Abstract
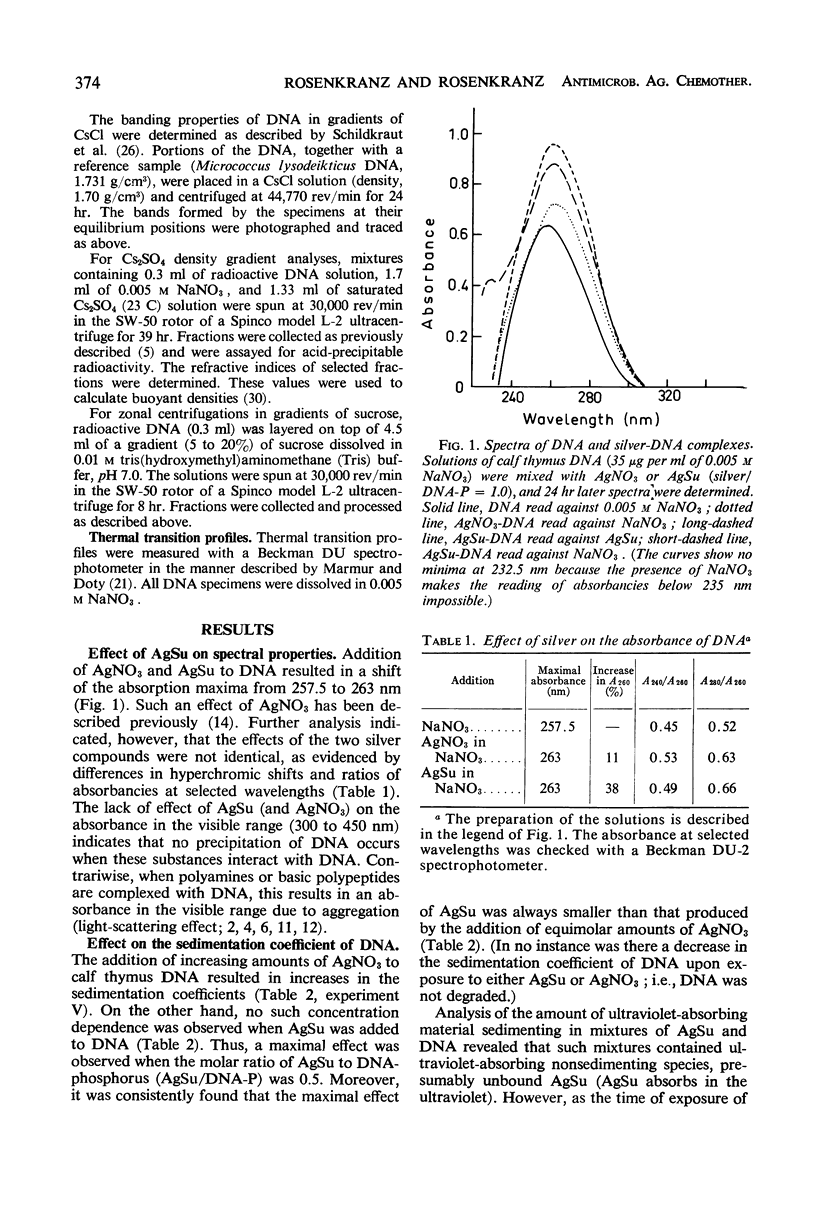
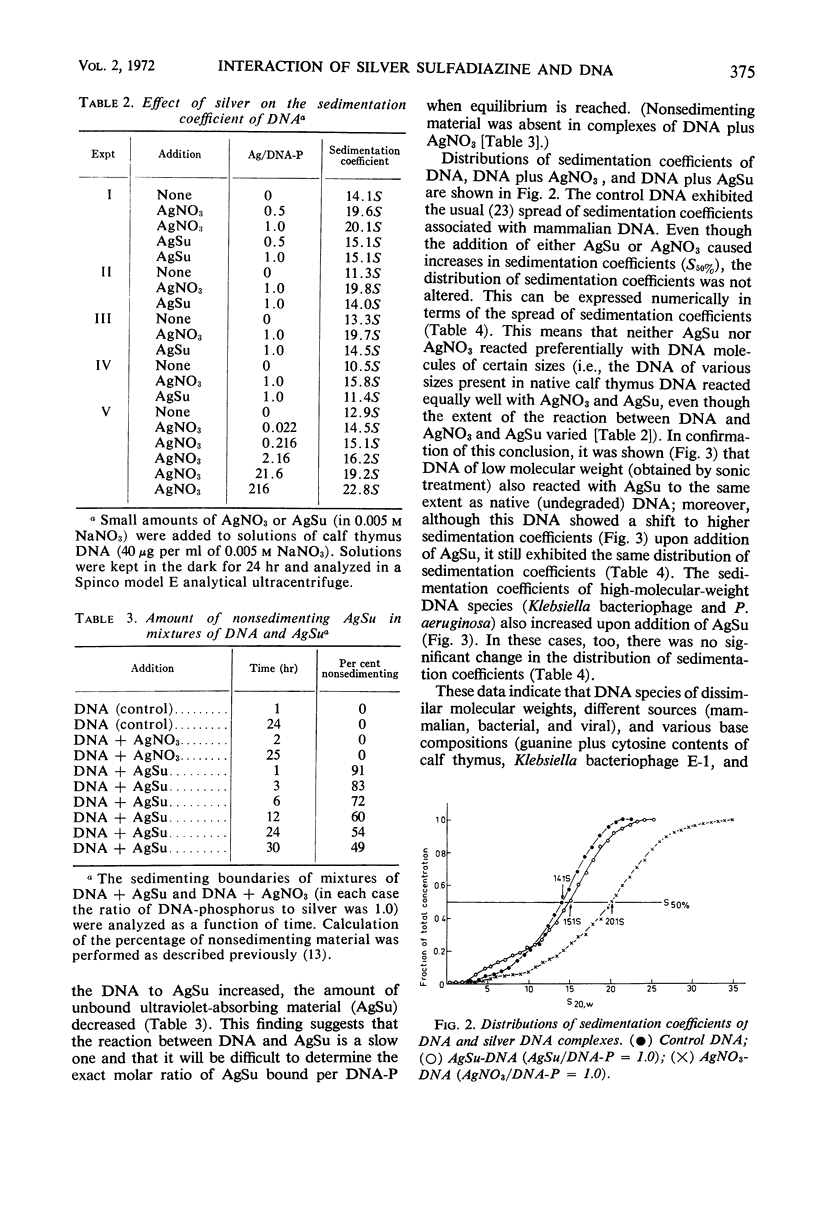
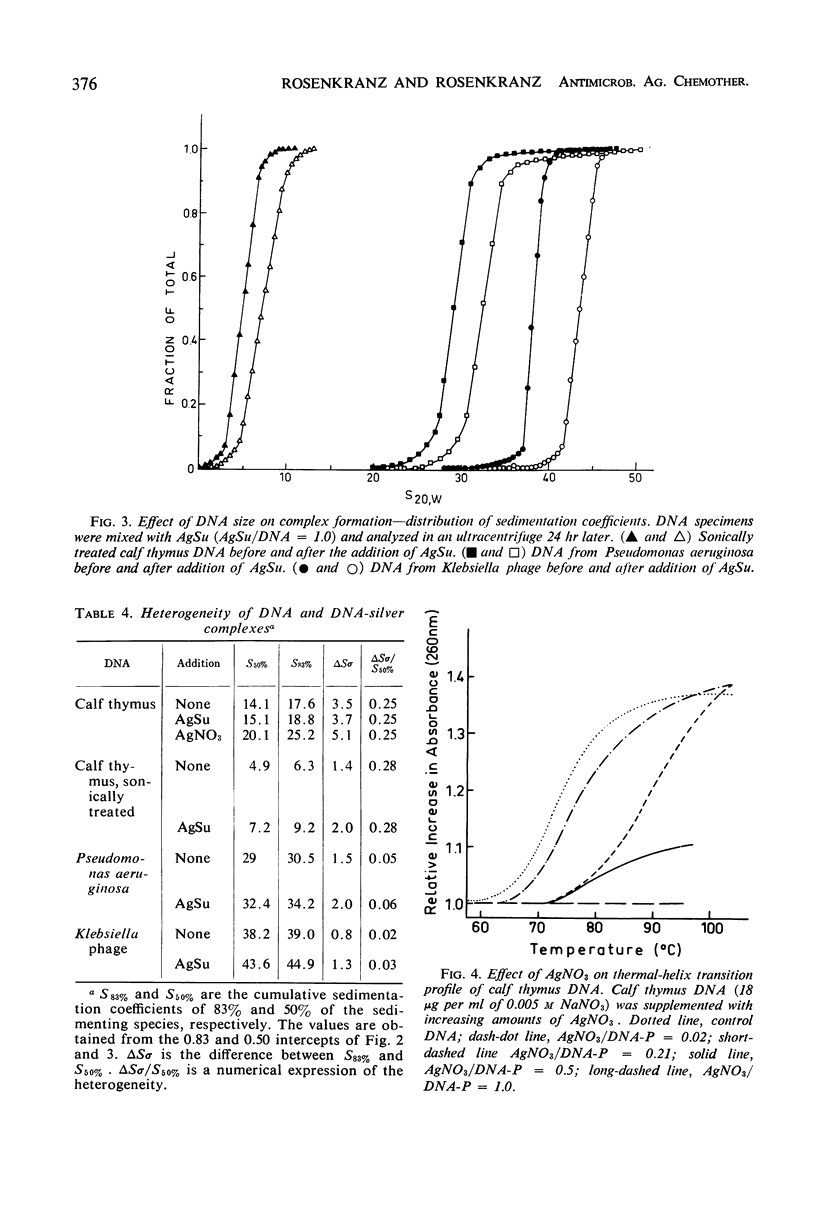
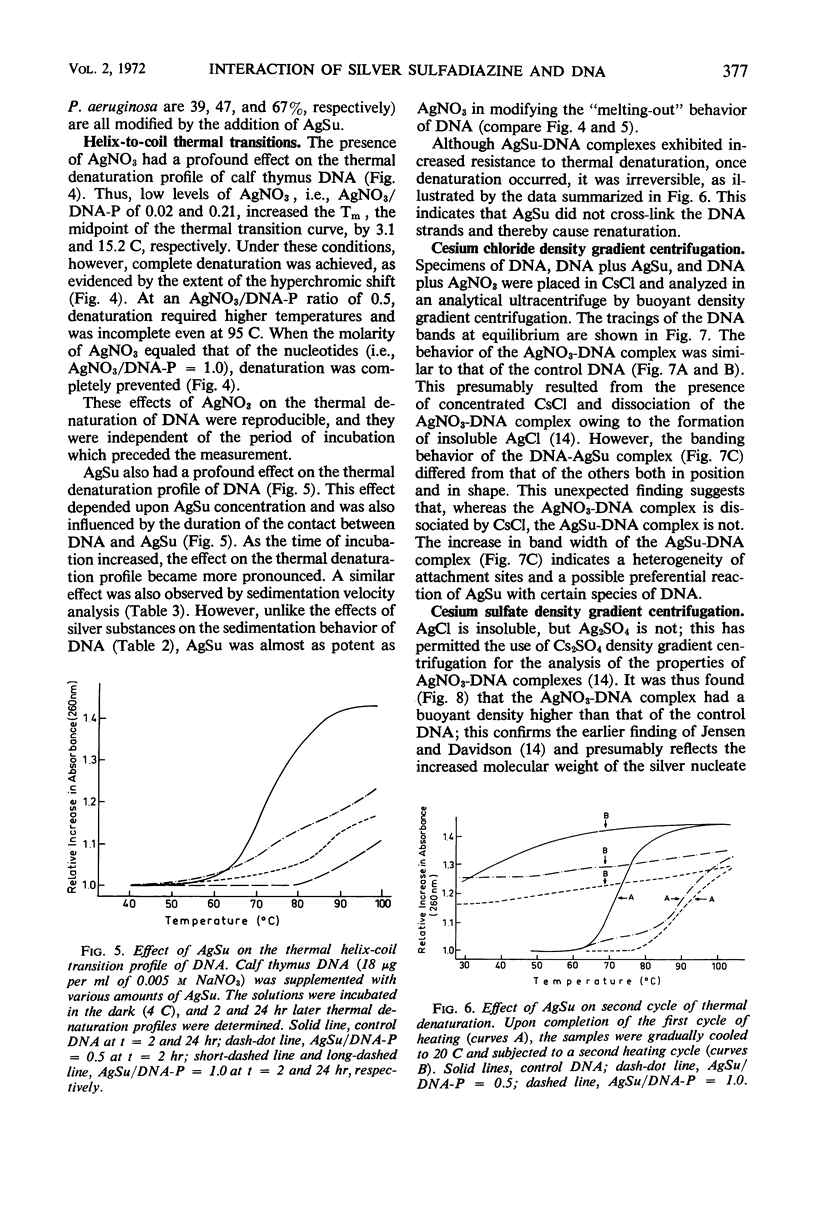
Silver sulfadiazine (AgSu) was found to interact with isolated deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) to form nondissociable complexes. These complexes differ in physical and chemical properties from those that are established when silver nitrate is added to DNA. The reaction between AgSu and DNA is visualized as occurring in two stages: (i) a weak and reversible interaction (intercalation) between DNA and the sulfadiazine moiety and (ii) a tight binding involving the silver atom. In the first stage, sodium sulfadiazine competes with AgSu for the DNA.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- CHIH R., HUANG C., BONNER J., MURRAY K. PHYSICAL AND BIOLOGICAL PROPERTIES OF SOLUBLE NUCLEOHISTONES. J Mol Biol. 1964 Jan;8:54–64. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(64)80148-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COHEN S. N., YIELDING K. L. SPECTROPHOTOMETRIC STUDIES OF THE INTERACTION OF CHLOROQUINE WITH DEOXYRIBONUCLEIC ACID. J Biol Chem. 1965 Jul;240:3123–3131. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COLEMAN J., EDELHOCH H. Macromolecular interactions: proteins and nucleic acids. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1956 Aug;63(2):382–393. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(56)90053-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson B., Fasman G. D. The single-stranded polyadenylic acid-poly-L-lysine complex. A conformational study and characterization. Biochemistry. 1969 Oct;8(10):4116–4126. doi: 10.1021/bi00838a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FELSENFELD G., HUANG S. The interaction of polynucleotides with cations. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1959 Jul;34:234–242. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(59)90253-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox C. L., Jr, Rappole B. W., Stanford W. Control of pseudomonas infection in burns by silver sulfadiazine. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1969 May;128(5):1021–1026. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox C. L., Jr Silver sulfadiazine--a new topical therapy for Pseudomonas in burns. Therapy of Pseudomonas infection in burns. Arch Surg. 1968 Feb;96(2):184–188. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1968.01330200022004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houssier C., Fredericq E. Electrooptical properties of nucleic acids and nucleoproteins. II. Study of the deoxyribonucleohistone-proflavine complexes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Jul 13;120(3):434–447. doi: 10.1016/0926-6585(66)90310-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs S. J., Rosenkranz H. S. Detection of a reactive intermediate in the reaction between DNA and hydroxyurea. Cancer Res. 1970 Apr;30(4):1084–1094. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleinwächter V., Balcarová Z., Bohácek J. Thermal stability of complexes of diaminoacridines with deoxyribonucleic acids of varying base content. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Jan 21;174(1):188–201. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(69)90242-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LERMAN L. S. The structure of the DNA-acridine complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1963 Jan 15;49:94–102. doi: 10.1073/pnas.49.1.94. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LUZZATI V., MASSON F., LERMAN L. S. Interaction of DNA and proflavine: a small-angle x-ray scattering study. J Mol Biol. 1961 Oct;3:634–639. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(61)80026-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LePecq J. B., Paoletti C. A fluorescent complex between ethidium bromide and nucleic acids. Physical-chemical characterization. J Mol Biol. 1967 Jul 14;27(1):87–106. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90353-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARMUR J., DOTY P. Determination of the base composition of deoxyribonucleic acid from its thermal denaturation temperature. J Mol Biol. 1962 Jul;5:109–118. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(62)80066-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARTIN R. G., AMES B. N. A method for determining the sedimentation behavior of enzymes: application to protein mixtures. J Biol Chem. 1961 May;236:1372–1379. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahler H. R., Green G., Goutarel R., Khuong-Huu Q. Nucleic acid-small molecule interactions. VII. Further characterization of deoxyribonucleic acid-diamino steroid complexes. Biochemistry. 1968 Apr;7(4):1568–1582. doi: 10.1021/bi00844a046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenkranz H. S., Carr H. S. Silver sulfadiazine: effect on the growth and metabolism of bacteria. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1972 Nov;2(5):367–372. doi: 10.1128/aac.2.5.367. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHILDKRAUT C. L., MARMUR J., DOTY P. Determination of the base composition of deoxyribonucleic acid from its buoyant density in CsCl. J Mol Biol. 1962 Jun;4:430–443. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(62)80100-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHUMAKER V. N., SCHACHMAN H. K. Ultracentrifugal analysis of dilute solutions. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1957 Mar;23(3):628–639. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(57)90386-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanford W., Rappole B. W., Fox C. L., Jr Clinical experience with silver sulfadiazine, a new topical agent for control of pseudomonas infections in burns. J Trauma. 1969 May;9(5):377–388. doi: 10.1097/00005373-196905000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YAMANE T., DAVIDSON N. On the complexing of deoxyribonucleic acid by silver (I). Biochim Biophys Acta. 1962 May 14;55:609–621. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(62)90839-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


