Abstract
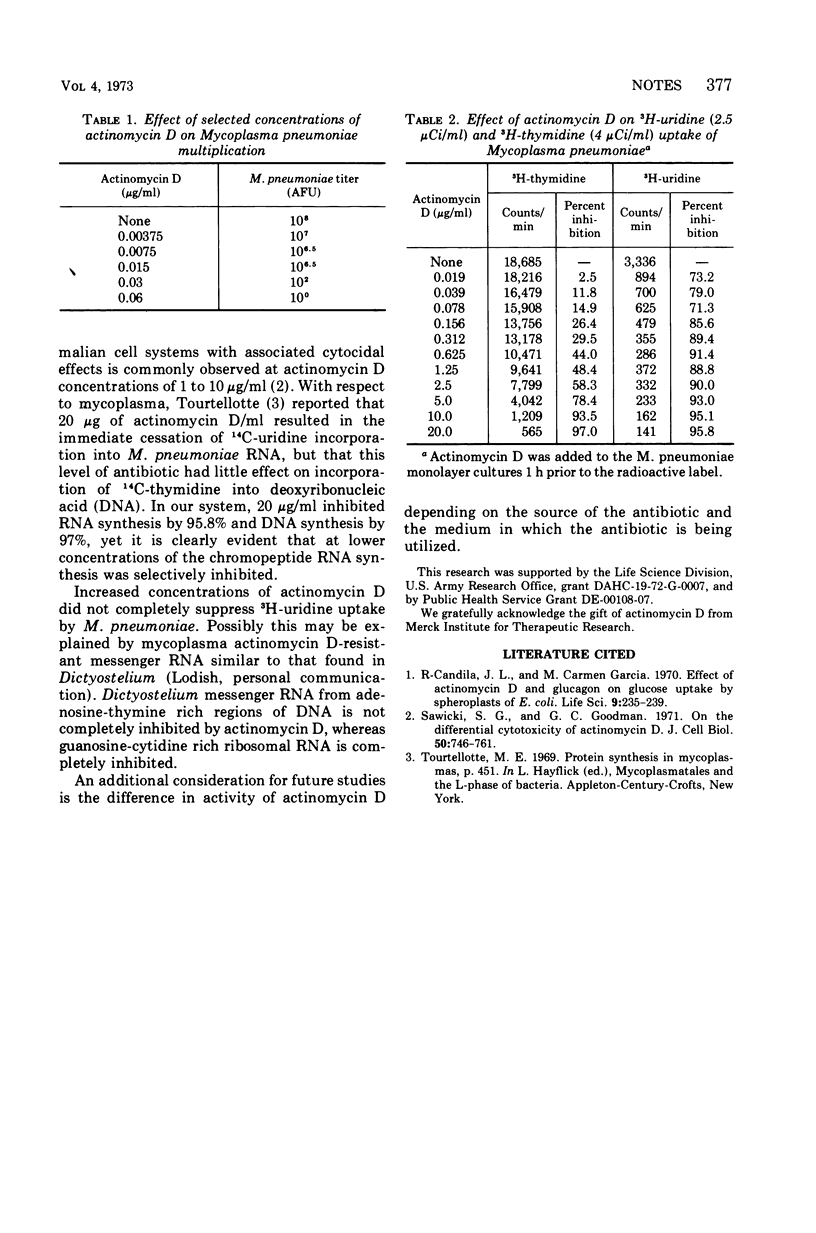
Growth of Mycoplasma pneumoniae was completely prevented by 0.06 μg of actinomycin D/ml, and 0.00375 μg/ml caused 90% inhibition. It thus appears that M. pneumoniae is more susceptible to actinomycin D than previously reported. Low concentrations (0.019 μg/ml) of the antibiotic primarily inhibited ribonucleic acid synthesis and high concentrations (20 μg/ml) inhibited both ribonucleic and deoxyribonucleic acid synthesis.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Candela J. L., García M. C. Effect of actinomycin D and glucagon on glucose uptake by spheroplasts of E. coli. Life Sci. 1970 Feb 22;9(4):235–239. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(70)90230-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawicki S. G., Godman G. C. On the differential cytotoxicity of actinomycin D. J Cell Biol. 1971 Sep;50(3):746–761. doi: 10.1083/jcb.50.3.746. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



