Abstract
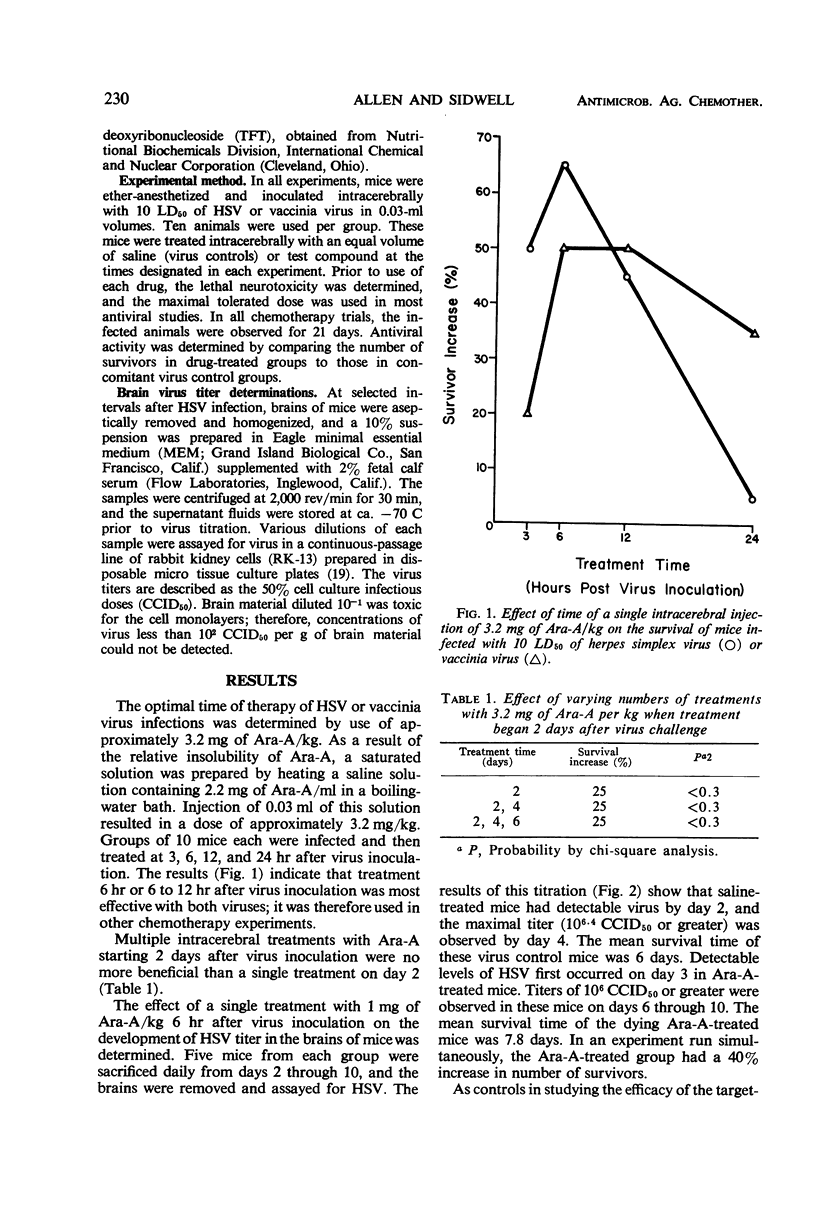
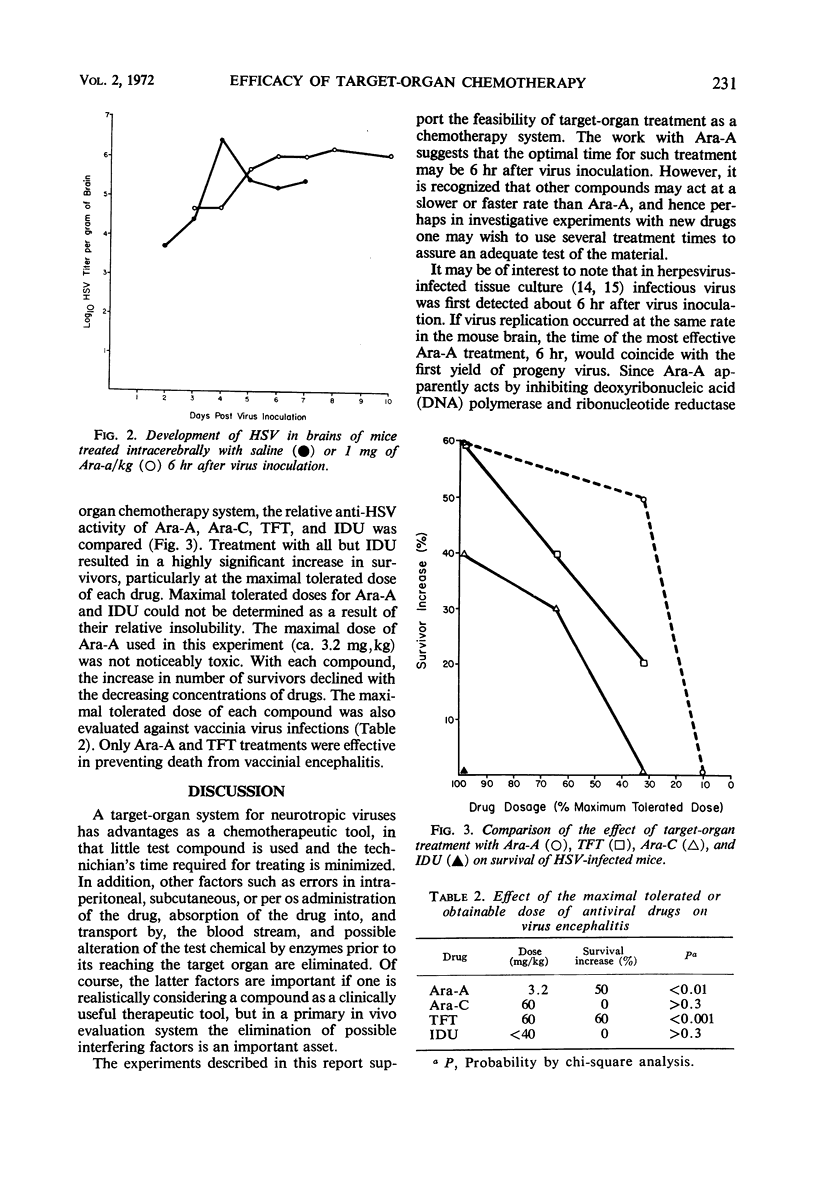
A sensitive in vivo system was studied for use in evaluating relatively small quantities of antiviral compounds. Swiss mice were injected intracerebrally with 10 LD50 of type 1 herpes simplex virus (HSV) or vaccinia virus. Test compounds were injected intracerebrally into mice at a standard time interval after virus inoculation. Significant increases in the number of survivors in drug-treated, infected animals as compared to saline-treated virus controls was the criterion for evaluation of antiviral activity. 9-β-d-Arabinofuranosyladenine (Ara-A) was used to determine an optimal time of therapy for this system. Significant survival increases occurred when the drug was injected 3, 6, 12, and 48 hr after HSV inoculation, with maximal effect occurring after the 6-hr treatment interval. Determination of brain virus titer of 6-hr Ara-A- and saline-treated mice at various intervals indicated that treatment with the drug delayed development of detectable levels of HSV by 1 day. 1-β-d-Arabinofuranosylcytosine (Ara-C), trifluorothymidine (TFT), and 5-iodo-2′-deoxyuridine (IDU) were also evaluated with the use of the 6-hr treatment time against HSV and vaccinia virus. Ara-A and TFT increased the number of survivors among mice infected with either virus, whereas Ara-C increased the survivors among HSV-infected, but not vaccinia virus-infected, mice. IDU was inactive against both viruses.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akerfeldt S., Westin G., Jansson T. Aromatic sulfonic acids as viral inhibitors. Structure-activity study using rhino, adeno 3, herpes simplex, and influenza viruses. J Med Chem. 1971 Jul;14(17):595–600. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BUTHALA D. A. CELL CULTURE STUDIES ON ANTIVIRAL AGENTS. I. ACTION OF CYTOSINE ARABINOSIDE AND SOME COMPARISONS WITH 5-IODO-2-DEOXYURIDINE. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1964 Jan;115:69–77. doi: 10.3181/00379727-115-28834. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camiener G. W., Smith C. G. Studies of the enzymatic deamination of cytosine arabinoside. I. Enzyme distribution and species specificity. Biochem Pharmacol. 1965 Oct;14(10):1405–1416. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(65)90175-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen S. S. Introduction to the biochemistry of D-arabinosyl nucleosides. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1966;5:1–88. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60231-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Creasey W. A., Papac R. J., Markiw M. E., Calabresi P., Welch A. D. Biochemical and pharmacological studies with 1-beta-D-arabinofuranosylcytosine in man. Biochem Pharmacol. 1966 Oct;15(10):1417–1428. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(66)90186-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixon G. J., Sidwell R. W., Miller F. A., Sloan B. J. Antiviral activity of 9-beta-D-arabinofuranosyladenine. V. Activity against intracerebral Vaccinia virus infections in mice. Antimicrob Agents Chemother (Bethesda) 1968;8:172–179. doi: 10.1128/AAC.8.2.172. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dollinger M. R., Burchenal J. H., Kreis W., Fox J. J. Analogs of 1-beta-D-arabinofuranosylcytosine. Studies on mechanisms of action in Burkitt's cell culture and mouse leukemia, and in vitro deamination studies. Biochem Pharmacol. 1967 Apr;16(4):689–706. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(67)90082-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furth J. J., Cohen S. S. Inhibition of mammalian DNA polymerase by the 5'-triphosphate of 1-beta-d-arabinofuranosylcytosine and the 5'-triphosphate of 9-beta-d-arabinofuranoxyladenine. Cancer Res. 1968 Oct;28(10):2061–2067. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAUFMAN H. E. CHEMOTHERAPY OF VIRUS DISEASE. Chemotherapy. 1963;59:1–16. doi: 10.1159/000220099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAUFMAN H. E., HEIDELBERGER C. THERAPEUTIC ANTIVIRAL ACTION OF 5-TRIFLUOROMETHYL-2'-DEOXYURIDINE IN HERPES SIMPLEX KERATITIS. Science. 1964 Aug 7;145(3632):585–586. doi: 10.1126/science.145.3632.585. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAUFMAN H. E., NESBURN A. B., MALONEY E. D. IDU therapy of herpes simplex. Arch Ophthalmol. 1962 May;67:583–591. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1962.00960020583012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufmann H. E. In vivo studies with antiviral agents. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1965 Jul 30;130(1):168–180. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1965.tb12550.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROIZMAN B., AURELIAN L., ROANE P. R., Jr THE MULTIPLICATION OF HERPES SIMPLEX VIRUS. I. THE PROGRAMMING OF VIRAL DNA DUPLICATION IN HEP-2 CELLS. Virology. 1963 Nov;21:482–498. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(63)90209-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renis H. E., Hollowell C. A., Underwood G. E. Nucleic acids. 3. Antiviral activity of nucleotides and dinucleoside phosphates containing ara-cytidine. J Med Chem. 1967 Sep;10(5):777–782. doi: 10.1021/jm00317a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schabel F. M., Jr The antiviral activity of 9-beta-D-arabinofuranosyladenine (ARA-A). Chemotherapy. 1968;13(6):321–338. doi: 10.1159/000220567. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sidwell R. W., Dixon G. J., Sellers S. M., Schabel F. M., Jr In vivo antiviral properties of biologically active compounds. II. Studies with influenza and vaccinia viruses. Appl Microbiol. 1968 Feb;16(2):370–392. doi: 10.1128/am.16.2.370-392.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sidwell R. W., Huffman J. H. Use of disposable micro tissue culture plates for antiviral and interferon induction studies. Appl Microbiol. 1971 Nov;22(5):797–801. doi: 10.1128/am.22.5.797-801.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sloan B. J., Miller F. A., Ehrlich J., McLean I. W., Machamer H. E. Antiviral activity of 0-beta-D-arabinofuranosyladenine. IV. Activity against intracerebral herpes simplex virus infections in mice. Antimicrob Agents Chemother (Bethesda) 1968;8:161–171. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umeda M., Heidelberger C. Fluorinated pyrimidines. XXXI. Mechanisms of inhibition of vaccinia virus replication in HeLa cells by pyrimidine nucleosides. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1969 Jan;130(1):24–29. doi: 10.3181/00379727-130-33480. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



