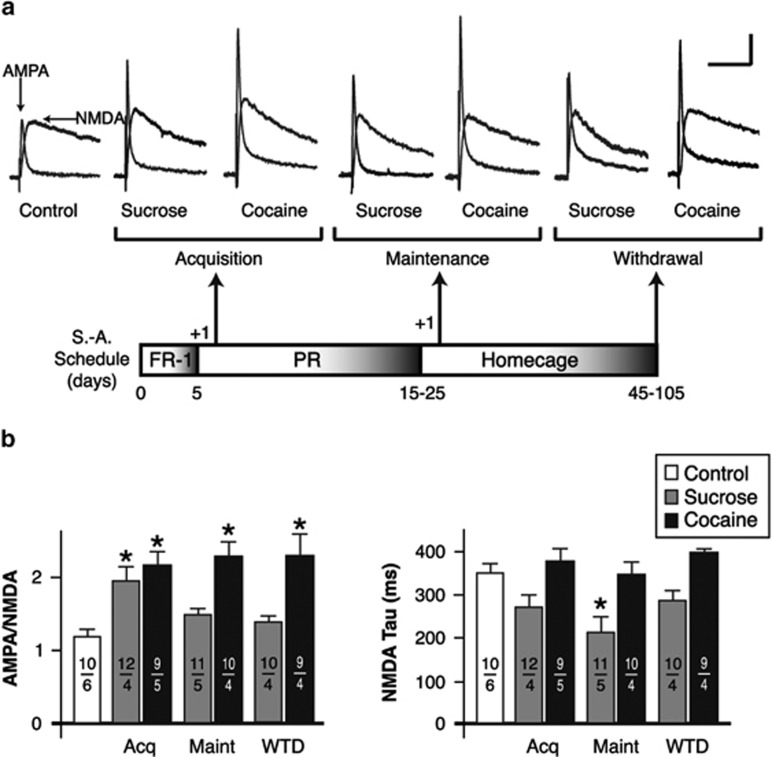
Figure 1.
Effect of self-administration on the strength of oval bed nucleus of the stria terminalis (ovBNST) excitatory synapses. (a) Representative whole-cell recordings of ovBNST excitatory postsynaptic currents (EPSCs). Neurons were voltage clamped at +40 mV and the α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid (AMPA) and N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) components were isolated pharmacologically (amino-5-phosphonopentanoic acid (AP-5), 50 μM). As depicted in the lower part of panel, recordings were obtained in brain slices prepared at three times-points and compared with those measured in age-matched untrained rats (control). Bar scale: 100 pA and 100 ms. (b) Summary of the effects of self-administration trainings on the ratio of AMPA to NMDA (left) and decay time of NMDA (right) currents. Numbers on each bar indicate the numbers of recorded neurons and rats. Asterisks indicate statistically significant difference compared with control, p<0.05.FR-1, fixed ratio-1; PR, progressive ratio; S-A, self-administration.