Abstract
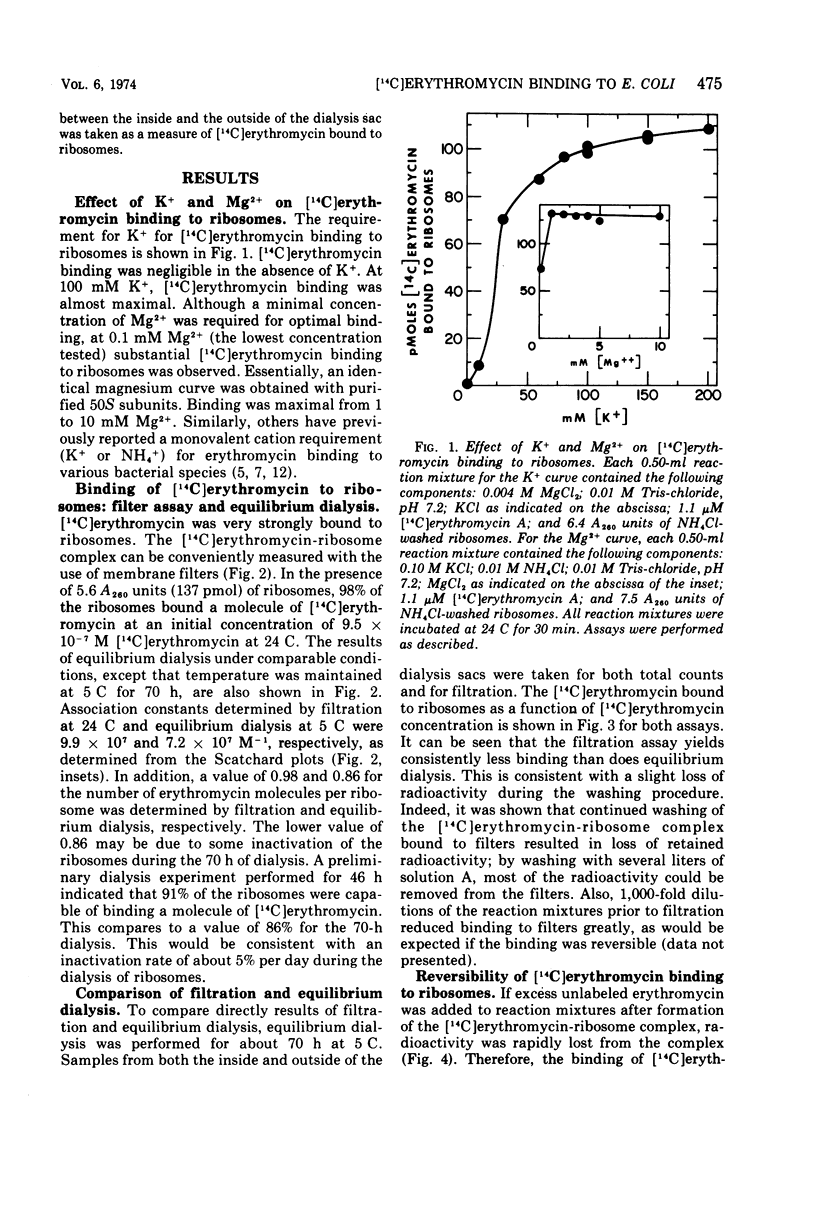
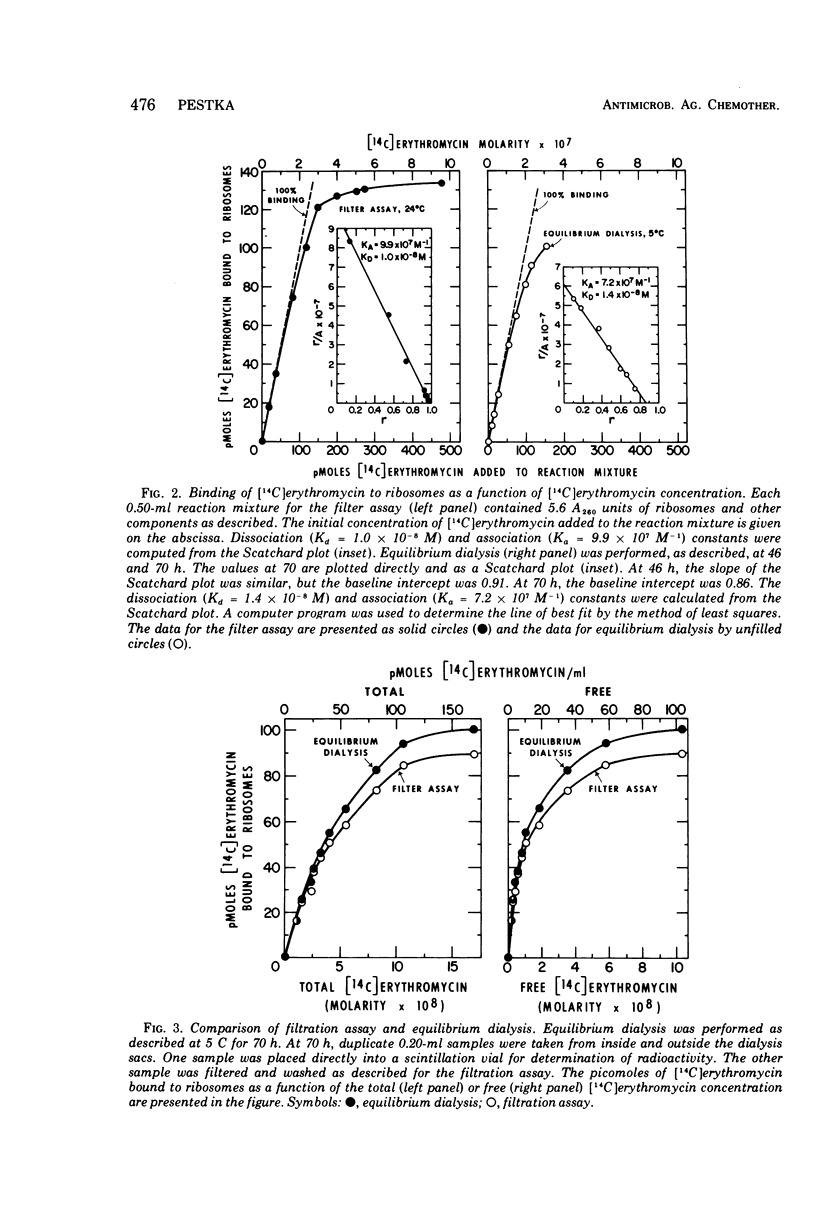
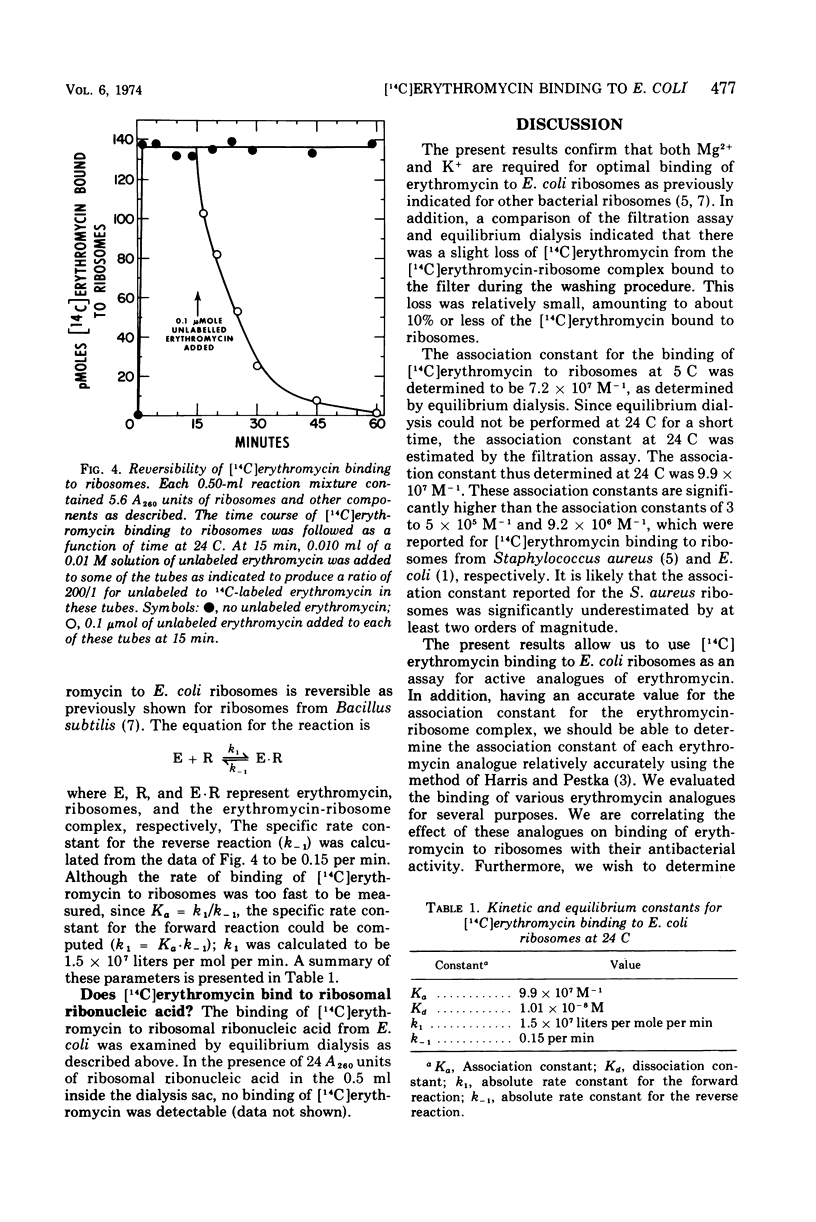
Erythromycin binding to Escherichia coli ribosomes required K+ and Mg2+. Under optimal conditions, the dissociation constant for erythromycin binding to E. coli ribosomes was found to be 1.0 × 10−8 M and 1.4 × 10−8 M at 24 C and 5 C, respectively. One molecule of [14C]erythromycin was bound to each 70S ribosome at equilibrium. Binding of erythromycin to ribosomes was rapid and reversible. The specific rate constants for the forward and reverse reactions were 1.7 × 107 liters per mol per min and 0.15 per min, respectively.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Fernández-Muñoz R., Vazquez D. Quantitative binding of 14C-erythromycin a to E. coli ribosomes. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1973 Feb;26(2):107–108. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.26.107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris R., Pestka S. Studies on the formation of transfer ribonucleic acid-ribosome complexes. XXIV. Effects of antibiotics on binding of aminoacyl-oligonucleotides to ribosomes. J Biol Chem. 1973 Feb 25;248(4):1168–1174. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mao J. C., Putterman M. The intermolecular complex of erythromycin and ribosome. J Mol Biol. 1969 Sep 14;44(2):347–361. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90180-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mao J. C., Tardrew P. L. Demethylation of erythromycins by rabbit tissues in vitro. Biochem Pharmacol. 1965 Jul;14(7):1049–1058. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(65)90033-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mao J. C. The stoichiometry of erythromycin binding to ribosomal particles of Staphylococcus aureus. Biochem Pharmacol. 1967 Dec;16(12):2441–2443. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(67)90232-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oleinick N. L., Corcoran J. W. Two types of binding of erythromycin to ribosomes from antibiotic-sensitive and -resistant Bacillus subtilis 168. J Biol Chem. 1969 Feb 25;244(4):727–735. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pestka S. Inhibitors of ribosome functions. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1971;25:487–562. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.25.100171.002415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pestka S. Studies on the formation of transfer ribonucleic acid-ribosome complexes. 3. The formation of peptide bonds by ribosomes in the absence of supernatant enzymes. J Biol Chem. 1968 May 25;243(10):2810–2820. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka K., Teraoka H., Nagira T., Tamaki M. Formation of C14-erythromycin-ribosome complex. J Biochem. 1966 Jun;59(6):632–634. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a128355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taubman S. B., Jones N. R., Young F. E., Corcoran J. W. Sensitivity and resistance to erythromycin in Bacillus subtilis 168: the ribosomal binding of erythromycin and chloramphenicol. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Aug 17;123(2):438–440. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(66)90301-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teraoka H. A reversible change in the ability of Escherichia coli ribosomes to bind to erythromycin. J Mol Biol. 1970 Mar;48(3):511–515. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90062-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teraoka H. Binding of erythromycin to Escherichia coli ribosomes. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1971 May;24(5):302–309. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.24.302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



