Abstract
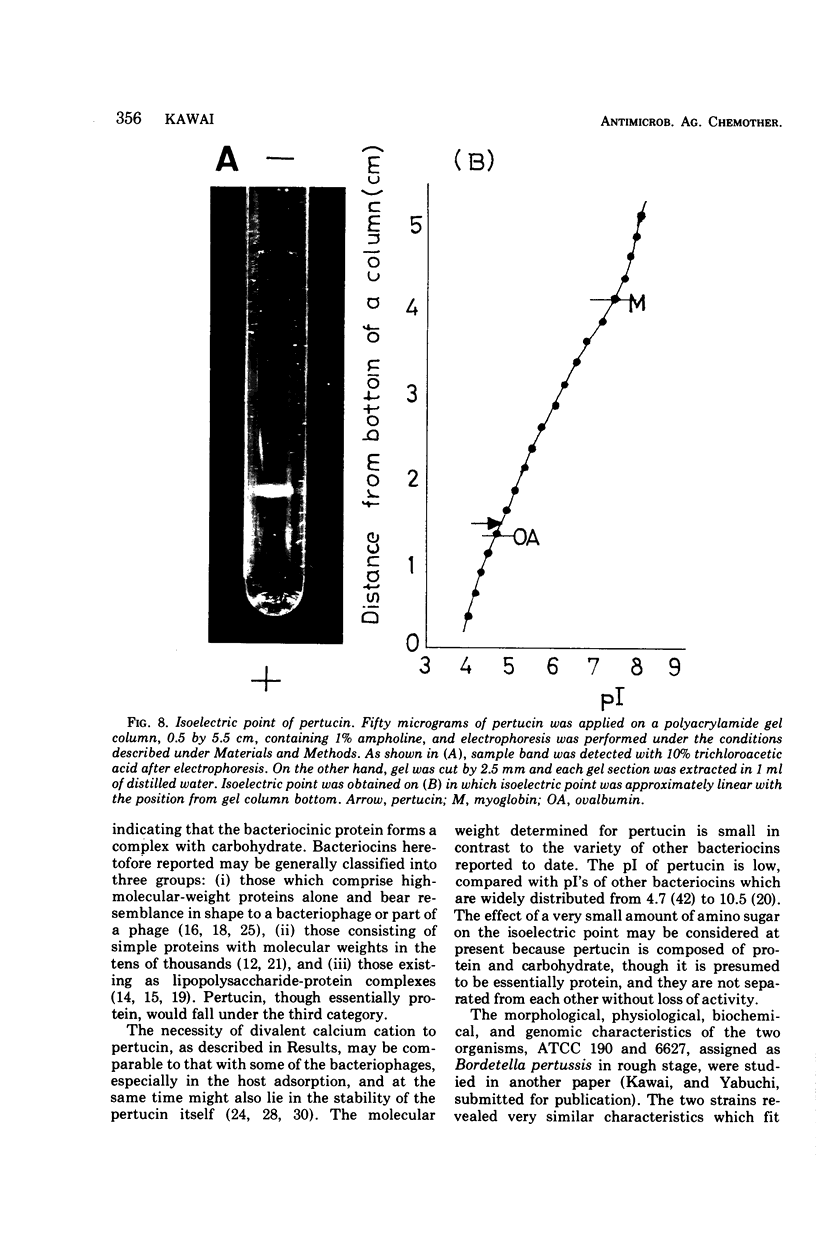
Pertucin, a bacteriocin active against phase I organisms of Bordetella pertussis, was extracted from Pseudomonas pertucinogena, strain 190 or 6627, by freezing and thawing of bacteria-free agar medium and was purified by ammonium sulfate fractionation, dialysis, zinc chloride precipitation, and polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. The specific activity of purified pertucin was approximately 80 times that of the crude extract. The purified pertucin preparation was homogeneous on ultracentrifugal analysis and polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, and was found to be composed of protein (80%) and carbohydrate (20%), the latter assumed not to be bound covalently to the protein. Neither nucleic acids nor lipids were demonstrated. N-terminal analysis by dansylation revealed only methionine in strain 190 and only glycine in strain 6627. The isoelectric point was found to be 4.8, and the molecular weight was estimated to be 31,500. Amino acid analysis of the protein moiety demonstrated that it contained all of the common amino acids with somewhat more of the hydrophilic amino acids. With respect to thermostability, pH stability, and effects of metal ions and various buffers, pertucin behaves like a protein and is stable in 0.05 M tris(hydroxymethyl)aminomethane buffer, pH 8.0, containing 0.01 M Ca2+.
Full text
PDF
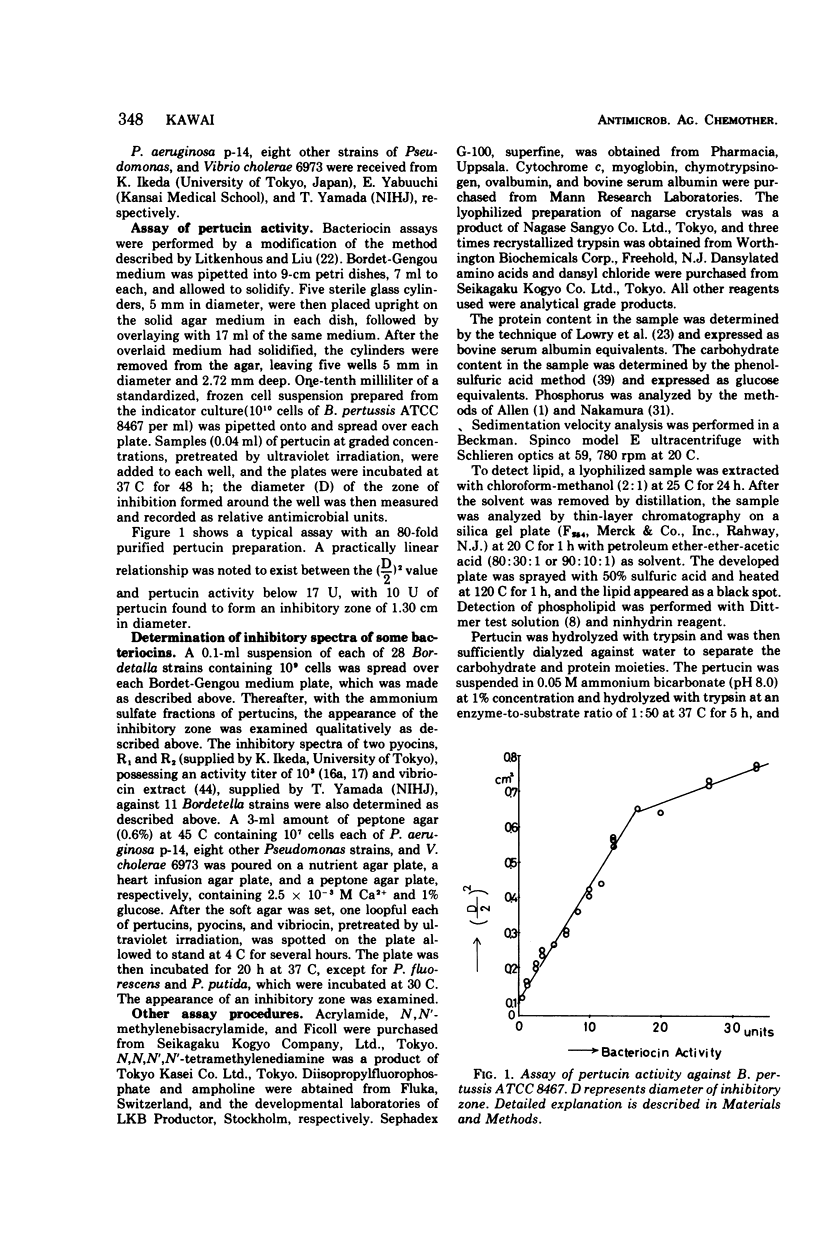

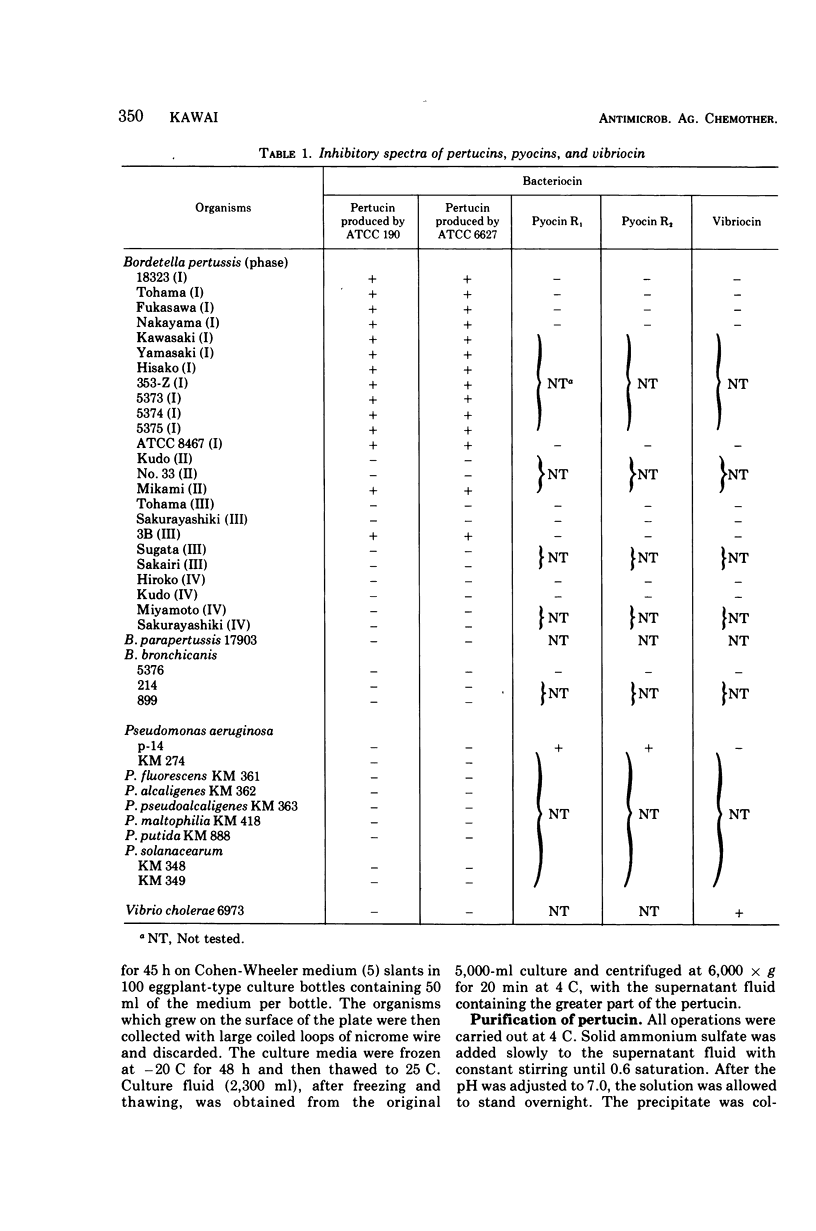
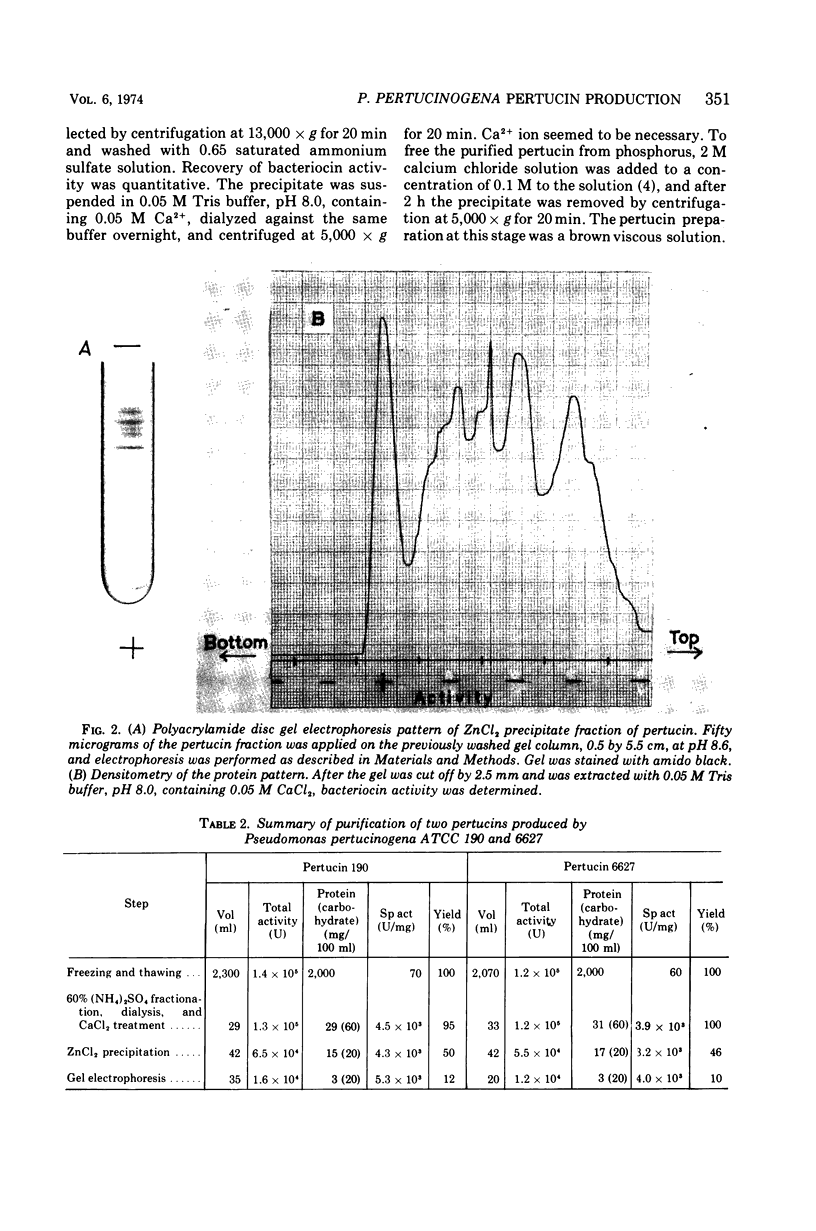
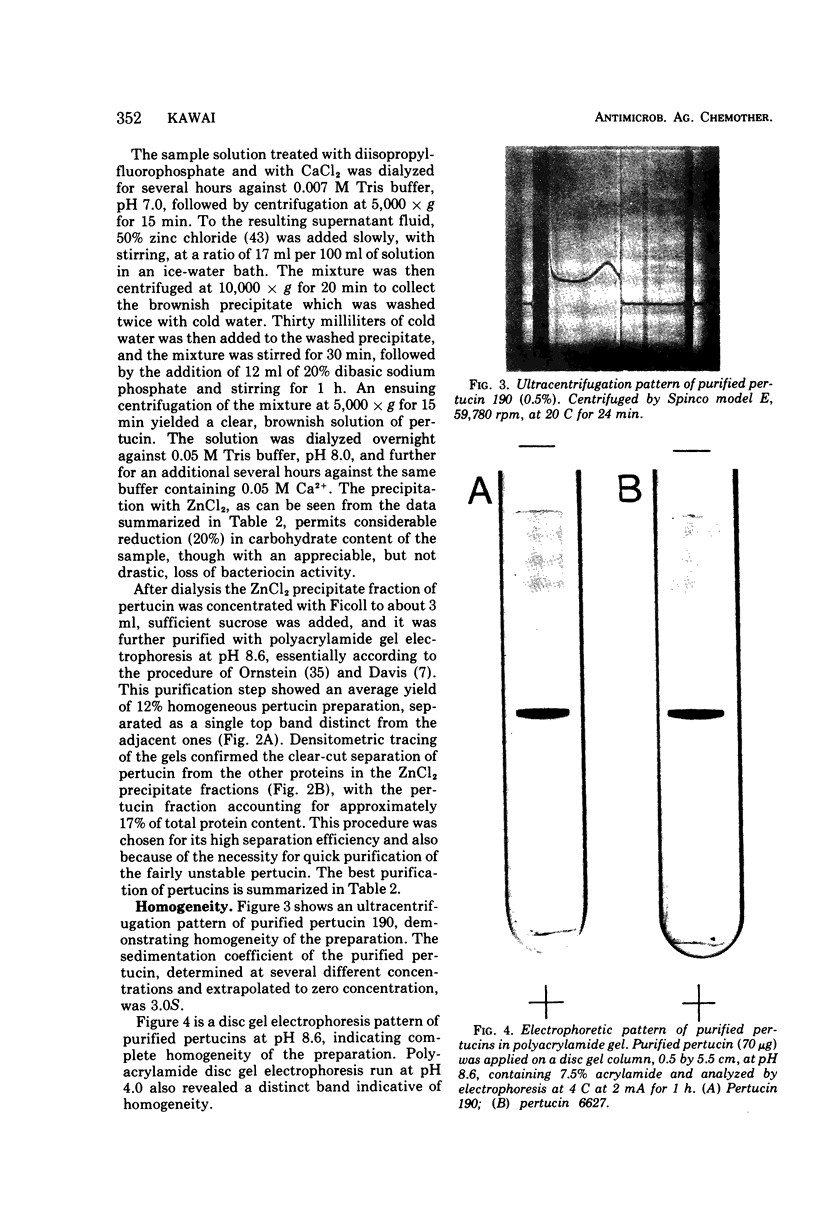
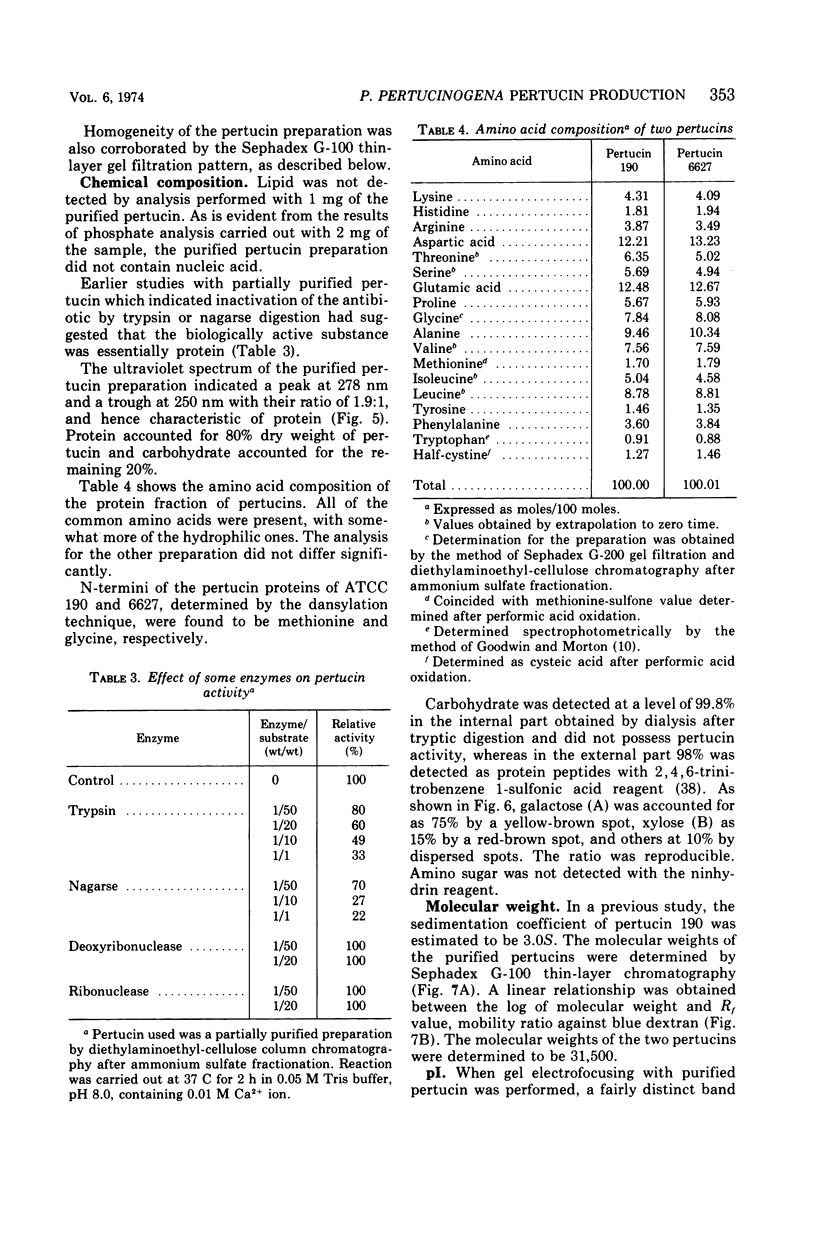
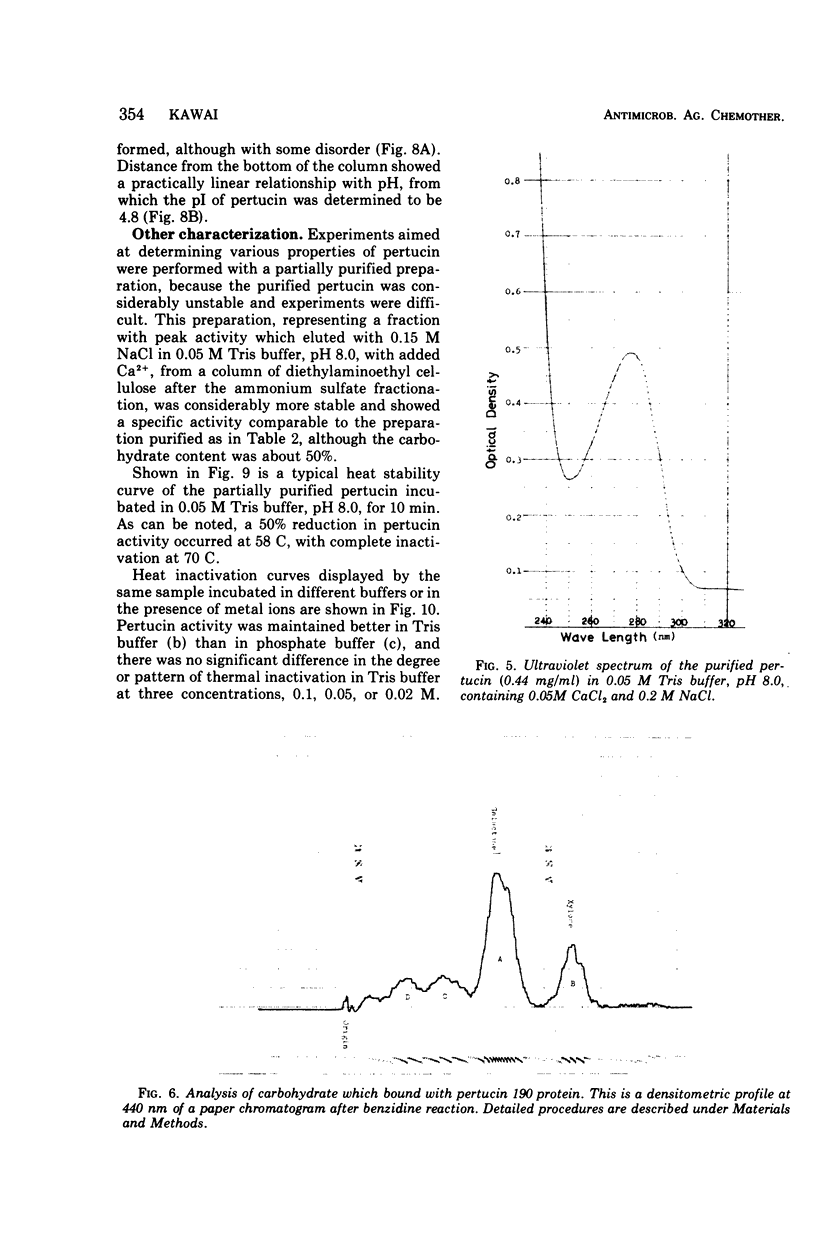
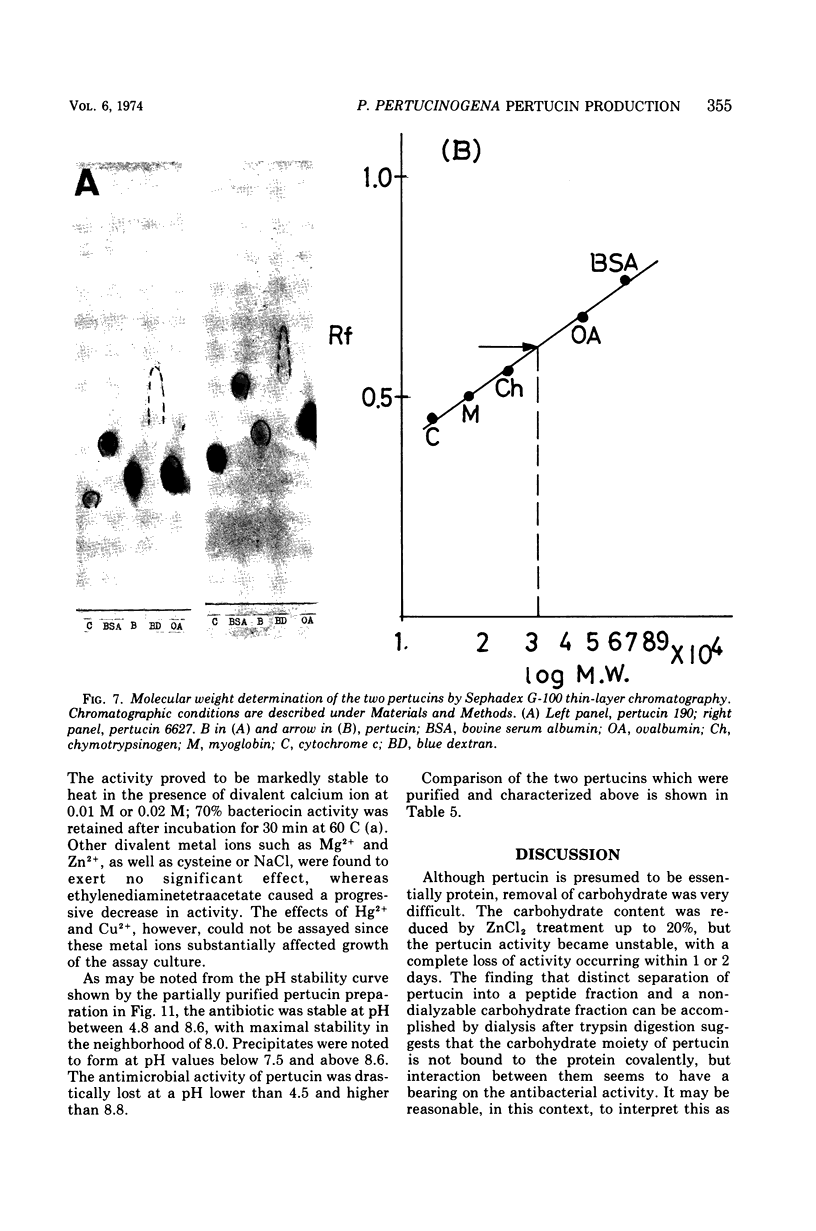


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen R. J. The estimation of phosphorus. Biochem J. 1940 Jun;34(6):858–865. doi: 10.1042/bj0340858. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BACON J. S. D., EDELMAN J. The carbohydrates of the Jerusalem artichoke and other Compositae. Biochem J. 1951 Jan;48(1):114–126. doi: 10.1042/bj0480114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burrell J. I., Robbins K. C., Pillemer L. Effect of Calcium Chloride on the Preparation of Extracts of H. pertussis. Science. 1948 Sep 17;108(2803):311–311. doi: 10.1126/science.108.2803.311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen S. M., Wheeler M. W. Pertussis Vaccine Prepared with Phase-I Cultures Grown in Fluid Medium. Am J Public Health Nations Health. 1946 Apr;36(4):371–376. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS B. J. DISC ELECTROPHORESIS. II. METHOD AND APPLICATION TO HUMAN SERUM PROTEINS. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Dec 28;121:404–427. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1964.tb14213.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DITTMER J. C., LESTER R. L. A SIMPLE, SPECIFIC SPRAY FOR THE DETECTION OF PHOSPHOLIPIDS ON THIN-LAYER CHROMATOGRAMS. J Lipid Res. 1964 Jan;5:126–127. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dale G., Latner A. L. Isoelectric focusing in polyacrylamide gels. Lancet. 1968 Apr 20;1(7547):847–848. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(68)90303-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOEBEL W. F., BARRY G. T. Colicine K. II. The preparation and properties of a substance having colicine K activity. J Exp Med. 1958 Feb 1;107(2):185–209. doi: 10.1084/jem.107.2.185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodwin T. W., Morton R. A. The spectrophotometric determination of tyrosine and tryptophan in proteins. Biochem J. 1946;40(5-6):628–632. doi: 10.1042/bj0400628. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gros C., Labouesse B. Study of the dansylation reaction of amino acids, peptides and proteins. Eur J Biochem. 1969 Feb;7(4):463–470. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1969.tb19632.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HIRS C. H. The oxidation of ribonuclease with performic acid. J Biol Chem. 1956 Apr;219(2):611–621. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOMMA J. Y., SUZUKI N. "CELL-WALL PROTEIN A" OF PSEUDOMONAS AERUGINOSA AND ITS RELATIONSHIP TO "ORIGINAL ENDOTOXIN PROTEIN". J Bacteriol. 1964 Mar;87:630–640. doi: 10.1128/jb.87.3.630-640.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUTTON J. J., GOEBEL W. F. Colicine V. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1961 Sep 15;47:1498–1500. doi: 10.1073/pnas.47.9.1498. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herschman H. R., Helinski D. R. Purification and characterization of colicin E2 and colicin E3. J Biol Chem. 1967 Nov 25;242(22):5360–5368. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishii S. I., Nishi Y., Egami F. The fine structure of a pyocin. J Mol Biol. 1965 Sep;13(2):428–431. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80107-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAGEYAMA M., EGAMI F. On the purification and some properties of a pyocin, a bacteriocin produced by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Life Sci. 1962 Sep;1:471–476. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(62)90055-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konisky J. Characterization of colicin Ia and colicin Ib. Chemical studies of protein structure. J Biol Chem. 1972 Jun 25;247(12):3750–3755. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konisky J., Richards F. M. Characterization of colicin Ia and colicin Ib. Purification and some physical properties. J Biol Chem. 1970 Jun 10;245(11):2972–2978. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Litkenhous C., Liu P. V. Bacteriocin produced by Bordetella pertussis. J Bacteriol. 1967 May;93(5):1484–1488. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.5.1484-1488.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCCONN J. D., TSURU D., YASUNOBU K. T. BACILLUS SUBTILIS NEUTRAL PROTEINASE. I. A ZINC ENZYME OF HIGH SPECIFIC ACTIVITY. J Biol Chem. 1964 Nov;239:3706–3715. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MORRIS C. J. THIN-LAYER CHROMATOGRAPHY OF PROTEINS ON SEPHADEX G-100 AND G-200. J Chromatogr. 1964 Oct;16:167–175. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(01)82451-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mennigmann H. D. Electron microscopy of the anti-bacterial agent produced by Escherichia coli 15. J Gen Microbiol. 1965 Nov;41(2):151–154. doi: 10.1099/00221287-41-2-151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Momotani Y. [Electrofocusing with acrylamide gel as a support]. Tanpakushitsu Kakusan Koso. 1969 Oct;14(11):1024–1025. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moyer R. W., Buchanan J. M. Effect of calcium ions on synthesis of T5-specific proteins. J Biol Chem. 1970 Nov 25;245(22):5897–5903. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NOMURA M., NAKAMURA M. Reversibility of inhibition of nucleic acids and protein synthesis by colicin K. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1962 May 4;7:306–309. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(62)90196-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nomura M. Colicins and related bacteriocins. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1967;21:257–284. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.21.100167.001353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ORNSTEIN L. DISC ELECTROPHORESIS. I. BACKGROUND AND THEORY. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Dec 28;121:321–349. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1964.tb14207.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REEVES P. THE BACTERIOCINS. Bacteriol Rev. 1965 Mar;29:24–45. doi: 10.1128/br.29.1.24-45.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REISFELD R. A., LEWIS U. J., WILLIAMS D. E. Disk electrophoresis of basic proteins and peptides on polyacrylamide gels. Nature. 1962 Jul 21;195:281–283. doi: 10.1038/195281a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tagg J. R., Dajani A. S., Wannamaker L. W., Gray E. D. Group A streptococcal bacteriocin. Production, purification, and mode of action. J Exp Med. 1973 Nov 1;138(5):1168–1183. doi: 10.1084/jem.138.5.1168. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timmis K. Purification and characterization of colicin D. J Bacteriol. 1972 Jan;109(1):12–20. doi: 10.1128/jb.109.1.12-20.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsao S. S., Goebel W. F. Colicin K. 8. The immunological properties of mitomycin-induced colicin K. J Exp Med. 1969 Dec 1;130(6):1313–1335. doi: 10.1084/jem.130.6.1313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Klerk H. C., Hugo N. Phage-like structures from Lactobacillus acidophilus. J Gen Virol. 1970 Sep;8(3):231–234. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-8-3-231. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Klerk H. C., Smit J. A. Properties of a Lactobacillus fermenti bacteriocin. J Gen Microbiol. 1967 Aug;48(2):309–316. doi: 10.1099/00221287-48-2-309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]