Abstract
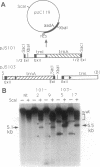
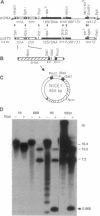
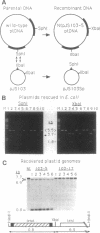
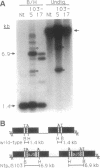
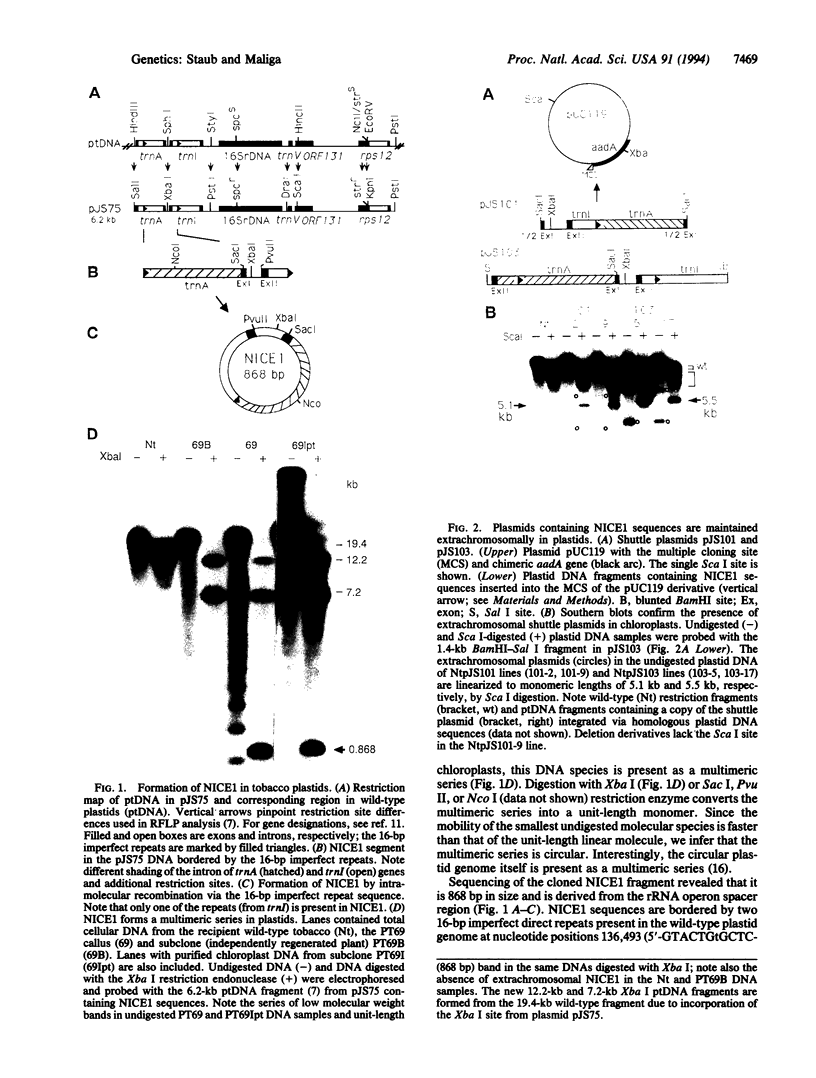
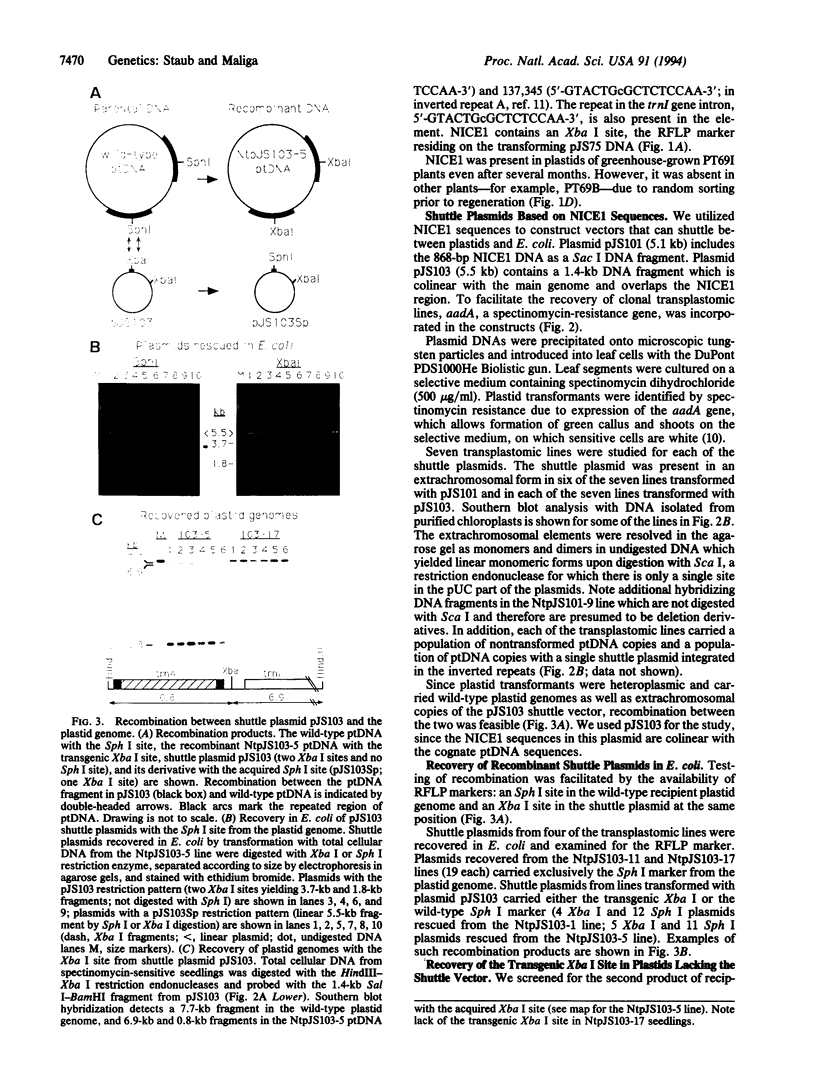
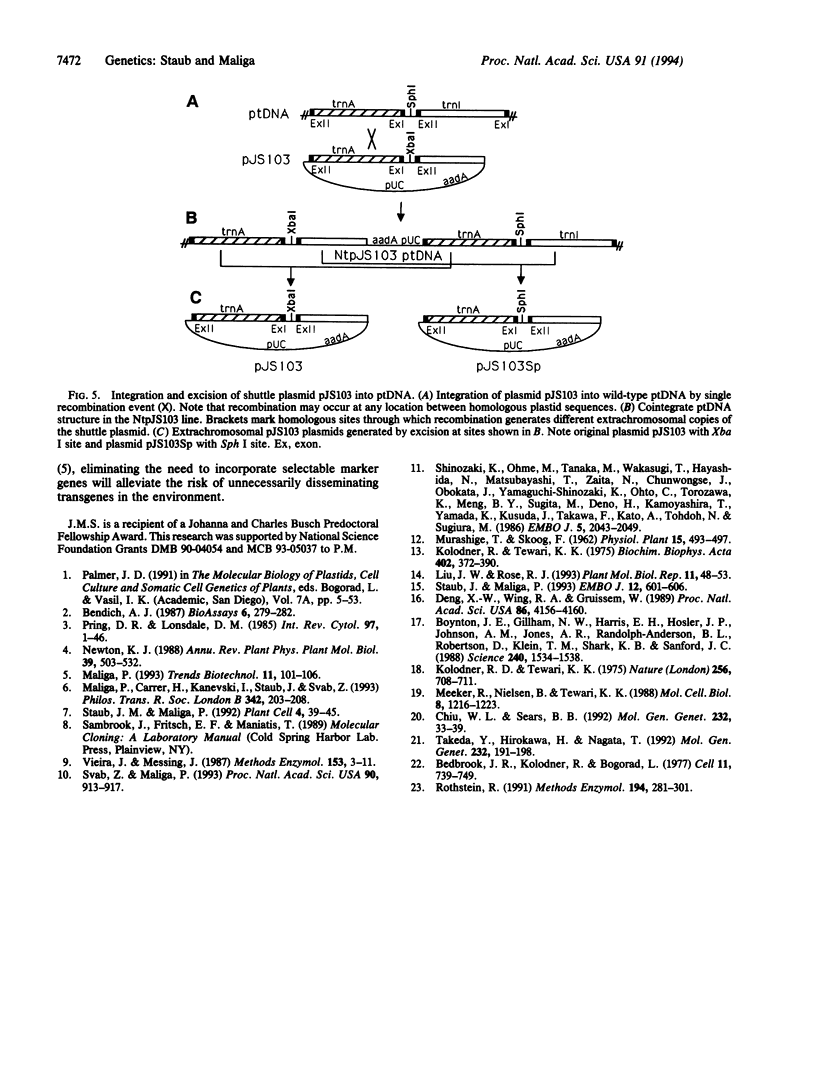
The plastid genome of higher plants is a circular double-stranded DNA molecule which is present in multiple identical copies. We report here an 868-bp plastid DNA minicircle, NICE1, that formed in tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum) plastids during transformation, as an unexpected product of homologous recombination. Such extrachromosomal elements are normally absent in plastids of higher plants. We have constructed shuttle plasmids containing NICE1 sequences which are maintained extrachromosomally when reintroduced into plastids by particle bombardment. Furthermore, recombination between homologous sequences in the shuttle plasmids and the main plastid genome occurs. Recombination products were characterized after recovery of the shuttle plasmids in Escherichia coli and of recombinant plastid genomes in the progeny of transformed plants. Our findings indicate that shuttle plasmids can be used to engineer plastid genes without concomitant integration of foreign DNA and to recover plastid mutations in E. coli.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bedbrook J. R., Kolodner R., Bogorad L. Zea mays chloroplast ribosomal RNA genes are part of a 22,000 base pair inverted repeat. Cell. 1977 Aug;11(4):739–749. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90288-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bendich A. J. Why do chloroplasts and mitochondria contain so many copies of their genome? Bioessays. 1987 Jun;6(6):279–282. doi: 10.1002/bies.950060608. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boynton J. E., Gillham N. W., Harris E. H., Hosler J. P., Johnson A. M., Jones A. R., Randolph-Anderson B. L., Robertson D., Klein T. M., Shark K. B. Chloroplast transformation in Chlamydomonas with high velocity microprojectiles. Science. 1988 Jun 10;240(4858):1534–1538. doi: 10.1126/science.2897716. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiu W. L., Sears B. B. Electron microscopic localization of replication origins in Oenothera chloroplast DNA. Mol Gen Genet. 1992 Mar;232(1):33–39. doi: 10.1007/BF00299134. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deng X. W., Wing R. A., Gruissem W. The chloroplast genome exists in multimeric forms. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jun;86(11):4156–4160. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.11.4156. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolodner R. D., Tewari K. K. Chloroplast DNA from higher plants replicates by both the Cairns and the rolling circle mechanism. Nature. 1975 Aug 28;256(5520):708–711. doi: 10.1038/256708a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolodner R., Tewari K. K. The molecular size and conformation of the chloroplast DNA from higher plants. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Sep 1;402(3):372–390. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(75)90273-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maliga P., Carrer H., Kanevski I., Staub J., Svab Z. Plastid engineering in land plants: a conservative genome is open to change. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1993 Nov 29;342(1301):203–208. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1993.0148. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meeker R., Nielsen B., Tewari K. K. Localization of replication origins in pea chloroplast DNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Mar;8(3):1216–1223. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.3.1216. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothstein R. Targeting, disruption, replacement, and allele rescue: integrative DNA transformation in yeast. Methods Enzymol. 1991;194:281–301. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)94022-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinozaki K., Ohme M., Tanaka M., Wakasugi T., Hayashida N., Matsubayashi T., Zaita N., Chunwongse J., Obokata J., Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K. The complete nucleotide sequence of the tobacco chloroplast genome: its gene organization and expression. EMBO J. 1986 Sep;5(9):2043–2049. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04464.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staub J. M., Maliga P. Accumulation of D1 polypeptide in tobacco plastids is regulated via the untranslated region of the psbA mRNA. EMBO J. 1993 Feb;12(2):601–606. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05692.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staub J. M., Maliga P. Long regions of homologous DNA are incorporated into the tobacco plastid genome by transformation. Plant Cell. 1992 Jan;4(1):39–45. doi: 10.1105/tpc.4.1.39. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svab Z., Maliga P. High-frequency plastid transformation in tobacco by selection for a chimeric aadA gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Feb 1;90(3):913–917. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.3.913. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeda Y., Hirokawa H., Nagata T. The replication origin of proplastid DNA in cultured cells of tobacco. Mol Gen Genet. 1992 Mar;232(2):191–198. doi: 10.1007/BF00279996. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vieira J., Messing J. Production of single-stranded plasmid DNA. Methods Enzymol. 1987;153:3–11. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)53044-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]