Abstract
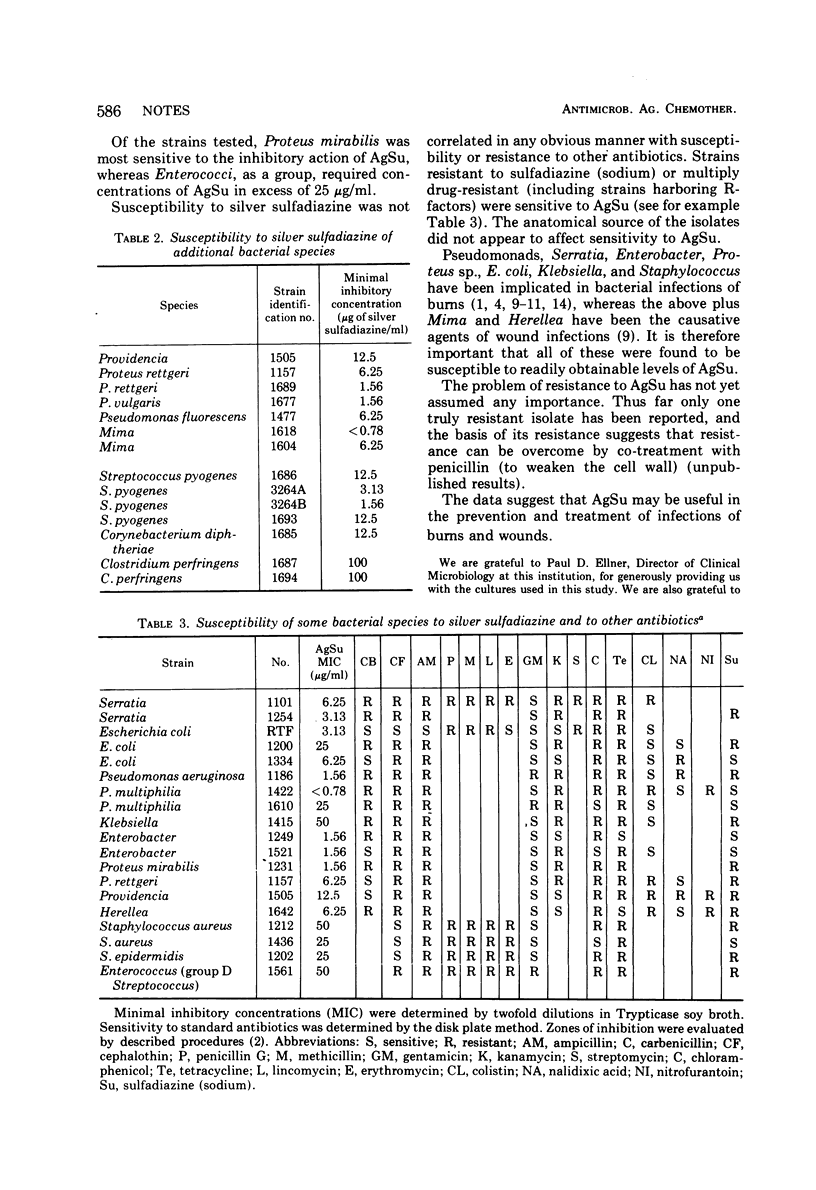
Isolates (657) representing 22 bacterial species were tested for susceptibility to silver sulfadiazine. All of the strains tested were inhibited by concentration levels of the drug which are easily achieved topically. It is suggested that silver sulfadiazine may be useful as a broad-spectrum antimicrobial substance for the prevention and treatment of infections of burns and wounds.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alexander J. W. Control of infection following burn injury. Arch Surg. 1971 Oct;103(4):435–441. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1971.01350100029006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coward J. E., Carr H. S., Rosenkranz H. S. Silver sulfadiazine: effect on the ultrastructure of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1973 May;3(5):621–624. doi: 10.1128/aac.3.5.621. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis B., Lilly H. A., Lowbury E. J. Gram-negative bacilli in burns. J Clin Pathol. 1969 Nov;22(6):634–641. doi: 10.1136/jcp.22.6.634. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox C. L., Jr, Rappole B. W., Stanford W. Control of pseudomonas infection in burns by silver sulfadiazine. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1969 May;128(5):1021–1026. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox C. L., Jr Silver sulfadiazine--a new topical therapy for Pseudomonas in burns. Therapy of Pseudomonas infection in burns. Arch Surg. 1968 Feb;96(2):184–188. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1968.01330200022004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grossman A. R. Silver sulfadiazine cream in the management of burns. Am Fam Physician GP. 1970 Feb;1(2):69–75. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klainer A. S., Beisel W. R. Opportunistic infection: a review. Am J Med Sci. 1969 Dec;258(6):431–456. doi: 10.1097/00000441-196912000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markley K. V. Systemic and local infection and immunity. The role of bacteria in burn mortality. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1968 Aug 14;150(3):922–930. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1968.tb14743.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RABIN E. R., GRABER C. D., VOGEL E. H., Jr, FINKELSTEIN R. A., TUMBUSCH W. A. Fatal pseudomonas infection in burned patients. A clinical, bacteriologic and anatomic study. N Engl J Med. 1961 Dec 21;265:1225–1231. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196112212652501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenkranz H. S., Carr H. S. Silver sulfadiazine: effect on the growth and metabolism of bacteria. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1972 Nov;2(5):367–372. doi: 10.1128/aac.2.5.367. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenkranz H. S., Rosenkranz S. Silver sulfadiazine: interaction with isolated deoxyribonucleic acid. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1972 Nov;2(5):373–383. doi: 10.1128/aac.2.5.373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shuck J. M. Infection control in burns. Topical and systemic. Surg Clin North Am. 1972 Dec;52(6):1425–1438. doi: 10.1016/s0039-6109(16)39887-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanford W., Rappole B. W., Fox C. L., Jr Clinical experience with silver sulfadiazine, a new topical agent for control of pseudomonas infections in burns. J Trauma. 1969 May;9(5):377–388. doi: 10.1097/00005373-196905000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



