Abstract
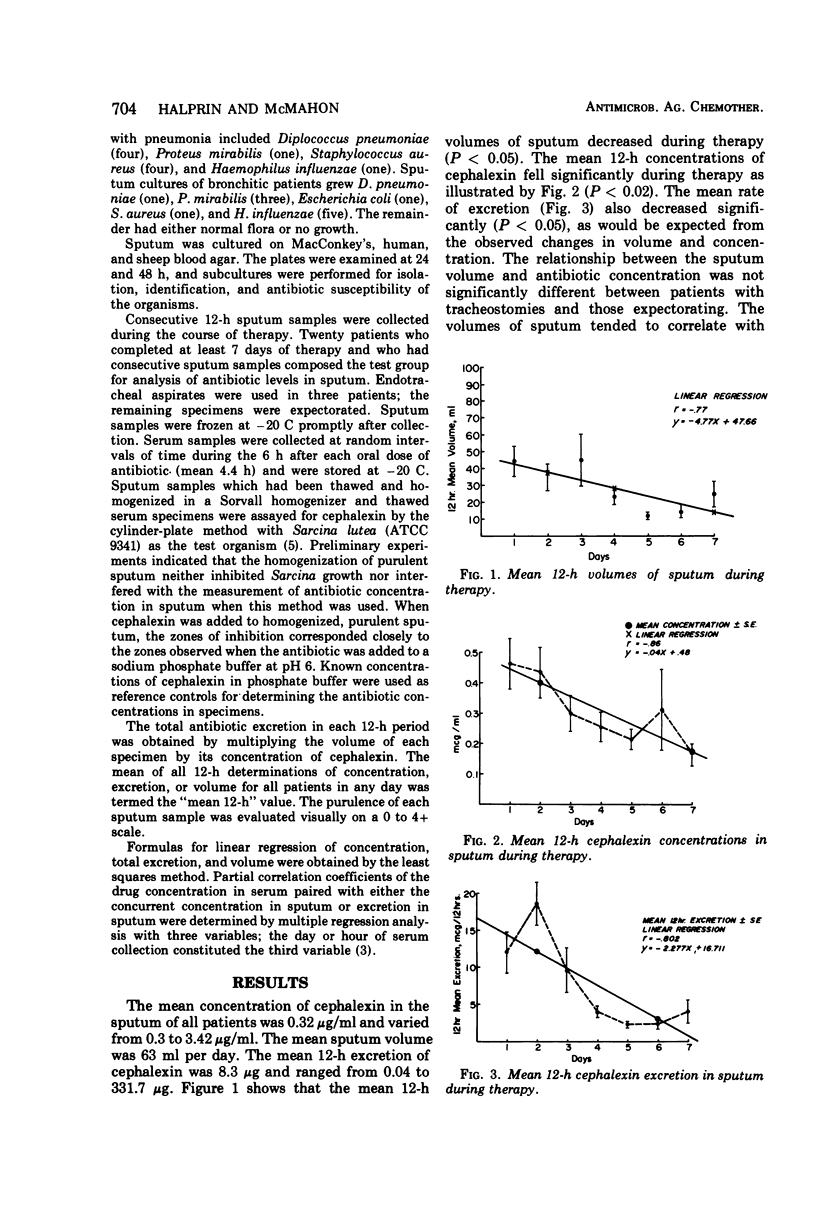
In 20 patients with acute pulmonary infections, sputum purulence, sputum volume, and concentration and excretion of cephalexin in the sputum significantly decreased concurrently during therapy. The concentration of cephalexin in the serum remained unchanged. Significant correlations were observed between drug concentrations in sputum and serum and between drug excretion in sputum and concentration in serum. These observations may be explained by decreased integrity of the “blood-bronchus barrier” during inflammation, with diffusion of serum into bronchial mucus, without the necessity of postulating active transport.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Applestein J. M., Crosby E. B., Johnson W. D., Kaye D. In vitro antimicrobial activity and human pharmacology of cephaloglycin. Appl Microbiol. 1968 Jul;16(7):1006–1010. doi: 10.1128/am.16.7.1006-1010.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crofton J. Some principles in the chemotherapy of bacterial infections. II. Br Med J. 1969 Apr 26;2(5651):209–212. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5651.209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAFEZ F. F., STEWART S. M., BURNET M. E. PENICILLIN LEVELS IN SPUTUM. Thorax. 1965 May;20:219–225. doi: 10.1136/thx.20.3.219. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunin C. M. A guide to use of antibiotics in patients with renal disease. A table of recommended doses and factors governing serum levels. Ann Intern Med. 1967 Jul;67(1):151–158. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-67-1-151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunin C. M. Clinical significance of protein binding of the penicillins. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1967 Sep 27;145(2):282–290. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1967.tb50225.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAY J. R. AMPICILLIN IN THE THERAPY OF CHRONIC BRONCHITIS. Postgrad Med J. 1964 Dec;40:SUPPL–SUPPL:197. doi: 10.1136/pgmj.40.suppl.193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAY J. R., DELVES D. M. TREATMENT OF CHRONIC BRONCHITIS WITH AMPICILLIN: SOME PHARMACOLOGICAL OBSERVATION. Lancet. 1965 May 1;1(7392):929–933. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(65)91253-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perkins R. L., Carlisle H. N., Saslaw S. Cephalexin: in vitro bacterial susceptibility, absorption in volunteers, and antibacterial activity of sera and urine. Am J Med Sci. 1968 Aug;256(2):122–129. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saggers B. A., Lawson D. In vivo penetration of antibiotics into sputum in cystic fibrosis. Arch Dis Child. 1968 Aug;43(230):404–409. doi: 10.1136/adc.43.230.404. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saggers B. A., Lawson D. Some observations on the penetration of antibiotics through mucus in vitro. J Clin Pathol. 1966 Jul;19(4):313–317. doi: 10.1136/jcp.19.4.313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart S. M., Fisher M., Young J. E., Lutz W. Ampicillin levels in sputum, serum, and saliva. Thorax. 1970 May;25(3):304–311. doi: 10.1136/thx.25.3.304. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thornhill T. S., Levison M. E., Johnson W. D., Kaye D. In vitro antimicrobial activity and human pharmacology of cephalexin, a new orally absorbed cephalosporin C antibiotic. Appl Microbiol. 1969 Mar;17(3):457–461. doi: 10.1128/am.17.3.457-461.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



