Abstract
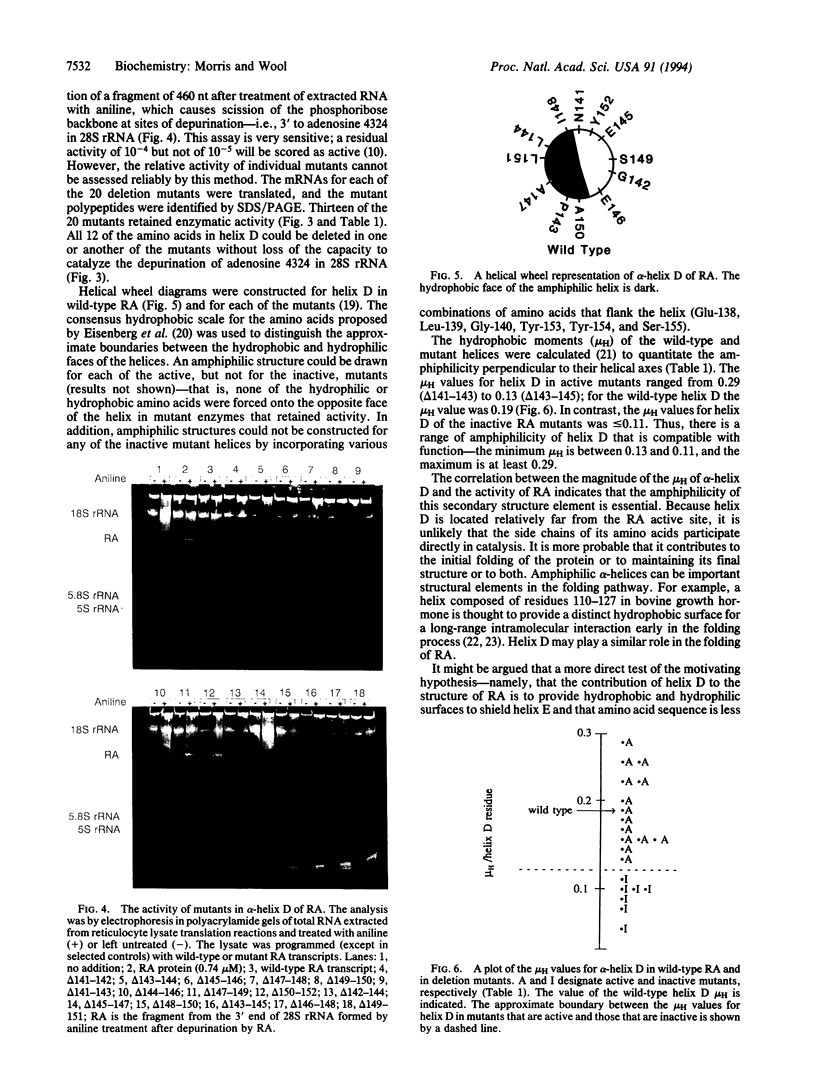
The A chain of ricin is a cytotoxic RNA N-glycosidase that inactivates eukaryotic ribosomes. The contribution of the amphiphilic helix D, which is distant from the active site, to the catalysis of the depurination of the adenosine at position 4324 in 28S rRNA has been examined by systematic deletion of amino acids. Two sets of consecutive two- or three-amino acid deletions of the 12 residues in helix D, a total of 20 mutants, were constructed. All 12 of the amino acids could be deleted in one mutant or another without loss of activity; however, mutations that disrupted the amphiphilicity of the helix led to inactivation of the enzyme. Thus, the minimum contribution of helix D to the structure of the ricin A chain is to provide hydrophobic and hydrophilic surfaces to shield helix E, which has the active-site residues; moreover, no amino acid side chain in helix D makes a specific contribution to the recognition of the RNA substrate or to catalysis; and, finally, phasing of the amino acid deletions can be important to the phenotype of mutants.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bradley J. L., McGuire P. M. Site-directed mutagenesis of ricin A chain Trp 211 to Phe. Int J Pept Protein Res. 1990 Apr;35(4):365–366. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-3011.1990.tb00062.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brems D. N., Plaisted S. M., Kauffman E. W., Havel H. A. Characterization of an associated equilibrium folding intermediate of bovine growth hormone. Biochemistry. 1986 Oct 21;25(21):6539–6543. doi: 10.1021/bi00369a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg D., Weiss R. M., Terwilliger T. C. The helical hydrophobic moment: a measure of the amphiphilicity of a helix. Nature. 1982 Sep 23;299(5881):371–374. doi: 10.1038/299371a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endo Y., Mitsui K., Motizuki M., Tsurugi K. The mechanism of action of ricin and related toxic lectins on eukaryotic ribosomes. The site and the characteristics of the modification in 28 S ribosomal RNA caused by the toxins. J Biol Chem. 1987 Apr 25;262(12):5908–5912. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endo Y., Tsurugi K. RNA N-glycosidase activity of ricin A-chain. Mechanism of action of the toxic lectin ricin on eukaryotic ribosomes. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jun 15;262(17):8128–8130. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frankel A., Schlossman D., Welsh P., Hertler A., Withers D., Johnston S. Selection and characterization of ricin toxin A-chain mutations in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Feb;9(2):415–420. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.2.415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frankel A., Welsh P., Richardson J., Robertus J. D. Role of arginine 180 and glutamic acid 177 of ricin toxin A chain in enzymatic inactivation of ribosomes. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Dec;10(12):6257–6263. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.12.6257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Havel H. A., Kauffman E. W., Plaisted S. M., Brems D. N. Reversible self-association of bovine growth hormone during equilibrium unfolding. Biochemistry. 1986 Oct 21;25(21):6533–6538. doi: 10.1021/bi00369a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katzin B. J., Collins E. J., Robertus J. D. Structure of ricin A-chain at 2.5 A. Proteins. 1991;10(3):251–259. doi: 10.1002/prot.340100309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A., Roberts J. D., Zakour R. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Methods Enzymol. 1987;154:367–382. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)54085-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- May M. J., Hartley M. R., Roberts L. M., Krieg P. A., Osborn R. W., Lord J. M. Ribosome inactivation by ricin A chain: a sensitive method to assess the activity of wild-type and mutant polypeptides. EMBO J. 1989 Jan;8(1):301–308. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03377.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mlsna D., Monzingo A. F., Katzin B. J., Ernst S., Robertus J. D. Structure of recombinant ricin A chain at 2.3 A. Protein Sci. 1993 Mar;2(3):429–435. doi: 10.1002/pro.5560020315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montfort W., Villafranca J. E., Monzingo A. F., Ernst S. R., Katzin B., Rutenber E., Xuong N. H., Hamlin R., Robertus J. D. The three-dimensional structure of ricin at 2.8 A. J Biol Chem. 1987 Apr 15;262(11):5398–5403. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monzingo A. F., Robertus J. D. X-ray analysis of substrate analogs in the ricin A-chain active site. J Mol Biol. 1992 Oct 20;227(4):1136–1145. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90526-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris K. N., Wool I. G. Determination by systematic deletion of the amino acids essential for catalysis by ricin A chain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jun 1;89(11):4869–4873. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.11.4869. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ready M. P., Kim Y., Robertus J. D. Site-directed mutagenesis of ricin A-chain and implications for the mechanism of action. Proteins. 1991;10(3):270–278. doi: 10.1002/prot.340100311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ready M., Wilson K., Piatak M., Robertus J. D. Ricin-like plant toxins are evolutionarily related to single-chain ribosome-inhibiting proteins from Phytolacca. J Biol Chem. 1984 Dec 25;259(24):15252–15256. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rutenber E., Katzin B. J., Ernst S., Collins E. J., Mlsna D., Ready M. P., Robertus J. D. Crystallographic refinement of ricin to 2.5 A. Proteins. 1991;10(3):240–250. doi: 10.1002/prot.340100308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiffer M., Edmundson A. B. Use of helical wheels to represent the structures of proteins and to identify segments with helical potential. Biophys J. 1967 Mar;7(2):121–135. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(67)86579-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlossman D., Withers D., Welsh P., Alexander A., Robertus J., Frankel A. Role of glutamic acid 177 of the ricin toxin A chain in enzymatic inactivation of ribosomes. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Nov;9(11):5012–5021. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.11.5012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]