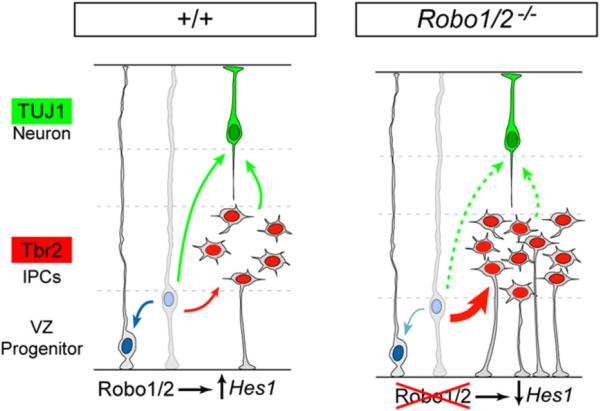
Figure 9. A Model of the Function of Robo Signaling on the Dynamics of Telencephalic Progenitors.
In normal development (+/+), Robo signaling drives Hes1 transcription in neocortical VZ progenitors, which contributes to maintain the balance between VZ progenitor self-renewal (blue arrow), generation of Tbr2+ IPCs (red arrow), and generation of TUJ1+ neurons (green arrows). In the absence of Robo receptors (Robo1/2-/-), Hes1 mRNA levels decrease and the dynamics of VZ progenitors are unbalanced, favoring the generation of IPCs over self-renewal. For unknown reasons, a large proportion of Robo1/2 mutant IPCs retain a ventricle-contacting apical process and stall before entering into mitosis, which indirectly prevents the premature overproduction of neurons in Robo1/2 mutants.