Abstract
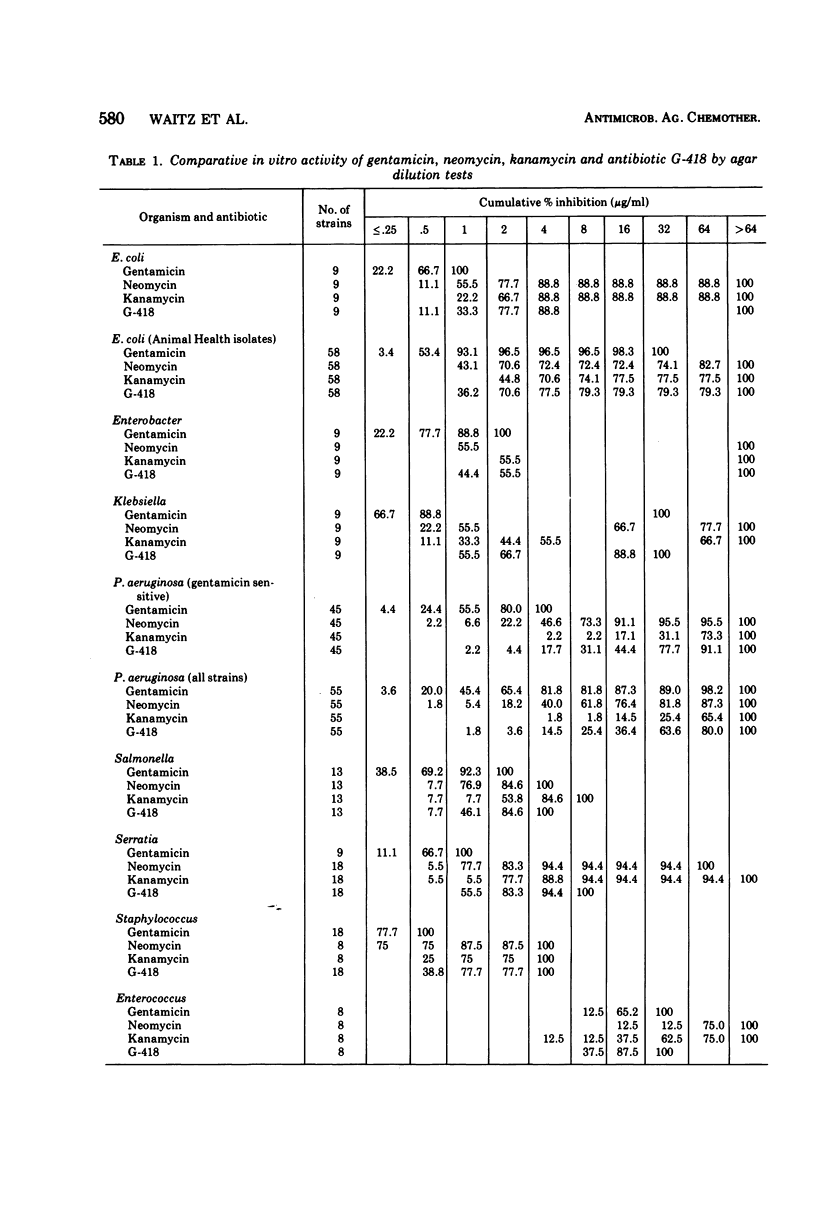
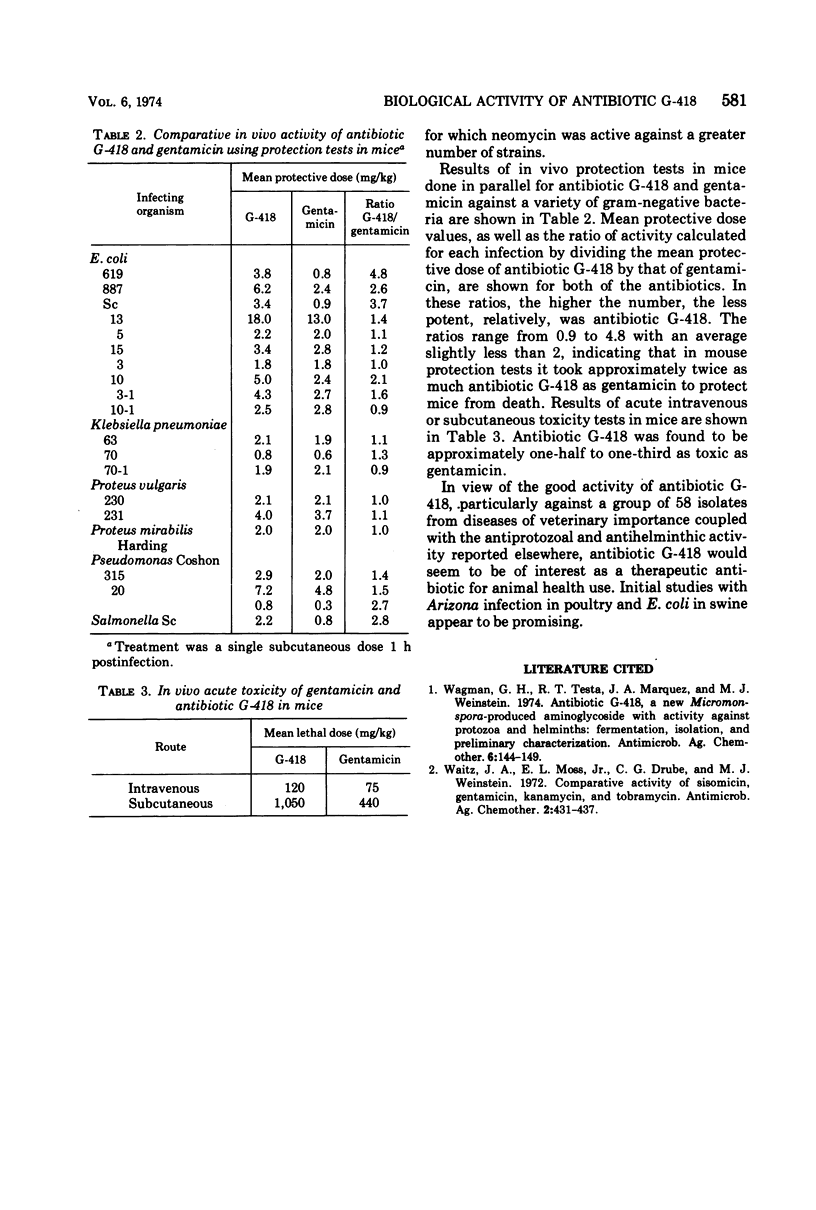
On the basis of parallel in vitro studies with antibiotic G-418, gentamicin, neomycin, and kanamycin, antibiotic G-418 was found to be less potent than gentamicin but more active than either kanamycin or neomycin against most strains, with the exception of Pseudomonas, for which neomycin was more active than antibiotic G-418, and enterococci, for which antibiotic G-418 was more active than the other three antibiotics. Mouse protection tests indicated that antibiotic G-418 is approximately half as potent as gentamicin and its acute toxicity is one-half to one-third that of gentamicin.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Wagman G. H., Testa R. T., Marquez J. A., Weinstein M. J. Antibiotic G-418, a new Micromonospora-produced aminoglycoside with activity against protozoa and helminths: fermentation, isolation, and preliminary characterization. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1974 Aug;6(2):144–149. doi: 10.1128/aac.6.2.144. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waitz J. A., Moss E. L., Jr, Drube C. G., Weinstein M. J. Comparative activity of sisomicin, gentamicin, kanamycin, and tobramycin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1972 Dec;2(6):431–437. doi: 10.1128/aac.2.6.431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


