Abstract
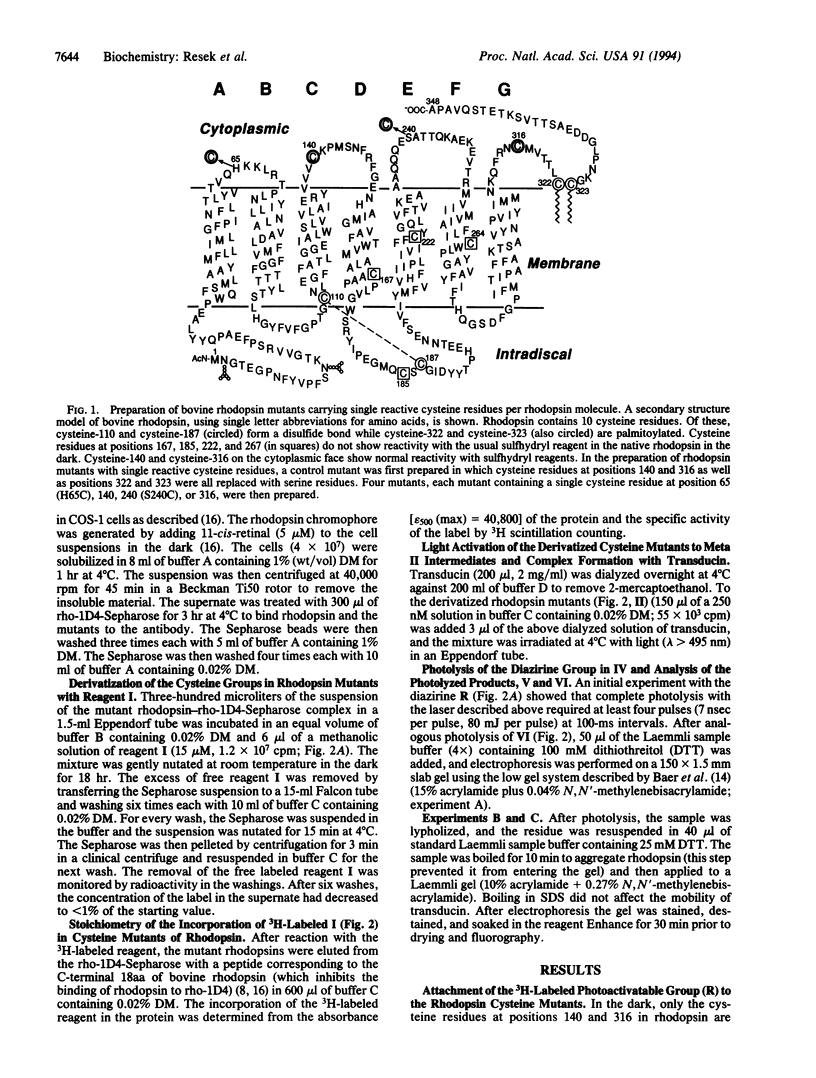
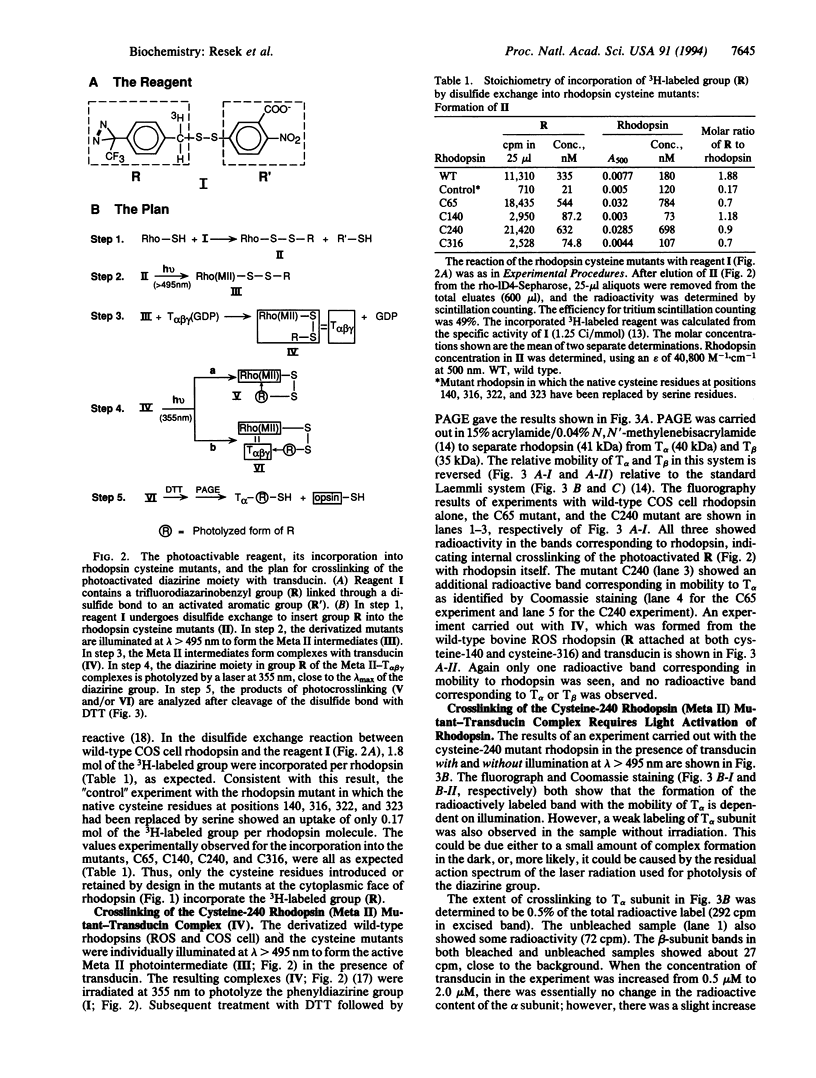
We prepared rhodopsin mutants that contained a single reactive cysteine residue per rhodopsin molecule at position 65, 140, 240, or 316 on the cytoplasmic face. A carbene-generating photoactivatable group was linked by a disulfide bond to the cysteine sulfhydryl group of each of the rhodopsin mutants. The resulting derivative was then light-activated at lambda > 495 nm to form the metarhodopsin II intermediate, which bound transducin. Subsequent photoactivation (355 nm) of the carbene-generating group resulted in crosslinking of the rhodopsin mutant carrying a cysteine residue at position 240 to transducin. This crosslinking was determined to be specifically with the alpha subunit of transducin. An alternative reaction observed during photolysis of the rhodopsin mutants was intramolecular insertion of the carbene into rhodopsin.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bennett N., Michel-Villaz M., Kühn H. Light-induced interaction between rhodopsin and the GTP-binding protein. Metarhodopsin II is the major photoproduct involved. Eur J Biochem. 1982 Sep;127(1):97–103. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb06842.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunner J., Senn H., Richards F. M. 3-Trifluoromethyl-3-phenyldiazirine. A new carbene generating group for photolabeling reagents. J Biol Chem. 1980 Apr 25;255(8):3313–3318. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chabre M., Bigay J., Bruckert F., Bornancin F., Deterre P., Pfister C., Vuong T. M. Visual signal transduction: the cycle of transducin shuttling between rhodopsin and cGMP phosphodiesterase. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1988;53(Pt 1):313–324. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1988.053.01.038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chowdhry V., Westheimer F. H. Photoaffinity labeling of biological systems. Annu Rev Biochem. 1979;48:293–325. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.48.070179.001453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dratz E. A., Furstenau J. E., Lambert C. G., Thireault D. L., Rarick H., Schepers T., Pakhlevaniants S., Hamm H. E. NMR structure of a receptor-bound G-protein peptide. Nature. 1993 May 20;363(6426):276–281. doi: 10.1038/363276a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emeis D., Kühn H., Reichert J., Hofmann K. P. Complex formation between metarhodopsin II and GTP-binding protein in bovine photoreceptor membranes leads to a shift of the photoproduct equilibrium. FEBS Lett. 1982 Jun 21;143(1):29–34. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(82)80266-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franke R. R., König B., Sakmar T. P., Khorana H. G., Hofmann K. P. Rhodopsin mutants that bind but fail to activate transducin. Science. 1990 Oct 5;250(4977):123–125. doi: 10.1126/science.2218504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franke R. R., Sakmar T. P., Graham R. M., Khorana H. G. Structure and function in rhodopsin. Studies of the interaction between the rhodopsin cytoplasmic domain and transducin. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jul 25;267(21):14767–14774. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamm H. E., Deretic D., Arendt A., Hargrave P. A., Koenig B., Hofmann K. P. Site of G protein binding to rhodopsin mapped with synthetic peptides from the alpha subunit. Science. 1988 Aug 12;241(4867):832–835. doi: 10.1126/science.3136547. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho Y. K., Fung B. K. Characterization of transducin from bovine retinal rod outer segments. The role of sulfhydryl groups. J Biol Chem. 1984 May 25;259(10):6694–6699. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khorana H. G. Rhodopsin, photoreceptor of the rod cell. An emerging pattern for structure and function. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jan 5;267(1):1–4. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- König B., Arendt A., McDowell J. H., Kahlert M., Hargrave P. A., Hofmann K. P. Three cytoplasmic loops of rhodopsin interact with transducin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(18):6878–6882. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.18.6878. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- König B., Welte W., Hofmann K. P. Photoactivation of rhodopsin and interaction with transducin in detergent micelles. Effect of 'doping' with steroid molecules. FEBS Lett. 1989 Oct 23;257(1):163–166. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)81811-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kühn H., Hargrave P. A. Light-induced binding of guanosinetriphosphatase to bovine photoreceptor membranes: effect of limited proteolysis of the membranes. Biochemistry. 1981 Apr 28;20(9):2410–2417. doi: 10.1021/bi00512a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molday R. S., MacKenzie D. Monoclonal antibodies to rhodopsin: characterization, cross-reactivity, and application as structural probes. Biochemistry. 1983 Feb 1;22(3):653–660. doi: 10.1021/bi00272a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oprian D. D., Molday R. S., Kaufman R. J., Khorana H. G. Expression of a synthetic bovine rhodopsin gene in monkey kidney cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(24):8874–8878. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.24.8874. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Redies C., Spillmann L., Kunz K. Colored neon flanks and line gap enhancement. Vision Res. 1984;24(10):1301–1309. doi: 10.1016/0042-6989(84)90185-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Resek J. F., Farahbakhsh Z. T., Hubbell W. L., Khorana H. G. Formation of the meta II photointermediate is accompanied by conformational changes in the cytoplasmic surface of rhodopsin. Biochemistry. 1993 Nov 16;32(45):12025–12032. doi: 10.1021/bi00096a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SINGH A., THORNTON E. R., WESTHEIMER F. H. The photolysis of diazoacetylchymotrypsin. J Biol Chem. 1962 Sep;237:3006–3008. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson R. A., Tracy R. P., Katzmann J. A., Wilson D. M., Young D. S. Beta 2-microglobulin determined by radioimmunoassay with monoclonal antibody. Clin Chem. 1982 Oct;28(10):2033–2039. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wald G. The molecular basis of visual excitation. Nature. 1968 Aug 24;219(5156):800–807. doi: 10.1038/219800a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- West R. E., Jr, Moss J., Vaughan M., Liu T., Liu T. Y. Pertussis toxin-catalyzed ADP-ribosylation of transducin. Cysteine 347 is the ADP-ribose acceptor site. J Biol Chem. 1985 Nov 25;260(27):14428–14430. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]