Abstract
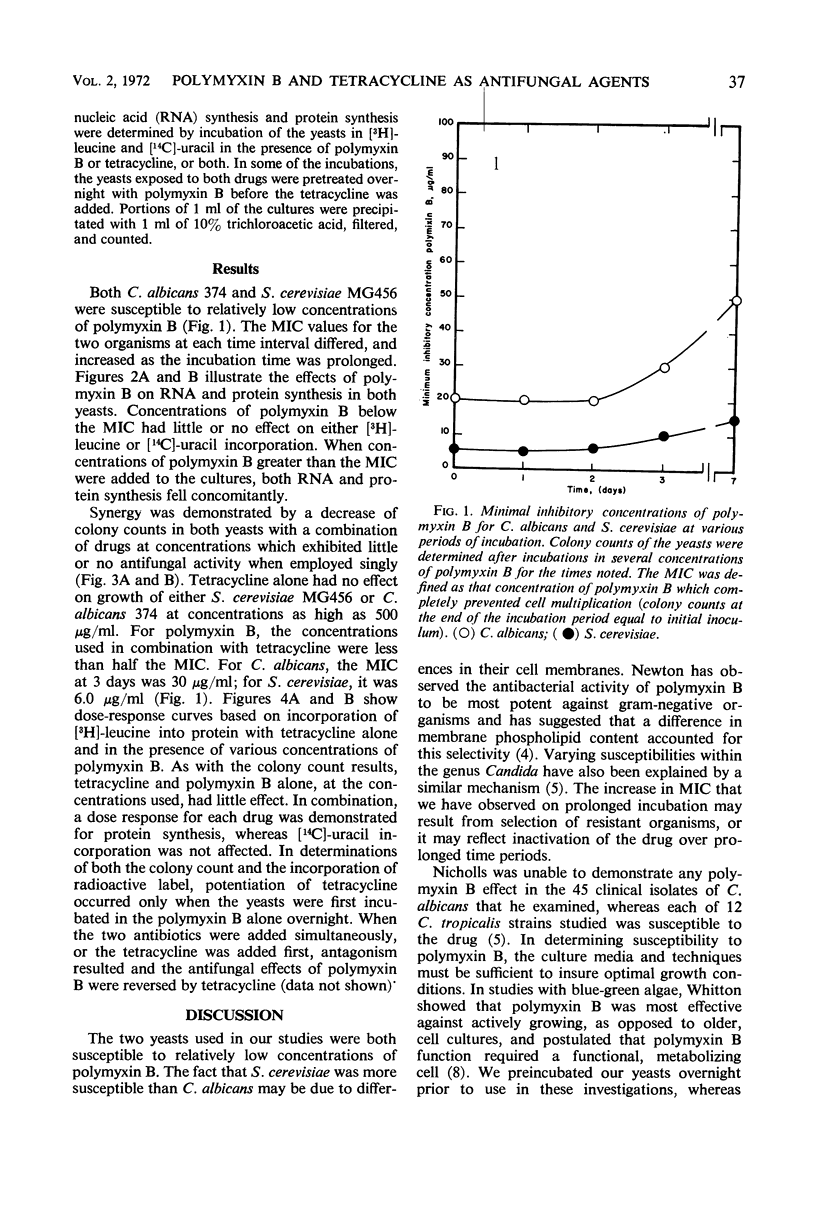
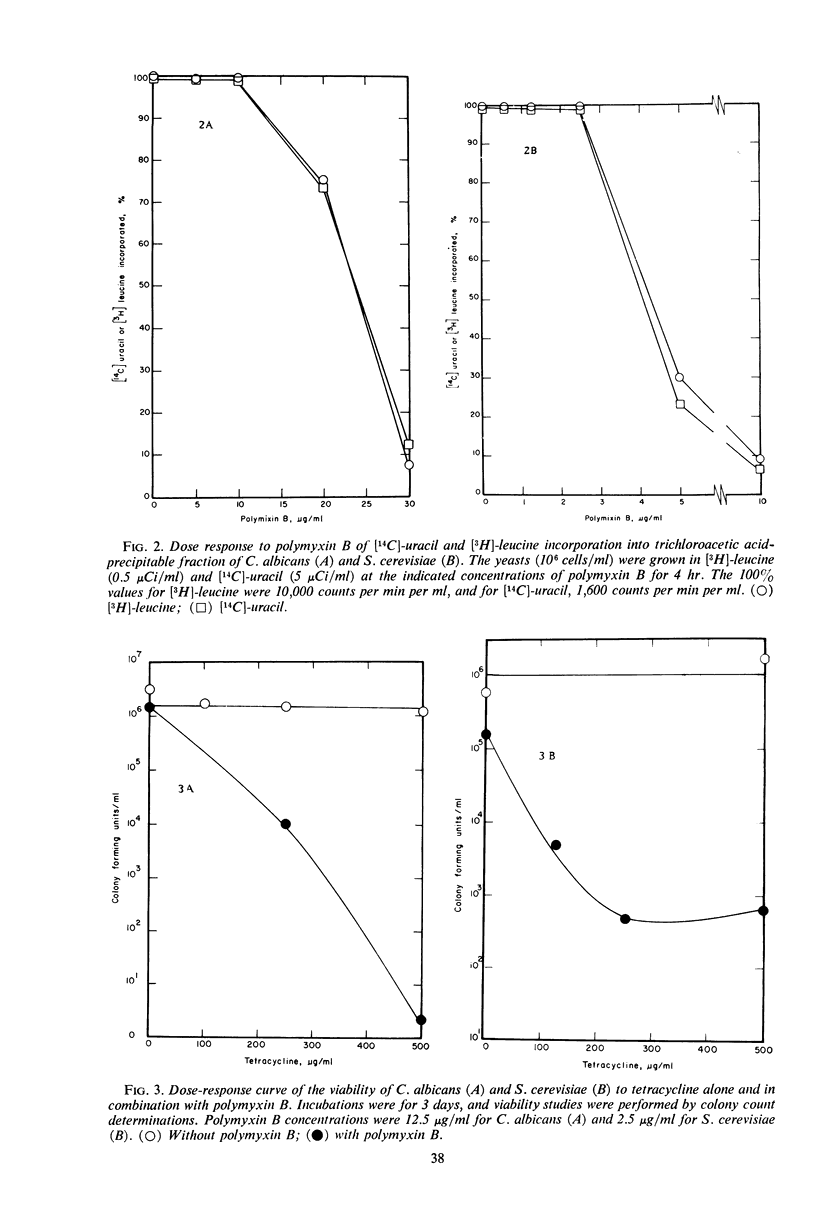
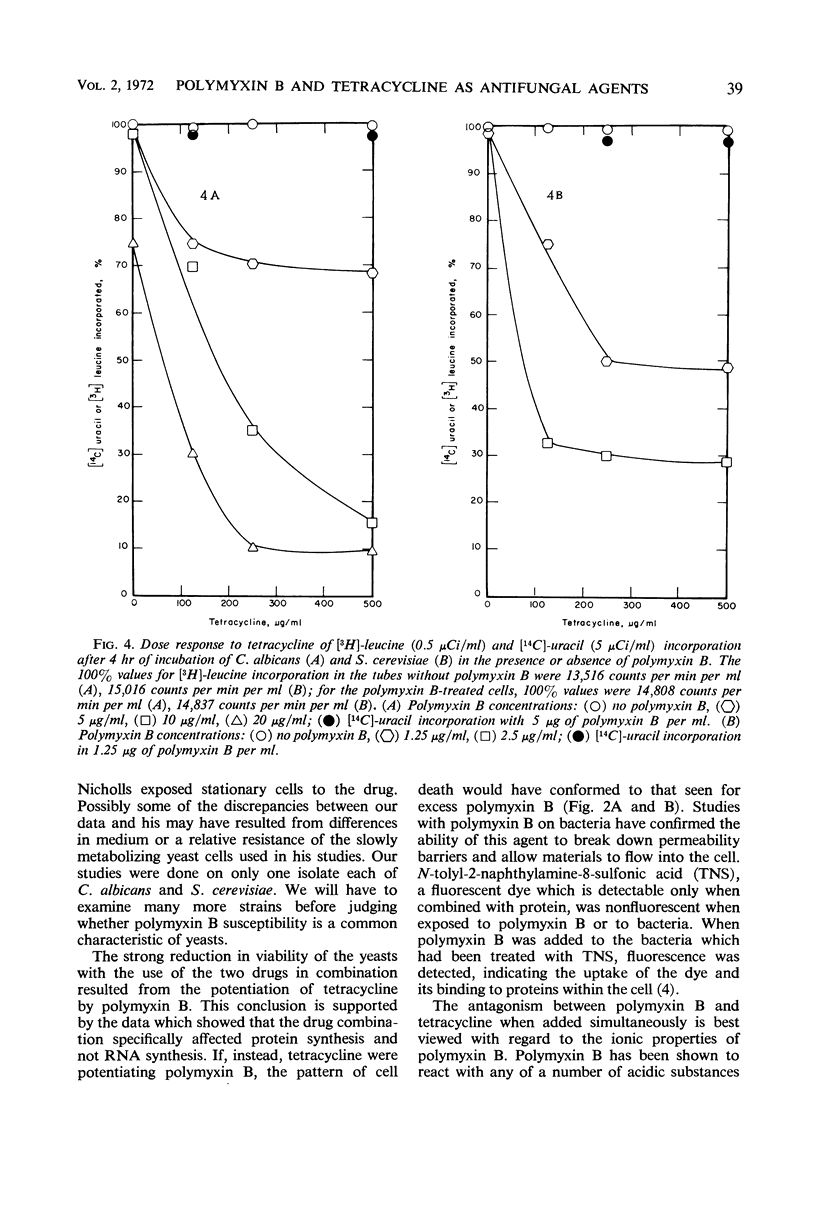
High concentrations of polymyxin B inhibited the growth of Candida albicans and Saccharomyces cerevisiae. When these yeasts were incubated with concentrations of polymyxin B too low to affect growth, and were then exposed to tetracycline, protein synthesis was inhibited and at least 99% of the organisms were killed. Neither inhibition of protein synthesis nor cell death occurred in cultures treated with high concentrations of tetracycline alone. We conclude that polymyxin B at high concentrations affects the cell membrane of yeasts, which results in inhibition of growth. At low concentrations, it increases the permeability of the yeast cell membrane to tetracycline, which then inhibits protein synthesis and leads to cell death.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Battaner E., Vazquez D. Inhibitors of protein synthesis by ribosomes of the 80-S type. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Dec 16;254(2):316–330. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(71)90840-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medoff G., Comfort M., Kobayashi G. S. Synergistic action of amphotericin B and 5-fluorocytosine against yeast-like organisms. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1971 Nov;138(2):571–574. doi: 10.3181/00379727-138-35943. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medoff G., Kobayashi G. S., Kwan C. N., Schlessinger D., Venkov P. Potentiation of rifampicin and 5-fluorocytosine as antifungal antibiotics by amphotericin B (yeast-membrane permeability-ribosomal RNA-eukaryotic cell-synergism). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jan;69(1):196–199. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.1.196. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NEWTON B. A. The properties and mode of action of the polymyxins. Bacteriol Rev. 1956 Mar;20(1):14–27. doi: 10.1128/br.20.1.14-27.1956. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholls M. W. Polymyxin sensitivity of Candida tropicalis. J Med Microbiol. 1970 Aug;3(3):529–538. doi: 10.1099/00222615-3-3-529. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preston T. M., O'Dell D. S. Synergistic effect of polymixin B with other antibiotics on the transformation of Naegleria gruberi. Exp Cell Res. 1971 Oct;68(2):465–466. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(71)90177-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer S. J., Nicolson G. L. The structure and chemistry of mammalian cell membranes. Am J Pathol. 1971 Nov;65(2):427–437. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitton B. A. Studies on the toxicity of polymyxin B to blue-green algae. Can J Microbiol. 1967 Aug;13(8):987–993. doi: 10.1139/m67-132. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



