Abstract
A number of actinomycetes isolated from soil were found to produce one or more members of a new family of antibiotics, the cephamycins, which are structurally related to cephalosporin C. The cephamycins were produced in submerged fermentation in a wide variety of media by one or more of eight different species of Streptomyces, including a newly described species, S. lactamdurans. These antibiotics exhibit antibacterial activity against a broad spectrum of bacteria which includes many that are resistant to the cephalosporins and penicillins.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
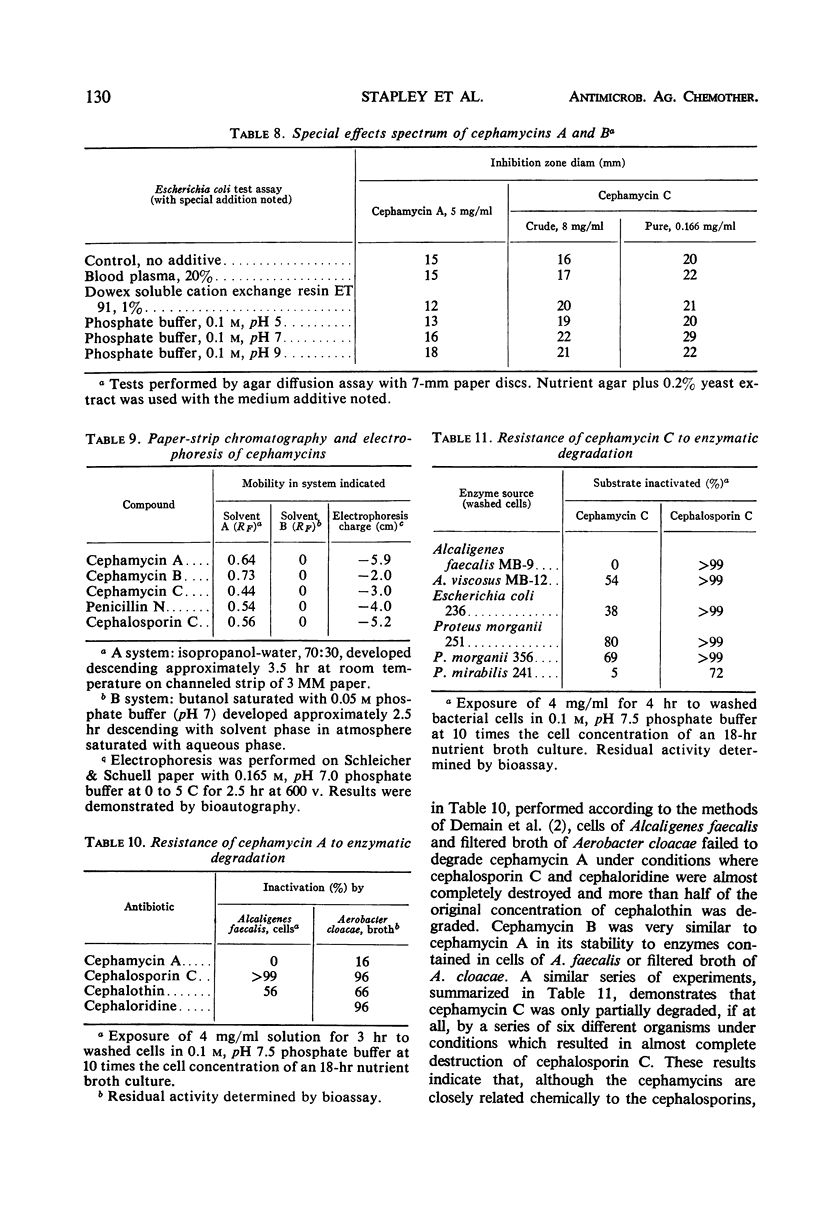
- DEMAIN A. L., WALTON R. B., NEWKIRK J. F., MILLER I. M. MICROBIAL DEGRADATION OF CEPHALOSPORIN C. Nature. 1963 Aug 31;199:909–910. doi: 10.1038/199909a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lederberg J. BACTERIAL PROTOPLASTS INDUCED BY PENICILLIN. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1956 Sep;42(9):574–577. doi: 10.1073/pnas.42.9.574. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller T. W., Goegelman R. T., Weston R. G., Putter I., Wolf F. J. Cephamycins, a new family of beta-lactam antibiotics. II. Isolation and chemical characterization. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1972 Sep;2(3):132–135. doi: 10.1128/aac.2.3.132. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagarajan R., Boeck L. D., Gorman M., Hamill R. L., Higgens C. E., Hoehn M. M., Stark W. M., Whitney J. G. Beta-lactam antibiotics from Streptomyces. J Am Chem Soc. 1971 May 5;93(9):2308–2310. doi: 10.1021/ja00738a035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PRIDHAM T. G., HESSELTINE C. W., BENEDICT R. G. A guide for the classification of streptomycetes according to selected groups; placement of strains in morphological sections. Appl Microbiol. 1958 Jan;6(1):52–79. doi: 10.1128/am.6.1.52-79.1958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pridham T. G., Gottlieb D. The Utilization of Carbon Compounds by Some Actinomycetales as an Aid for Species Determination. J Bacteriol. 1948 Jul;56(1):107–114. doi: 10.1128/jb.56.1.107-114.1948. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STAPLEY E. O. Cross-resistance studies and antibiotic identification. Appl Microbiol. 1958 Nov;6(6):392–398. doi: 10.1128/am.6.6.392-398.1958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


