused the AMPK activator (AICAR, concentration in the bath: 10 μM) into the recording chamber and recorded GTCs again. We found that activation of AMPK with AICAR significantly increased GTC amplitudes and charge transfers (p < 0.01, n = 8, fig. 7A). The effects of AICAR disappeared within 10 min following washout. In contrast, when we recorded GTCs from sham-operated GFP-GFAP mice and examined the effects of AMPK inhibition on GTCs, we found that perfusion of the AMPK inhibitor (Compound C, concentration in the bath: 10 μM) suppressed GTC amplitudes and charge transfers (p < 0.001, n = 9, fig. 7B). Such effects disappeared within 10 min following washout of Compound C. These data provide direct evidence that activities of glial GTs are rapidly regulated by AMPK activities, and increased activation of AMPK in neuropathic animals can reverse the injury-induced suppression on glial GT activities. The prompt changes of glial GT activities induced by the alteration of AMPK activities led us to hypothesize that post-translational mechanisms may be used by the AMPK activator and inhibitor to regulate glial GT activities.
Figure 7.
Glutamate transporter currents (GTCs) recordings from green fluorescent protein labeled glial fibrillary acid protein promoter (GFP-GFAP) mouse astrocytes. (A) GTCs in spinal slices taken from neuropathic mice were significantly enhanced by bath perfusion with an adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase (AMPK) activator [5-Aminoimidazole-4-carboxamide ribonucleotide (AICAR), 10 μM]. (B) Perfusion of an AMPK inhibitor (Compound C, 10 μM) reversibly suppressed glial GT activities in spinal slices taken from sham-operated mice. Original recordings of GTCs prior to the tested agents (baseline), during and after washout of the tested agents are shown to the left. Bar graphs on the right show mean (+ SEM) of the GTC amplitude and charge transfer at baseline, during and after washout of the tested agents. ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001.
AMPK activation attenuated GLT-1 internalization induced by IL-1β
We recently reported that enhancement of glial GT endocytosis is a critical posttranslational mechanism by which endogenous IL-1β in mice and rats with neuropathic pain or exogenous IL-1β suppresses spinal glial GT activities. 14 We then tested if the activation of AMPK can alter glial GT endocytosis induced by IL-1β. Spinal slices obtained from the spinal L4–5 segment of naïve rats were prepared (450 μm thick) and incubated in aCSF for 15 min in three conditions: artificial CSF only, IL-1β (10 ng/ml), and IL-1β (10 ng/ml) plus the AMPK activator (AICAR, 10 μM). Consistent with our previous findings 14, spinal slices incubated with IL-1β (10 ng/ml) displayed a significant increase in the endocytosis of GLT-1, as evident by an increase in cytosolic GLT-1 expression with a reduction of GLT-1 expression in the plasma membrane in comparison with slices treated with only artificial CSF (fig. 8). These effects were significantly attenuated by the AMPK activator in the IL-1β plus AMPK activator group (fig. 8). These results establish that AMPK can alter glial GT activities through a post-translational mechanism, i.e., the regulation of trafficking of glial GTs between the cell surface and cytosol.
Figure 8.
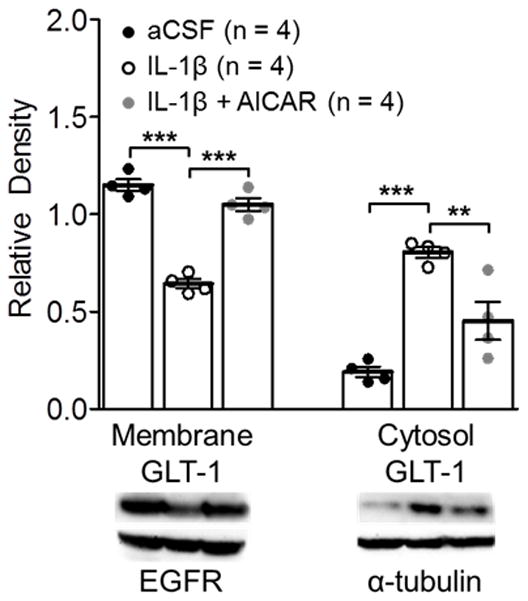
Adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase (AMPK) activation attenuated the interleukin-1beta (IL-1β) increased internalization of glial glutamate transporter 1 (GLT-1) in naïve rat spinal slices. Samples of GLT-1 protein expression in the cell surface (membrane) and cytosol in spinal dorsal horn slices treated with artificial cerebrospinal fluid (aCSF), IL-1β, and IL-1β + [5-aminoimidazole-4-carboxamide ribonucleotide (AICAR)] for 15 min are shown. Bar graphs show the mean (± SEM) relative density of GLT-1 in the plasma membrane to epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) and the mean (± SEM) relative density of GLT-1 in the cytosol to α-tubulin in each group. Data obtained from individual animals are shown in the scatter plot. ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001.
Discussion
Regulation of spinal nociceptive processing by AMPK
Emerging studies suggest that pain signaling pathways are regulated by AMPK activities. Systemic daily administration of AMPK activators (metformin and A769662) attenuated mechanical allodynia in rodents with neuropathic pain induced by spinal nerve ligation or spared nerve injury. 7 Mechanical allodynia induced by surgical incision or subcutaneous injection of IL-6 were attenuated by topical injection of another AMPK activator (resveratrol) into the peripheral lesion site. 6 Suppression of the mechanistic target of rapamycin and the extracellular-signal-regulated kinase activities at peripheral sensory neurons is suggested to underlie the effects induced by AMPK activators on these models. 6,7 Intraperitoneal injection of AMPK activators (AICAR and/or metformin) suppressed inflammatory pain and tissue edema induced by subcutaneous injection of formalin or zymosan. 11 The antinociceptive effects in the formalin model are partially mediated by the reduced activation of different MAP-kinases in the spinal cord. 11 Systemic or spinal administration of resveratrol significantly attenuated the development of morphine tolerance in mice and suppressed morphine-induced microglial activation in the spinal cord. 51 It remains unknown whether and how changes of AMPK activities in the SDH contribute to the genesis of pathological pain. In this study, we found: a) the ratio of pAMPK over tAMPK in the SDH ipsilateral to the injury side in rats with neuropathic pain was reduced; b) activation of AMPK at the spinal cord with the AMPK activator (AICAR) attenuated thermal hyperalgesia in neuropathic rats; c) pharmacological inhibition with Compound C and the genetic knockdown or knockout of AMPK in the spinal cord caused behavioral hypersensitivity. These findings suggest that attenuation of spinal AMPK activities causes abnormal pain signaling at the spinal level. Hence, normalization of AMPK activities at the spinal cord may provide a novel approach to ameliorate neuropathic pain.
Mechanisms underlying the enhanced pain signaling in the spinal dorsal horn induced by the suppression of AMPK activities
We revealed two mechanisms by which suppressed AMPK activities lead to enhanced pain signaling in the SDH: increased neuroinflammation and the suppression of glial GT functions. We found that suppressed AMPK activities in the dorsal horn in rats with neuropathic pain are temporally associated with activation of astrocytes and increased production of IL-1β. More importantly, the genetic deletion of AMPK resulted in thermal hyperalgesia and the activation of astrocytes (one major type of glial cells) and over production of IL-1β. Ample studies have demonstrated that the activation of glial cells and subsequent production of proinflammatory mediators, including IL-1β, play an important role in the enhanced neuronal activation at the spinal cord under different pathological pain conditions, including chronic pain induced by nerve injury, 52,53 inflammation induced by complete Freund’s adjuvant, 54,55 carrageenan, 56 and bone cancer. 57 TNF-α and IL-1β can increase excitatory glutamatergic synaptic activities in the SDH. 27,58 We recently demonstrated that endogenous IL-1β in neuropathic animals increases presynaptic glutamate release from nociceptive primary afferents through coupling with presynaptic NMDA receptors. 27,31 Furthermore, postsynaptic AMPA receptors activities are also enhanced by endogenous IL-1β in neuropathic animals through the MyD88 signaling pathway at postsynaptic neurons. 27 Thus, it is conceivable that through increasing the activation of glial cells and production of IL-1β, suppression of AMPK activities leads to enhanced activation of neurons in the SDH and induces hypersensitivity in animal nociceptive behaviors. While our study is the first to show AMPK regulates neuroinflammation in the SDH in vivo, in vitro studies in line with our findings have been reported. For example, stimulation of macrophages with lipopolysaccharide suppressed AMPK activities. 59,60 In primary cultured astrocytes, AMPK knockout significantly increased IL-6, TNF-α, inducible nitric oxide synthase, chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 2, and C-X-C motif chemokine 10 gene expression. 8 Likewise, dominant negative AMPKα1 macrophages enhanced TNF-α and IL-6 protein synthesis in response to lipopolysaccharide stimulation and a constitutively active form of AMPKα1 suppressed the lipopolysaccharide-induced TNF-α and IL-6 production. 61 In this regard, our siRNA and Cre-loxP mediated experiments not only demonstrated the role of AMPK in regulating neuroinflammation in the spinal cord of intact animals, but also revealed that GSK3β activities are regulated by AMPK, more specifically by the AMPKα1 isoform.
GSK3β is a serine/threonine protein kinase shown to be involved in multiple neurological disorders related to neuroinflammation and recently pathological pain. 62,63 We and others have shown that inhibition of GSK3β attenuates preexisting mechanical hypersensitivity induced by pSNL in mice 64 and rats. 25 We further demonstrated that GSK3β activities in the SDH are increased in rats with neuropathic pain induced by partial sciatic nerve ligation 25 and following paclitaxel treatment. 29 Currently, signaling molecules regulating GSK3β activities in the spinal cord remain unknown. This study demonstrated that GSK3β activities are increased upon suppression of AMPK function as evident by a decreased ratio of pGSK3β/tGSK3β induced by deletion of AMPKα or AMPKα1 in the siRNA and Cre-loxP experiments. Multiple lines of data from other tissues support these findings. In fasted mice, AMPK activation suppresses GSK3β activities in the liver. 65 In differentiated adipocytes, AICAR pretreatment decreases GSK3 activities following insulin stimulation. 66 In HepG2 cells, AMPK activation with resveratrol increases GSK3β phosphorylation which is prevented with Compound C pretreatment. 67 More relevantly, in cortical neurons, AMPK inhibition with Compound C enhances GSK3β activities. 68
One of the novel findings in this study is that AMPK regulates spinal pain signaling through altering glial GT functions. GTs are key factors regulating the activation of glutamate receptors in the CNS including the SDH. While both neurons and astrocytes possess GTs, glial GTs, particularly GLT-1, is a major glial GT in the CNS. 12,69 Multiple studies have demonstrated that dysfunctional glial GTs are critically implicated in the genesis of pathological pain. The down regulation of glial GT expression in the SDH is found in animals with neuropathic pain induced by chronic constriction nerve injury, 13 partial sciatic nerve ligation, 25,70 spinal cord injury, 71 chemotherapy (paclitaxel), 29,72 animals with inflammatory pain induced by complete Freund’s adjuvant, 73 and animals with morphine tolerance. 74,75 We have shown that deficient glial glutamate uptake enhances activation of AMPA and NMDA receptors, and causes glutamate to spill into the extrasynaptic space and activate extrasynaptic NMDA receptors in spinal sensory neurons. 15,35,76 Furthermore, we have also shown that deficient glial glutamate uptake in the SDH results in a decrease of GABAergic synaptic activities due to impairment in GABA synthesis through the glutamate-glutamine cycle. 77 Identifying endogenous mechanisms regulating glial GT functions would reveal new targets for the development of analgesics. In this context, both transcriptional and post-translational mechanisms are involved. Our recent studies suggest that suppression of GSK3β activities in the SDH in rats with neuropathic pain can increase GLT-1 protein expression at the transcriptional level. 25,29 Based on these studies and our current findings that the suppression of GLT-1 protein expression induced by genetic knockdown of AMPK or knockout of the AMPKα1 isoform was simultaneously associated with suppressed pGSK3β protein expression (an increased GSK3β activity), it is conceivable that AMPK, through regulating GSK3β activities, controls the protein expression of GLT-1 at the transcriptional level.
Recent studies by others and us have also shown that posttranslational regulation of glial GTs in the SDH occurs in animals with pathological pain. The posttranslational mechanisms that reduce glial GT functions in the SDH include: nitration of glial GTs 78 in rats with chemotherapy induced pain, 78 proteasome-mediated degradation of the glutamate aspartate transporter and GLT-1 proteins in rats with inflammatory pain induced by complete Freund’s adjuvant, 73 and endocytosis of the glutamate aspartate transporter and GLT-1 from the cell surface into the cytosol in rats with neuropathic pain 14 and morphine tolerance. 79 We also showed that the endocytosis of glial GTs in neuropathic pain is induced by endogenous IL-1β and activation of protein kinase C. 14 Our current study demonstrated that AMPK is another molecule involving in the signaling pathways regulating trafficking of glial GTs in the spinal cord. More importantly, activation of AMPK can attenuate endocytosis of glial GTs in rats with neuropathic pain.
General implications
Neuroinflammation and dysfunction of glial GTs are shared by many pathological pain conditions and neurological diseases such as brain injury or ischemia, Alzheimer’s disease, and depression. 80–84 The regulation of neuroinflammation and glial GT functions by AMPK revealed in this study may shed light into mechanisms related to diseases associated with neuroinflammation and glutamatergic synaptic plasticity in the CNS. Given that AMPK activators like metformin are widely used for diabetes, our studies suggest a potential application of this class of drugs in the clinic.
Final Boxed Summary Statement.
What We Already Know About This Topic
Activation of adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase (AMPK), a metabolic stress sensing protein, leads to suppression of inflammation and a reduction in allodynia in experimental models of pain
Similarly, enhancement of astrocyte glutamate transporter (GT) function prevents the development of pathologic pain whereas down regulation of this transporter induces allodynia
The precise mechanism by which AMPK regulates nociception is not clear. The authors employed a partial sciatic nerve ligation model to determine whether AMPK modulates nociception by suppressing inflammation and regulating glutamate transporters in the spinal cord
What This Article Tells Us That Is New
Nerve injury reduced AMPK activity, increased inflammation, reduced GT expression in the spinal cord and induced thermal hyperalgesia
Activation of AMPK increased GT activity and reduced neuropathic pain; by contrast, knockdown of AMPK induced allodynia
These data indicate that AMPK plays an important role in nociceptive processing in the spinal cord and extend the novel possibility of manipulation of AMPK activity as a therapeutic target in experimental models of pain
Acknowledgments
Financial Support: National Institutes of Health (Bethesda, Maryland) RO1 grant (NS064289) to H.R.W
Footnotes
The authors declare no competing interests
References
- 1.Steinberg GR, Kemp BE. AMPK in health and disease. Physiol Rev. 2009;89:1025–78. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00011.2008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Hardie DG. AMP-activated protein kinase—an energy sensor that regulates all aspects of cell function. Genes Dev. 2011;25:1895–908. doi: 10.1101/gad.17420111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.O’Neill LA, Hardie DG. Metabolism of inflammation limited by AMPK and pseudo-starvation. Nature. 2013;493:346–55. doi: 10.1038/nature11862. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Giri S, Nath N, Smith B, Viollet B, Singh AK, Singh I. 5-aminoimidazole-4-carboxamide-1-β-4-ribofuranoside inhibits proinflammatory response in glial cells: A possible role of AMP-activated protein kinase. J Neurosci. 2004;24:479–87. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4288-03.2004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Hattori Y, Suzuki K, Hattori S, Kasai K. Metformin inhibits cytokine-induced nuclear factor kappaB activation via AMP-activated protein kinase activation in vascular endothelial cells. Hypertension. 2006;47:1183–8. doi: 10.1161/01.HYP.0000221429.94591.72. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Tillu DV, Melemedjian OK, Asiedu MN, Qu N, De Felice M, Dussor G, Price TJ. Resveratrol engages AMPK to attenuate ERK and mTOR signaling in sensory neurons and inhibits incision-induced acute and chronic pain. Mol Pain. 2012;8:5. doi: 10.1186/1744-8069-8-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Melemedjian OK, Asiedu MN, Tillu DV, Sanoja R, Yan J, Lark A, Khoutorsky A, Johnson J, Peebles KA, Lepow T, Sonenberg N, Dussor G, Price TJ. Targeting adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase (AMPK) in preclinical models reveals a potential mechanism for the treatment of neuropathic pain. Mol Pain. 2011;7:70. doi: 10.1186/1744-8069-7-70. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Meares GP, Qin H, Liu Y, Holdbrooks AT, Benveniste EN. AMP-activated protein kinase restricts IFN-γ signaling. J Immunol. 2013;190:372–80. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1202390. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Turnley AM, Stapleton D, Mann RJ, Witters LA, Kemp BE, Bartlett PF. Cellular distribution and developmental expression of AMP-activated protein kinase isoforms in mouse central nervous system. J Neurochem. 1999;72:1707–16. doi: 10.1046/j.1471-4159.1999.721707.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Price TJ, Dussor G. AMPK: An emerging target for modification of injury-induced pain plasticity. Neurosci Lett. 2013;557(Pt A):9–18. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2013.06.060. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Russe OQ, Moser CV, Kynast KL, King TS, Stephan H, Geisslinger G, Niederberger E. Activation of the AMP-activated protein kinase reduces inflammatory nociception. J Pain. 2013;14:1330–40. doi: 10.1016/j.jpain.2013.05.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Danbolt NC. Glutamate uptake. Prog Neurobiol. 2001;65:1–105. doi: 10.1016/s0301-0082(00)00067-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Sung B, Lim G, Mao J. Altered expression and uptake activity of spinal glutamate transporters after nerve injury contribute to the pathogenesis of neuropathic pain in rats. J Neurosci. 2003;23:2899–910. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.23-07-02899.2003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Yan X, Yadav R, Gao M, Weng HR. Interleukin-1 beta enhances endocytosis of glial glutamate transporters in the spinal dorsal horn through activating protein kinase C. Glia. 2014;62:1093–109. doi: 10.1002/glia.22665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Nie H, Weng HR. Impaired glial glutamate uptake induces extrasynaptic glutamate spillover in the spinal sensory synapses of neuropathic rats. J Neurophysiol. 2010;103:2570–80. doi: 10.1152/jn.00013.2010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Hu Y, Li W, Lu L, Cai J, Xian X, Zhang M, Li Q, Li L. An anti-nociceptive role for ceftriaxone in chronic neuropathic pain in rats. Pain. 2010;148:284–301. doi: 10.1016/j.pain.2009.11.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Maeda S, Kawamoto A, Yatani Y, Shirakawa H, Nakagawa T, Kaneko S. Gene transfer of GLT-1, a glial glutamate transporter, into the spinal cord by recombinant adenovirus attenuates inflammatory and neuropathic pain in rats. Mol Pain. 2008;4:65. doi: 10.1186/1744-8069-4-65. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Kemp B, Stapleton D, Campbell D, Chen Z, Murthy S, Walter M, Gupta A, Adams J, Katsis F, van Denderen B. AMP-activated protein kinase, super metabolic regulator. Biochem Soc Trans. 2003;31:162–8. doi: 10.1042/bst0310162. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Hardie DG. AMP-activated/SNF1 protein kinases: conserved guardians of cellular energy. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2007;8:774–85. doi: 10.1038/nrm2249. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Oakhill JS, Steel R, Chen ZP, Scott JW, Ling N, Tam S, Kemp BE. AMPK is a direct adenylate charge-regulated protein kinase. Science. 2011;332:1433–5. doi: 10.1126/science.1200094. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Zhuo L, Theis M, Alvarez-Maya I, Brenner M, Willecke K, Messing A. hGFAP-cre transgenic mice for manipulation of glial and neuronal function in vivo. Genesis. 2001;31:85–94. doi: 10.1002/gene.10008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Nakada D, Saunders TL, Morrison SJ. Lkb1 regulates cell cycle and energy metabolism in haematopoietic stem cells. Nature. 2010;468:653–8. doi: 10.1038/nature09571. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Zhuo L, Sun B, Zhang C-L, Fine A, Chiu S-Y, Messing A. Live astrocytes visualized by green fluorescent protein in transgenic mice. Dev Biol. 1997;187:36–42. doi: 10.1006/dbio.1997.8601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Seltzer Ze, Dubner R, Shir Y. A novel behavioral model of neuropathic pain disorders produced in rats by partial sciatic nerve injury. Pain. 1990;43:205–18. doi: 10.1016/0304-3959(90)91074-S. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Weng H-R, Gao M, Maixner DW. Glycogen synthase kinase 3 beta regulates glial glutamate transporter protein expression in the spinal dorsal horn in rats with neuropathic pain. Exp Neurol. 2014;252:18–27. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2013.11.018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Hargreaves K, Dubner R, Brown F, Flores C, Joris J. A new and sensitive method for measuring thermal nociception in cutaneous hyperalgesia. Pain. 1988;32:77–88. doi: 10.1016/0304-3959(88)90026-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Yan X, Weng H-R. Endogenous interleukin-1β in neuropathic rats enhances glutamate release from the primary afferents in the spinal dorsal horn through coupling with presynaptic N-methyl-D-aspartic acid receptors. J Biol Chem. 2013;288:30544–57. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.495465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Weng H, Chen J, Cata J. Inhibition of glutamate uptake in the spinal cord induces hyperalgesia and increased responses of spinal dorsal horn neurons to peripheral afferent stimulation. Neuroscience. 2006;138:1351–60. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2005.11.061. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Gao M, Yan X, Weng HR. Inhibition of glycogen synthase kinase 3beta activity with lithium prevents and attenuates paclitaxel-induced neuropathic pain. Neuroscience. 2013;254:301–11. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2013.09.033. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Weng HR, Cordella JV, Dougherty PM. Changes in sensory processing in the spinal dorsal horn accompany vincristine-induced hyperalgesia and allodynia. Pain. 2003;103:131–8. doi: 10.1016/s0304-3959(02)00445-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Yan X, Jiang E, Gao M, Weng H-R. Endogenous activation of presynaptic NMDA receptors enhances glutamate release from the primary afferents in the spinal dorsal horn in a rat model of neuropathic pain. J Physiol. 2013;591:2001. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2012.250522. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Yaksh TL, Rudy TA. Analgesia mediated by a direct spinal action of narcotics. Science. 1976;192:1357–8. doi: 10.1126/science.1273597. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Luo M-C, Zhang D-Q, Ma S-W, Huang Y-Y, Shuster SJ, Porreca F, Lai J. An efficient intrathecal delivery of small interfering RNA to the spinal cord and peripheral neurons. Mol Pain. 2005;1:29. doi: 10.1186/1744-8069-1-29. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Lee JH, Budanov AV, Talukdar S, Park EJ, Park HL, Park H-W, Bandyopadhyay G, Li N, Aghajan M, Jang I. Maintenance of metabolic homeostasis by Sestrin2 and Sestrin3. Cell Metab. 2012;16:311–21. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2012.08.004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Weng HR, Chen J, Pan Z, Nie H. Glial glutamate transporter 1 regulates the spatial and temporal coding of glutamatergic synaptic transmission in spinal lamina II neurons. Neuroscience. 2007;149:898–907. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2007.07.063. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Bergles DE, Jahr CE. Synaptic activation of glutamate transporters in hippocampal astrocytes. Neuron. 1997;19:1297–308. doi: 10.1016/s0896-6273(00)80420-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Devaraju P, Sun M-Y, Myers TL, Lauderdale K, Fiacco TA. Astrocytic group I mGluR-dependent potentiation of astrocytic glutamate and potassium uptake. J Neurophysiol. 2013;109:2404–14. doi: 10.1152/jn.00517.2012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Day P, Sharff A, Parra L, Cleasby A, Williams M, Horer S, Nar H, Redemann N, Tickle I, Yon J. Structure of a CBS-domain pair from the regulatory 1 subunit of human AMPK in complex with AMP and ZMP. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 2007;63:587–96. doi: 10.1107/S0907444907009110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Ducommun S, Ford RJ, Bultot L, Deak M, Bertrand L, Kemp BE, Steinberg GR, Sakamoto K. Enhanced activation of cellular AMPK by dual-small molecule treatment: AICAR and A769662. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2014;306:E688–96. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00672.2013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Giri S, Rattan R, Haq E, Khan M, Yasmin R, Won J-s, Key L, Singh AK, Singh I. AICAR inhibits adipocyte differentiation in 3T3L1 and restores metabolic alterations in diet-induced obesity mice model. Nutr Metab. 2006;3:31. doi: 10.1186/1743-7075-3-31. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Theodoropoulou S, Brodowska K, Kayama M, Morizane Y, Miller JW, Gragoudas ES, Vavvas DG. Aminoimidazole carboxamide ribonucleotide (AICAR) inhibits the growth of retinoblastoma in vivo by decreasing angiogenesis and inducing apoptosis. PloS One. 2013;8:e52852. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0052852. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Grimes CA, Jope RS. The multifaceted roles of glycogen synthase kinase 3β in cellular signaling. Prog Neurobiol. 2001;65:391–426. doi: 10.1016/s0301-0082(01)00011-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Woodgett JR. Molecular cloning and expression of glycogen synthase kinase-3/Factor A. EMBO J. 1990;9:2431–8. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07419.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Sutherland C, Leighton IA, Cohen P. Inactivation of glycogen synthase kinase-3 beta by phosphorylation: New kinase connections in insulin and growth-factor signalling. Biochem J. 1993;296(Pt 1):15–9. doi: 10.1042/bj2960015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Moore SA, Saito F, Chen J, Michele DE, Henry MD, Messing A, Cohn RD, Ross-Barta SE, Westra S, Williamson RA, Hoshi T, Campbell KP. Deletion of brain dystroglycan recapitulates aspects of congenital muscular dystrophy. Nature. 2002;418:422–5. doi: 10.1038/nature00838. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Ango F, Wu C, Van der Want JJ, Wu P, Schachner M, Huang ZJ. Bergmann glia and the recognition molecule CHL1 organize GABAergic axons and direct innervation of purkinje cell dendrites. PLoS Biol. 2008;6:e103. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.0060103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Schwenk F, Baron U, Rajewsky K. A cre-transgenic mouse strain for the ubiquitous deletion of loxP-flanked gene segments including deletion in germ cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1995;23:5080. doi: 10.1093/nar/23.24.5080. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Wadiche JI, Arriza JL, Amara SG, Kavanaugh MP. Kinetics of a human glutamate transporter. Neuron. 1995;14:1019–27. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(95)90340-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Levy LM, Warr O, Attwell D. Stoichiometry of the glial glutamate transporter GLT-1 expressed inducibly in a Chinese hamster ovary cell line selected for low endogenous Na+-dependent glutamate uptake. J Neurosci. 1998;18:9620–8. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.18-23-09620.1998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Adolph O, Koster S, Rath M, Georgieff M, Weigt HU, Engele J, Senftleben U, Fohr KJ. Rapid increase of glial glutamate uptake via blockade of the protein kinase A pathway. Glia. 2007;55:1699–707. doi: 10.1002/glia.20583. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Han Y, Jiang C, Tang J, Wang C, Wu P, Zhang G, Liu W, Jamangulova N, Wu X, Song X. Resveratrol reduces morphine tolerance by inhibiting microglial activation via AMPK signalling. Eur J Pain. 2014;18:1458–70. doi: 10.1002/ejp.511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Xin W-J, Weng H-R, Dougherty PM. Plasticity in expression of the glutamate transporters GLT-1 and GLAST in spinal dorsal horn glial cells following partial sciatic nerve ligation. Mol Pain. 2009;5:5. doi: 10.1186/1744-8069-5-15. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Coyle DE. Partial peripheral nerve injury leads to activation of astroglia and microglia which parallels the development of allodynic behavior. Glia. 1998;23:75–83. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Lindia JA, McGowan E, Jochnowitz N, Abbadie C. Induction of CX3CL1 expression in astrocytes and CX3CR1 in microglia in the spinal cord of a rat model of neuropathic pain. J Pain. 2005;6:434–8. doi: 10.1016/j.jpain.2005.02.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Raghavendra V, Tanga FY, DeLeo JA. Complete Freunds adjuvant-induced peripheral inflammation evokes glial activation and proinflammatory cytokine expression in the CNS. Eur J Neurosci. 2004;20:467–73. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2004.03514.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Watkins LR, Maier SF. Beyond neurons: Evidence that immune and glial cells contribute to pathological pain states. Physiol Rev. 2002;82:981–1011. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00011.2002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Zhang R-X, Liu B, Wang L, Ren K, Qiao J-T, Berman BM, Lao L. Spinal glial activation in a new rat model of bone cancer pain produced by prostate cancer cell inoculation of the tibia. Pain. 2005;118:125–36. doi: 10.1016/j.pain.2005.08.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Kawasaki Y, Zhang L, Cheng J-K, Ji R-R. Cytokine mechanisms of central sensitization: Distinct and overlapping role of interleukin-1β, interleukin-6, and tumor necrosis factor-α in regulating synaptic and neuronal activity in the superficial spinal cord. J Neurosci. 2008;28:5189–94. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3338-07.2008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Yang Z, Kahn BB, Shi H, Xue BZ. Macrophage alpha1 AMP-activated protein kinase (alpha1AMPK) antagonizes fatty acid-induced inflammation through SIRT1. J Biol Chem. 2010;285:19051–9. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.123620. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Tadie JM, Bae HB, Deshane JS, Bell CP, Lazarowski ER, Chaplin DD, Thannickal VJ, Abraham E, Zmijewski JW. Toll-like receptor 4 engagement inhibits adenosine 5′-monophosphate-activated protein kinase activation through a high mobility group box 1 protein-dependent mechanism. Mol Med. 2012;18:659–68. doi: 10.2119/molmed.2011.00401. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Sag D, Carling D, Stout RD, Suttles J. Adenosine 5′-monophosphate-activated protein kinase promotes macrophage polarization to an anti-inflammatory functional phenotype. J Immunol. 2008;181:8633–41. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.181.12.8633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Martins DF, Rosa AO, Gadotti VM, Mazzardo-Martins L, Nascimento FP, Egea J, Lopez MG, Santos AR. The antinociceptive effects of AR-A014418, a selective inhibitor of glycogen synthase kinase-3 beta, in mice. J Pain. 2011;12:315–22. doi: 10.1016/j.jpain.2010.06.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Maixner DW, Weng H-R. The role of glycogen synthase kinase 3 beta in neuroinflammation and pain. J Pharm Pharmacol. 2013;1:001. doi: 10.13188/2327-204X.1000001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Mazzardo-Martins L, Martins DF, Stramosk J, Cidral-Filho FJ, Santos ARS. Glycogen synthase kinase 3-specific inhibitor AR-A014418 decreases neuropathic pain in mice: Evidence for the mechanisms of action. Neuroscience. 2012;226:411–20. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2012.09.020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Horike N, Sakoda H, Kushiyama A, Ono H, Fujishiro M, Kamata H, Nishiyama K, Uchijima Y, Kurihara Y, Kurihara H. AMP-activated protein kinase activation increases phosphorylation of glycogen synthase kinase 3β and thereby reduces cAMP-responsive element transcriptional activity and phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase C gene expression in the liver. J Biol Chem. 2008;283:33902–10. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M802537200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Tao R, Gong J, Luo X, Zang M, Guo W, Wen R, Luo Z. AMPK exerts dual regulatory effects on the PI3K pathway. J Mol Signal. 2010;5:1. doi: 10.1186/1750-2187-5-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Shin SM, Cho IJ, Kim SG. Resveratrol protects mitochondria against oxidative stress through AMP-activated protein kinase-mediated glycogen synthase kinase-3β inhibition downstream of Poly(ADP-ribose)polymerase-LKB1 pathway. Mol Pharmacol. 2009;76:884–95. doi: 10.1124/mol.109.058479. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Park H, Kam T-I, Kim Y, Choi H, Gwon Y, Kim C, Koh J-Y, Jung Y-K. Neuropathogenic role of adenylate kinase-1 in Aβ-mediated tau phosphorylation via AMPK and GSK3β. Hum Mol Genet. 2012;21:2725–37. doi: 10.1093/hmg/dds100. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Tanaka K, Watase K, Manabe T, Yamada K, Watanabe M, Takahashi K, Iwama H, Nishikawa T, Ichihara N, Kikuchi T, Okuyama S, Kawashima N, Hori S, Takimoto M, Wada K. Epilepsy and exacerbation of brain injury in mice lacking the glutamate transporter GLT-1. Science. 1997;276:1699–702. doi: 10.1126/science.276.5319.1699. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Nie H, Zhang H, Weng HR. Minocycline prevents impaired glial glutamate uptake in the spinal sensory synapses of neuropathic rats. Neuroscience. 2010;170:901–12. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2010.07.049. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Putatunda R, Hala TJ, Chin J, Lepore AC. Chronic at-level thermal hyperalgesia following rat cervical contusion spinal cord injury is accompanied by neuronal and astrocyte activation and loss of the astrocyte glutamate transporter, GLT1, in superficial dorsal horn. Brain Res. 2014;1581:64–79. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2014.05.003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Weng HR, Aravindan N, Cata JP, Chen JH, Shaw AD, Dougherty PM. Spinal glial glutamate transporters downregulate in rats with taxol-induced hyperalgesia. Neurosci Lett. 2005;386:18–22. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2005.05.049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Kim HN, Kim YR, Jang JY, Shin HK, Choi BT. Electroacupuncture confers antinociceptive effects via inhibition of glutamate transporter downregulation in complete Freund’s adjuvant-Injected rats. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2012;2012:643973. doi: 10.1155/2012/643973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Mao J, Sung B, Ji RR, Lim G. Chronic morphine induces downregulation of spinal glutamate transporters: Implications in morphine tolerance and abnormal pain sensitivity. J Neurosci. 2002;22:8312–23. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.22-18-08312.2002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Yang L, Wang S, Lim G, Sung B, Zeng Q, Mao J. Inhibition of the ubiquitin-proteasome activity prevents glutamate transporter degradation and morphine tolerance. Pain. 2008;140:472–8. doi: 10.1016/j.pain.2008.09.028. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Nie H, Weng HR. Glutamate transporters prevent excessive activation of NMDA receptors and extrasynaptic glutamate spillover in the spinal dorsal horn. J Neurophysiol. 2009;101:2041–51. doi: 10.1152/jn.91138.2008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Jiang E, Yan X, Weng HR. Glial glutamate transporter and glutamine synthetase regulate GABAergic synaptic strength in the spinal dorsal horn. J Neurochem. 2012;121:526–36. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2012.07694.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Doyle T, Chen Z, Muscoli C, Bryant L, Esposito E, Cuzzocrea S, Dagostino C, Ryerse J, Rausaria S, Kamadulski A, Neumann WL, Salvemini D. Targeting the overproduction of peroxynitrite for the prevention and reversal of paclitaxel-induced neuropathic pain. J Neurosci. 2012;32:6149–60. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.6343-11.2012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Tai YH, Wang YH, Tsai RY, Wang JJ, Tao PL, Liu TM, Wang YC, Wong CS. Amitriptyline preserves morphine’s antinociceptive effect by regulating the glutamate transporter GLAST and GLT-1 trafficking and excitatory amino acids concentration in morphine-tolerant rats. Pain. 2007;129:343–54. doi: 10.1016/j.pain.2007.01.031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Kaul M, Garden GA, Lipton SA. Pathways to neuronal injury and apoptosis in HIV-associated dementia. Nature. 2001;410:988–94. doi: 10.1038/35073667. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Mitosek-Szewczyk K, Sulkowski G, Stelmasiak Z, Struzynska L. Expression of glutamate transporters GLT-1 and GLAST in different regions of rat brain during the course of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Neuroscience. 2008;155:45–52. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2008.05.025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Rossi DJ, Brady JD, Mohr C. Astrocyte metabolism and signaling during brain ischemia. Nat Neurosci. 2007;10:1377–86. doi: 10.1038/nn2004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Shigeri Y, Seal RP, Shimamoto K. Molecular pharmacology of glutamate transporters, EAATs and VGLUTs. Brain research Brain Res Rev. 2004;45:250–65. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresrev.2004.04.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Medina A, Burke S, Thompson RC, Bunney W, Jr, Myers RM, Schatzberg A, Akil H, Watson SJ. Glutamate transporters: A key piece in the glutamate puzzle of major depressive disorder. J Psychiatr Res. 2013;47:1150–6. doi: 10.1016/j.jpsychires.2013.04.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]