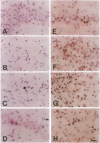
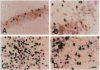
Abstract
The p53 tumor-suppressor gene encodes a growth-regulatory protein that has been implicated in programmed cell death. To investigate the possible role of p53 in neuronal death, we studied p53 expression associated with excitotoxicity in the adult rat brain. Within hours of systemic administration of the glutamate analogue kainic acid, p53 mRNA levels were increased in neurons exhibiting morphological features of damage within kainate-vulnerable brain regions. A similar distribution was found for neurons exhibiting DNA damage as evidenced by in situ end-labeling of fragmented DNA. Pretreatment with the protein synthesis inhibitor cycloheximide prevented both kainate-mediated p53 induction and neuronal damage. The distinctive pattern of excitotoxin-mediated p53 expression suggests that p53 induction is a marker of irreversible injury in postmitotic cells of the central nervous system and could have functional significance in determining selective neuronal vulnerability.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agoff S. N., Hou J., Linzer D. I., Wu B. Regulation of the human hsp70 promoter by p53. Science. 1993 Jan 1;259(5091):84–87. doi: 10.1126/science.8418500. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bienz B., Zakut-Houri R., Givol D., Oren M. Analysis of the gene coding for the murine cellular tumour antigen p53. EMBO J. 1984 Sep;3(9):2179–2183. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02110.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chopp M., Li Y., Zhang Z. G., Freytag S. O. p53 expression in brain after middle cerebral artery occlusion in the rat. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Feb 14;182(3):1201–1207. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(92)91859-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke A. R., Purdie C. A., Harrison D. J., Morris R. G., Bird C. C., Hooper M. L., Wyllie A. H. Thymocyte apoptosis induced by p53-dependent and independent pathways. Nature. 1993 Apr 29;362(6423):849–852. doi: 10.1038/362849a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devary Y., Gottlieb R. A., Lau L. F., Karin M. Rapid and preferential activation of the c-jun gene during the mammalian UV response. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 May;11(5):2804–2811. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.5.2804. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farmer G., Bargonetti J., Zhu H., Friedman P., Prywes R., Prives C. Wild-type p53 activates transcription in vitro. Nature. 1992 Jul 2;358(6381):83–86. doi: 10.1038/358083a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fritsche M., Haessler C., Brandner G. Induction of nuclear accumulation of the tumor-suppressor protein p53 by DNA-damaging agents. Oncogene. 1993 Feb;8(2):307–318. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gold R., Schmied M., Rothe G., Zischler H., Breitschopf H., Wekerle H., Lassmann H. Detection of DNA fragmentation in apoptosis: application of in situ nick translation to cell culture systems and tissue sections. J Histochem Cytochem. 1993 Jul;41(7):1023–1030. doi: 10.1177/41.7.8515045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez M. F., Shiraishi K., Hisanaga K., Sagar S. M., Mandabach M., Sharp F. R. Heat shock proteins as markers of neural injury. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 1989 Jul;6(1):93–100. doi: 10.1016/0169-328x(89)90033-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollstein M., Sidransky D., Vogelstein B., Harris C. C. p53 mutations in human cancers. Science. 1991 Jul 5;253(5015):49–53. doi: 10.1126/science.1905840. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hupp T. R., Meek D. W., Midgley C. A., Lane D. P. Regulation of the specific DNA binding function of p53. Cell. 1992 Nov 27;71(5):875–886. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90562-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kastan M. B., Onyekwere O., Sidransky D., Vogelstein B., Craig R. W. Participation of p53 protein in the cellular response to DNA damage. Cancer Res. 1991 Dec 1;51(23 Pt 1):6304–6311. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kley N., Chung R. Y., Fay S., Loeffler J. P., Seizinger B. R. Repression of the basal c-fos promoter by wild-type p53. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Aug 11;20(15):4083–4087. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.15.4083. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane D. P. Cancer. p53, guardian of the genome. Nature. 1992 Jul 2;358(6381):15–16. doi: 10.1038/358015a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine A. J., Momand J., Finlay C. A. The p53 tumour suppressor gene. Nature. 1991 Jun 6;351(6326):453–456. doi: 10.1038/351453a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowe S. W., Schmitt E. M., Smith S. W., Osborne B. A., Jacks T. p53 is required for radiation-induced apoptosis in mouse thymocytes. Nature. 1993 Apr 29;362(6423):847–849. doi: 10.1038/362847a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manome Y., Datta R., Fine H. A. Early response gene induction following DNA damage in astrocytoma cell lines. Biochem Pharmacol. 1993 Apr 22;45(8):1677–1684. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(93)90309-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nitecka L., Tremblay E., Charton G., Bouillot J. P., Berger M. L., Ben-Ari Y. Maturation of kainic acid seizure-brain damage syndrome in the rat. II. Histopathological sequelae. Neuroscience. 1984 Dec;13(4):1073–1094. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(84)90289-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papas S., Crépel V., Hasboun D., Jorquera I., Chinestra P., Ben-Ari Y. Cycloheximide Reduces the Effects of Anoxic Insult In Vivo and In Vitro. Eur J Neurosci. 1992;4(8):758–765. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.1992.tb00185.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinhasi-Kimhi O., Michalovitz D., Ben-Zeev A., Oren M. Specific interaction between the p53 cellular tumour antigen and major heat shock proteins. Nature. 1986 Mar 13;320(6058):182–184. doi: 10.1038/320182a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreiber S. S., Tocco G., Najm I., Thompson R. F., Baudry M. Cycloheximide prevents kainate-induced neuronal death and c-fos expression in adult rat brain. J Mol Neurosci. 1993 Fall;4(3):149–159. doi: 10.1007/BF02782498. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwob J. E., Fuller T., Price J. L., Olney J. W. Widespread patterns of neuronal damage following systemic or intracerebral injections of kainic acid: a histological study. Neuroscience. 1980;5(6):991–1014. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(80)90181-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shah G., Ghosh R., Amstad P. A., Cerutti P. A. Mechanism of induction of c-fos by ultraviolet B (290-320 nm) in mouse JB6 epidermal cells. Cancer Res. 1993 Jan 1;53(1):38–45. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw P., Bovey R., Tardy S., Sahli R., Sordat B., Costa J. Induction of apoptosis by wild-type p53 in a human colon tumor-derived cell line. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 May 15;89(10):4495–4499. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.10.4495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sloviter R. S., Lowenstein D. H. Heat shock protein expression in vulnerable cells of the rat hippocampus as an indicator of excitation-induced neuronal stress. J Neurosci. 1992 Aug;12(8):3004–3009. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.12-08-03004.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smeyne R. J., Vendrell M., Hayward M., Baker S. J., Miao G. G., Schilling K., Robertson L. M., Curran T., Morgan J. I. Continuous c-fos expression precedes programmed cell death in vivo. Nature. 1993 May 13;363(6425):166–169. doi: 10.1038/363166a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich S. J., Anderson C. W., Mercer W. E., Appella E. The p53 tumor suppressor protein, a modulator of cell proliferation. J Biol Chem. 1992 Aug 5;267(22):15259–15262. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wijsman J. H., Jonker R. R., Keijzer R., van de Velde C. J., Cornelisse C. J., van Dierendonck J. H. A new method to detect apoptosis in paraffin sections: in situ end-labeling of fragmented DNA. J Histochem Cytochem. 1993 Jan;41(1):7–12. doi: 10.1177/41.1.7678025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yonish-Rouach E., Resnitzky D., Lotem J., Sachs L., Kimchi A., Oren M. Wild-type p53 induces apoptosis of myeloid leukaemic cells that is inhibited by interleukin-6. Nature. 1991 Jul 25;352(6333):345–347. doi: 10.1038/352345a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zambetti G. P., Bargonetti J., Walker K., Prives C., Levine A. J. Wild-type p53 mediates positive regulation of gene expression through a specific DNA sequence element. Genes Dev. 1992 Jul;6(7):1143–1152. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.7.1143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zauberman A., Barak Y., Ragimov N., Levy N., Oren M. Sequence-specific DNA binding by p53: identification of target sites and lack of binding to p53 - MDM2 complexes. EMBO J. 1993 Jul;12(7):2799–2808. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05941.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhan Q., Carrier F., Fornace A. J., Jr Induction of cellular p53 activity by DNA-damaging agents and growth arrest. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Jul;13(7):4242–4250. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.7.4242. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]