Abstract
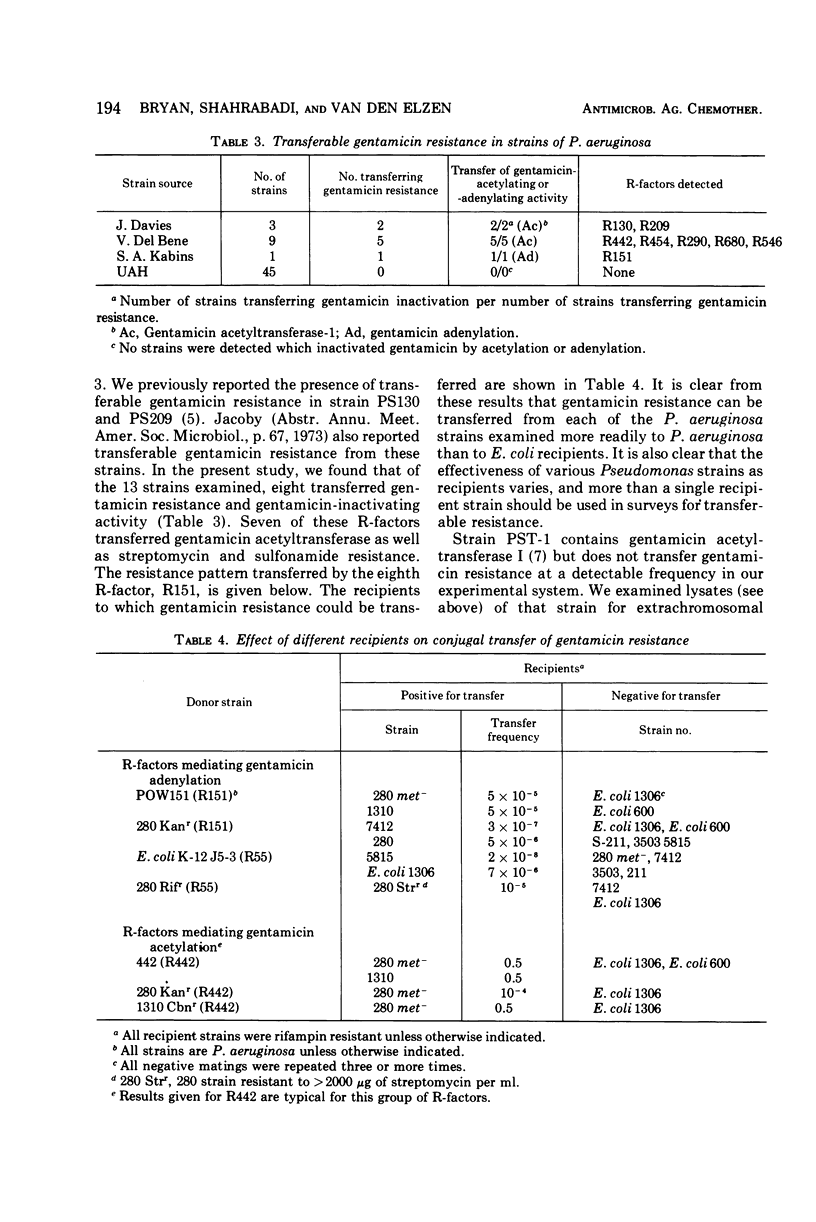
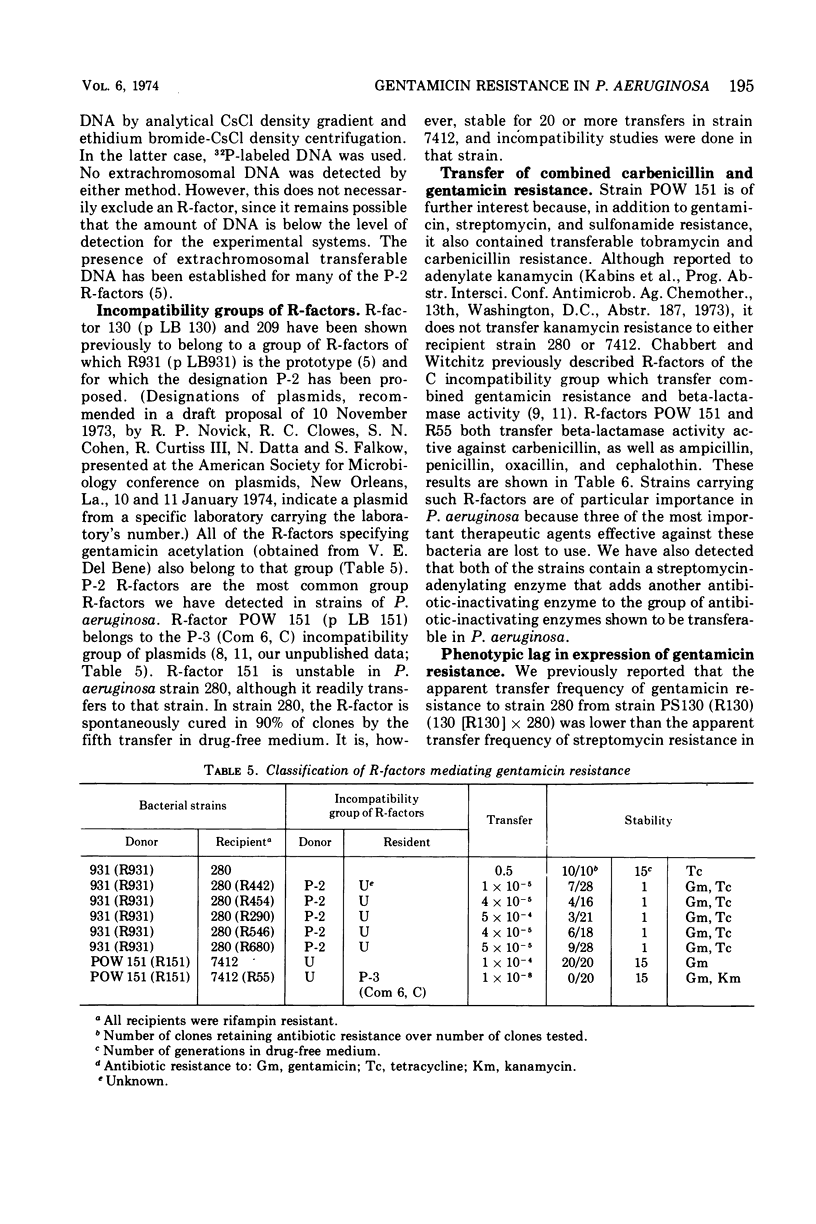
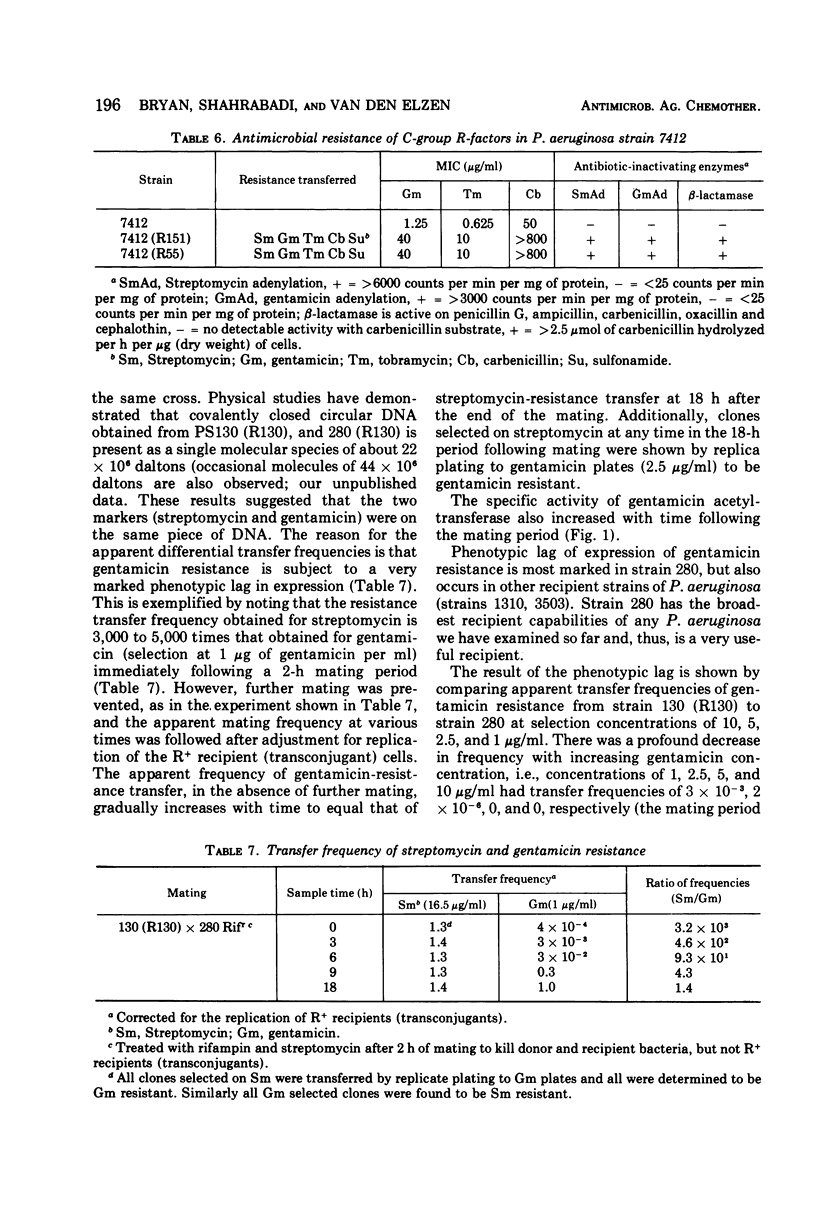
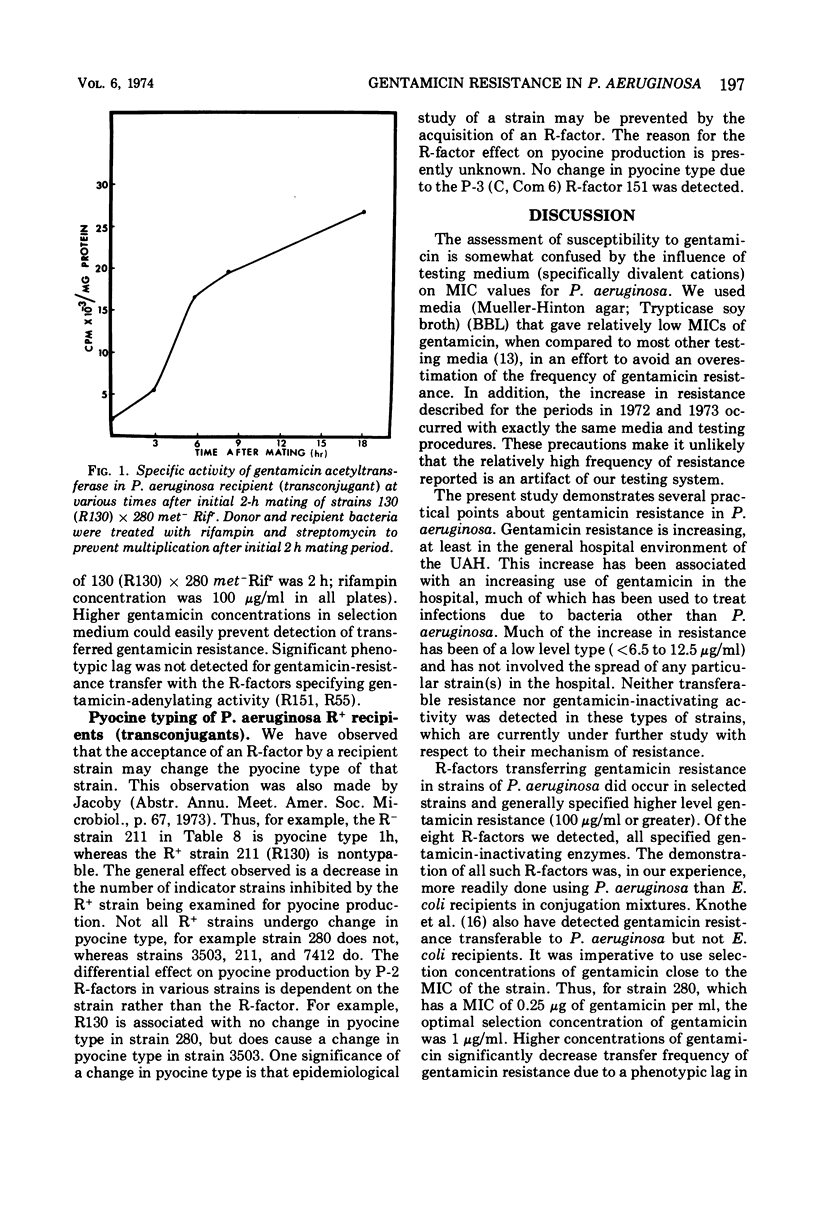
By disk diffusion antimicrobial susceptibility testing, 11% of 313 consecutive strains of Pseudomonas aeruginosa, examined during July to October 1973, were resistant to gentamicin (minimal inhibitory concentration 12.5 to >100 μg/ml), and a further 31% were moderately resistant (6.25 to 12.5 μg/ml) to gentamicin at the University of Alberta Hospital in Edmonton, Canada. Of 45 gentamicin-resistant strains from that hospital, none possessed R-factors or gentamicin-inactivating enzymes. Eight of 13 strains obtained from three American sources, which contained gentamicin-acetylating (12 strains) or -adenylating (1 strain) activity, conjugally transferred both gentamicin resistance and antibiotic-inactivating activity. P. aeruginosa recipients were much more effective for detection of transferable gentamicin resistance than Escherichia coli recipients, although not all P. aeruginosa were equally as effective as recipients. One strain, POW 151, transferred resistance to both carbenicillin and gentamicin as well as to several other antibiotics. R-factors detected belonged to P-2 and P-3 (Com 6, C) incompatibility groups. Expression of gentamicin resistance due to acetylation of gentamicin was subject to marked phenotypic lag, especially in recipient strain P. aeruginosa 280. This was shown to result in the failure to detect gentamicin resistance transfer if the concentration of gentamicin in selection media was too high (>2.5 μg/ml for strain 280). Some but not all recipients were changed in pyocine type upon acquisition of R-factors.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bauer A. W., Kirby W. M., Sherris J. C., Turck M. Antibiotic susceptibility testing by a standardized single disk method. Am J Clin Pathol. 1966 Apr;45(4):493–496. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benveniste R., Davies J. Enzymatic acetylation of aminoglycoside antibiotics by Escherichia coli carrying an R factor. Biochemistry. 1971 May 11;10(10):1787–1796. doi: 10.1021/bi00786a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benveniste R., Davies J. Mechanisms of antibiotic resistance in bacteria. Annu Rev Biochem. 1973;42:471–506. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.42.070173.002351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodey G. P., Stewart D. In vitro studies of BB-K8, a new aminoglycoside antibiotic. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1973 Aug;4(2):186–192. doi: 10.1128/aac.4.2.186. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryan L. E., Semaka S. D., Van den Elzen H. M., Kinnear J. E., Whitehouse R. L. Characteristics of R931 and other Pseudomonas aeruginosa R factors. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1973 May;3(5):625–637. doi: 10.1128/aac.3.5.625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryan L. E., Van Den Elzen H. M., Tseng J. T. Transferable drug resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1972 Jan;1(1):22–29. doi: 10.1128/aac.1.1.22. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brzezinska M., Benveniste R., Davies J., Daniels P. J., Weinstein J. Gentamicin resistance in strains of Pseudomonas aeruginosa mediated by enzymatic N-acetylation of the deoxystreptamine moiety. Biochemistry. 1972 Feb 29;11(5):761–765. doi: 10.1021/bi00755a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chabbert Y. A., Scavizzi M. R., Witchitz J. L., Gerbaud G. R., Bouanchaud D. H. Incompatibility groups and the classification of fi - resistance factors. J Bacteriol. 1972 Nov;112(2):666–675. doi: 10.1128/jb.112.2.666-675.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Datta N., Hedges R. W. R factors identified in Paris, some conferring gentamicin resistance, constitute a new compatibility group. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1972 Dec;123(6):849–852. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doi O., Ogura M., Tanaka N., Umezawa H. Inactivation of kanamycin, neomycin, and streptomycin by enzymes obtained in cells of Pseudomonas aeruginoa. Appl Microbiol. 1968 Sep;16(9):1276–1281. doi: 10.1128/am.16.9.1276-1281.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duncan I. B. Susceptibility of 1,500 isolates of Pseudomonas aeruginosa to gentamicin, carbenicillin, colistin, and polymyxin B. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1974 Jan;5(1):9–15. doi: 10.1128/aac.5.1.9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dámaso D., Moreno-López M. Study on in vitro activity of the antibiotics tobramycin and gentamicin against Pseudomonas aeruginosa clinical strains. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1973 Apr;26(4):233–237. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.26.233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fullbrook P. D., Elson S. W., Slocombe B. R-factor mediated beta-lactamase in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Nature. 1970 Jun 13;226(5250):1054–1056. doi: 10.1038/2261054a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Govan J. R., Gillies R. R. Further studies in the pyocine typing of Pseudomonas pyocyanea. J Med Microbiol. 1969 Feb;2(1):17–25. doi: 10.1099/00222615-2-1-17. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knothe H., Krcméry V., Sietzen W., Borst J. Transfer of gentamicin resistance from Pseudomonas aeruginosa strains highly resistant to gentamicin and carbenicillin. Chemotherapy. 1973;18(4):229–234. doi: 10.1159/000221266. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lockwood W. R., Lawson L. A. Studies on the susceptibility of 150 consecutive clinical isolates of Pseudomonas aeruginosa to tobramycin, gentamicin, colistin, carbenicillin, and five other antimicrobials. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1973 Sep;4(3):281–284. doi: 10.1128/aac.4.3.281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitsuhashi S., Kobayashi F., Yamaguchi M. Enzymatic inactivation of gentamicin C components by cell-free extract from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1971 Jun;24(6):400–401. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.24.400. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PERRET C. J. Iodometric assay of penicillinase. Nature. 1954 Nov 27;174(4439):1012–1013. doi: 10.1038/1741012a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sykes R. B., Richmond M. H. Intergeneric transfer of a beta-lactamase gene between Ps. aeruginosa and E. coli. Nature. 1970 Jun 6;226(5249):952–954. doi: 10.1038/226952a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tseng J. T., Bryan L. E., Van den Elzen H. M. Mechanisms and spectrum of streptomycin resistance in a natural population of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1972 Sep;2(3):136–141. doi: 10.1128/aac.2.3.136. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



