Abstract
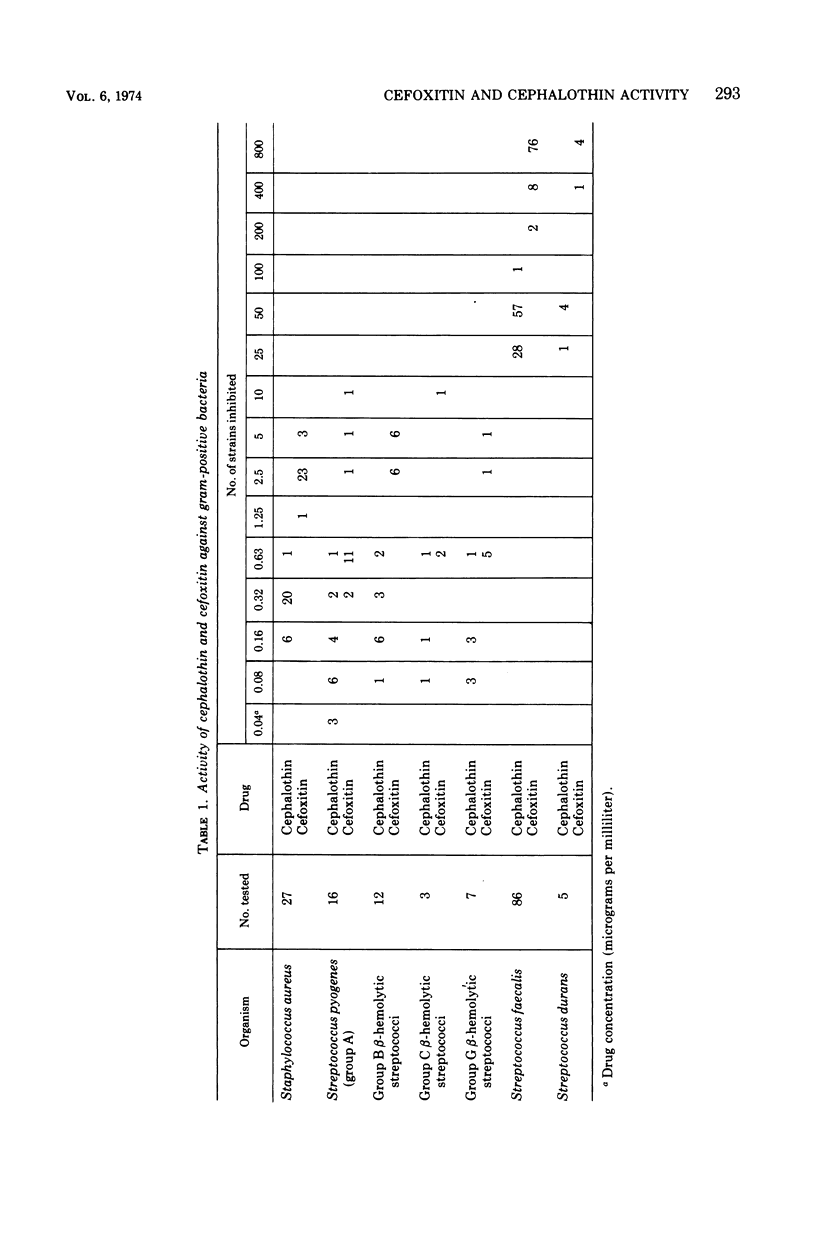
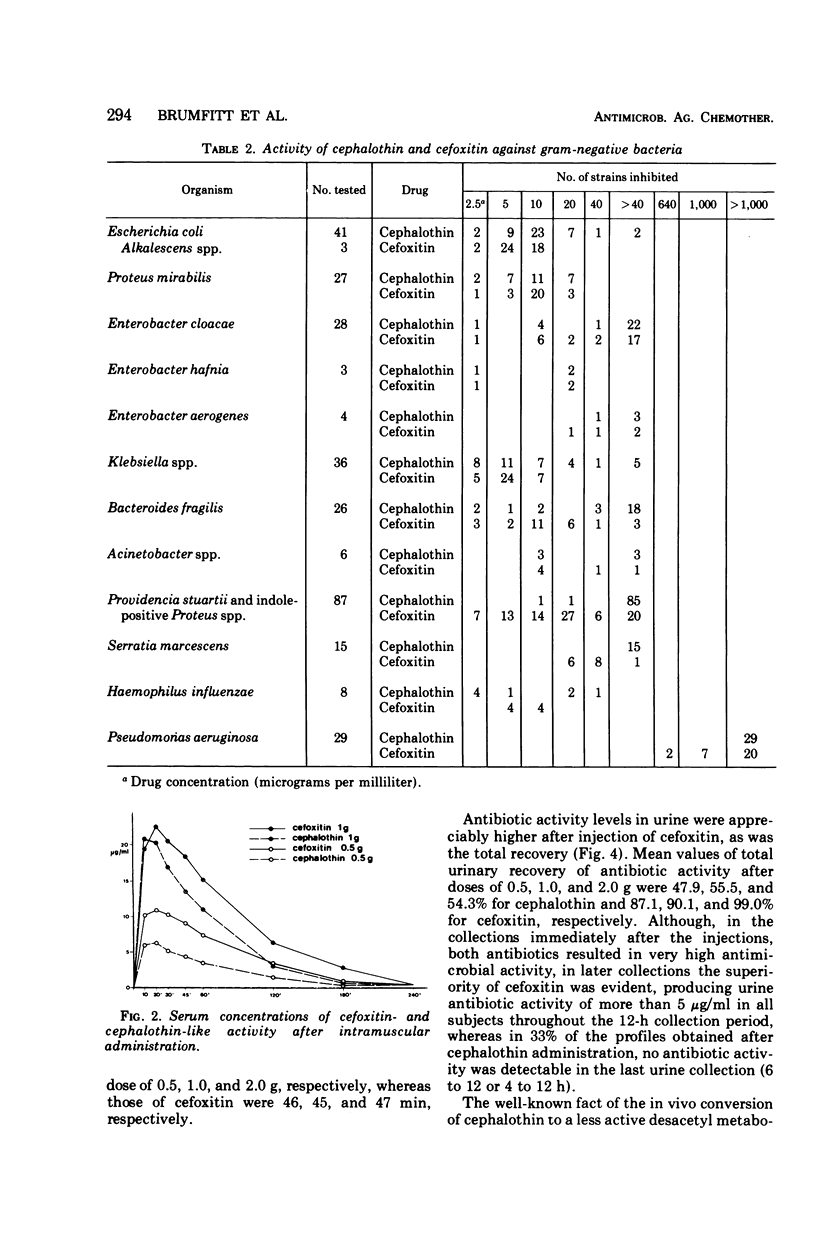
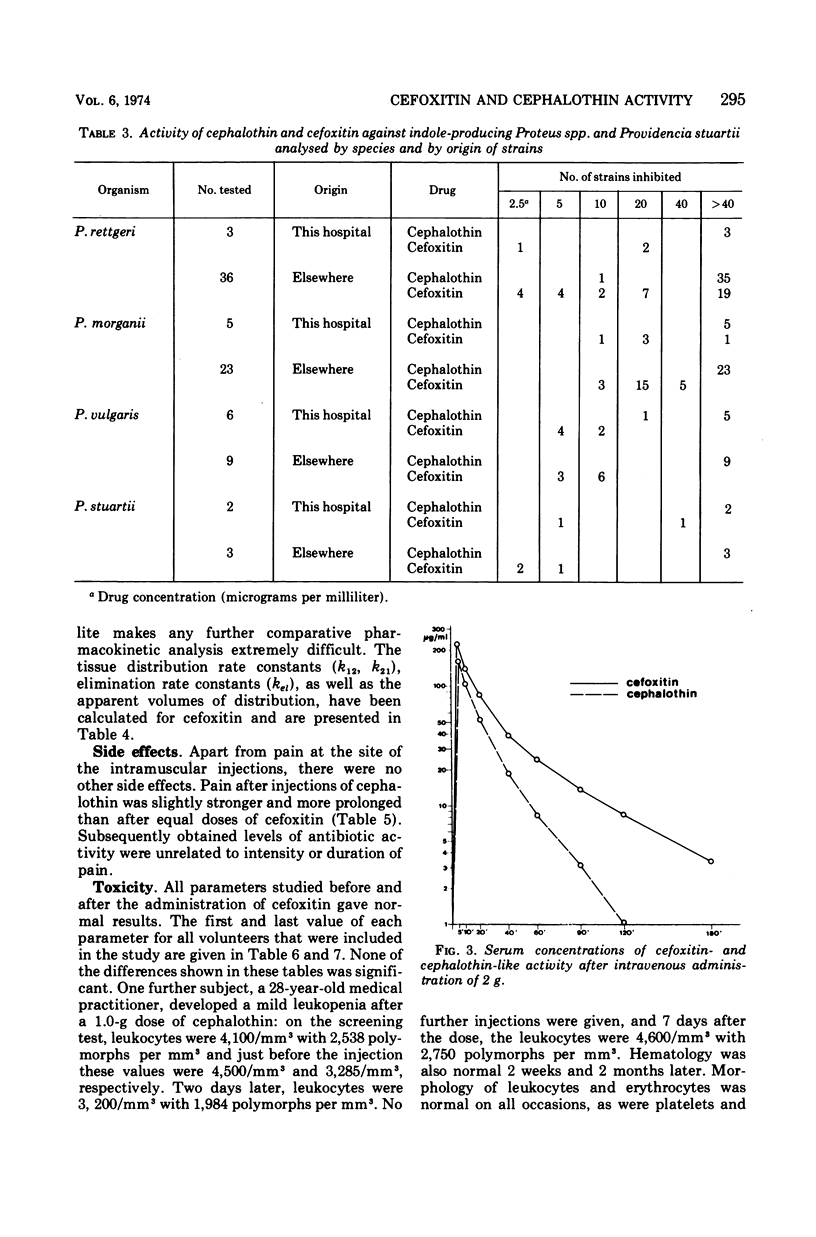
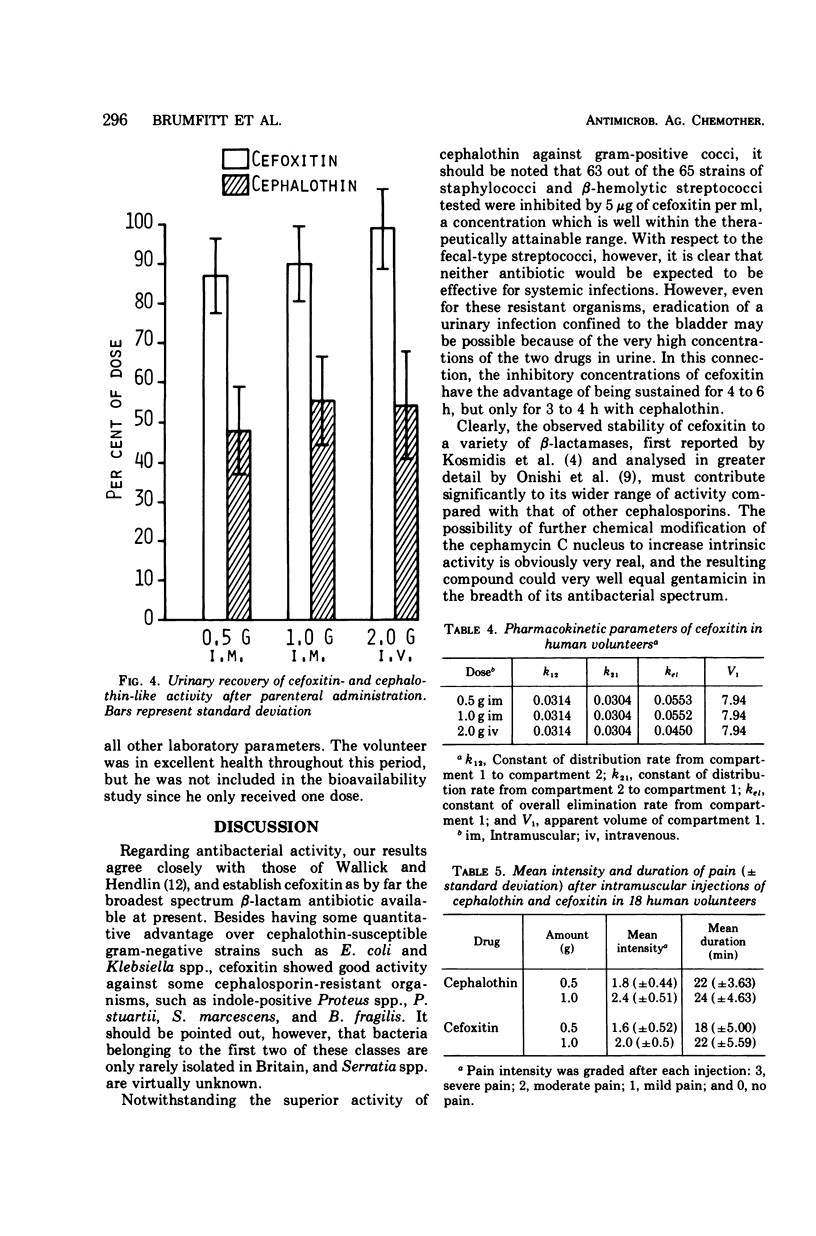
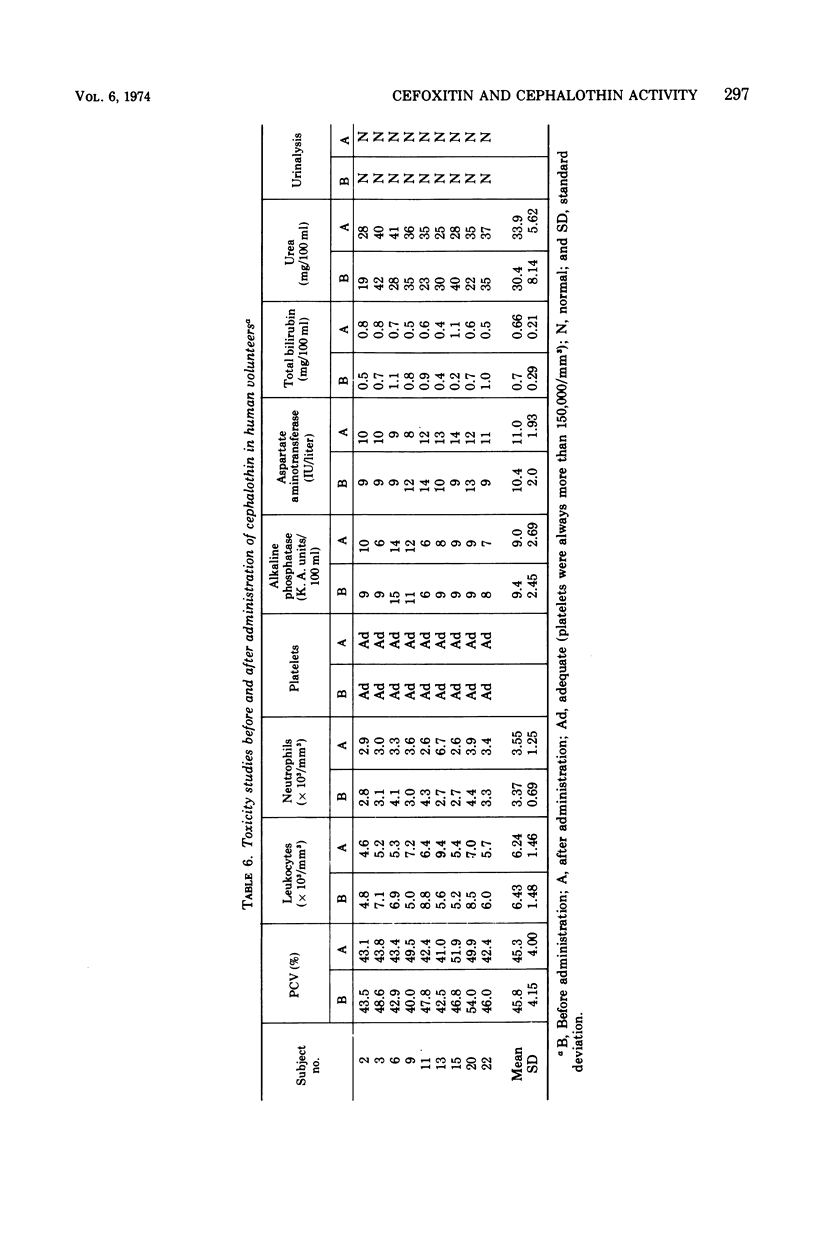
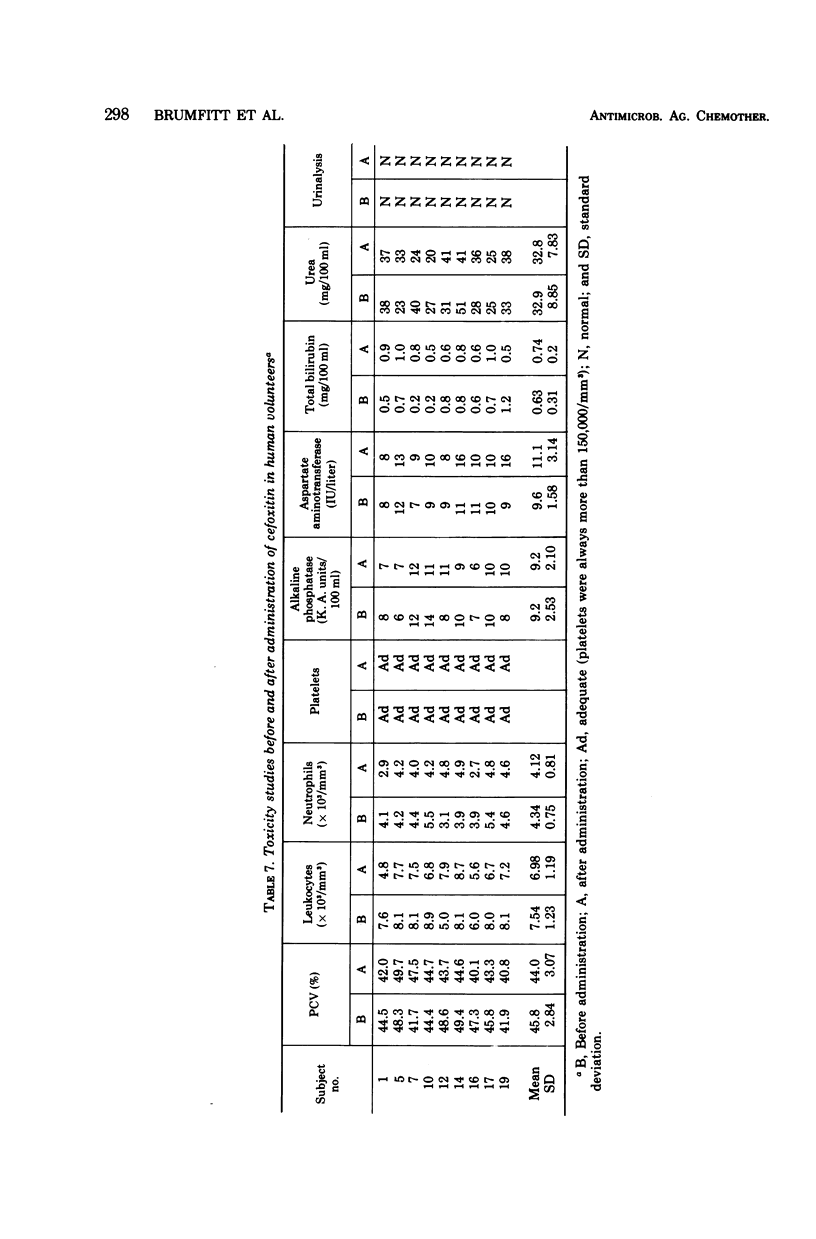
Cefoxitin, a semisynthetic cephamycin, has been compared with the widely used parenteral cephalosporin, cephalothin, in terms of antibacterial activity, human pharmacokinetics, and toxicity. For both compounds, minimal inhibitory concentrations were within the therapeutic range against the 156 gram-positive cocci tested (except group D streptococci), but cephalothin was 8 to 20 times more active. Regarding the 313 gram-negative organisms tested, both antibiotics were of approximately equal activity against cephalothin-susceptible strains, but cefoxitin was outstandingly superior against Providencia spp. and indole-producing Proteus spp., and markedly better against Serratia marcescens and Bacteroides fragilis. Against these organisms, cefoxitin but not cephalothin would be expected to be therapeutically valuable. Antibiotic activity levels in the serum and urine of 18 human volunteers after parenteral administration were higher and more prolonged in the case of cefoxitin, which had an average terminal serum half-life of about 45 min and a urinary recovery of about 90%. Cefoxitin was entirely nontoxic and, given intramuscularly, slightly less painful then cephalothin. These preliminary results suggest that cephamycins may prove to be a significant chemotherapeutic advance.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Daoust D. R., Onishi H. R., Wallick H., Hendlin D., Stapley E. O. Cephamycins, a new family of beta-lactam antibiotics: antibacterial activity and resistance to beta-lactamase degradation. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1973 Feb;3(2):254–261. doi: 10.1128/aac.3.2.254. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kosmidis J., Hamilton-Miller J. M., Gilchrist J. N., Kerry D. W., Brumfitt W. Cefoxitin, a new semi-synthetic cephamycin: an in-vitro and in-vivo comparison with cephalothin. Br Med J. 1973 Dec 15;4(5893):653–655. doi: 10.1136/bmj.4.5893.653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwan K. C., Till A. E. Novel method for bioavailability assessment. J Pharm Sci. 1973 Sep;62(9):1494–1497. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600620923. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwan K. C., Wadke D. A., Foltz E. L. Pharmacokinetics of phosphonomycin in Man. I. Intravenous administration. J Pharm Sci. 1971 May;60(5):678–685. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600600504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller A. K., Celozzi E., Kong Y., Pelak B. A., Hendlin D., Stapley E. O. Cefoxitin, a semisynthetic cephamycin antibiotic: in vivo evaluation. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1974 Jan;5(1):33–37. doi: 10.1128/aac.5.1.33. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagarajan R., Boeck L. D., Gorman M., Hamill R. L., Higgens C. E., Hoehn M. M., Stark W. M., Whitney J. G. Beta-lactam antibiotics from Streptomyces. J Am Chem Soc. 1971 May 5;93(9):2308–2310. doi: 10.1021/ja00738a035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Onishi H. R., Daoust D. R., Zimmerman S. B., Hendlin D., Stapley E. O. Cefoxitin, a semisynthetic cephamycin antibiotic: resistance to beta-lactamase inactivation. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1974 Jan;5(1):38–48. doi: 10.1128/aac.5.1.38. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stapley E. O., Jackson M., Hernandez S., Zimmerman S. B., Currie S. A., Mochales S., Mata J. M., Woodruff H. B., Hendlin D. Cephamycins, a new family of beta-lactam antibiotics. I. Production by actinomycetes, including Streptomyces lactamdurans sp. n. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1972 Sep;2(3):122–131. doi: 10.1128/aac.2.3.122. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallick H., Hendlin D. Cefoxitin, a semisynthetic cephamycin antibiotic: susceptibility studies. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1974 Jan;5(1):25–32. doi: 10.1128/aac.5.1.25. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



