Abstract
The promoter region of the rat kidney neutral and basic amino acid transporter (NBAT) gene has been isolated and sequenced. The major transcription initiation site was mapped by primer extension. The entire promoter region and a set of 5' deletions within it were expressed at a high level in LLC-PK1 cells using the luciferase indicator gene. Positive and negative regulatory elements in the promoter region were observed. A human genomic clone of the transporter was also obtained and was used to localize the NBAT gene at the p21 region of chromosome 2.
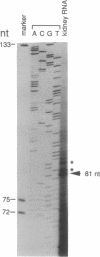
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bertran J., Werner A., Chillarón J., Nunes V., Biber J., Testar X., Zorzano A., Estivill X., Murer H., Palacín M. Expression cloning of a human renal cDNA that induces high affinity transport of L-cystine shared with dibasic amino acids in Xenopus oocytes. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jul 15;268(20):14842–14849. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bertran J., Werner A., Moore M. L., Stange G., Markovich D., Biber J., Testar X., Zorzano A., Palacin M., Murer H. Expression cloning of a cDNA from rabbit kidney cortex that induces a single transport system for cystine and dibasic and neutral amino acids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jun 15;89(12):5601–5605. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.12.5601. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breathnach R., Chambon P. Organization and expression of eucaryotic split genes coding for proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:349–383. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.002025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fouser L., Avner E. D. Normal and abnormal nephrogenesis. Am J Kidney Dis. 1993 Jan;21(1):64–70. doi: 10.1016/s0272-6386(12)80723-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanash S. M., Beretta L., Barcroft C. L., Sheldon S., Glover T. W., Ungar D., Sonenberg N. Mapping of the gene for interferon-inducible dsRNA-dependent protein kinase to chromosome region 2p21-22: a site of rearrangements in myeloproliferative disorders. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 1993 Sep;8(1):34–37. doi: 10.1002/gcc.2870080107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hecht B. K., Hecht F., Münke M. Forebrain cleavage gene causing holoprosencephaly: deletion mapping to chromosome band 2p21. Am J Med Genet. 1991 Jul 1;40(1):130–130. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320400131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horiuchi M., Nakamura N., Tang S. S., Barrett G., Dzau V. J. Molecular mechanism of tissue-specific regulation of mouse renin gene expression by cAMP. Identification of an inhibitory protein that binds nuclear transcriptional factor. J Biol Chem. 1991 Aug 25;266(24):16247–16254. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones K. A., Luciw P. A., Duchange N. Structural arrangements of transcription control domains within the 5'-untranslated leader regions of the HIV-1 and HIV-2 promoters. Genes Dev. 1988 Sep;2(9):1101–1114. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.9.1101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee W. S., Wells R. G., Sabbag R. V., Mohandas T. K., Hediger M. A. Cloning and chromosomal localization of a human kidney cDNA involved in cystine, dibasic, and neutral amino acid transport. J Clin Invest. 1993 May;91(5):1959–1963. doi: 10.1172/JCI116415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathew S., Murty V. V., Hunziker W., Chaganti R. S. Subregional mapping of 13 single-copy genes on the long arm of chromosome 12 by fluorescence in situ hybridization. Genomics. 1992 Nov;14(3):775–779. doi: 10.1016/s0888-7543(05)80184-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosckovitz R., Yan N., Heimer E., Felix A., Tate S. S., Udenfriend S. Characterization of the rat neutral and basic amino acid transporter utilizing anti-peptide antibodies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 May 1;90(9):4022–4026. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.9.4022. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mount S. M. A catalogue of splice junction sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Jan 22;10(2):459–472. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.2.459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pickel V. M., Nirenberg M. J., Chan J., Mosckovitz R., Udenfriend S., Tate S. S. Ultrastructural localization of a neutral and basic amino acid transporter in rat kidney and intestine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Aug 15;90(16):7779–7783. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.16.7779. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinkel D., Straume T., Gray J. W. Cytogenetic analysis using quantitative, high-sensitivity, fluorescence hybridization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(9):2934–2938. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.9.2934. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rousseau-Merck M. F., Atger M., Loosfelt H., Milgrom E., Berger R. The chromosomal localization of the human follicle-stimulating hormone receptor gene (FSHR) on 2p21-p16 is similar to that of the luteinizing hormone receptor gene. Genomics. 1993 Jan;15(1):222–224. doi: 10.1006/geno.1993.1041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
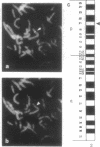
- Rousseau-Merck M. F., Misrahi M., Atger M., Loosfelt H., Milgrom E., Berger R. Localization of the human luteinizing hormone/choriogonadotropin receptor gene (LHCGR) to chromosome 2p21. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1990;54(1-2):77–79. doi: 10.1159/000132962. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rupp R. A., Sippel A. E. Chicken liver TGGCA protein purified by preparative mobility shift electrophoresis (PMSE) shows a 36.8 to 29.8 kd microheterogeneity. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Dec 10;15(23):9707–9726. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.23.9707. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schüle R., Muller M., Otsuka-Murakami H., Renkawitz R. Cooperativity of the glucocorticoid receptor and the CACCC-box binding factor. Nature. 1988 Mar 3;332(6159):87–90. doi: 10.1038/332087a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shieh B. H., Xia Y., Sparkes R. S., Klisak I., Lusis A. J., Nicoll D. A., Philipson K. D. Mapping of the gene for the cardiac sarcolemmal Na(+)-Ca2+ exchanger to human chromosome 2p21-p23. Genomics. 1992 Mar;12(3):616–617. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(92)90459-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tate S. S., Yan N., Udenfriend S. Expression cloning of a Na(+)-independent neutral amino acid transporter from rat kidney. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jan 1;89(1):1–5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Winkle L. J., Campione A. L., Gorman J. M. Na+-independent transport of basic and zwitterionic amino acids in mouse blastocysts by a shared system and by processes which distinguish between these substrates. J Biol Chem. 1988 Mar 5;263(7):3150–3163. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiner A. M., Deininger P. L., Efstratiadis A. Nonviral retroposons: genes, pseudogenes, and transposable elements generated by the reverse flow of genetic information. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:631–661. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.003215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wells R. G., Hediger M. A. Cloning of a rat kidney cDNA that stimulates dibasic and neutral amino acid transport and has sequence similarity to glucosidases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jun 15;89(12):5596–5600. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.12.5596. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yan N., Mosckovitz R., Udenfriend S., Tate S. S. Distribution of mRNA of a Na(+)-independent neutral amino acid transporter cloned from rat kidney and its expression in mammalian tissues and Xenopus laevis oocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Nov 1;89(21):9982–9985. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.21.9982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]