Abstract
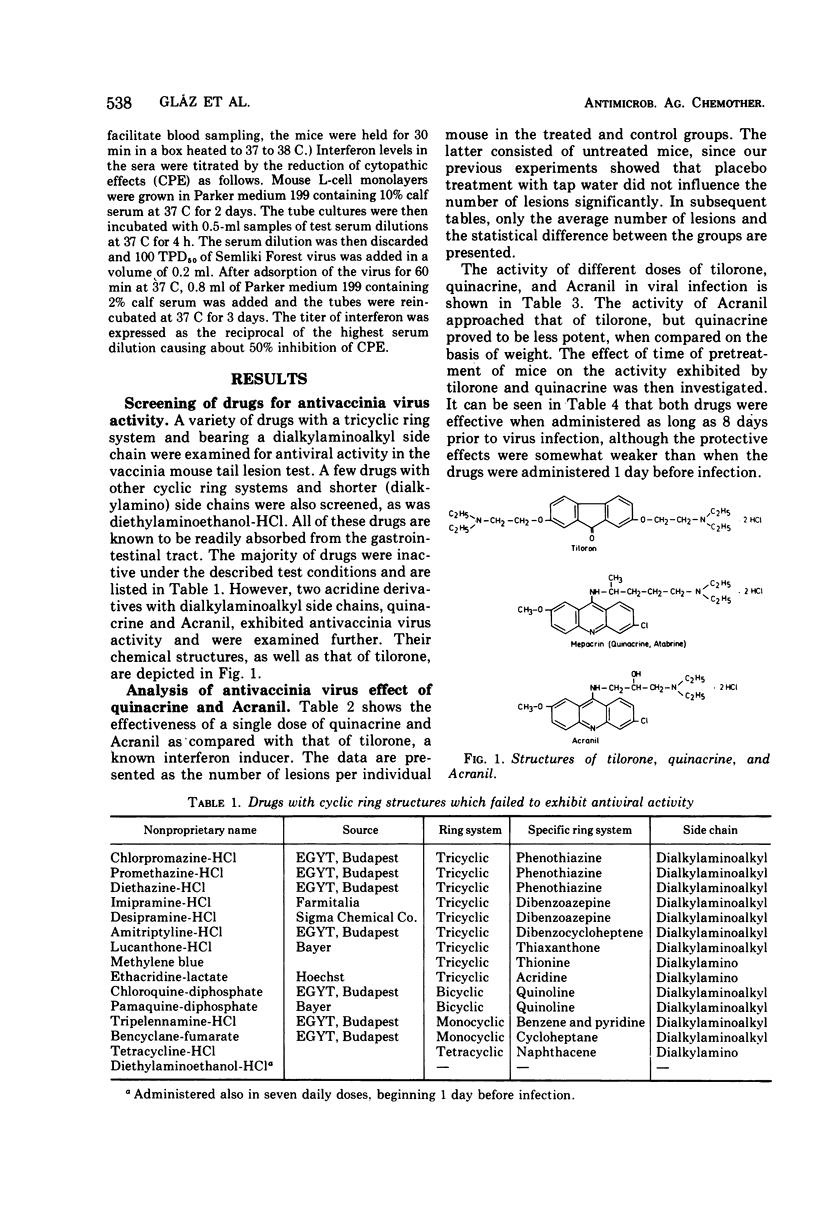
Several drugs with certain structural similarities (tricyclic ring system with dialkylaminoalkyl side chains) to tilorone, a potent interferon inducer, were screened for antiviral activity in vivo. Two acridine drugs, Acranil and quinacrine, were found to be effective, the former being almost as protective as tilorone and the latter less so. Both agents induced an interferon-like substance which could be detected in the serum of treated mice. The concentration of the inhibitory factor in the serum was highest after exposure to tilorone, followed in turn by Acranil and quinacrine, based on the administration of equal weights of drugs. Both tilorone and Acranil induced lower levels of circulating interferon-like substance in Balb/c mice than in other strains of mice. The serum factor induced by Acranil was shown to be stable at pH 2.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boyle J. J., Haff R. F., Stewart R. C. Evaluation of antiviral compounds by suppression of tail lesions in vaccinia-infected mice. Antimicrob Agents Chemother (Bethesda) 1966;6:536–539. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DULBECCO R., VOGT M. Studies on the induction of mutations in poliovirus by proflavin. Virology. 1958 Apr;5(2):236–243. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(58)90021-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Clercq E., De Somer P. Prolonged antiviral protection by interferon inducers. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1969 Nov;132(2):699–703. doi: 10.3181/00379727-132-34291. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Maeyer E., De Maeyer-Guignard J. Influence of animal genotype and age on the amount of circulating interferoh induced by Newcastle disease virus. J Gen Virol. 1968 May;2(3):445–449. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-2-3-445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freshman M. M., Merigan T. C., Remington J. S., Brownlee I. E. In vitro and in vivo antiviral action of an interferon-like substance induced by Toxoplasma gondii. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1966 Dec;123(3):862–866. doi: 10.3181/00379727-123-31625. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HURST E. W., MELVIN P., PETERS J. M. The prevention of encephalitis due to the viruses of eastern equine encephalomyelitis and louping-ill: experiments with trypan red, mepacrine, and many other substances. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1952 Sep;7(3):455–472. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1952.tb00713.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HURST E. W., PETERS J. M., MELVIN P. The action of mepacrine and trypan red in a number of virus diseases. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1952 Sep;7(3):473–481. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1952.tb00714.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang K. Y., Schultz W. W., Gordon F. B. Interferon induced by Plasmodium berghei. Science. 1968 Oct 4;162(3849):123–124. doi: 10.1126/science.162.3849.123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jahiel R. I., Vilcek J., Nussenzweig R. S. Exogenous interferon protects mice against Plasmodium berghei malaria. Nature. 1970 Sep 26;227(5265):1350–1351. doi: 10.1038/2271350a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jahiel R. I., Vilcek J., Nussenzweig R., Vanderberg J. Interferon inducers protect mice against plasmodium berghei malaria. Science. 1968 Aug 23;161(3843):802–804. doi: 10.1126/science.161.3843.802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer G. D., Krueger R. F. Tilorone hydrochloride: mode of action. Science. 1970 Sep 18;169(3951):1214–1215. doi: 10.1126/science.169.3951.1214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munson A. E., Munson J. A., Regelson W., Wampler G. L. Effect of Tilorone hydrochloride and congeners on reticuloendothelial system, tumors, and the immune response. Cancer Res. 1972 Jul;32(7):1397–1403. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Remington J. S., Merigan T. C. Interferon: protection of cells infected with an intracellular protozoan (Toxoplasma gondii). Science. 1968 Aug 23;161(3843):804–806. doi: 10.1126/science.161.3843.804. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rytel M. W., Marsden P. D. Induction of an interferon-like inhibitor by Trypanosoma cruzi infection in mice. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1970 Nov;19(6):929–931. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1970.19.929. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultz W. W., Huang K. Y., Gordon F. B. Role of interferon in experimental mouse malaria. Nature. 1968 Nov 16;220(5168):709–710. doi: 10.1038/220709a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


