Abstract
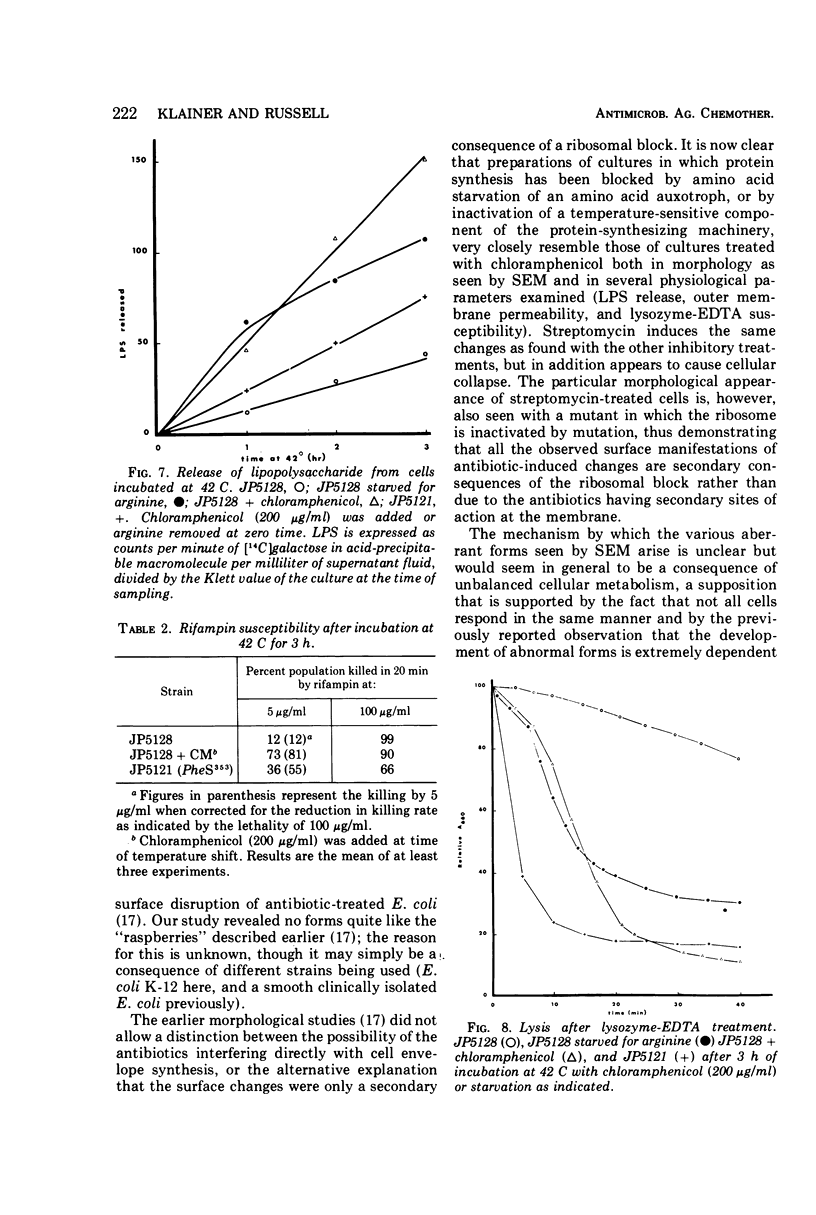
The consequences for cell envelope integrity of Escherichia coli K-12 of the inhibition of protein synthesis by a variety of means have been examined. Protein synthesis was blocked by the antibiotics chloramphenicol and streptomycin, by amino acid starvation of an amino acid auxotroph, and by inactivation of temperature-sensitive aminoacyl transfer ribonucleic acid synthetase and ribosomal mutations. Closely similar morphological and physiological effects were found irrespective of the means by which protein synthesis was blocked. Scanning electron microscopy revealed a spectrum of changes after protein inhibition, with granular material derived from cells and spheroplasts commonly seen. Streptomycin caused additional changes manifested in a collapsed appearance of treated cells. Measurements of the release of lipopolysaccharide from the cell surface, alterations in outer membrane penetrability, and lysis of lysozyme-ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid-treated cultures also showed that the various inhibitory treatments all had similar effects on cell envelope properties. The close correspondence between the effects seen with antibiotic-treated cultures and those in which protein synthesis inhibition was achieved by use of mutants indicates that the effects of chloramphenicol and streptomycin on the cell envelope are indirect consequences of ribosomal block, rather than due to multiple sites of action of the antibiotics.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ADELBERG E. A., BURNS S. N. Genetic variation in the sex factor of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1960 Mar;79:321–330. doi: 10.1128/jb.79.3.321-330.1960. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ALLISON J. L., HARTMAN R. E., HARTMAN R. S., WOLFE A. D., CIAK J., HAHN F. E. Mode of action of chloramphenicol. VII. Growth and multiplication of Escherichia coli in the presence of chloramphenicol. J Bacteriol. 1962 Mar;83:609–615. doi: 10.1128/jb.83.3.609-615.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BERGERSEN F. J. Cytological changes induced in Bacterium coli by chloramphenicol. J Gen Microbiol. 1953 Dec;9(3):353–356. doi: 10.1099/00221287-9-3-353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birdsell D. C., Cota-Robles E. H. Production and ultrastructure of lysozyme and ethylenediaminetetraacetate-lysozyme spheroplasts of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1967 Jan;93(1):427–437. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.1.427-437.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broda P. Ribonucleic acid synthesis and glutamate excretion in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1968 Nov;96(5):1528–1534. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.5.1528-1534.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burman L. G., Nordström K., Bloom G. D. Murein and the outer penetration barrier of Escherichia coli K-12, Proteus mirabilis, and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1972 Dec;112(3):1364–1374. doi: 10.1128/jb.112.3.1364-1374.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crowfoot P. D., Esfahani M., Wakil S. J. Relation between protein synthesis and phospholipid synthesis and turnover in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1972 Dec;112(3):1408–1415. doi: 10.1128/jb.112.3.1408-1415.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Petris S. Ultrastructure of the cell wall of Escherichia coli and chemical nature of its constituent layers. J Ultrastruct Res. 1967 Jul;19(1):45–83. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(67)80059-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DePamphilis M. L. Isolation of bacteriophages T2 and T4 attached to the outer membrane of Escherichia coli. J Virol. 1971 May;7(5):683–686. doi: 10.1128/jvi.7.5.683-686.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egan A. F., Russell R. R. Conditional mutations affecting the cell envelope of Escherichia coli K-12. Genet Res. 1973 Apr;21(2):139–152. doi: 10.1017/s001667230001332x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenwood D., O'Grady F. A comparison of the effects of ampicillin on Escherichia coli and proteus mirabilis. J Med Microbiol. 1969 Nov 4;2(4):435–441. doi: 10.1099/00222615-2-4-435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenwood D., O'Grady F. Trimodal response of Escherichia coli and Proteus mirabilis to penicillins. Nature. 1970 Oct 31;228(5270):457–458. doi: 10.1038/228457a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kang S. S. A mutant of Escherichia coli with temperature-sensitive streptomycin protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Mar;65(3):544–550. doi: 10.1073/pnas.65.3.544. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klainer A. S., Betsch C. J. Scanning-beam electron microscopy of selected microorganisms. J Infect Dis. 1970 Mar;121(3):339–343. doi: 10.1093/infdis/121.3.339. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klainer A. S., Perkins R. L. Antibiotic-induced alterations in the surface morphology of bacterial cells: a scanning-beam electron miscroscopy study. J Infect Dis. 1970 Oct;122(4):323–328. doi: 10.1093/infdis/122.4.323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klainer A. S., Perkins R. L. Surface manifestations of antibiotic-induced alterations in protein synthesis in bacterial cells. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1972 Feb;1(2):164–170. doi: 10.1128/aac.1.2.164. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knox K. W., Vesk M., Work E. Relation between excreted lipopolysaccharide complexes and surface structures of a lysine-limited culture of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1966 Oct;92(4):1206–1217. doi: 10.1128/jb.92.4.1206-1217.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matzura H., Broda P. Sensitization of Escherichia coli to actinomycin D by the arrest of protein synthesis. J Bacteriol. 1968 Nov;96(5):1877–1879. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.5.1877-1879.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan C., Rosenkranz H. S., Carr H. S., Rose H. M. Electron microscopy of chloramphenicol-treated Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1967 Jun;93(6):1987–2002. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.6.1987-2002.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishino T., Nakazawa S. Spheroplast-like structures in Escherichia coli demonstrated by scanning electron microscopy. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1972 Oct;25(10):602–603. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.25.602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Normark S., Westling B. Nature of the penetration barrier in Escherichia coli K-12: effect of macromolecular inhibition of penetrability in strains containing the envA gene. J Bacteriol. 1971 Oct;108(1):45–50. doi: 10.1128/jb.108.1.45-50.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PULVERTAFT R. J. V. The effect of antibiotics on growing cultures of Bacterium coli. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1952 Jan;64(1):75–89. doi: 10.1002/path.1700640110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reid P., Speyer J. Rifampicin inhibition of ribonucleic acid and protein synthesis in normal and ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid-treated Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1970 Oct;104(1):376–389. doi: 10.1128/jb.104.1.376-389.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothfield L., Pearlman-Kothencz M. Synthesis and assembly of bacterial membrane components. A lipopolysaccharide-phospholipid-protein complex excreted by living bacteria. J Mol Biol. 1969 Sep 28;44(3):477–492. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90374-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell R. R., Pittard A. J. Mutants of Escherichia coli unable to make protein at 42 C. J Bacteriol. 1971 Nov;108(2):790–798. doi: 10.1128/jb.108.2.790-798.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell R. R. Temperature-sensitive osmotic remedial mutants of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1972 Nov;112(2):661–665. doi: 10.1128/jb.112.2.661-665.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan A. M., Borek E. The relaxed control phenomenon. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1971;11:193–228. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60328-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheie P., Ehrenspeck S. Large surface blebs on Escherichia coli heated to inactivating temperatures. J Bacteriol. 1973 May;114(2):814–818. doi: 10.1128/jb.114.2.814-818.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sokawa J., Sokawa Y., Kaziro Y. Stringent control in Escherichia coli. Nat New Biol. 1972 Dec 20;240(103):242–245. doi: 10.1038/newbio240242a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]