Abstract
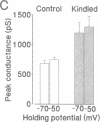
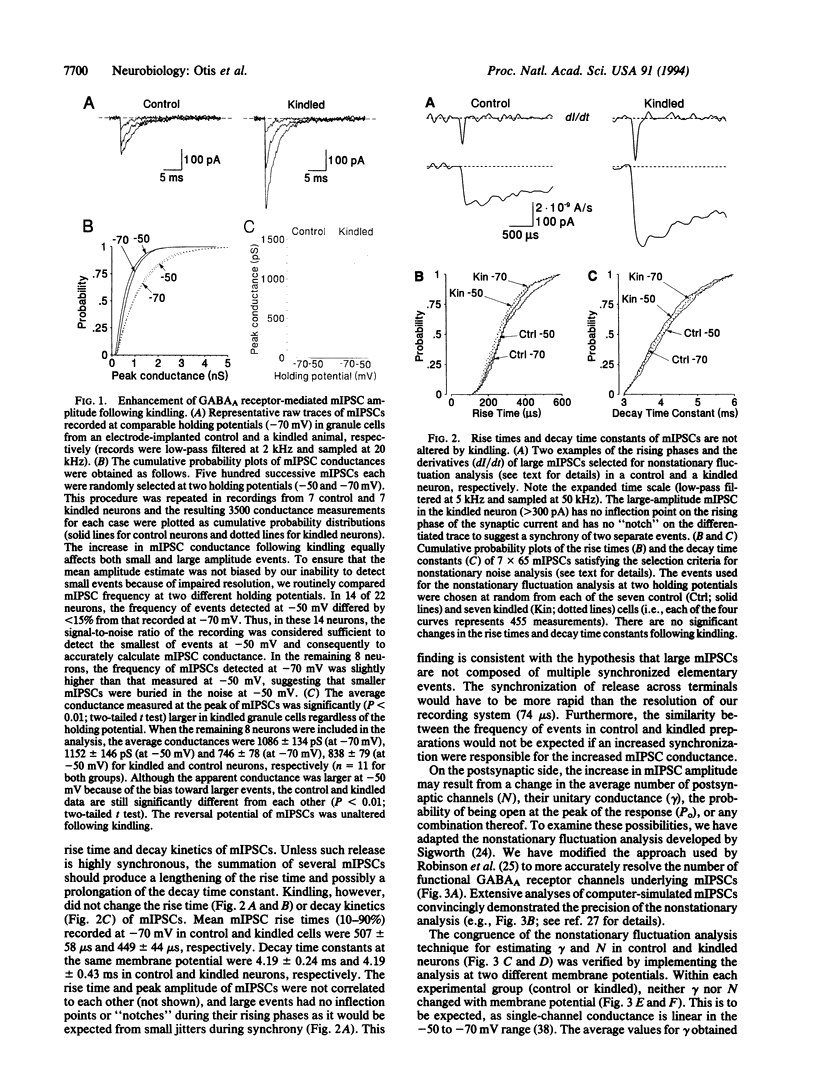
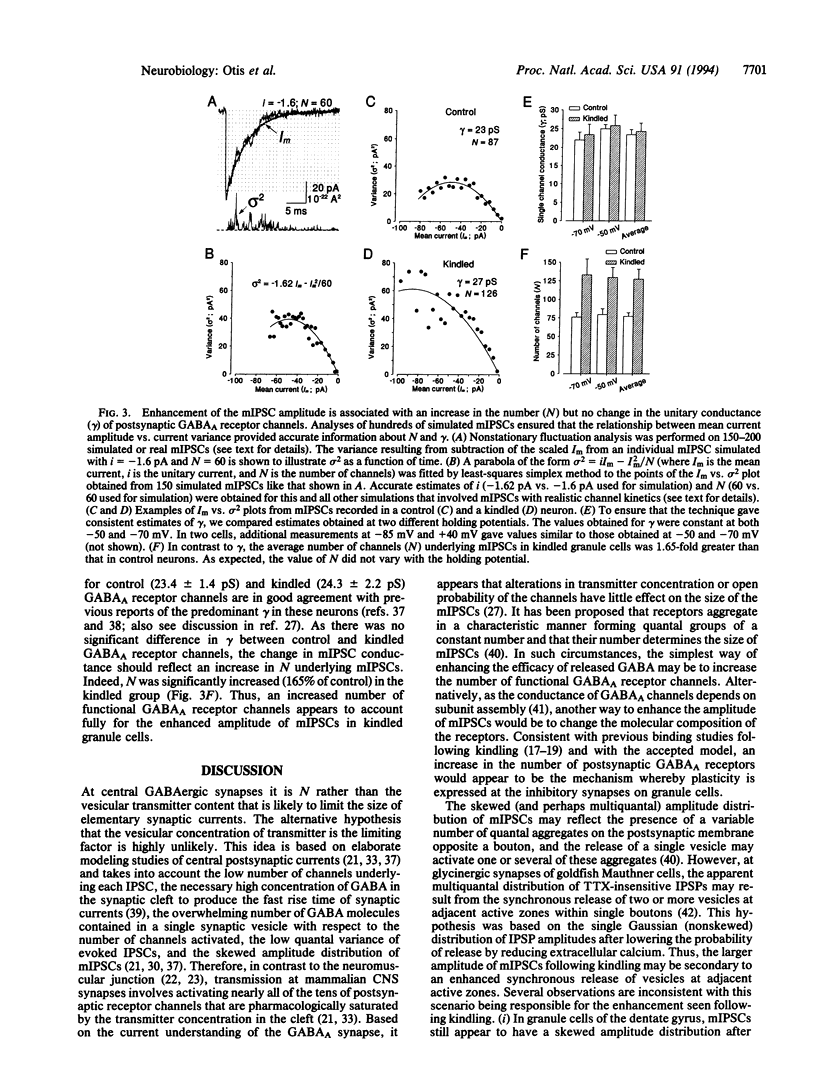
Whole-cell patch-clamp recordings unveiled a substantial increase in the amplitude, but no change in the frequency, of miniature inhibitory postsynaptic currents (mIPSCs) in dentate gyrus granule cells following chronic epilepsy induced by kindling. This novel and persistent enhancement of gamma-aminobutyric acid type A (GABAA) receptor-mediated inhibition lasted for at least 48 hr following its induction. Nearly a doubling of the number of activated functional postsynaptic GABAA receptor channels during mIPSCs without any change in single-channel conductance or kinetics could be demonstrated using nonstationary fluctuation analysis. As postsynaptic GABAA receptors are likely to be pharmacologically saturated by the transmitter concentration in the cleft, incrementing the number of functional receptor channels may be the most effective means to augment inhibition in the mammalian brain.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bliss T. V., Collingridge G. L. A synaptic model of memory: long-term potentiation in the hippocampus. Nature. 1993 Jan 7;361(6407):31–39. doi: 10.1038/361031a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Busch C., Sakmann B. Synaptic transmission in hippocampal neurons: numerical reconstruction of quantal IPSCs. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1990;55:69–80. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1990.055.01.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colquhoun D., Hawkes A. G. On the stochastic properties of bursts of single ion channel openings and of clusters of bursts. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1982 Dec 24;300(1098):1–59. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1982.0156. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies C. H., Starkey S. J., Pozza M. F., Collingridge G. L. GABA autoreceptors regulate the induction of LTP. Nature. 1991 Feb 14;349(6310):609–611. doi: 10.1038/349609a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Koninck Y., Mody I. Noise analysis of miniature IPSCs in adult rat brain slices: properties and modulation of synaptic GABAA receptor channels. J Neurophysiol. 1994 Apr;71(4):1318–1335. doi: 10.1152/jn.1994.71.4.1318. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards F. A., Konnerth A., Sakmann B. Quantal analysis of inhibitory synaptic transmission in the dentate gyrus of rat hippocampal slices: a patch-clamp study. J Physiol. 1990 Nov;430:213–249. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1990.sp018289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards F. Neurobiology. LTP is a long term problem. Nature. 1991 Mar 28;350(6316):271–272. doi: 10.1038/350271a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faber D. S., Young W. S., Legendre P., Korn H. Intrinsic quantal variability due to stochastic properties of receptor-transmitter interactions. Science. 1992 Nov 27;258(5087):1494–1498. doi: 10.1126/science.1279813. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray R., Johnston D. Rectification of single GABA-gated chloride channels in adult hippocampal neurons. J Neurophysiol. 1985 Jul;54(1):134–142. doi: 10.1152/jn.1985.54.1.134. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green W. N., Ross A. F., Claudio T. Acetylcholine receptor assembly is stimulated by phosphorylation of its gamma subunit. Neuron. 1991 Oct;7(4):659–666. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90378-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kairiss E. W., Racine R. J., Smith G. K. The development of the interictal spike during kindling in the rat. Brain Res. 1984 Nov 19;322(1):101–110. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(84)91185-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kano M., Rexhausen U., Dreessen J., Konnerth A. Synaptic excitation produces a long-lasting rebound potentiation of inhibitory synaptic signals in cerebellar Purkinje cells. Nature. 1992 Apr 16;356(6370):601–604. doi: 10.1038/356601a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirsch J., Wolters I., Triller A., Betz H. Gephyrin antisense oligonucleotides prevent glycine receptor clustering in spinal neurons. Nature. 1993 Dec 23;366(6457):745–748. doi: 10.1038/366745a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korn H., Bausela F., Charpier S., Faber D. S. Synaptic noise and multiquantal release at dendritic synapses. J Neurophysiol. 1993 Sep;70(3):1249–1254. doi: 10.1152/jn.1993.70.3.1249. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korn H., Oda Y., Faber D. S. Long-term potentiation of inhibitory circuits and synapses in the central nervous system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jan 1;89(1):440–443. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.1.440. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kosaka T., Hama K., Wu J. Y. GABAergic synaptic boutons in the granule cell layer of rat dentate gyrus. Brain Res. 1984 Feb 20;293(2):353–359. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(84)91242-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köhr G., De Koninck Y., Mody I. Properties of NMDA receptor channels in neurons acutely isolated from epileptic (kindled) rats. J Neurosci. 1993 Aug;13(8):3612–3627. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.13-08-03612.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köhr G., Mody I. Endogenous intracellular calcium buffering and the activation/inactivation of HVA calcium currents in rat dentate gyrus granule cells. J Gen Physiol. 1991 Nov;98(5):941–967. doi: 10.1085/jgp.98.5.941. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Land B. R., Salpeter E. E., Salpeter M. M. Acetylcholine receptor site density affects the rising phase of miniature endplate currents. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jun;77(6):3736–3740. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.6.3736. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Llano I., Leresche N., Marty A. Calcium entry increases the sensitivity of cerebellar Purkinje cells to applied GABA and decreases inhibitory synaptic currents. Neuron. 1991 Apr;6(4):565–574. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopes da Silva F. H., Kamphuis W., Wadman W. J. Epileptogenesis as a plastic phenomenon of the brain, a short review. Acta Neurol Scand Suppl. 1992;140:34–40. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0404.1992.tb04468.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maconochie D. J., Zempel J. M., Steinbach J. H. How quickly can GABAA receptors open? Neuron. 1994 Jan;12(1):61–71. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(94)90152-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manabe T., Renner P., Nicoll R. A. Postsynaptic contribution to long-term potentiation revealed by the analysis of miniature synaptic currents. Nature. 1992 Jan 2;355(6355):50–55. doi: 10.1038/355050a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNamara J. O., Peper A. M., Patrone V. Repeated seizures induce long-term increase in hippocampal benzodiazepine receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 May;77(5):3029–3032. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.5.3029. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miles R., Wong R. K. Latent synaptic pathways revealed after tetanic stimulation in the hippocampus. Nature. 1987 Oct 22;329(6141):724–726. doi: 10.1038/329724a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mody I., Heinemann U. NMDA receptors of dentate gyrus granule cells participate in synaptic transmission following kindling. Nature. 1987 Apr 16;326(6114):701–704. doi: 10.1038/326701a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mott D. D., Lewis D. V. Facilitation of the induction of long-term potentiation by GABAB receptors. Science. 1991 Jun 21;252(5013):1718–1720. doi: 10.1126/science.1675489. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliver M. W., Miller J. J. Alterations of inhibitory processes in the dentate gyrus following kindling-induced epilepsy. Exp Brain Res. 1985;57(3):443–447. doi: 10.1007/BF00237830. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otis T. S., Mody I. Modulation of decay kinetics and frequency of GABAA receptor-mediated spontaneous inhibitory postsynaptic currents in hippocampal neurons. Neuroscience. 1992 Jul;49(1):13–32. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(92)90073-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pitler T. A., Alger B. E. Postsynaptic spike firing reduces synaptic GABAA responses in hippocampal pyramidal cells. J Neurosci. 1992 Oct;12(10):4122–4132. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.12-10-04122.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Racine R. J. Modification of seizure activity by electrical stimulation. II. Motor seizure. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1972 Mar;32(3):281–294. doi: 10.1016/0013-4694(72)90177-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson H. P., Sahara Y., Kawai N. Nonstationary fluctuation analysis and direct resolution of single channel currents at postsynaptic sites. Biophys J. 1991 Feb;59(2):295–304. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(91)82223-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shin C., Pedersen H. B., McNamara J. O. gamma-Aminobutyric acid and benzodiazepine receptors in the kindling model of epilepsy: a quantitative radiohistochemical study. J Neurosci. 1985 Oct;5(10):2696–2701. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.05-10-02696.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sigworth F. J. The variance of sodium current fluctuations at the node of Ranvier. J Physiol. 1980 Oct;307:97–129. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013426. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staley K. J., Otis T. S., Mody I. Membrane properties of dentate gyrus granule cells: comparison of sharp microelectrode and whole-cell recordings. J Neurophysiol. 1992 May;67(5):1346–1358. doi: 10.1152/jn.1992.67.5.1346. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stelzer A., Slater N. T., ten Bruggencate G. Activation of NMDA receptors blocks GABAergic inhibition in an in vitro model of epilepsy. Nature. 1987 Apr 16;326(6114):698–701. doi: 10.1038/326698a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toyoshima C., Unwin N. Ion channel of acetylcholine receptor reconstructed from images of postsynaptic membranes. Nature. 1988 Nov 17;336(6196):247–250. doi: 10.1038/336247a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traynelis S. F., Silver R. A., Cull-Candy S. G. Estimated conductance of glutamate receptor channels activated during EPSCs at the cerebellar mossy fiber-granule cell synapse. Neuron. 1993 Aug;11(2):279–289. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(93)90184-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuff L. P., Racine R. J., Adamec R. The effects of kindling on GABA-mediated inhibition in the dentate gyrus of the rat. I. Paired-pulse depression. Brain Res. 1983 Oct 24;277(1):79–90. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(83)90909-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuff L. P., Racine R. J., Mishra R. K. The effects of kindling on GABA-mediated inhibition in the dentate gyrus of the rat. II. Receptor binding. Brain Res. 1983 Oct 24;277(1):91–98. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(83)90910-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unwin N. Nicotinic acetylcholine receptor at 9 A resolution. J Mol Biol. 1993 Feb 20;229(4):1101–1124. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1993.1107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valdes F., Dasheiff R. M., Birmingham F., Crutcher K. A., McNamara J. O. Benzodiazepine receptor increases after repeated seizures: evidence for localization to dentate granule cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jan;79(1):193–197. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.1.193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verdoorn T. A., Draguhn A., Ymer S., Seeburg P. H., Sakmann B. Functional properties of recombinant rat GABAA receptors depend upon subunit composition. Neuron. 1990 Jun;4(6):919–928. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90145-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyllie D. J., Manabe T., Nicoll R. A. A rise in postsynaptic Ca2+ potentiates miniature excitatory postsynaptic currents and AMPA responses in hippocampal neurons. Neuron. 1994 Jan;12(1):127–138. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(94)90158-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Jonge M., Racine R. J. The development and decay of kindling-induced increases in paired-pulse depression in the dentate gyrus. Brain Res. 1987 Jun 2;412(2):318–328. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(87)91139-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]