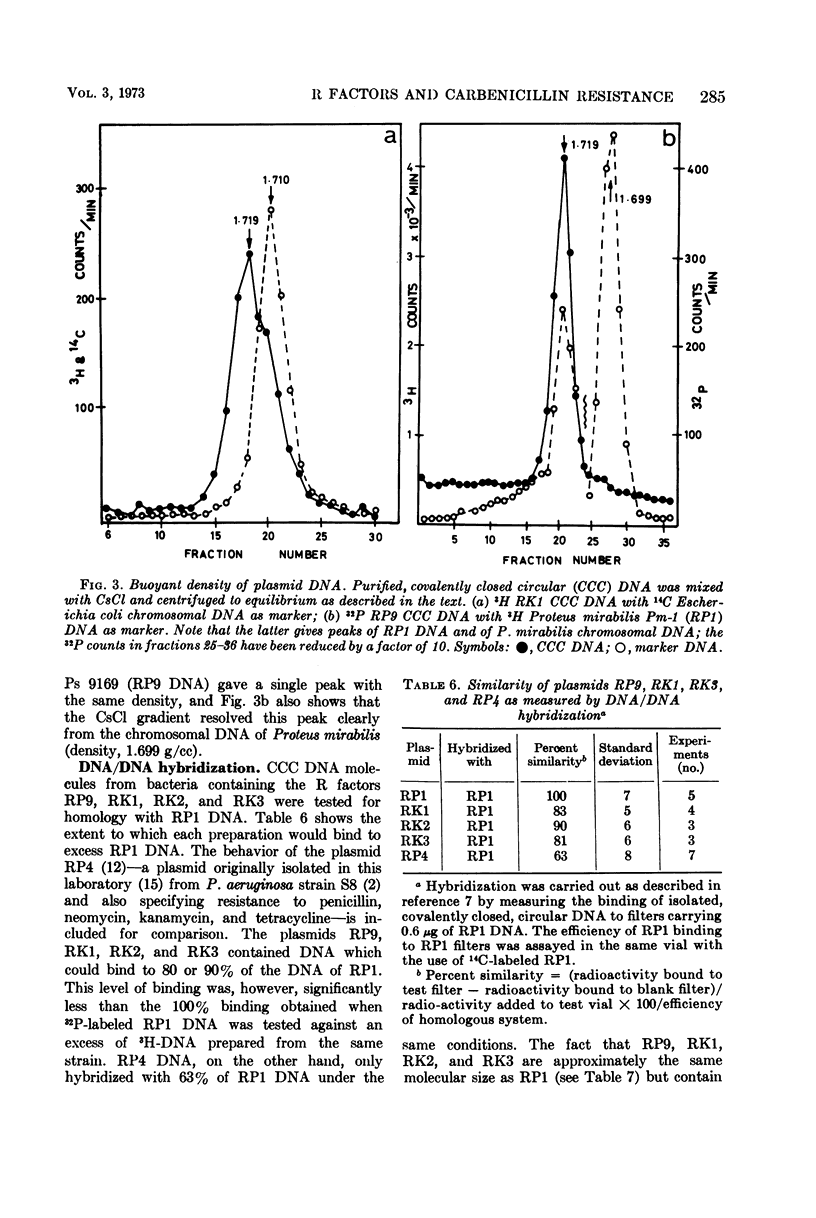
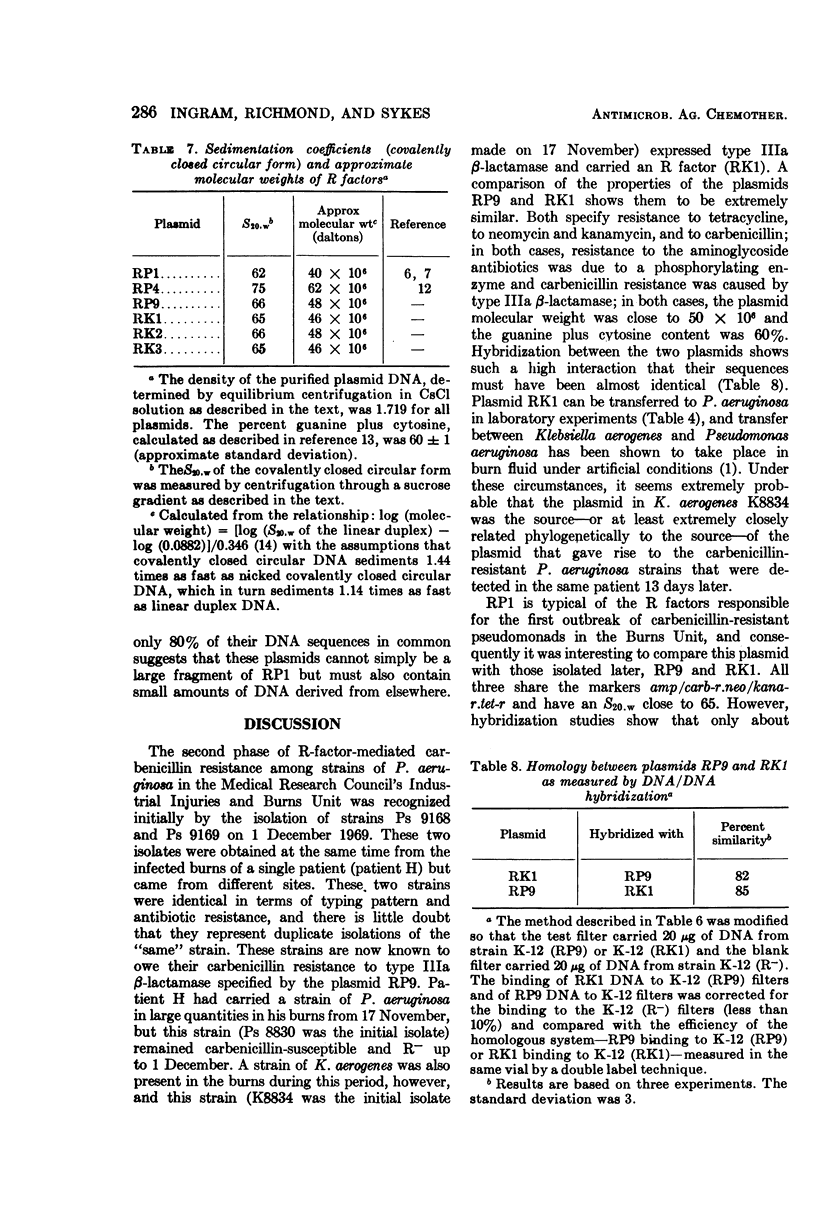
Abstract
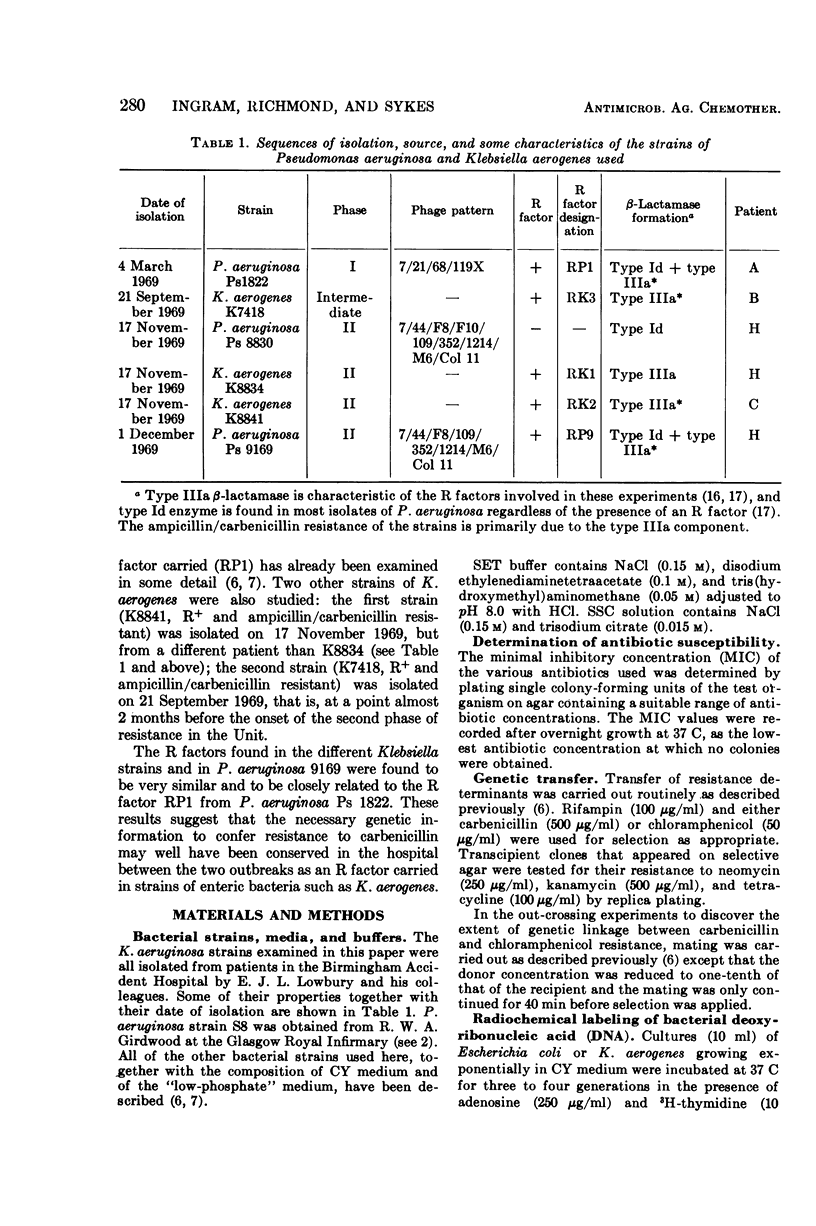
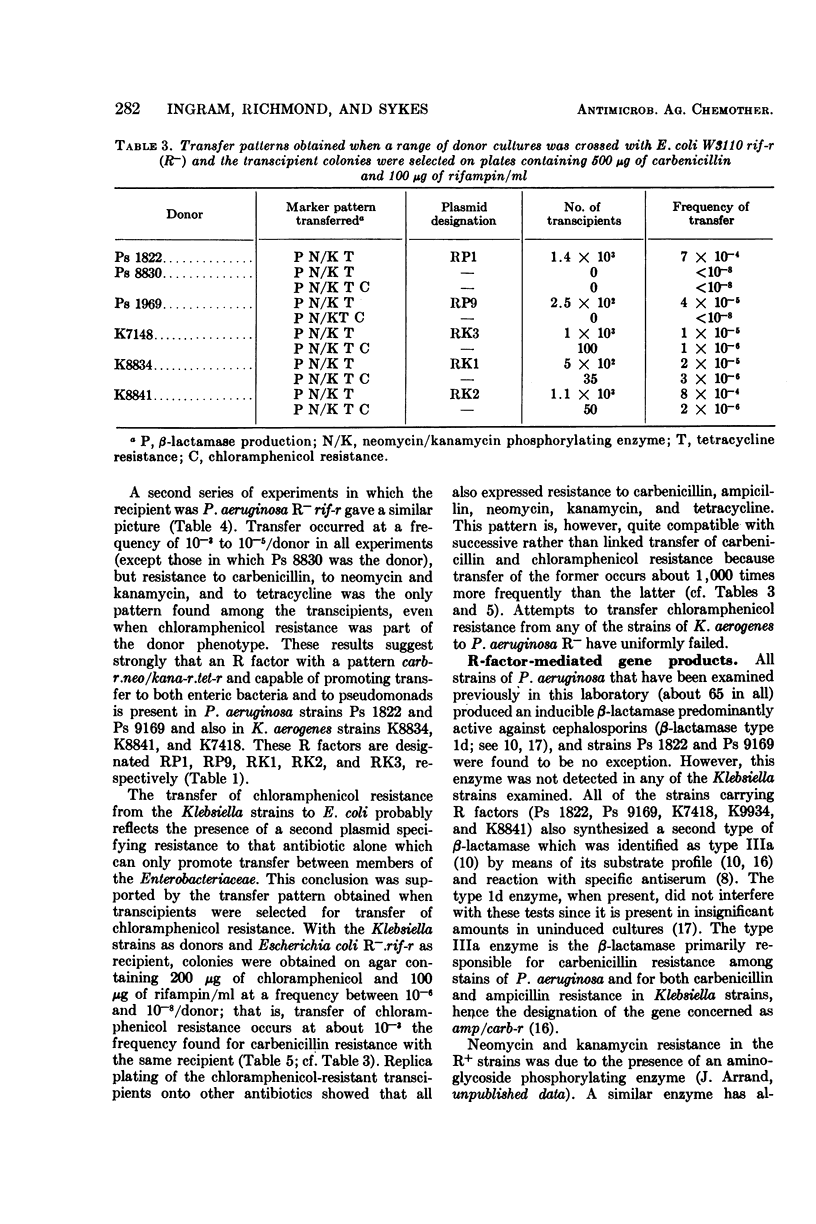
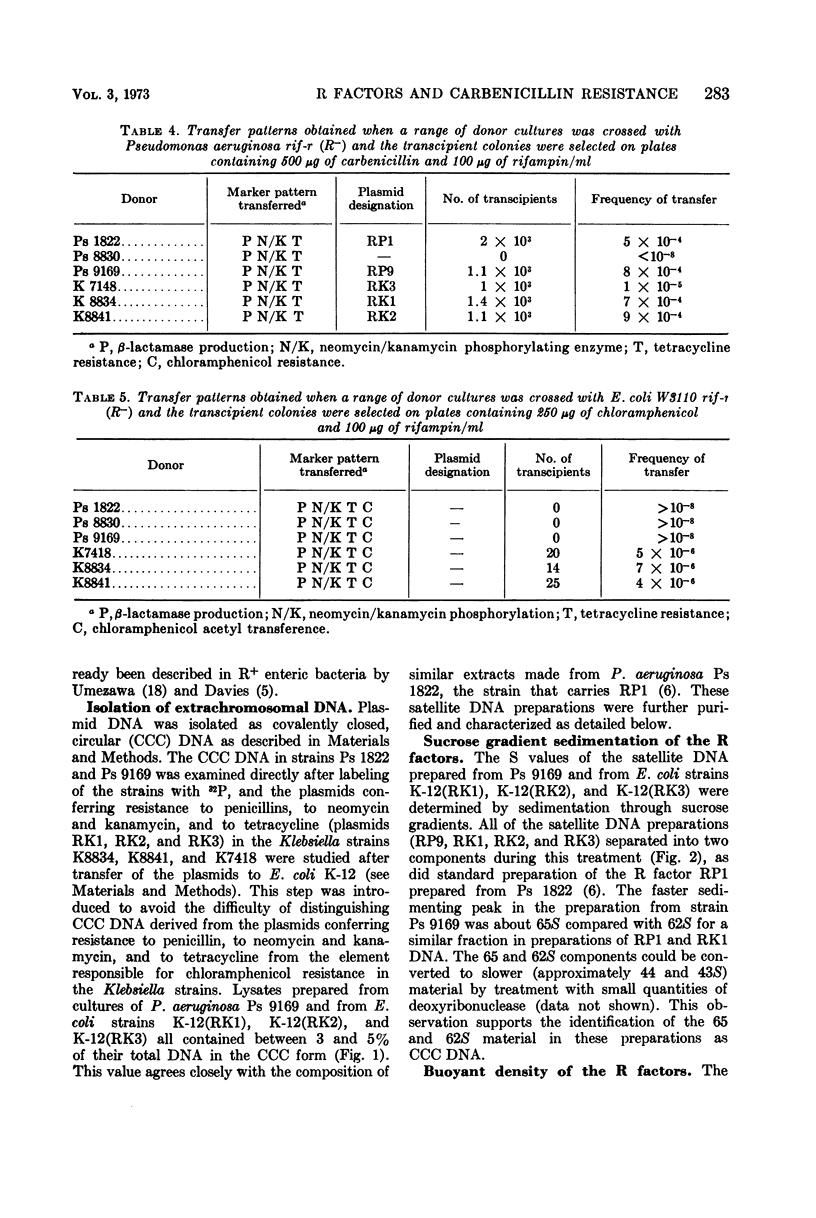
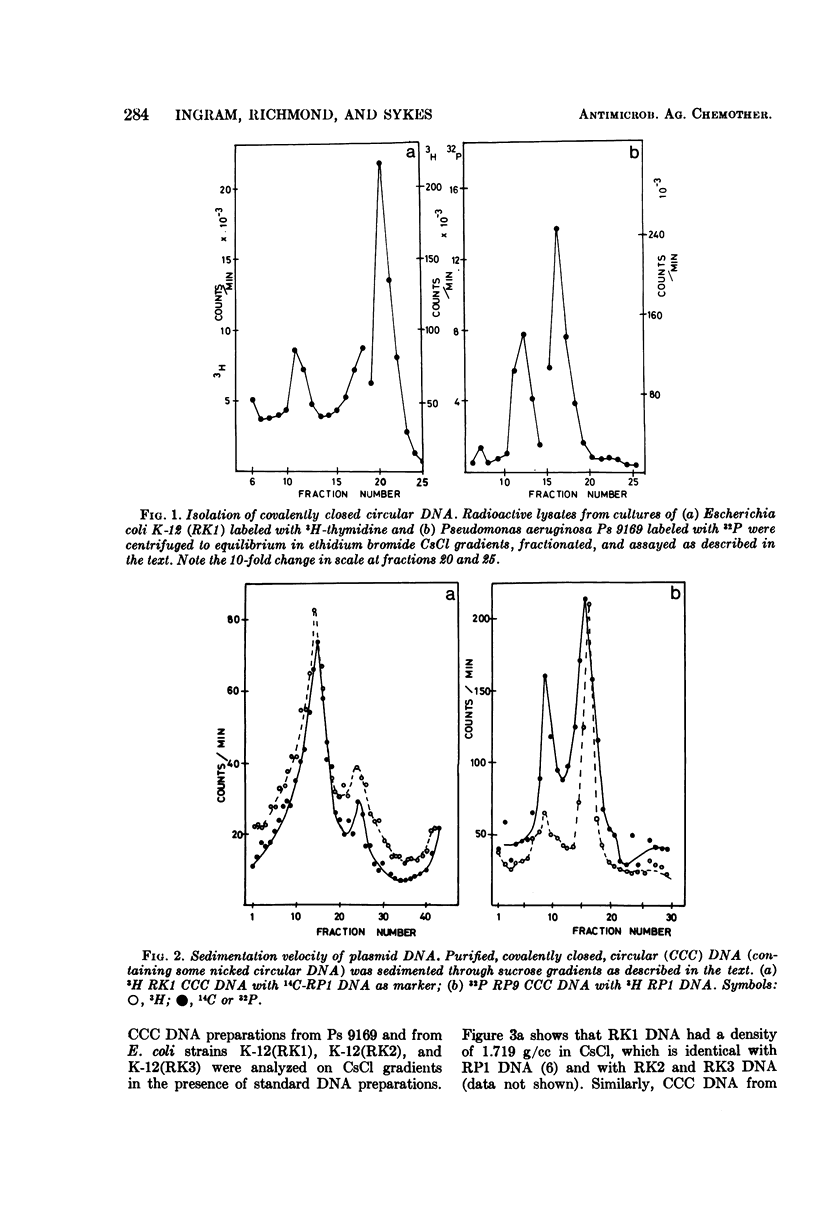
An outbreak of R-factor-mediated carbenicillin resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa in burned patients in March 1969 was followed by a second outbreak 6 months later. No R-factor-carrying P. aeruginosa strains were detected in the intervening period but R-factor-determined lactamase was commonly encountered, particularly in Klebsiella aerogenes strains. A comparison of the molecular properties of the R factors in pseudomonads from the first and second phases with those in the Klebsiella strains from the intervening period showed them to be very closely related. A single R-factor type therefore may have been maintained in the Burns Unit between the two Pseudomonas outbreaks as a plasmid conferring resistance to ampicillin in K. aerogenes.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ayliffe G. A., Lowbury E. J., Roe E. Transferable carbenicillin resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Nat New Biol. 1972 Feb 2;235(57):141–141. doi: 10.1038/newbio235141a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black W. A., Girdwood R. W. Carbenicillin resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Br Med J. 1969 Oct 25;4(5677):234–234. doi: 10.1136/bmj.4.5677.234-a. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Datta N., Hedges R. W., Shaw E. J., Sykes R. B., Richmond M. H. Properties of an R factor from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1971 Dec;108(3):1244–1249. doi: 10.1128/jb.108.3.1244-1249.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis B., Lilly H. A., Lowbury E. J. Gram-negative bacilli in burns. J Clin Pathol. 1969 Nov;22(6):634–641. doi: 10.1136/jcp.22.6.634. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grinsted J., Saunders J. R., Ingram L. C., Sykes R. B., Richmond M. H. Properties of a R factor which originated in Pseudomonas aeruginosa 1822. J Bacteriol. 1972 May;110(2):529–537. doi: 10.1128/jb.110.2.529-537.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingram L., Sykes R. B., Grinsted J., Saunders J. R., Richmond M. H. A transmissible resistance element from a strain of Pseudomonas aeruginosa containing no detectable extrachromosomal DNA. J Gen Microbiol. 1972 Sep;72(2):269–279. doi: 10.1099/00221287-72-2-269. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jack G. W., Richmond M. H. A comparative study of eight distinct beta-lactamases synthesized by gram-negative bacteria. J Gen Microbiol. 1970 Apr;61(1):43–61. doi: 10.1099/00221287-61-1-43. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowbury E. J., Lilly H. A., Kidson A., Ayliffe G. A., Jones R. J. Sensitivity of Pseudomonas aeruginosa to antibiotics: emergence of strains highly resistant to carbenicillin. Lancet. 1969 Aug 30;2(7618):448–452. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(69)90163-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richmond M. H., Sykes R. B. The beta-lactamases of gram-negative bacteria and their possible physiological role. Adv Microb Physiol. 1973;9:31–88. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2911(08)60376-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roe E., Jones R. J., Lowbury E. J. Transfer of anibioic resistanceetween Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Escherichia coli, and other gram-negative bacilli in rns. Lancet. 1971 Jan 23;1(7691):149–152. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)91930-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHILDKRAUT C. L., MARMUR J., DOTY P. Determination of the base composition of deoxyribonucleic acid from its buoyant density in CsCl. J Mol Biol. 1962 Jun;4:430–443. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(62)80100-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STUDIER F. W. SEDIMENTATION STUDIES OF THE SIZE AND SHAPE OF DNA. J Mol Biol. 1965 Feb;11:373–390. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80064-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saunders J. R., Grinsted J. Properties of RP4, an R factor which originated in Pseudomonas aeruginosa S8. J Bacteriol. 1972 Nov;112(2):690–696. doi: 10.1128/jb.112.2.690-696.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sykes R. B., Richmond M. H. Intergeneric transfer of a beta-lactamase gene between Ps. aeruginosa and E. coli. Nature. 1970 Jun 6;226(5249):952–954. doi: 10.1038/226952a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sykes R. B., Richmond M. H. R factors, beta-lactamase, and carbenicillin-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Lancet. 1971 Aug 14;2(7720):342–344. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)90060-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umezawa H., Doi O., Ogura M., Kondo S., Tanaka N. Phosphorylation and inactivation of kanamycin by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1968 Feb;21(2):154–155. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.21.154. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



