Abstract
The activity of nalidixic acid combined with each of 10 other antimicrobial agents on 95 strains of Enterobacteriaceae was studied. Synergism was found less often than antagonism, and the commonest outcome was indifference. Combinations of nalidixic acid with kanamycin, gentamicin, or colistin were more often synergistic than antagonistic, whereas with the other antibiotics the combination was more often antagonistic than synergistic. Synergistic effects were more common with Shigella than with other genera. In vitro examination for synergism or antagonism appears to be advisable before nalidixic acid is used therapeutically in combination with other antimicrobial agents.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Atlas E., Clark H., Silverblatt F., Turck M. Nalidixic acid and oxolinic acid in the treatment of chronic bacteriuria. Ann Intern Med. 1969 Apr;70(4):713–721. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-70-4-713. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Auriti R., Ravagnan L. Attività antibatterica in vitro dell'associazione acido nalidixico-neomicina. Antibiotica. 1968 Jun;6(2):72–80. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baudens J. G., Chabbert Y. A. Rifampicine: bactéricidie et bactériopause. Pathol Biol (Paris) 1969 Apr;17(7):392–397. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauernfeind A. Mode of action of nalidixic acid. Antibiot Chemother (1971) 1971;17:122–136. doi: 10.1159/000392368. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brisou J., Denis F. Comportement des "Serratia" d'origine hospitalière en présence de quelques associations d'antibiotiques. Pathol Biol (Paris) 1971 Jun-Jul;19(11):655–660. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brumfitt W., Pursell R. Observations on bacterial sensitivities to nalidixic acid and critical comments on the 6-centre survey. Postgrad Med J. 1971 Sep;47(Suppl):16–18. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
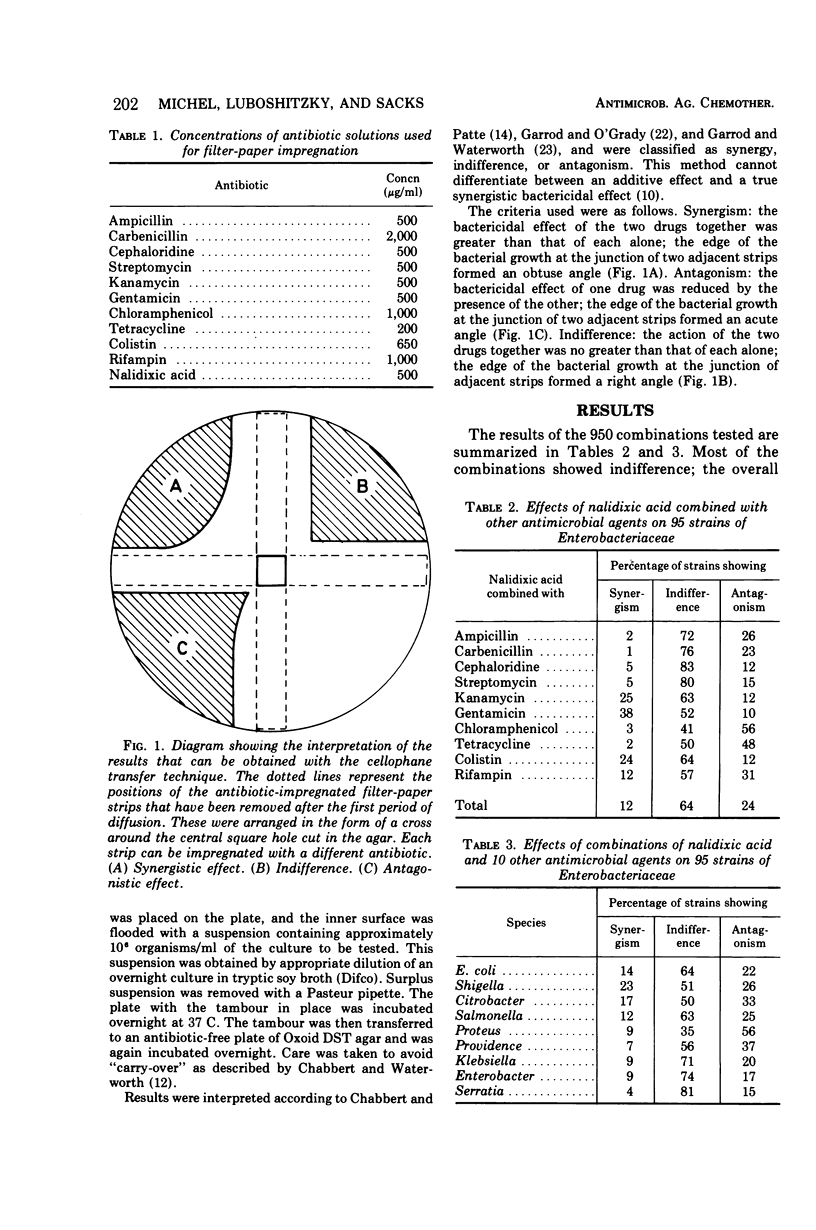
- CHABBERT Y. A., PATTE J. C. Cellophane transfer: application to the study of activity of combinations of antibiotics. Appl Microbiol. 1960 Jul;8:193–199. doi: 10.1128/am.8.4.193-199.1960. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHABBERT Y. A., WATERWORTH P. M. STUDIES ON THE "CARRY-OVER" OF ANTIBIOTICS USING THE CELLOPHANE TRANSFER TECHNIQUE. J Clin Pathol. 1965 May;18:314–316. doi: 10.1136/jcp.18.3.314. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHABBERT Y. Une technique nouvelle d'étude de l'action bactéricide des associations d'antibiotiques: le transfert sur cellophane. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1957 Sep;93(3):289–299. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CLUZEL R., VAURS R., CLUZEL-NIGAY M., VERNER M. [A new technic for the study of the bactericidal power of antibiotic combinations derived from "transfer on cellophane": the cross arrangement]. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1960 Jun;98:928–932. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chamfeuil R., Curcier H. Etude de l'activité de l'acide nalidixique sur 3186 souches de bacilles à Gram négatif. Application au traitement des infections urinaires. Presse Med. 1969 Nov 15;77(48):1763–1764. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cluzel R., Michel J., Cluzel M., Sirot J. Effets généraux des associations d'antibiotiques sur diverses entérobactéries (escherichia, salmonella, klebsiell) Pathol Biol (Paris) 1971 Jun-Jul;19(11):627–636. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cluzel R., Michel J., Cluzel M., Sirot J. Les modalités de la diffusion en gélose des antibiotiques dans la disposition en croix dérivée du transfert sur cellophane. C R Seances Soc Biol Fil. 1970;164(4):807–812. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dominici A., Perini C. [Interaction between nalidixic acid and some antibacterial substances]. Antibiotica. 1967 Sep;5(3):212–223. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finegold S. M., Miller L. G., Posnick D., Patterson D. K., Davis A. Nalidixic acid: clinical and laboratory studies. Antimicrob Agents Chemother (Bethesda) 1966;6:189–197. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finland M. Changing ecology of bacterial infections as related to antibacterial therapy. J Infect Dis. 1970 Nov;122(5):419–431. doi: 10.1093/infdis/122.5.419. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GARROD L. P., WATERWORTH P. M. Methods of testing combined antibiotic bactericidal action and the significance of the results. J Clin Pathol. 1962 Jul;15:328–338. doi: 10.1136/jcp.15.4.328. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LESHER G. Y., FROELICH E. J., GRUETT M. D., BAILEY J. H., BRUNDAGE R. P. 1,8-NAPHTHYRIDINE DERIVATIVES. A NEW CLASS OF CHEMOTHERAPEUTIC AGENTS. J Med Pharm Chem. 1962 Sep;91:1063–1065. doi: 10.1021/jm01240a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MANTEN A., WISSE M. J. Antagonism between antibacterial drugs. Nature. 1961 Nov 18;192:671–672. doi: 10.1038/192671a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McAllister T. A., Alexander J. G., Dulake C., Percival A., Boyce J. M., Wormald P. J. Multicentric study of sensitivities of urinary tract pathogens. Postgrad Med J. 1971 Sep;47(Suppl):7–14. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mouton R. P., Koelman A. The interaction patterns of combined antibacterial agents. Experiments with two agardiffusion methods. Chemotherapy. 1966;11(1):10–26. doi: 10.1159/000220434. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piguet J. D. Láction inhibitrice de la nitrofurantoïne sur le pouvoir bactériostatique in vitro de lácide nalidixique. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1969 Jan;116(1):43–48. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ronald A. R., Turck M., Petersdorf R. G. A critical evaluation of nalidixic acid in urinary-tract infections. N Engl J Med. 1966 Nov 17;275(20):1081–1089. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196611172752001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneierson S. S. Antibiotic susceptibility of pathogenic microorganisms isolated in 1969. N Y State J Med. 1970 Jul 15;70(14):1871–1874. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas M. E., Datta N. Emergence of Shigella sonnei resistant to kanamycin and to nalidixic acid, without exposure to these drugs. J Med Microbiol. 1969 Nov 4;2(4):457–461. doi: 10.1099/00222615-2-4-457. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



