Abstract
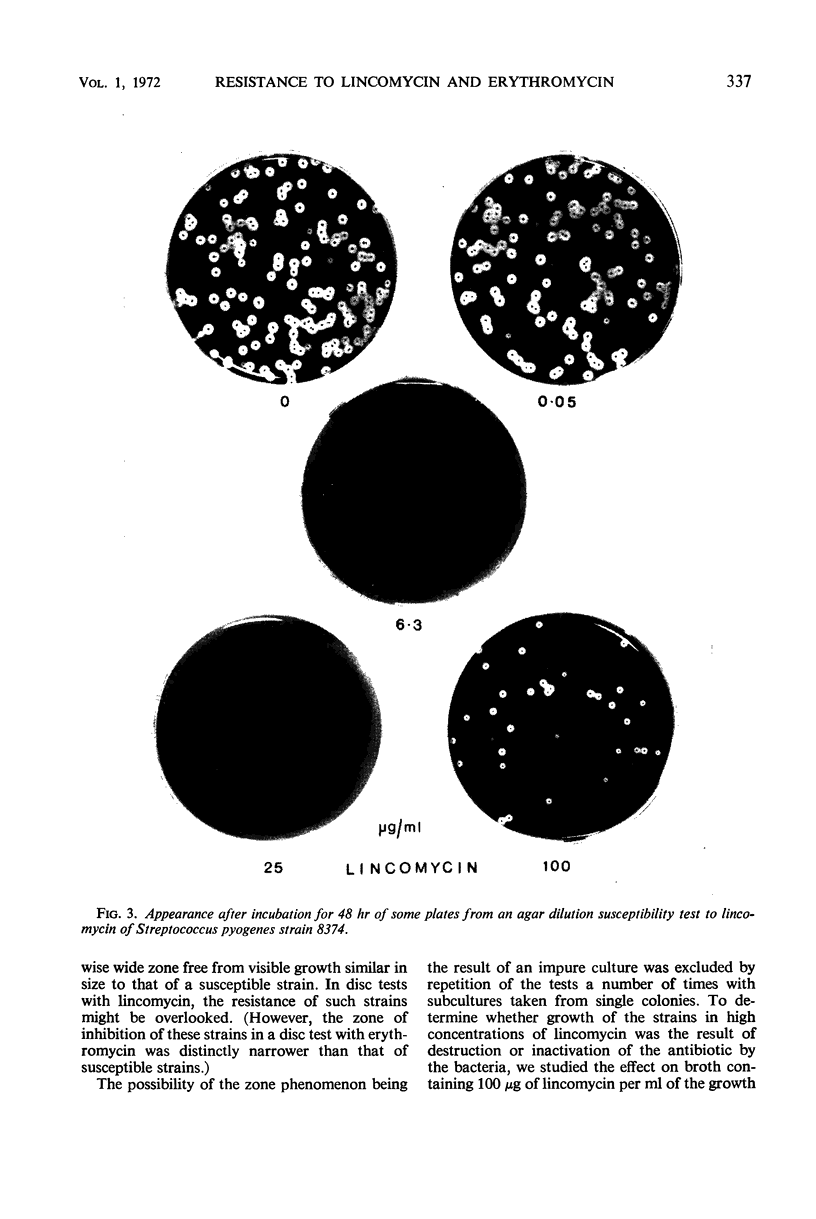
Ten (0.05%) of 18,628 strains of Streptococcus pyogenes isolated from clinical specimens in the 3 years 1968 to 1970 were resistant to lincomycin and erythromycin. All 10 strains were highly resistant to lincomycin, having minimal inhibitory concentration (MIC) values of 200 μg/ml. There were two degrees of resistance to erythromycin: four strains were highly resistant, having MIC values of 200 μg or more/ml; and six strains showed slight resistance, MIC values being 0.78 to 1.56 μg/ml. There was no known epidemiological relationship between any of the patients infected with the resistant strains, which belonged to a variety of T serotypes. A zonal pattern of resistance to lincomycin occurred in four strains, all of which were only slightly resistant to erythromycin. After incubation for 24 hr in a twofold dilution series of lincomycin in broth, the strains grew in 0.05 μg or less/ml and in 50 and 100 μg/ml, but not in intermediate concentrations. Tests in agar indicated that the bacterial population of one strain, but not of the other three, was homogeneous in respect to its ability to grow readily in low and high, but not in intermediate, concentrations. The zone phenomenon is of significance in the clinical laboratory, since unawareness of it might result in a highly resistant strain being regarded as susceptible to lincomycin in tube or plate MIC tests that do not include sufficiently high concentrations of lincomycin.
Full text
PDF

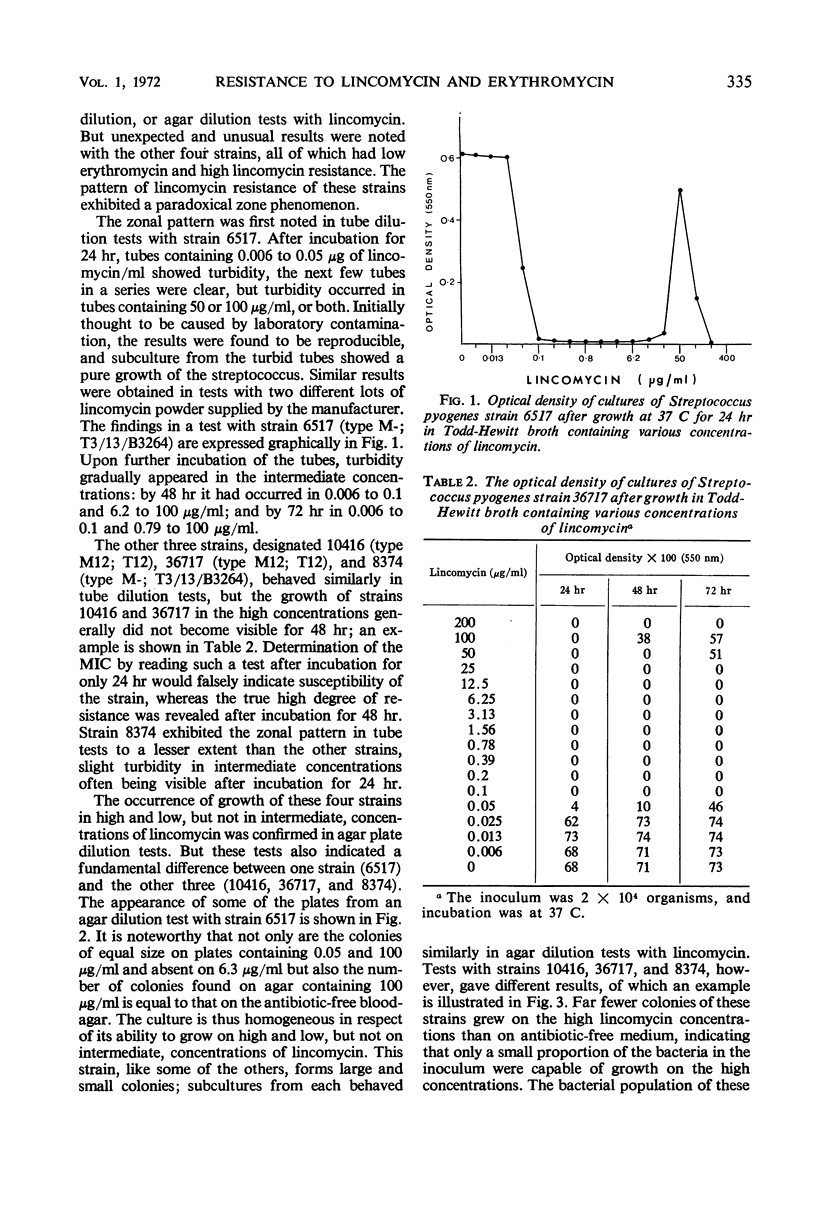
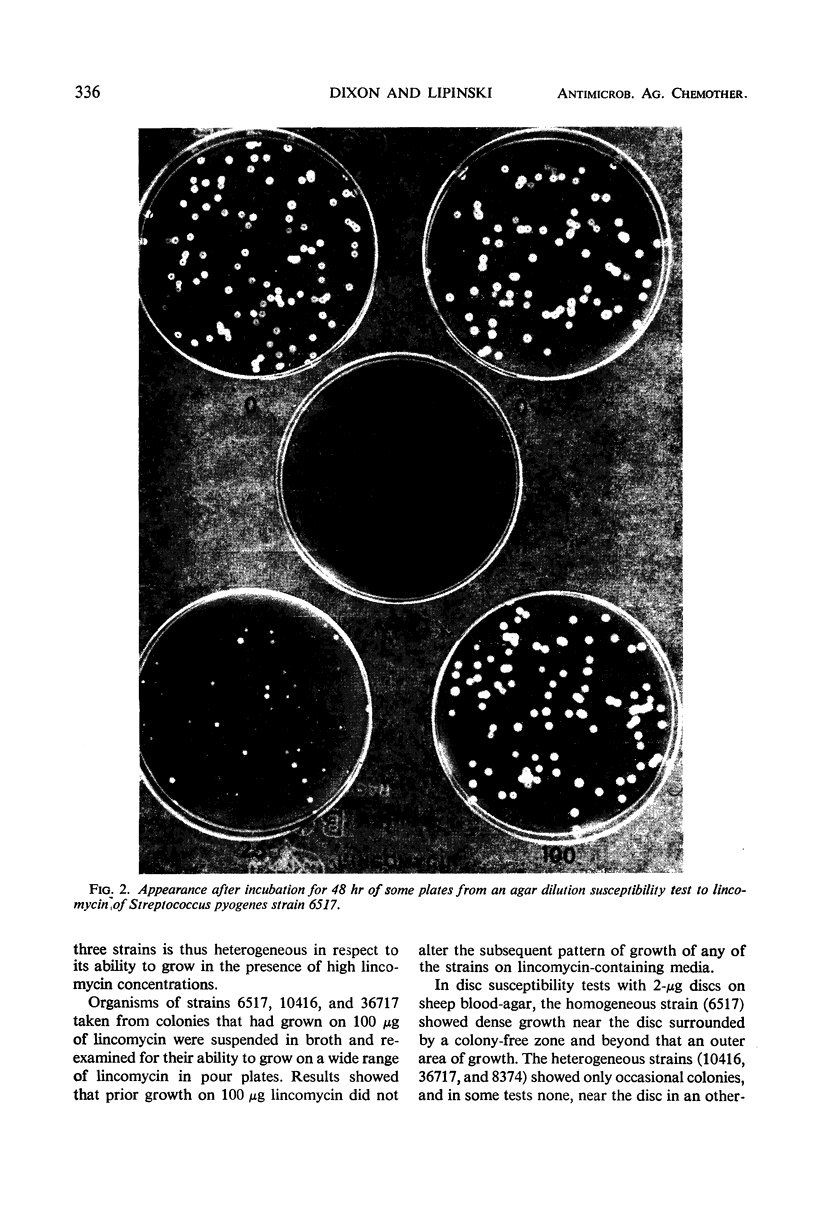


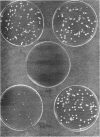
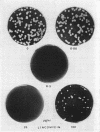
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Annear D. I., Hudson J. A. An unusual zone surrounding colistin discs in sensitivity tests of Serratia marcescens. Med J Aust. 1970 Apr 25;1(17):840–841. doi: 10.5694/j.1326-5377.1970.tb116779.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benner E. J., Adams A. P., Jr Unusual resistance of Staphylococcus aureus to lincomycin and 7-chlorolincomycin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother (Bethesda) 1969;9:100–103. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang F. N., Weisblum B. The specificity of lincomycin binding to ribosomes. Biochemistry. 1967 Mar;6(3):836–843. doi: 10.1021/bi00855a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desmyter J., Reybrouck G. Lincomycin sensitivity of erythromycin-resistant staphylococci. Chemotherapy. 1964;9(3):183–189. doi: 10.1159/000220359. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixon J. M. Group A Streptococcus resistant to erythromycin and lincomycin. Can Med Assoc J. 1968 Dec 7;99(22):1093–1094. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EAGLE H. Further observations on the zone phenomenon in the bactericidal action of penicillin. J Bacteriol. 1951 Nov;62(5):663–668. doi: 10.1128/jb.62.5.663-668.1951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GARROD L. P. The erythromycin group of antibiotics. Br Med J. 1957 Jul 13;2(5036):57–63. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5036.57. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KUHARIC H. A., ROBERTS C. E., Jr, KIR BY W. M. Tetracycline resistance of group A beta hemolytic streptococci. JAMA. 1960 Dec 3;174:1779–1782. doi: 10.1001/jama.1960.03030140001001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohn J., Hewitt J. H., Fraser C. A. Group A streptococci resistant to lincomycin. Br Med J. 1968 Mar 16;1(5593):703–703. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5593.703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWBURY E. J., CASON J. S. Aureomycin and erythromycin therapy for str. pyogenes in burns. Br Med J. 1954 Oct 16;2(4893):914–915. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.4893.914. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWBURY E. J., HURST L. The sensitivity of staphylococci and other wound bacteria to erythromycin, oleandomycin, and spiramycin. J Clin Pathol. 1959 Mar;12(2):163–169. doi: 10.1136/jcp.12.2.163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanders E., Foster M. T., Scott D. Group A beta-hemolytic streptococci resistant to erythromycin and lincomycin. N Engl J Med. 1968 Mar 7;278(10):538–540. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196803072781005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WATERWORTH P. M. An anomalous finding in a sensitivity test. J Med Lab Technol. 1956 Jan-Apr;13(5-6):385–386. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILLIAMS R. E. Laboratory diagnosis of streptococcal infections. Bull World Health Organ. 1958;19(1):153–176. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]