Abstract
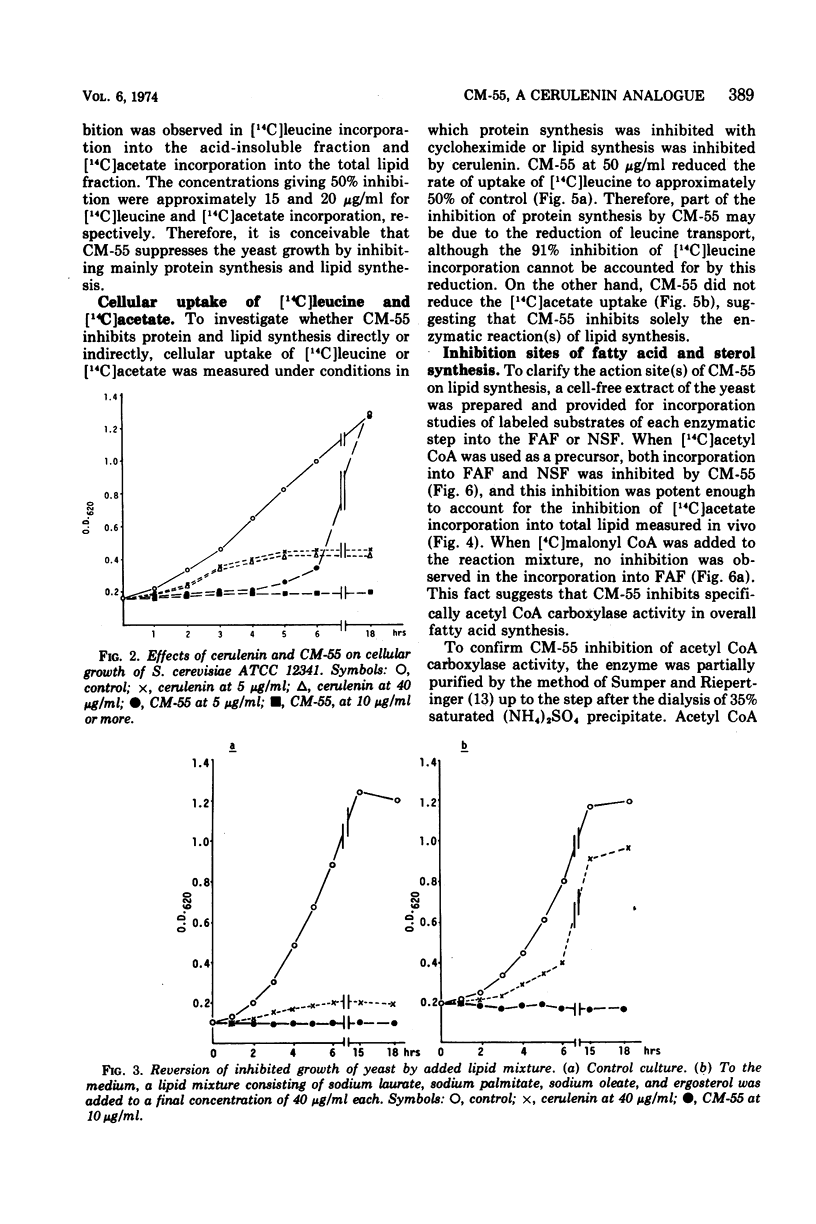
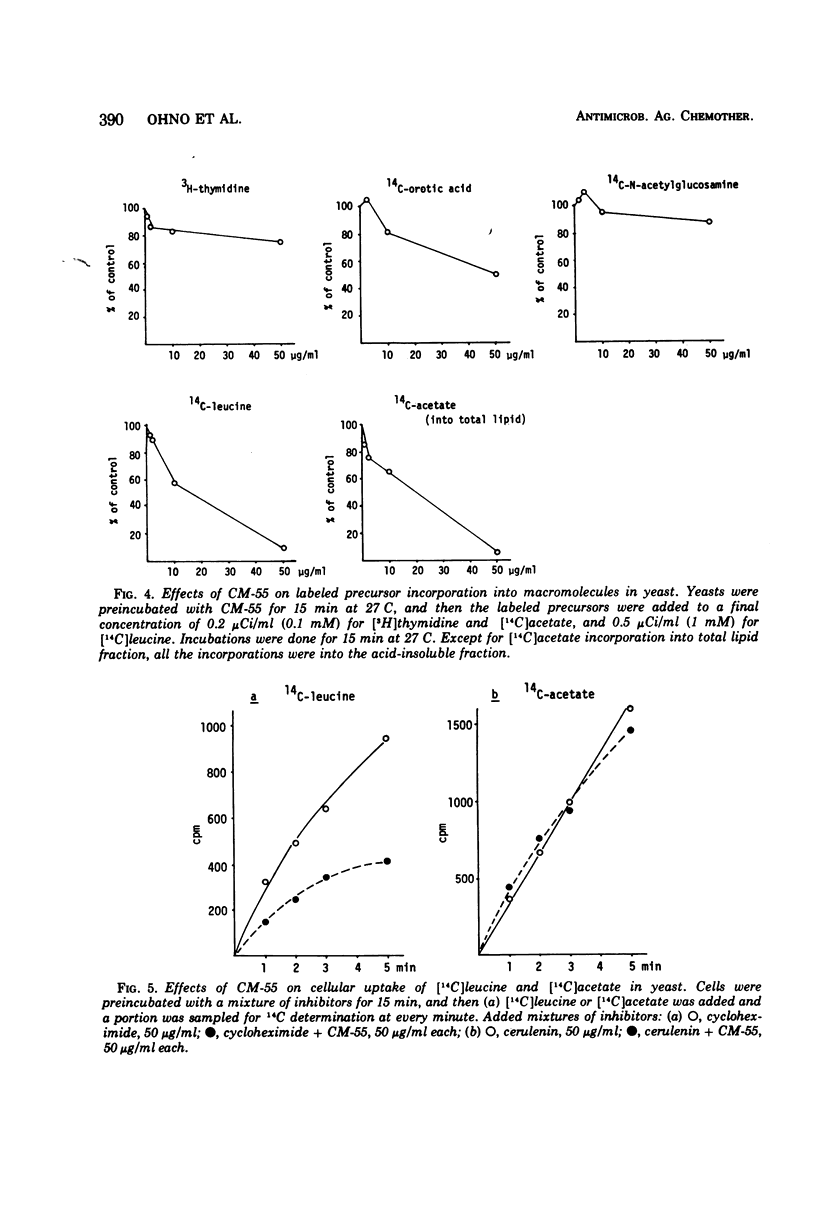
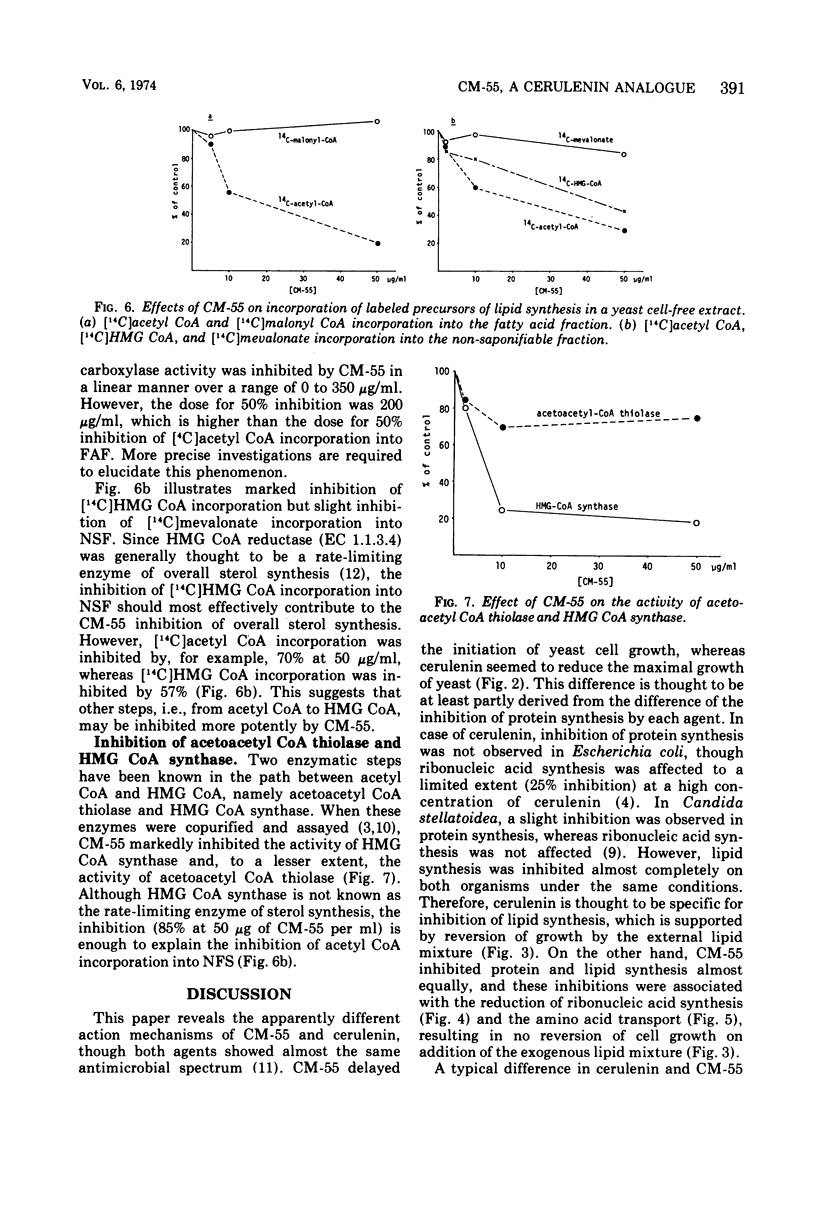
CM-55 is a synthetic analogue of the antibiotic cerulenin with the chemical structure of 2, 3-dodecenyl-4-oxo-dimethyl amide. This compound inhibited the growth of Saccharomyces cerevisiae ATCC 12341 and inhibited protein and lipid synthesis by 91 and 95%, respectively, at a concentration of 50 μg/ml (2.1 × 10−4 M). The inhibition of protein synthesis was associated with the partial reduction of ribonucleic acid synthesis and leucine transport. The mechanism of inhibition of lipid synthesis was further investigated in a cell-free extract of the yeast. CM-55 inhibited the incorporation of [14C]acetyl Coenzyme A (CoA) into both fatty acid (FAF) and non-saponifiable fractions (NSF). However, it did not inhibit [14C]malonyl CoA incorporation into FAF and only slightly inhibited [14C]mevalonate incorporation into NSF. The activity of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl CoA (HMG-CoA) synthase was inhibited more strongly than the incorporation of [14C]3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl CoA into NSF; this could account for the CM-55 inhibition of [14C]acetyl CoA incorporation into NSF.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arison B. H., Omura S. Revised structure of cerulenin. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1974 Jan;27(1):28–30. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.27.28. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Agnolo G., Rosenfeld I. S., Awaya J., Omura S., Vagelos P. R. Inhibition of fatty acid synthesis by the antibiotic cerulenin. Specific inactivation of beta-ketoacyl-acyl carrier protein synthetase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Nov 29;326(2):155–156. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(73)90241-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FERGUSON J. J., Jr, RUDNEY H. The biosynthesis of beta-hydroxy-beta-methylglutaryl coenzyme A in yeast. I. Identification and purification of the hydroxymethylglutaryl coenzymecondensing enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1959 May;234(5):1072–1075. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg I., Walker J. R., Bloch K. Inhibition of lipid synthesis in Escherichia coli cells by the antibiotic cerulenin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1973 May;3(5):549–554. doi: 10.1128/aac.3.5.549. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldfarb S., Pitot H. C. Improved assay of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase. J Lipid Res. 1971 Jul;12(4):512–515. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawaguchi A. Control of ergosterol biosynthesis in yeast. Existence of lipid inhibitors. J Biochem. 1970 Feb;67(2):219–227. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a129245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MATSUMAE A., KAMIO Y., HATA T. STUDIES ON CERULENIN. I. STUDIES ON CERULENIN PRODUCING STRAIN. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1963 Nov;16:236–238. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nomura S., Horiuchi T., Omura S., Hata T. The action mechanism of cerulenin. I. Effect of cerulenin on sterol and fatty acid biosynthesis in yeast. J Biochem. 1972 May;71(5):783–796. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a129827. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ono T., Kesado T., Awaya J., Omura S. Target of inhibition by the anti-lipogenic antibiotic cerulenin of sterol synthesis in yeast. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Apr 23;57(4):1119–1124. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(74)90812-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sumper M., Riepertinger C. Structural relationship of biotin-containing enzymes. Acetyl-CoA carboxylase and pyruvate carboxylase from yeast. Eur J Biochem. 1972 Sep 18;29(2):237–248. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1972.tb01980.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vance D., Goldberg I., Mitsuhashi O., Bloch K. Inhibition of fatty acid synthetases by the antibiotic cerulenin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Aug 7;48(3):649–656. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90397-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



