Abstract
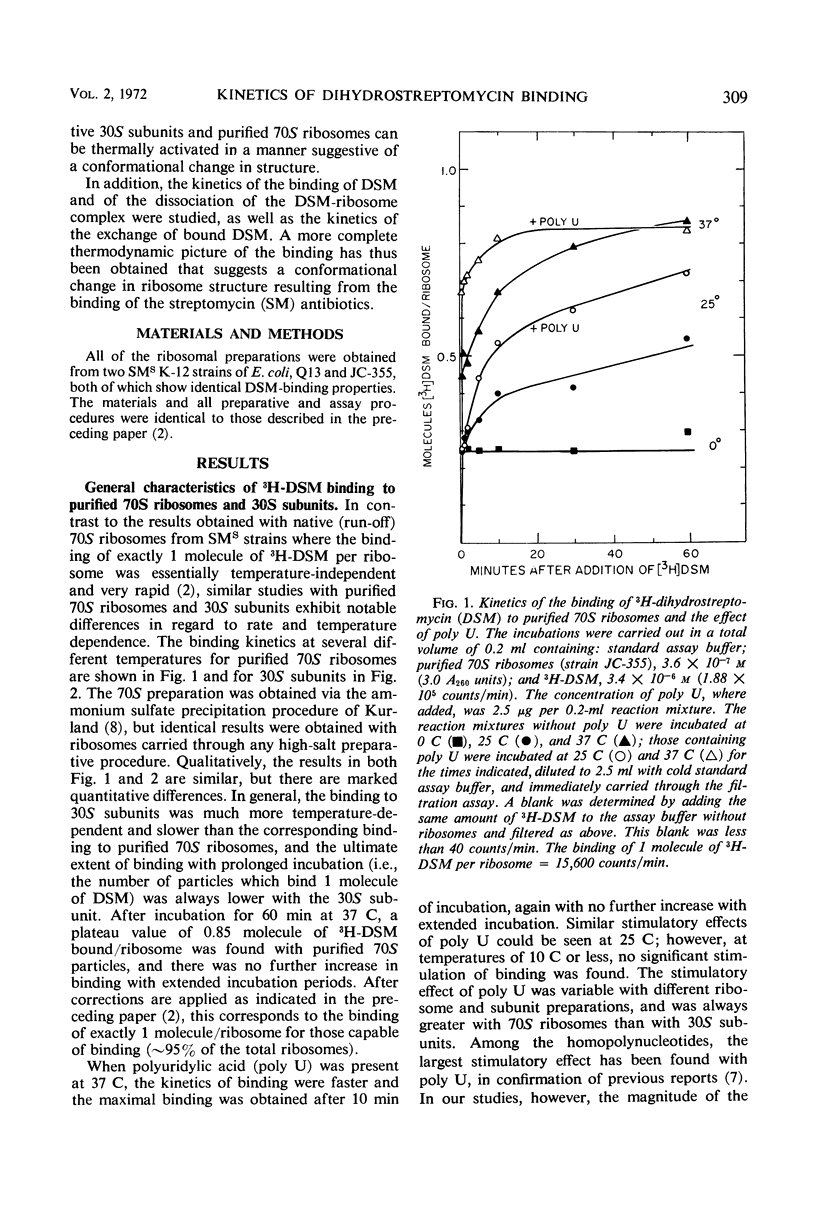
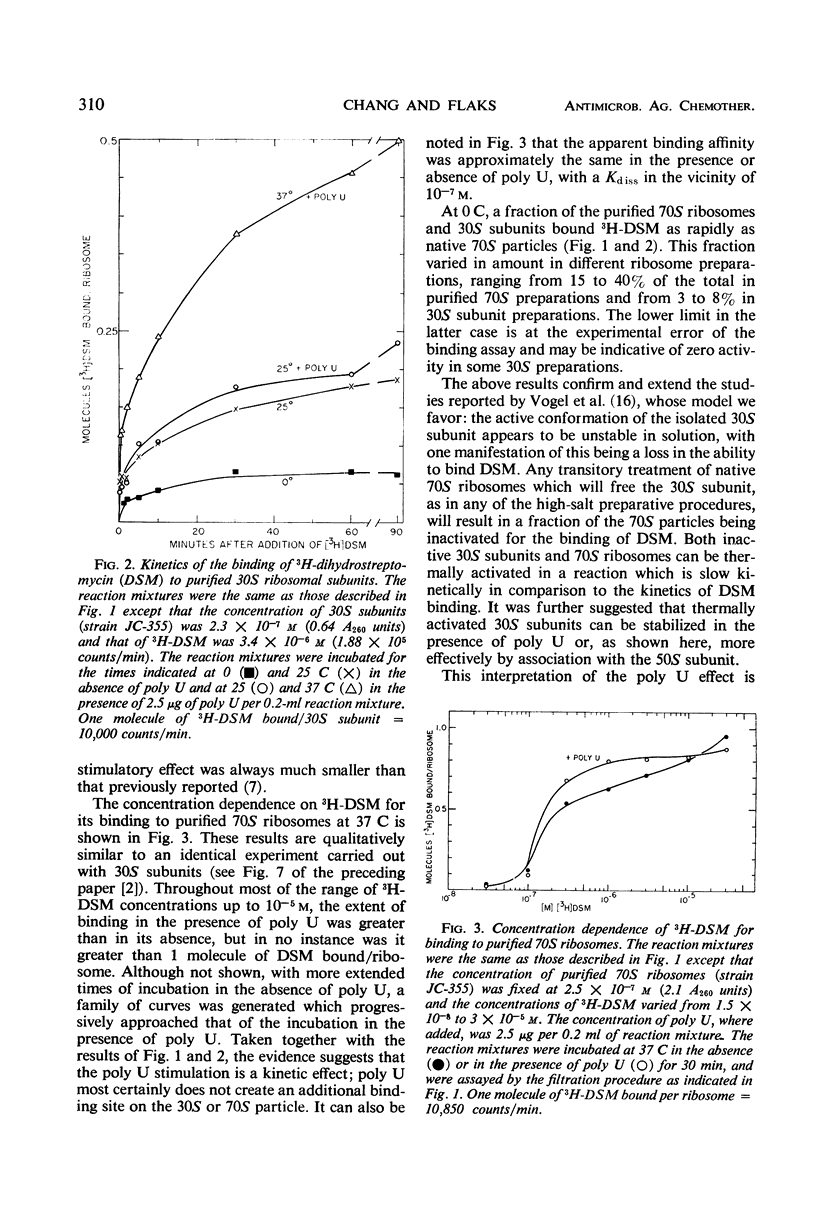
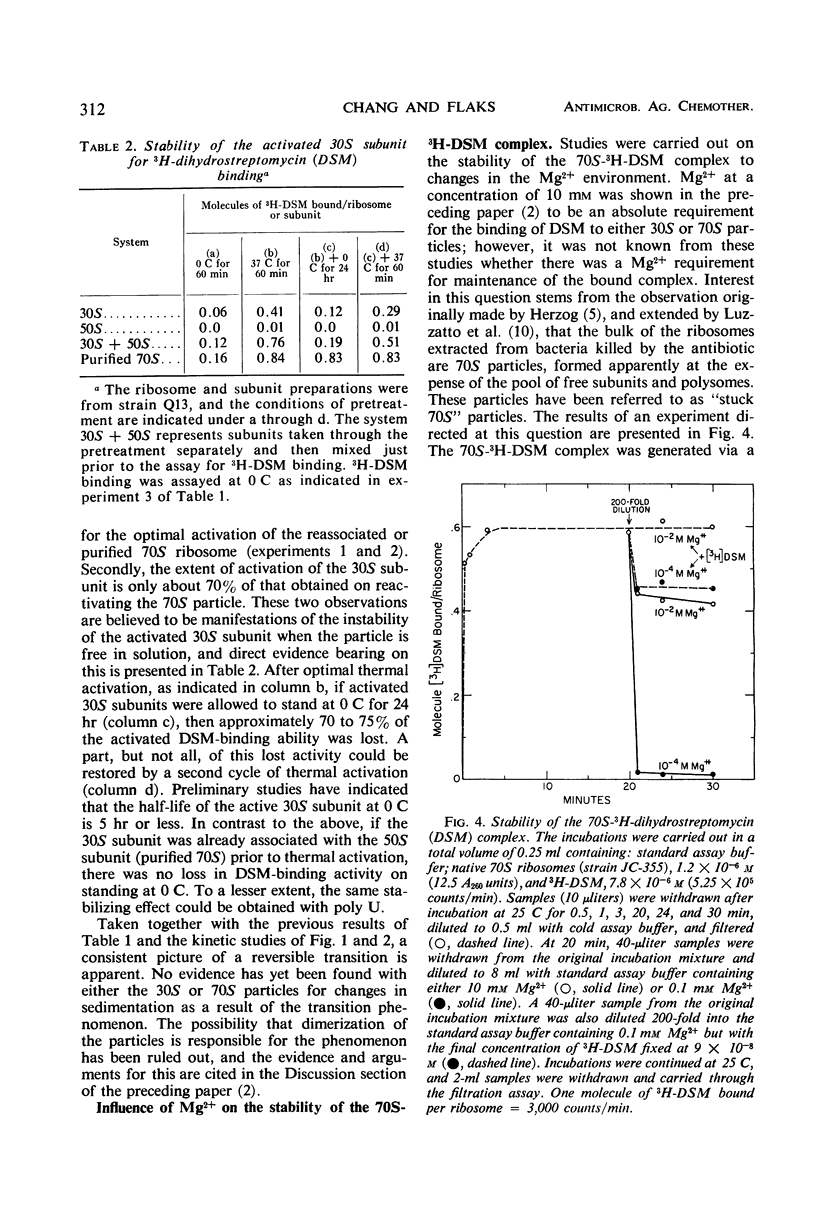
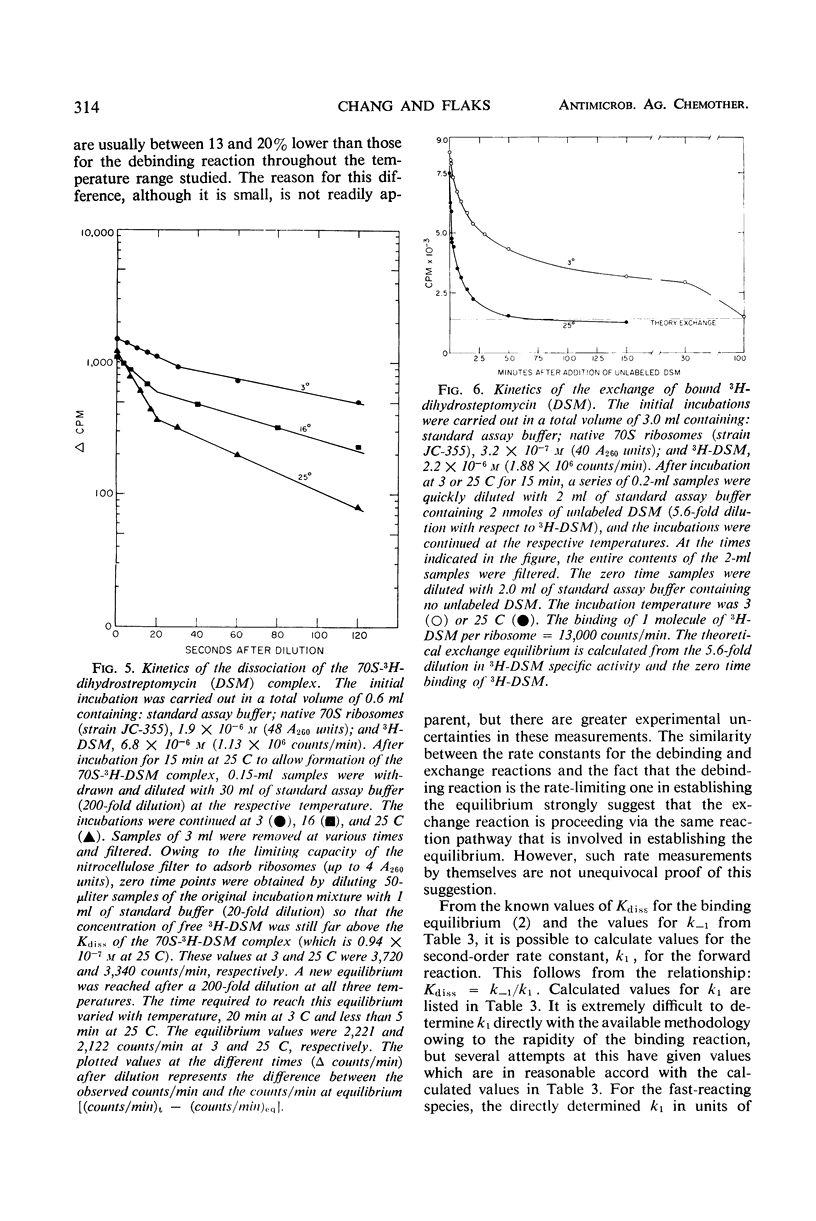
Investigations were carried out on the binding of dihydrostreptomycin to purified (and reassociated) 70S ribosomes and 30S subunits from streptomycin-susceptible strains, and the results were compared with those of similar studies with native (run-off) 70S ribosomes. At 0 C, only a small fraction of purified 70S ribosomes and 30S sub-units bound 1 molecule of the antibiotic tightly, and at a rate comparable to the binding occurring with native 70S ribosomes. At temperatures of 10 C and above, there was a temperature-dependent increase in the extent of antibiotic binding to purified 70S and 30S particles up to a maximum of 1 molecule/ribosomal particle, but the kinetics of binding was slow in comparison to that taking place at 0 C. These and other results suggest that a major fraction of 30S subunits and purified (or reassociated) 70S ribosomes are inactive in binding the antibiotic. This has been localized to an instability of the free 30S subunit, which in solution at 0 C has a half-life of 5 hr or less. Inactive 30S or 70S particles could be thermally activated, with the latter being identical in their streptomycin-binding properties to native 70S ribosomes. The activation kinetics were slow in comparison to the binding kinetics for the antibiotic and were indicative of a conformational change in ribosomal structure. There thus appears to be a reversible transition between active and inactive forms of the ribosomal particles for streptomycin binding, but additional binding sites for the antibiotic are not created by the transitions. The active form of the 30S subunit can be stabilized in the presence of polyuridylic acid, but much more effectively by association with the 50S subunit to form a 70S ribosome. The kinetics of dihydrostreptomycin binding were studied in both directions of the reaction, and the reaction in the direction of binding was found to be several orders of magnitude faster than that of the reverse, or debinding, direction. The kinetics of the exchange of bound dihydrostreptomycin with the free antibiotic were also determined and shown to have rate constants that are very similar to those of the debinding reaction, which is the rate-limiting step. It appears likely that the exchange reaction is proceeding via the same reaction pathway. The temperature dependence of the kinetics of dissociation of the bound complex was much greater than that in the direction of binding and accounted for most of the temperature dependence of the binding equilibrium. From the determined thermodynamic and activation parameters, it appears likely that binding of the antibiotic induces a conformational change in ribosomal structure to one that is less ordered than the native particle. Heterogeneity has been found in the kinetics of binding and of exchange, with a fraction of the 70S population showing slower kinetics for both directions of the reaction.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chang F. N., Flaks J. G. Binding of dihydrostreptomycin to Escherichia coli ribosomes: characteristics and equilibrium of the reaction. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1972 Oct;2(4):294–307. doi: 10.1128/aac.2.4.294. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grunberg-Manago M., Clark B. F., Revel M., Rudland P. S., Dondon J. Stability of different ribosomal complexes with initiator transfer RNA and synthetic messenger RNA. J Mol Biol. 1969 Feb 28;40(1):33–44. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90294-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaji H., Tanaka Y. Binding of dihydrostreptomycin to ribosomal subunits. J Mol Biol. 1968 Mar 14;32(2):221–230. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90006-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurland C. G. The requirements for specific sRNA binding by ribosomes. J Mol Biol. 1966 Jun;18(1):90–108. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(66)80079-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurland C. G., Voynow P., Hardy S. J., Randall L., Lutter L. Physical and functional heterogeneity of E. coli ribosomes. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1969;34:17–24. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1969.034.01.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luzzatto L., Apirion D., Schlessinger D. Mechanism of action of streptomycin in E. coli: interruption of the ribosome cycle at the initiation of protein synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Jul;60(3):873–880. doi: 10.1073/pnas.60.3.873. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLaughlin C. S., Dondon J., Grunberg-Manago M., Michelson A. M., Saunders G. Stability of the messenger RNA-sRNA-ribosome complex. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1966;31:601–610. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1966.031.01.078. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miskin R., Zamir A., Elson D. The inactivation and reactivation of ribosomal-peptidyl transferase of E. coli. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1968 Nov 25;33(4):551–557. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(68)90330-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pestka S. Studies on the formation of transfer ribonucleic acid-ribosome complexes. I. The effect of streptomycin and ribosomal dissociation on 14-C-aminoacyl transfer ribonucleic acid binding to ribosomes. J Biol Chem. 1966 Jan 25;241(2):367–372. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman M. I., Simpson M. V. The role of ribosomal conformation in protein biosynthesis: the streptomycin-ribosome interaction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Dec;64(4):1388–1395. doi: 10.1073/pnas.64.4.1388. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traut R. R., Delius H., Ahmad-Zadeh C., Bickle T. A., Pearson P., Tissières A. Ribosomal proteins of E. Coli: stoichiometry and implications for ribosome structure. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1969;34:25–38. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1969.034.01.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogel Z., Vogel T., Elson D., Zamir A. Ribosome activation and the binding of dihydrostreptomycin: effect of polynucleotides and temperature on activation. J Mol Biol. 1970 Dec 14;54(2):379–386. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90436-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WATSON J. D. THE SYNTHESIS OF PROTEINS UPON RIBOSOMES. Bull Soc Chim Biol (Paris) 1964;46:1399–1425. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


