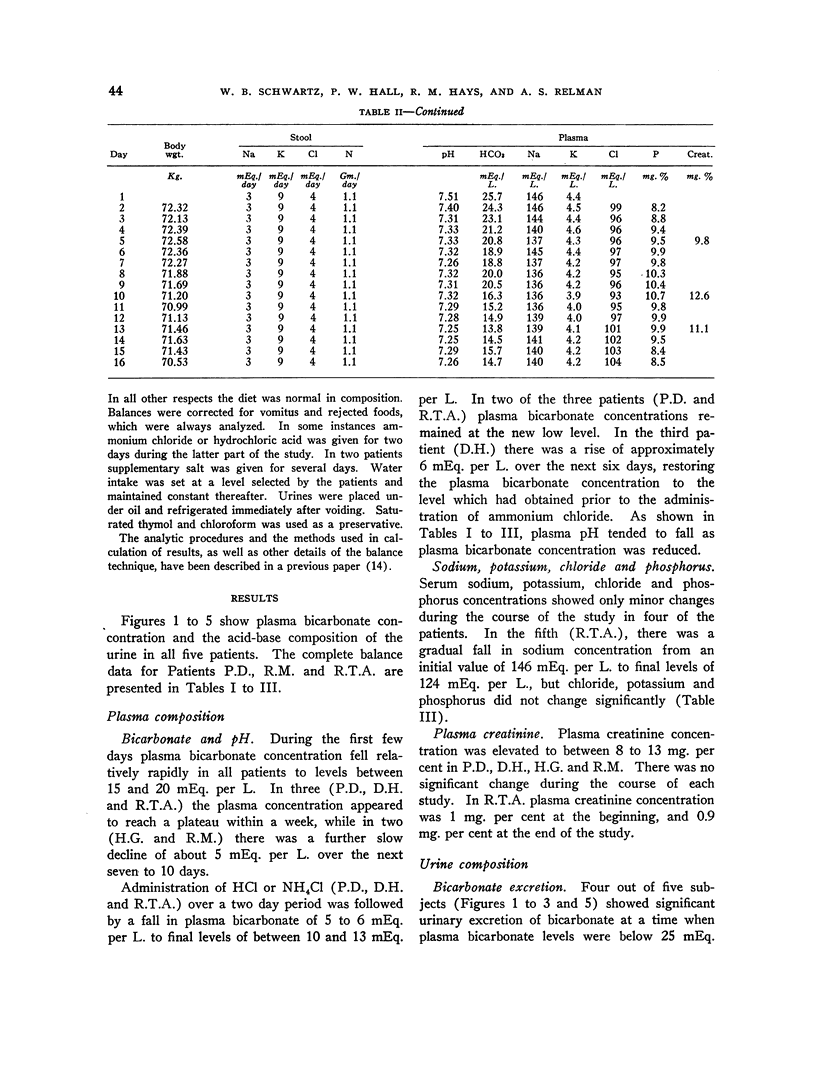
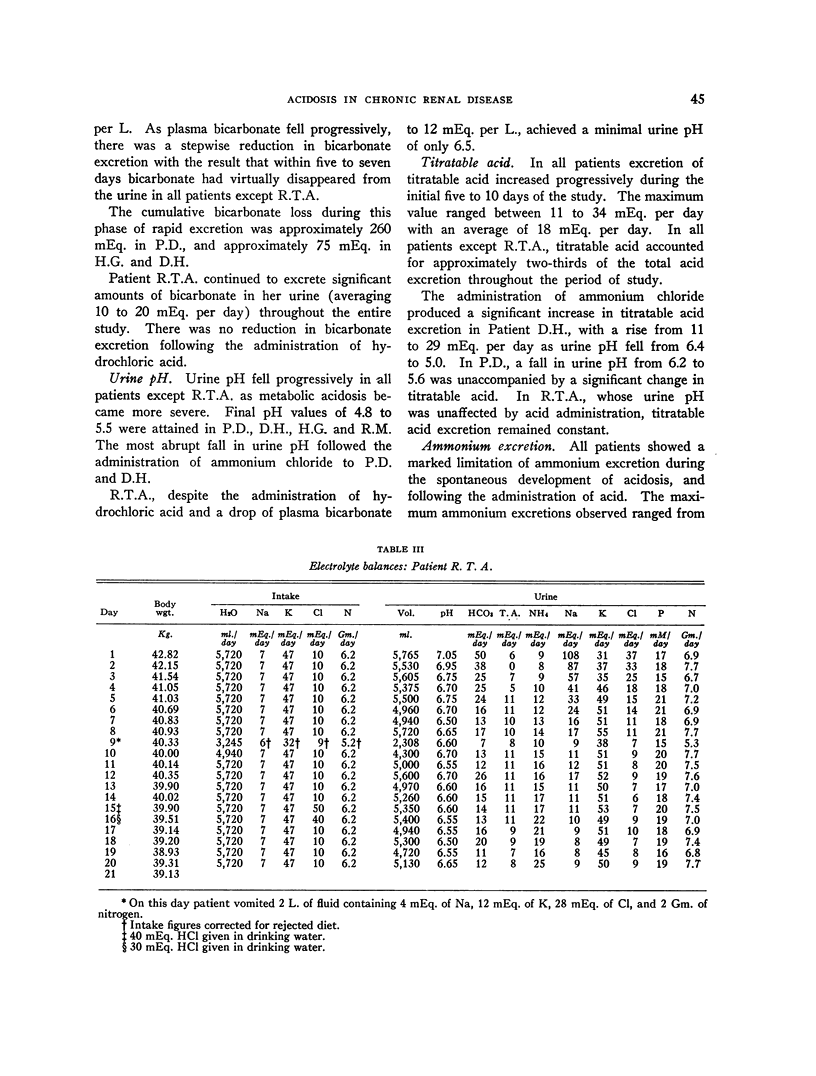
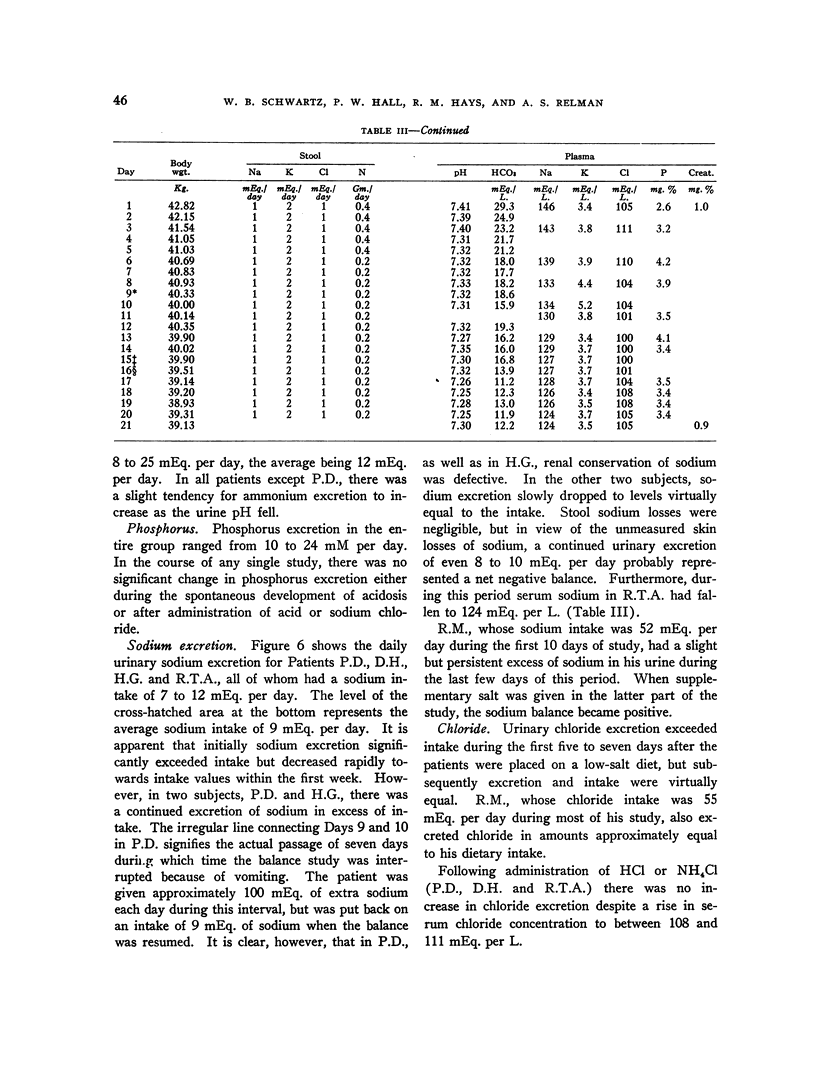
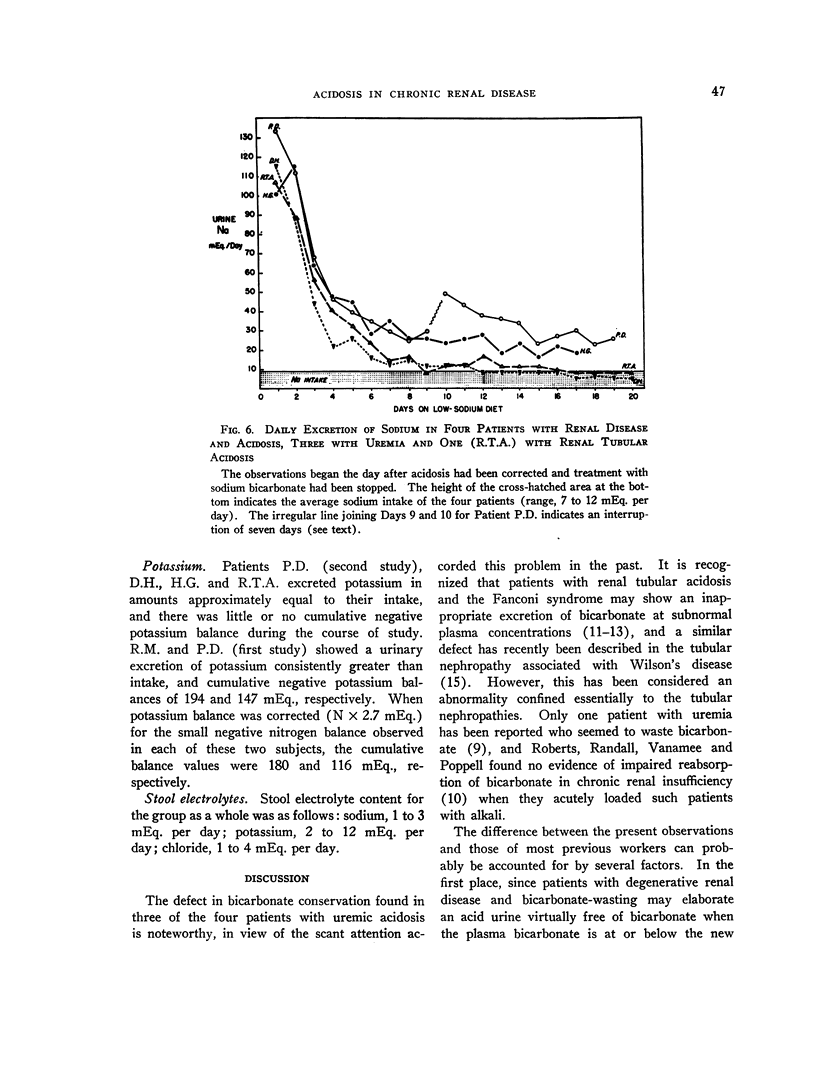
Full text
PDF
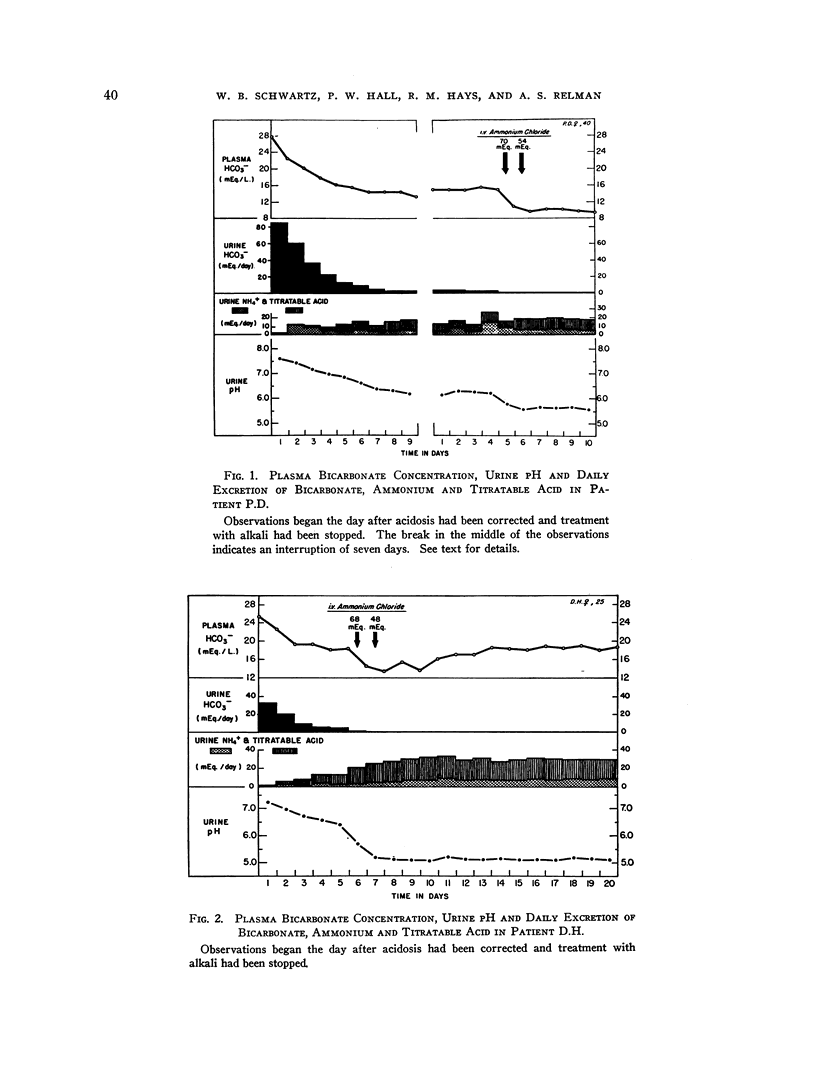
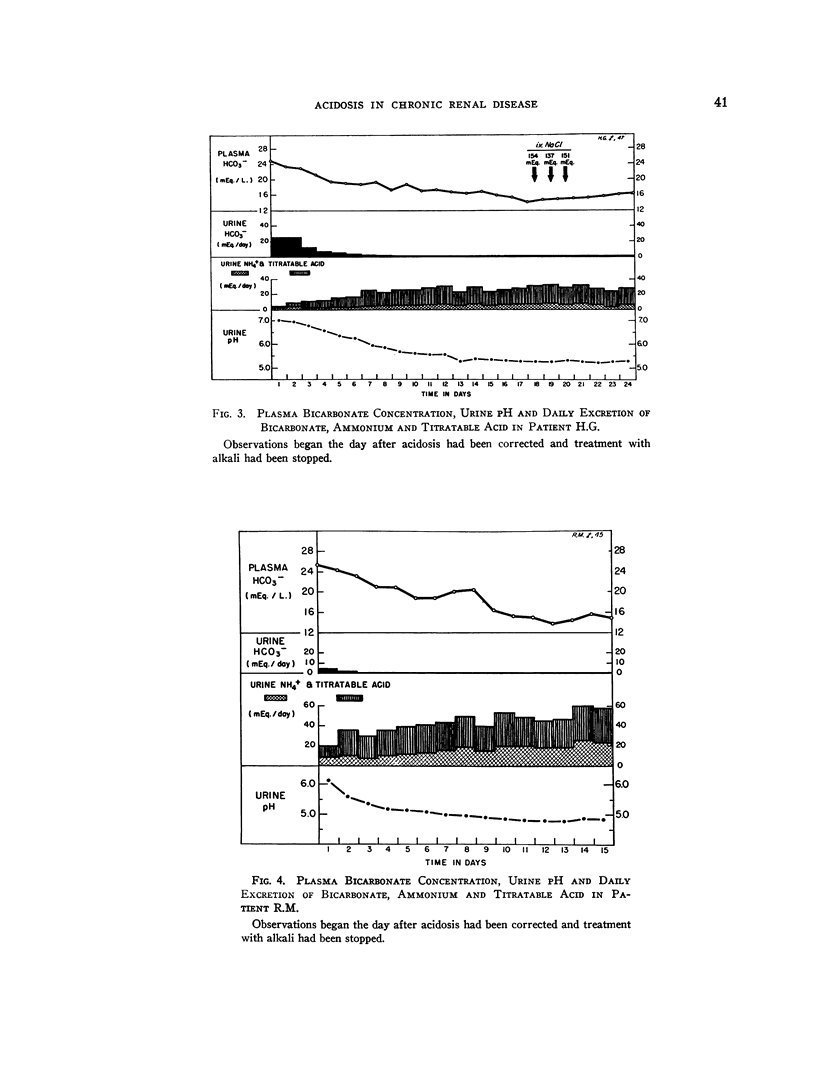
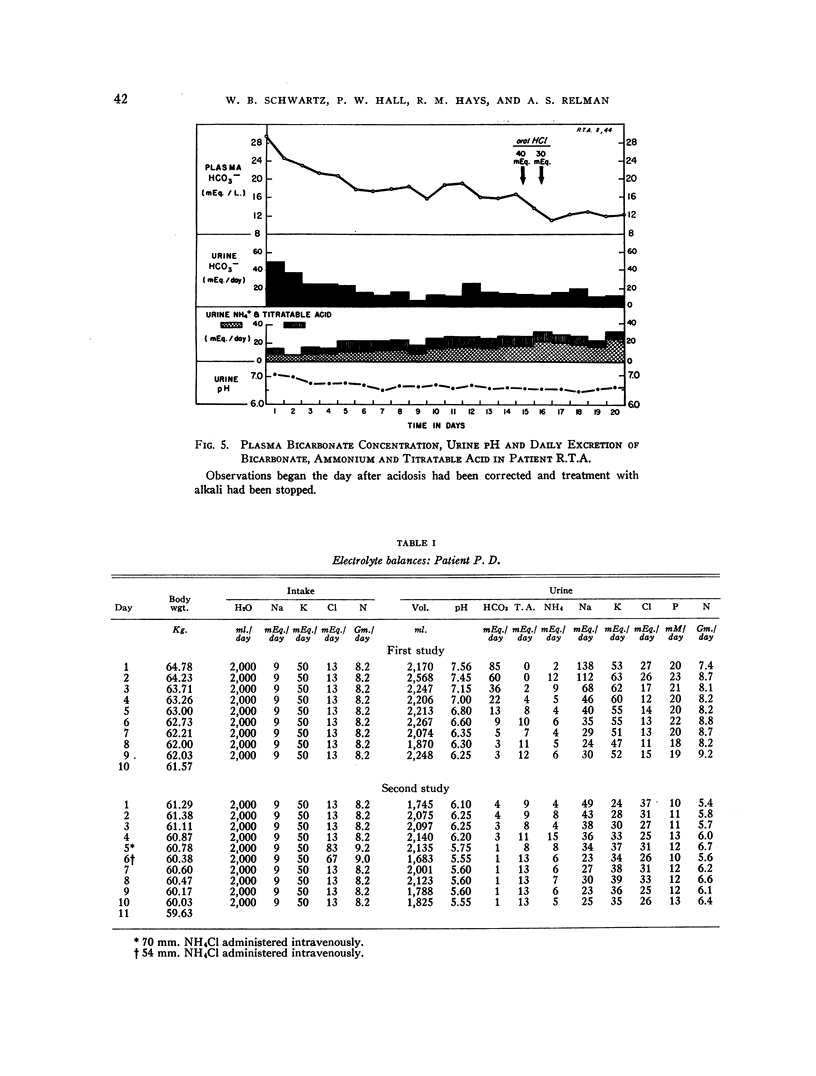
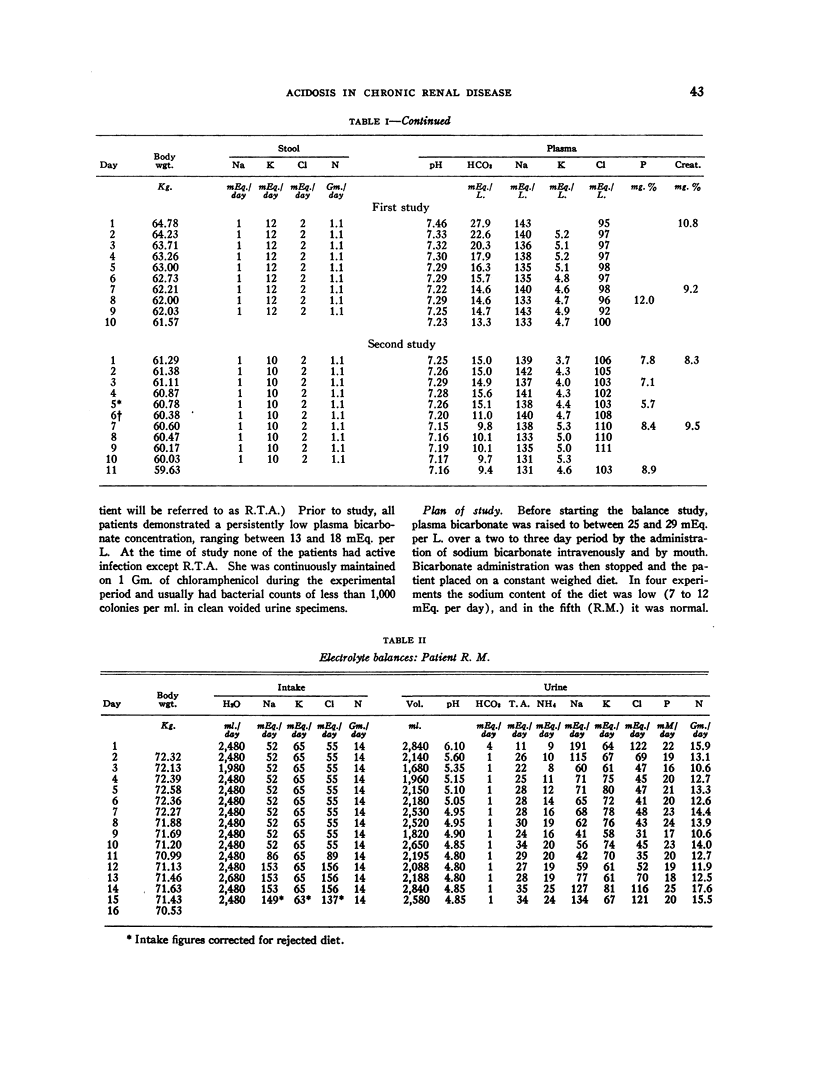





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BEARN A. G., YU T. F., GUTMAN A. B. Renal function in Wilson's disease. J Clin Invest. 1957 Jul;36(7):1107–1114. doi: 10.1172/JCI103506. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COUNIHAN T. B., EVANS B. M., MILNE M. D. Observations on the pharmacology of the carbonic anhydrase inhibitor diamox. Clin Sci. 1954 Nov;13(4):583–598. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIES H. E., WRONG O. Acidity of urine and excretion of ammonium in renal disease. Lancet. 1957 Sep 28;273(6996):625–625. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(57)91949-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gamble J. L., Blackfan K. D., Hamilton B. A STUDY OF THE DIURETIC ACTION OF ACID PRODUCING SALTS. J Clin Invest. 1925 Apr;1(4):359–388. doi: 10.1172/JCI100019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEAF A., SCHWARTZ W. B., RELMAN A. S. Oral administration of a potent carbonic anhydrase inhibitor (diamox). I. Changes in electrolyte and acid-base balance. N Engl J Med. 1954 May 6;250(18):759–764. doi: 10.1056/NEJM195405062501803. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MUDGE G. H. Clinical patterns of tubular dysfunction. Am J Med. 1958 May;24(5):785–804. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(58)90381-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PETERSEN V. P. Renal function and electrolyte metabolism in salt-losing nephritis. Acta Med Scand. 1956 May 3;154(3):187–199. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RELMAN A. S., SCHWARTZ W. B. The effect of DOCA on electrolyte balance in normal man and its relation to sodium chloride intake. Yale J Biol Med. 1952 Jun;24(6):540–558. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROBERTS K. E., RANDALL H. T., VANAMEE P., POPPELL J. W. Renal mechanisms involved in bicarbonate absorption. Metabolism. 1956 Jul;5(4):404–418. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHWARTZ W. B., FALBRIARD A., RELMAN A. S. An analysis of bicarbonate reabsorption during partial inhibition of carbonic anhydrase. J Clin Invest. 1958 May;37(5):744–751. doi: 10.1172/JCI103660. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHWARTZ W. B., JENSON R. L., RELMAN A. S. The disposition of acid administered to sodium-depleted subjects: the renal response and the role of the whole body buffers. J Clin Invest. 1954 Apr;33(4):587–597. doi: 10.1172/JCI102930. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHWARTZ W. B., RELMAN A. S. Acidosis in renal disease. N Engl J Med. 1957 Jun 20;256(25):1184–1186. doi: 10.1056/NEJM195706202562505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STANBURY S. W. Azotaemic renal osteodystrophy. Br Med Bull. 1957 Jan;13(1):57–60. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a069572. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Slyke D. D., Linder G. C., Hiller A., Leiter L., McIntosh J. F. THE EXCRETION OF AMMONIA AND TITRATABLE ACID IN NEPHRITIS. J Clin Invest. 1926 Feb;2(3):255–288. doi: 10.1172/JCI100045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOOD F. J. Ammonium chloride acidosis. Clin Sci. 1955 Feb;14(1):81–89. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



