Abstract
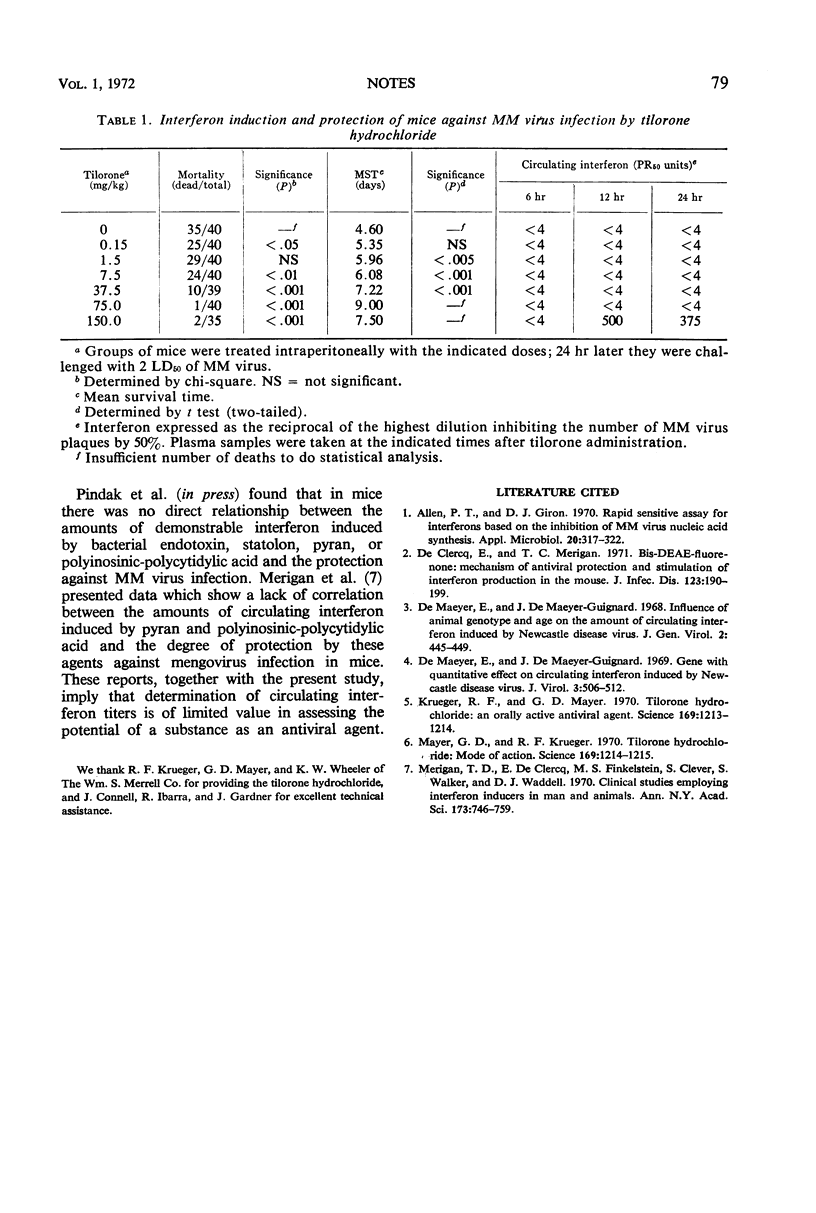
The protection of mice against MM virus infection and the induction of circulating interferon by tilorone hydrochloride were determined. Whereas protection was evident with doses of 0.15 and 1.5 mg/kg, interferon was not detected with doses lower than 150 mg/kg. Protection was apparently not dependent on interferon induction.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen P. T., Giron D. J. Rapid sensitive assay for interferons based on the inhibition of MM virus nucleic acid synthesis. Appl Microbiol. 1970 Sep;20(3):317–322. doi: 10.1128/am.20.3.317-322.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Clercq E., Merigan T. C. Bis-DEAE-fluorenone: mechanism of antiviral protection and stimulation of interferon production in the mouse. J Infect Dis. 1971 Feb;123(2):190–199. doi: 10.1093/infdis/123.2.190. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Maeyer E., De Maeyer-Guignard J. Influence of animal genotype and age on the amount of circulating interferoh induced by Newcastle disease virus. J Gen Virol. 1968 May;2(3):445–449. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-2-3-445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krueger R. E., Mayer G. D. Tilorone hydrochloride: an orally active antiviral agent. Science. 1970 Sep 18;169(3951):1213–1214. doi: 10.1126/science.169.3951.1213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer G. D., Krueger R. F. Tilorone hydrochloride: mode of action. Science. 1970 Sep 18;169(3951):1214–1215. doi: 10.1126/science.169.3951.1214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Maeyer E., de Maeyer-Guignard J. Gene with quantitative effect on circulating interferon induced by Newcastle disease virus. J Virol. 1969 May;3(5):506–512. doi: 10.1128/jvi.3.5.506-512.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


