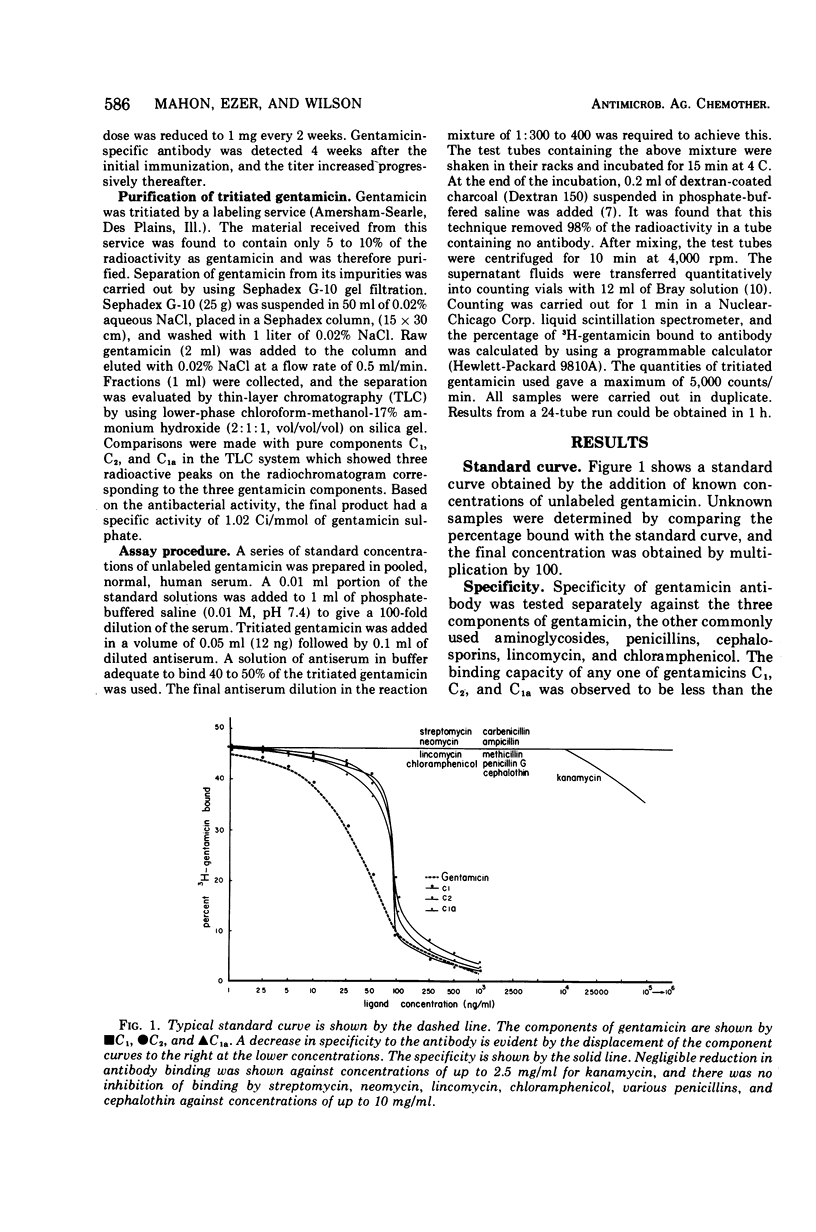
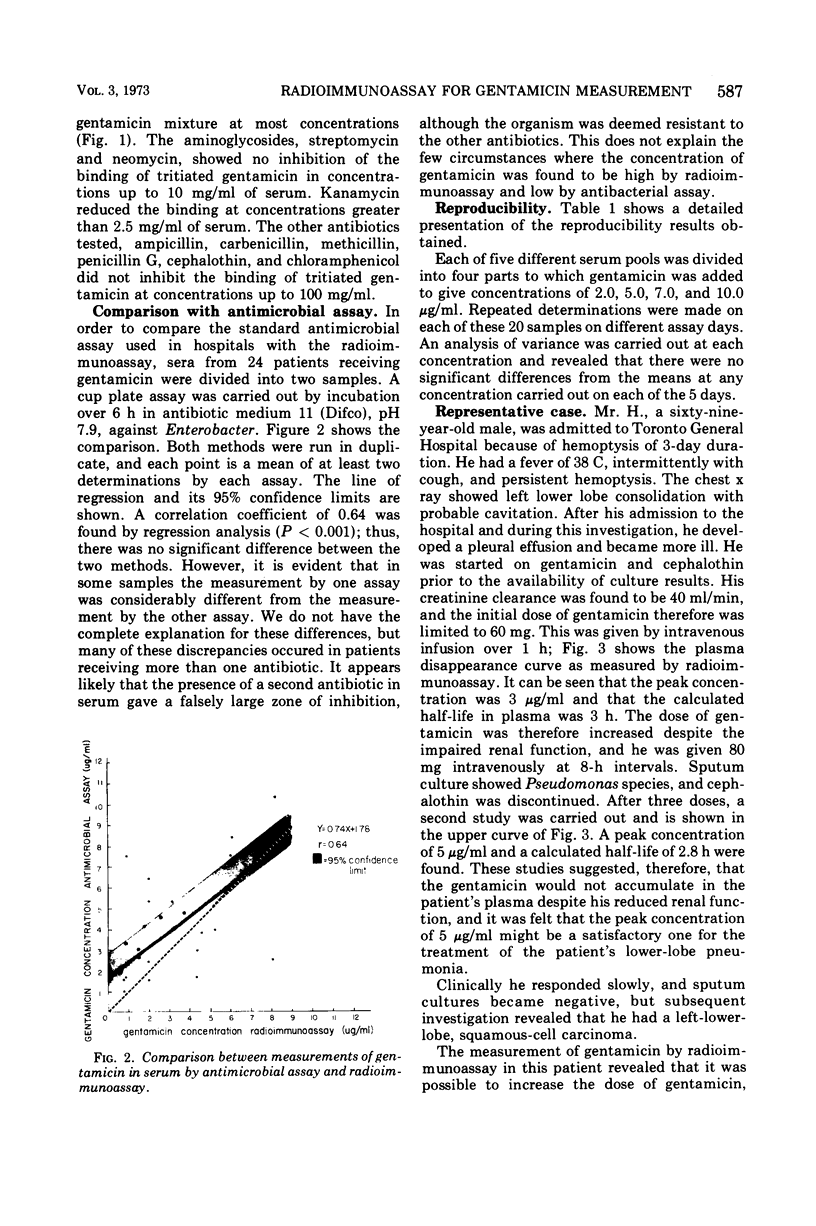
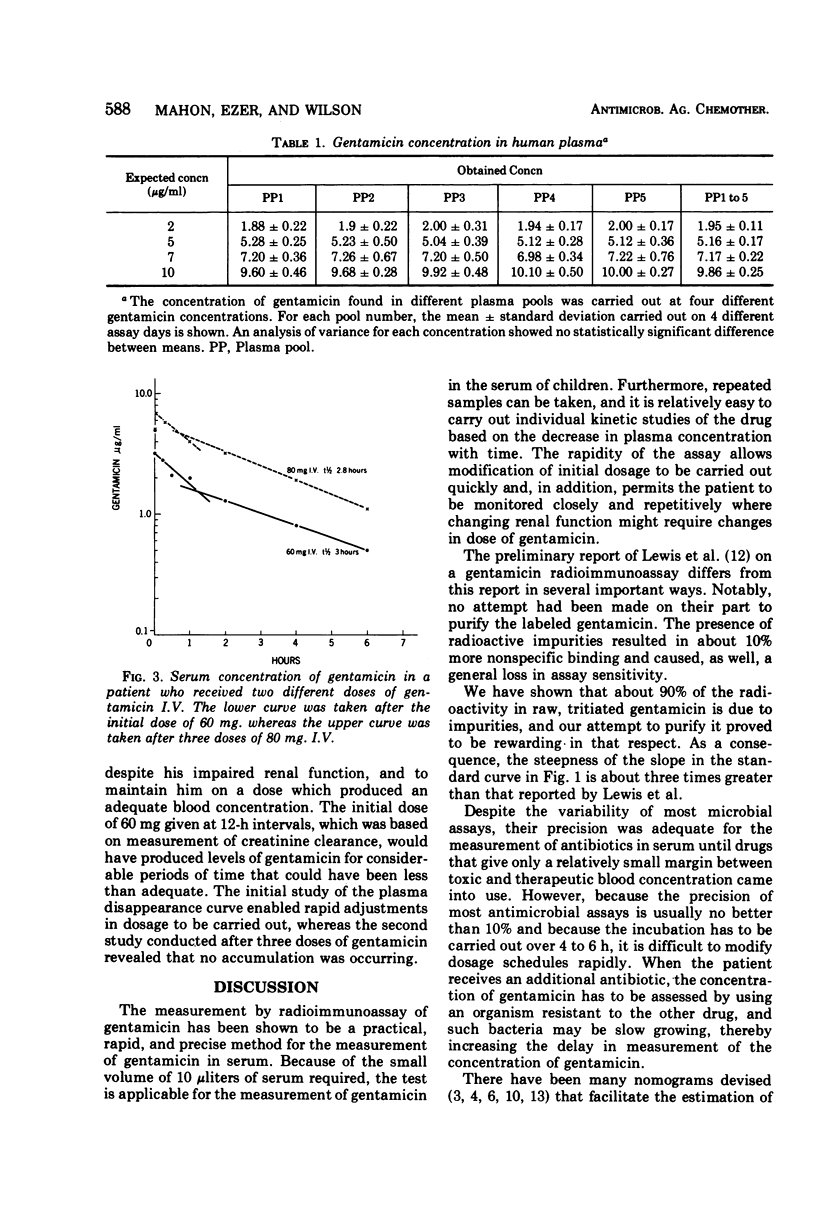
Abstract
Gentamicin toxicity has been shown to be related to high concentrations in serum. Because there is a narrow range between its therapeutic and toxic levels, serial monitoring of gentamicin is the most reliable method of guiding therapy. Microbiological assays commonly in use do not afford the desired speed and accuracy, and results may be difficult to interpret in the presence of other antimicrobials. Hence, a rapid, sensitive, and highly specific radioimmunoassay for measurement of gentamicin in serum has been developed. Antibody to gentamicin was raised in rabbits by using a gentamicin-albumin conjugate. Tritiated gentamicin (specific activity 1.0 Ci/mM) competes with unlabeled gentamicin for binding sites on the antibody. Dextran-coated charcoal separates the unbound from antibody-bound gentamicin. Serum levels of gentamicin are determined by comparison with a standard curve. This method can detect concentrations as low as 0.01 μg/ml. Results of a 24-tube run can be obtained in 1 h, thus allowing modification of gentamicin dosage to advantage.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BLACK J., CALESNICK B., WILLIAMS D., WEINSTEIN M. J. PHARMACOLOGY OF GENTAMICIN, A NEW BROAD-SPECTRUM ANTIBIOTIC. Antimicrob Agents Chemother (Bethesda) 1963;161:138–147. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan R. A., Benner E. J., Hoeprich P. D. Gentamicin therapy in renal failure: a nomogram for dosage. Ann Intern Med. 1972 May;76(5):773–778. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-76-5-773. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cutler R. E., Gyselynck A. M., Fleet W. P., Forrey A. W. Correlation of serum creatinine concentration and gentamicin half-life. JAMA. 1972 Feb 21;219(8):1037–1041. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gingell J. C., Waterworth P. M. Dose of gentamicin in patients with normal renal function and renal impairment. Br Med J. 1968 Apr 6;2(5596):19–22. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5596.19. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herbert V., Lau K. S., Gottlieb C. W., Bleicher S. J. Coated charcoal immunoassay of insulin. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1965 Oct;25(10):1375–1384. doi: 10.1210/jcem-25-10-1375. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JAO R. L., JACKSON G. G. GENTAMICIN SULFATE, NEW ANTIBIOTIC AGAINST GRAM-NEGATIVE BACILLI. LABORATORY, PHARMACOLOGICAL, AND CLINICAL EVALUATION. JAMA. 1964 Sep 14;189:817–822. doi: 10.1001/jama.1964.03070110019004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson G. G., Arcieri G. Ototoxicity of gentamicin in man: a survey and controlled analysis of clinical experience in the United States. J Infect Dis. 1971 Dec;124 (Suppl):S130–S137. doi: 10.1093/infdis/124.supplement_1.s130. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis J. E., Nelson J. C., Elder H. A. Radioimmunoassay of an antibiotic: gentamicin. Nat New Biol. 1972 Oct 18;239(94):214–216. doi: 10.1038/newbio239214a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McHenry M. C., Gavan T. L., Gifford R. W., Jr, Geurkink N. A., Van Ommen R. A., Town M. A., Wagner J. G. Gentamicin dosages for renal insufficiency. Adjustments based on endogenous creatinine clearance and serum creatinine concentration. Ann Intern Med. 1971 Feb;74(2):192–197. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-74-2-192. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riff L. J., Jackson G. G. Pharmacology of gentamicin in man. J Infect Dis. 1971 Dec;124 (Suppl):S98–105. doi: 10.1093/infdis/124.supplement_1.s98. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. H., Van Otto B., Smith A. L. A rapid chemical assay for gentamicin. N Engl J Med. 1972 Mar 16;286(11):583–586. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197203162861106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winters R. E., Litwack K. D., Hewitt W. L. Relation between dose and levels of gentamicin in blood. J Infect Dis. 1971 Dec;124 (Suppl):S90–S95. doi: 10.1093/infdis/124.supplement_1.s90. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]