Abstract
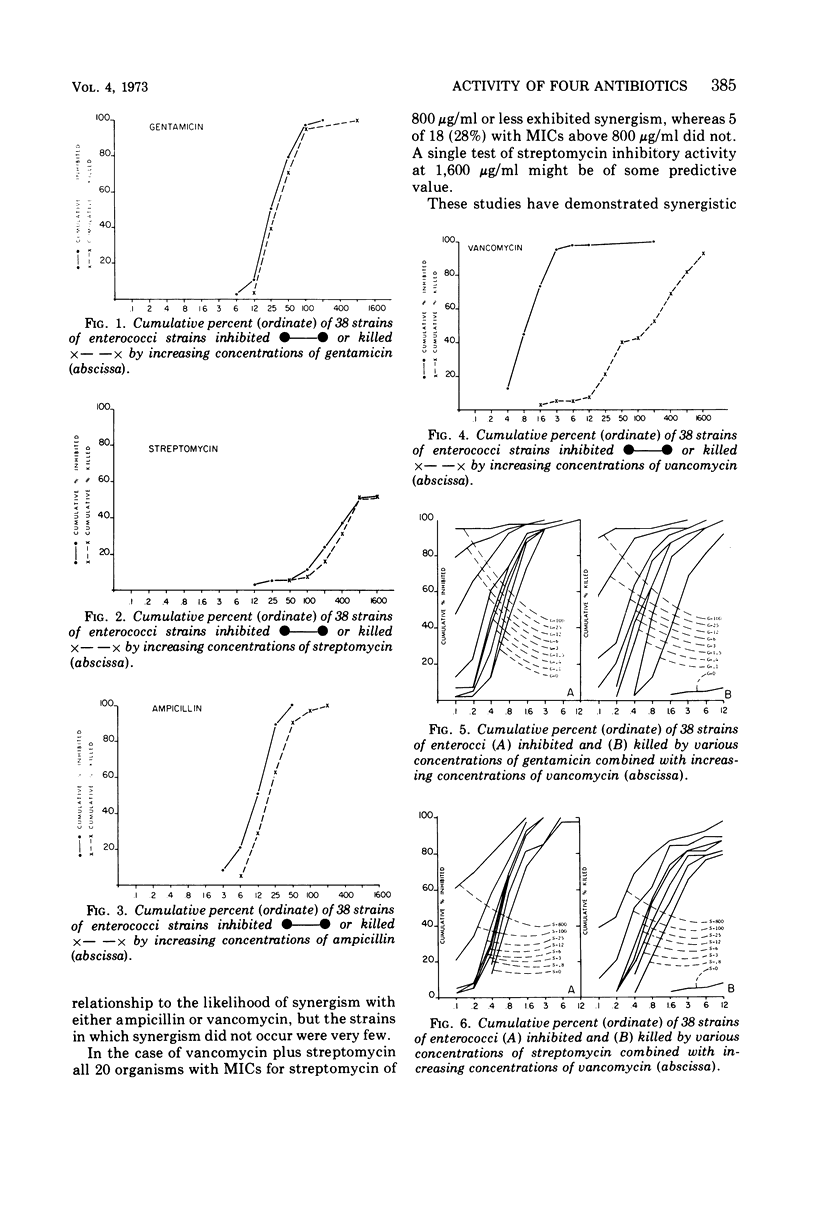
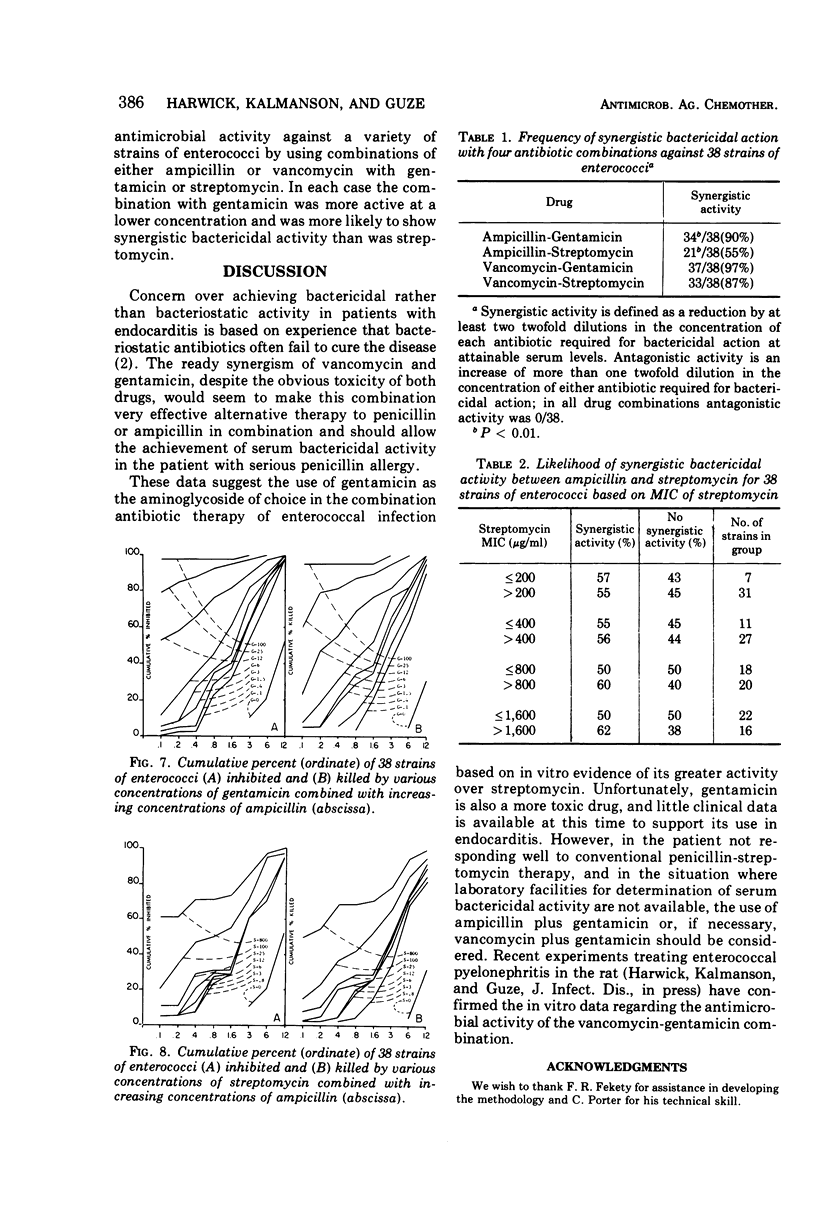
Minimum inhibitory and bactericidal concentrations of four antibiotics and their combinations were determined for 38 strains of enterococci by a microtitration tube dilution technique. The drugs were ampicillin, vancomycin, gentamicin, and streptomycin; the combinations were ampicillin-gentamicin, ampicillin-streptomycin, vancomycin-gentamicin, and vancomycin-streptomycin. At achievable serum concentrations, ampicillin alone killed 60% of strains, whereas combination with streptomycin increased this to 90% and with gentamicin to 100%. Vancomycin alone showed striking inhibitory activity, but very poor bactericidal activity at achievable concentrations. Combination with one of the aminoglycosides increased the bactericidal activity substantially. When combined with ampicillin, gentamicin was both more active and showed synergistic bactericidal activity significantly more often (P < 0.01) than streptomycin.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beaty H. N., Turck M., Petersdorf R. G. Ampicillin in the treatment of enterococcal endocarditis. Ann Intern Med. 1966 Oct;65(4):701–707. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-65-4-701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fekety F. R., Jr, Weiss P. Antibiotic synergism: enhanced susceptibility of enterococci to combinations of streptomycin and penicillins or cephalosporins. Antimicrob Agents Chemother (Bethesda) 1966;6:156–164. doi: 10.1128/AAC.6.2.156. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedberg C. K., Rosen K. M., Bienstock P. A. Vancomycin therapy for enterococcal and Streptococcus viridans endocarditis. Successful treatment of six patients. Arch Intern Med. 1968 Aug;122(2):134–140. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GUNNISON J. B., JAWETZ E., COLEMAN V. R. The effect of combinations of antibiotics on enterococci in vitro. J Lab Clin Med. 1950 Dec;36(6):900–911. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harwick H. J., Weiss P., Fekety F. R., Jr Application of microtitration techniques to bacteriostatic and bactericidal antibiotic susceptibility testing. J Lab Clin Med. 1968 Sep;72(3):511–516. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hewitt W. L., Seligman S. J., Deigh R. A. Kinetics of the synergism of penicillin-streptomycin and penicillin-kanamycin for enterococci and its relationship to L-phase variants. J Lab Clin Med. 1966 May;67(5):792–807. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KERR A., Jr BACTERIAL ENDOCARDITIS--REVISTED. Mod Concepts Cardiovasc Dis. 1964 Jan;33:831–836. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandell G. L., Kaye D., Levison M. E., Hook E. W. Enterococcal endocarditis. An analysis of 38 patients observed at the New York Hospital-Cornell Medical Center. Arch Intern Med. 1970 Feb;125(2):258–264. doi: 10.1001/archinte.125.2.258. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandell G. L., Lindsey E., Hook E. W. Synergism of vancomycin and streptomycin for enterococci. Am J Med Sci. 1970 May;259(5):346–349. doi: 10.1097/00000441-197005000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sapico F. L., Kalmanson G. M., Montgomerie J. Z., Hewitt W. L., Guze L. B. Pyelonephritis. XII. Comparison of penicillin, ampicillin, and streptomycin in enterococcal infection in rats. J Infect Dis. 1971 Jun;123(6):611–617. doi: 10.1093/infdis/123.6.611. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Standiford H. D., De Maine J. B., Kirby W. M. Antibiotic synergism of enterococci. Relation to inhibitory concentrations. Arch Intern Med. 1970 Aug;126(2):255–259. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westenfelder G. O., Paterson P. Y., Reisberg B. E., Carlson G. M. Vancomycin-streptomycin synergism in enterococcal endocarditis. JAMA. 1973 Jan 1;223(1):37–40. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


