Abstract
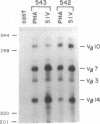
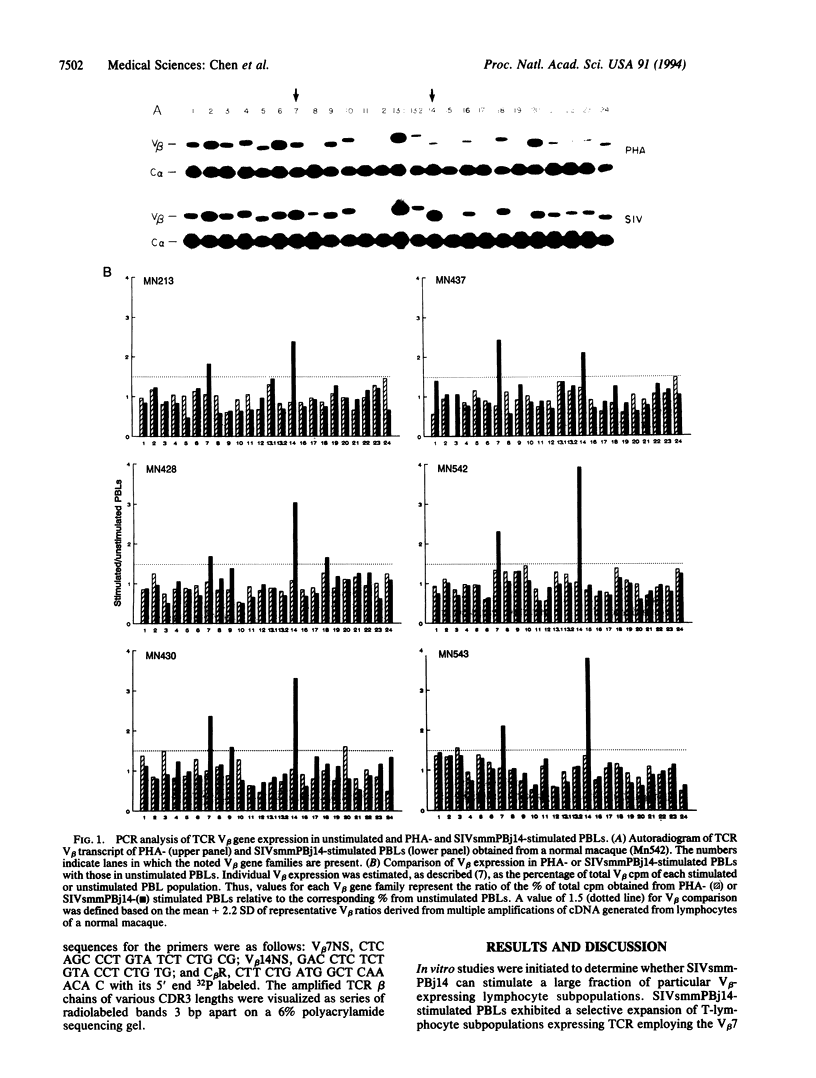
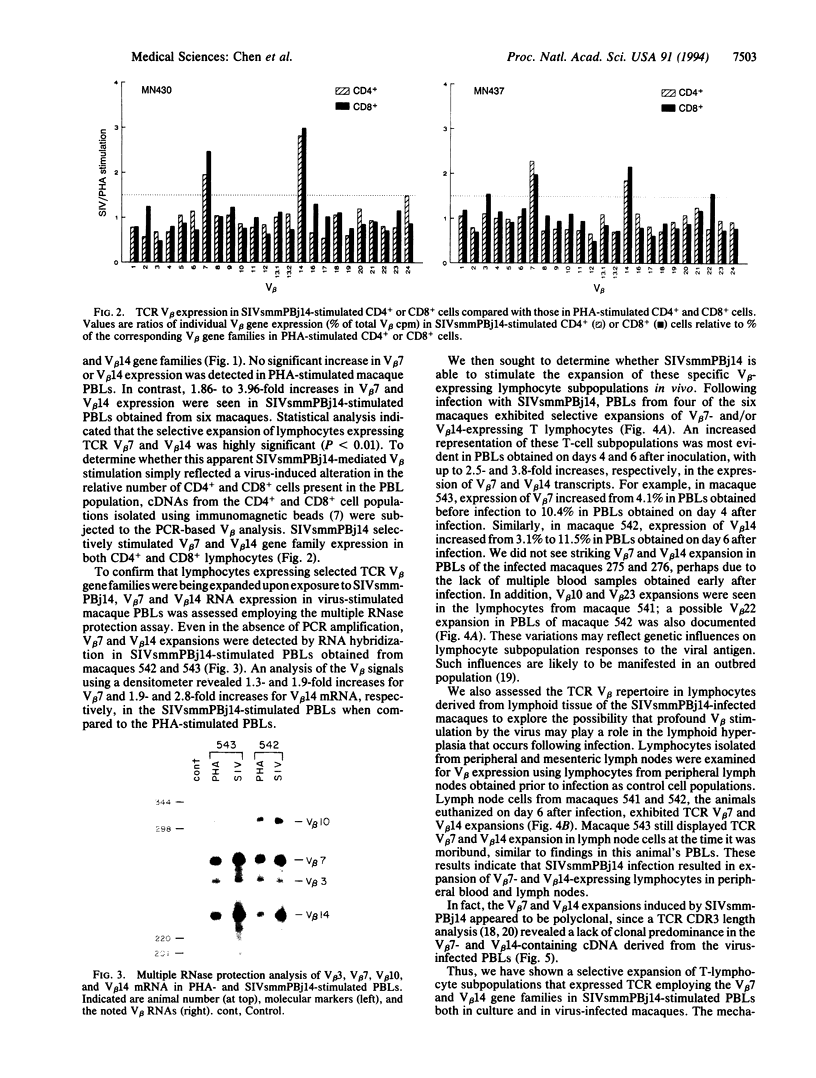
SIVsmmPBj14, a variant simian immunodeficiency virus isolated from a pig-tailed macaque, stimulates the proliferation of macaque T lymphocytes in vitro and induces an acutely lethal disease in macaques characterized, in part, by lymphadenopathy and splenomegaly. To determine whether SIVsmmPBj14 exhibits superantigen-like activity, in vitro and in vivo studies of T-cell receptor V beta repertoire were undertaken using PCR-based quantitative methods. Whereas in vitro phytohemagglutinin stimulation of macaque peripheral blood lymphocytes did not cause a perturbation of T-cell receptor V beta repertoire, SIVsmmPBj14 stimulated the expansion of both CD4+ and CD8+ T-lymphocyte subpopulations expressing the V beta 7 and V beta 14 gene families. Such V beta 7 and V beta 14 expansions could be confirmed by a multiple RNase protection assay. Furthermore, the expansion of the same lymphocyte subpopulations was also detected in peripheral blood lymphocytes and lymph node cells of virus-infected macaques. These observations suggest that SIVsmmPBj14-mediated V beta expansion may contribute to the induction of an acutely lethal disease in macaques.
Full text
PDF
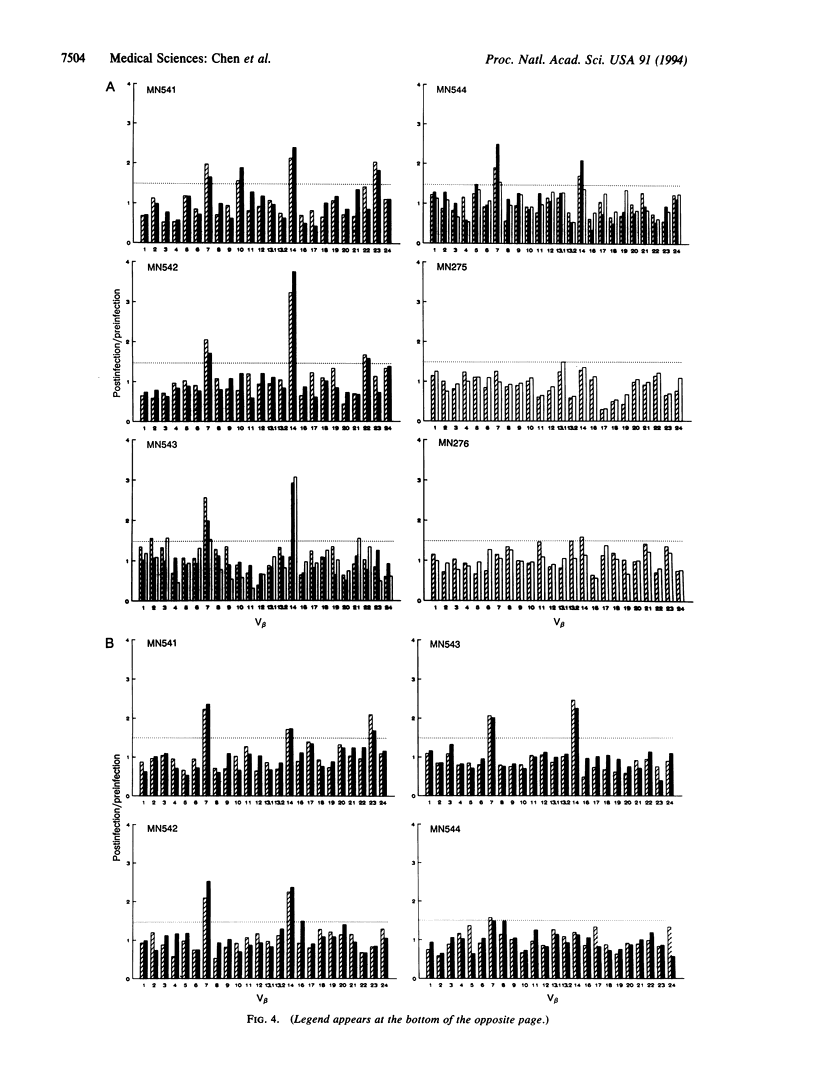

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bahadoran P., Rieux-Laucat F., Le Deist F., Blanche S., Fischer A., de Villartay J. P. Lack of selective V beta deletion in peripheral CD4+ T cells of human immunodeficiency virus-infected infants. Eur J Immunol. 1993 Aug;23(8):2041–2044. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830230850. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Candéias S., Waltzinger C., Benoist C., Mathis D. The V beta 17+ T cell repertoire: skewed J beta usage after thymic selection; dissimilar CDR3s in CD4+ versus CD8+ cells. J Exp Med. 1991 Nov 1;174(5):989–1000. doi: 10.1084/jem.174.5.989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Z. W., Kou Z. C., Shen L., Reimann K. A., Letvin N. L. Conserved T-cell receptor repertoire in simian immunodeficiency virus-infected rhesus monkeys. J Immunol. 1993 Aug 15;151(4):2177–2187. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole B. C., Balderas R. A., Ahmed E. A., Kono D., Theofilopoulos A. N. Genomic composition and allelic polymorphisms influence V beta usage by the Mycoplasma arthritidis superantigen. J Immunol. 1993 Apr 15;150(8 Pt 1):3291–3299. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desrosiers R. C. The simian immunodeficiency viruses. Annu Rev Immunol. 1990;8:557–578. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.08.040190.003013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dewhurst S., Embretson J. E., Anderson D. C., Mullins J. I., Fultz P. N. Sequence analysis and acute pathogenicity of molecularly cloned SIVSMM-PBj14. Nature. 1990 Jun 14;345(6276):636–640. doi: 10.1038/345636a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fultz P. N., McClure H. M., Anderson D. C., Switzer W. M. Identification and biologic characterization of an acutely lethal variant of simian immunodeficiency virus from sooty mangabeys (SIV/SMM). AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1989 Aug;5(4):397–409. doi: 10.1089/aid.1989.5.397. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fultz P. N. Replication of an acutely lethal simian immunodeficiency virus activates and induces proliferation of lymphocytes. J Virol. 1991 Sep;65(9):4902–4909. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.9.4902-4909.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graziosi C., Pantaleo G., Butini L., Demarest J. F., Saag M. S., Shaw G. M., Fauci A. S. Kinetics of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) DNA and RNA synthesis during primary HIV-1 infection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jul 15;90(14):6405–6409. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.14.6405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hingorani R., Choi I. H., Akolkar P., Gulwani-Akolkar B., Pergolizzi R., Silver J., Gregersen P. K. Clonal predominance of T cell receptors within the CD8+ CD45RO+ subset in normal human subjects. J Immunol. 1993 Nov 15;151(10):5762–5769. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imberti L., Sottini A., Bettinardi A., Puoti M., Primi D. Selective depletion in HIV infection of T cells that bear specific T cell receptor V beta sequences. Science. 1991 Nov 8;254(5033):860–862. doi: 10.1126/science.1948066. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawabe Y., Ochi A. Programmed cell death and extrathymic reduction of Vbeta8+ CD4+ T cells in mice tolerant to Staphylococcus aureus enterotoxin B. Nature. 1991 Jan 17;349(6306):245–248. doi: 10.1038/349245a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kotzin B. L., Leung D. Y., Kappler J., Marrack P. Superantigens and their potential role in human disease. Adv Immunol. 1993;54:99–166. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60534-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurence J., Hodtsev A. S., Posnett D. N. Superantigen implicated in dependence of HIV-1 replication in T cells on TCR V beta expression. Nature. 1992 Jul 16;358(6383):255–259. doi: 10.1038/358255a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Letvin N. L. Animal models for AIDS. Immunol Today. 1990 Sep;11(9):322–326. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(90)90127-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Letvin N. L., King N. W. Immunologic and pathologic manifestations of the infection of rhesus monkeys with simian immunodeficiency virus of macaques. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 1990;3(11):1023–1040. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis M. G., Zack P. M., Elkins W. R., Jahrling P. B. Infection of rhesus and cynomolgus macaques with a rapidly fatal SIV (SIVSMM/PBj) isolate from sooty mangabeys. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1992 Sep;8(9):1631–1639. doi: 10.1089/aid.1992.8.1631. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novembre F. J., Johnson P. R., Lewis M. G., Anderson D. C., Klumpp S., McClure H. M., Hirsch V. M. Multiple viral determinants contribute to pathogenicity of the acutely lethal simian immunodeficiency virus SIVsmmPBj variant. J Virol. 1993 May;67(5):2466–2474. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.5.2466-2474.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rammensee H. G., Kroschewski R., Frangoulis B. Clonal anergy induced in mature V beta 6+ T lymphocytes on immunizing Mls-1b mice with Mls-1a expressing cells. Nature. 1989 Jun 15;339(6225):541–544. doi: 10.1038/339541a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reimann K. A., Tenner-Racz K., Racz P., Montefiori D. C., Yasutomi Y., Lin W., Ransil B. J., Letvin N. L. Immunopathogenic events in acute infection of rhesus monkeys with simian immunodeficiency virus of macaques. J Virol. 1994 Apr;68(4):2362–2370. doi: 10.1128/jvi.68.4.2362-2370.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rellahan B. L., Jones L. A., Kruisbeek A. M., Fry A. M., Matis L. A. In vivo induction of anergy in peripheral V beta 8+ T cells by staphylococcal enterotoxin B. J Exp Med. 1990 Oct 1;172(4):1091–1100. doi: 10.1084/jem.172.4.1091. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinicco A., Palestro G., Caramello P., Giacobbi D., Giuliani G., Paggi G., Sciandra M., Gioannini P. Acute HIV-1 infection: clinical and biological study of 12 patients. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 1990;3(3):260–265. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tindall B., Cooper D. A. Primary HIV infection: host responses and intervention strategies. AIDS. 1991 Jan;5(1):1–14. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webb S., Morris C., Sprent J. Extrathymic tolerance of mature T cells: clonal elimination as a consequence of immunity. Cell. 1990 Dec 21;63(6):1249–1256. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90420-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]