Abstract
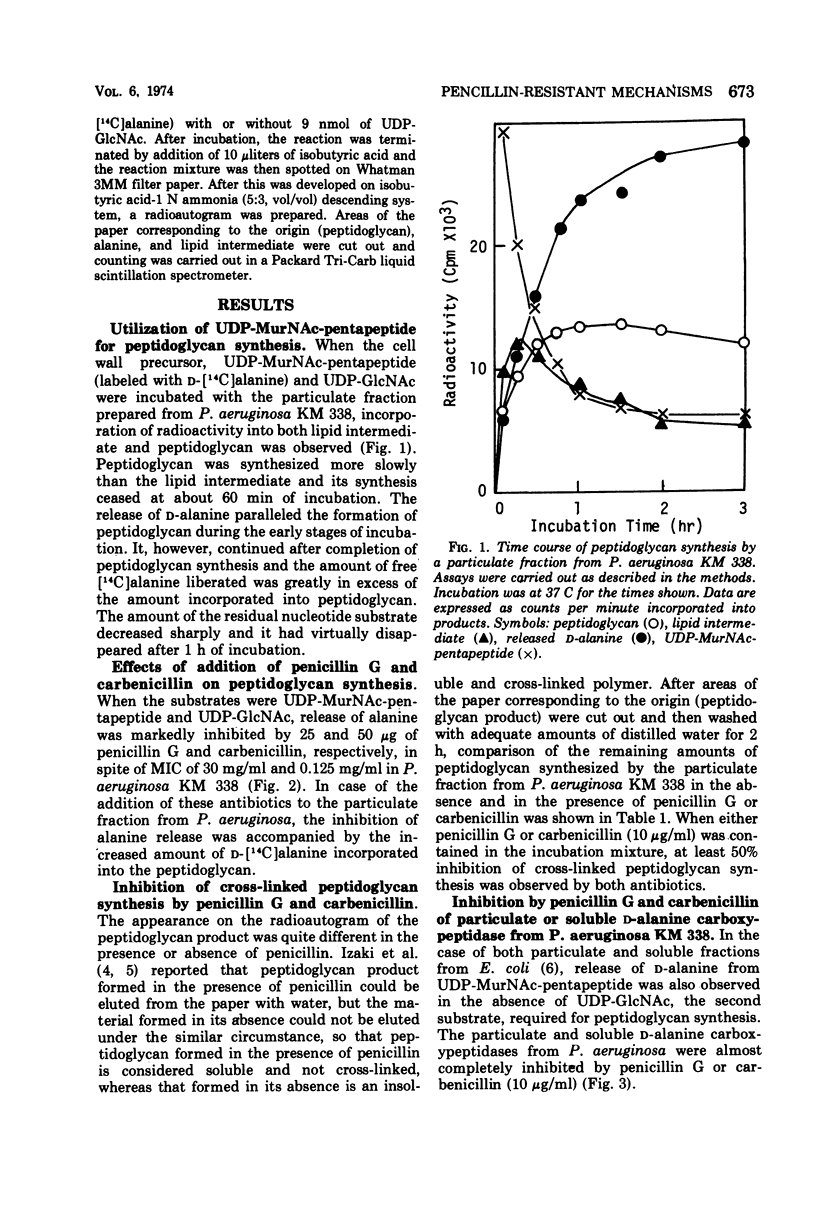
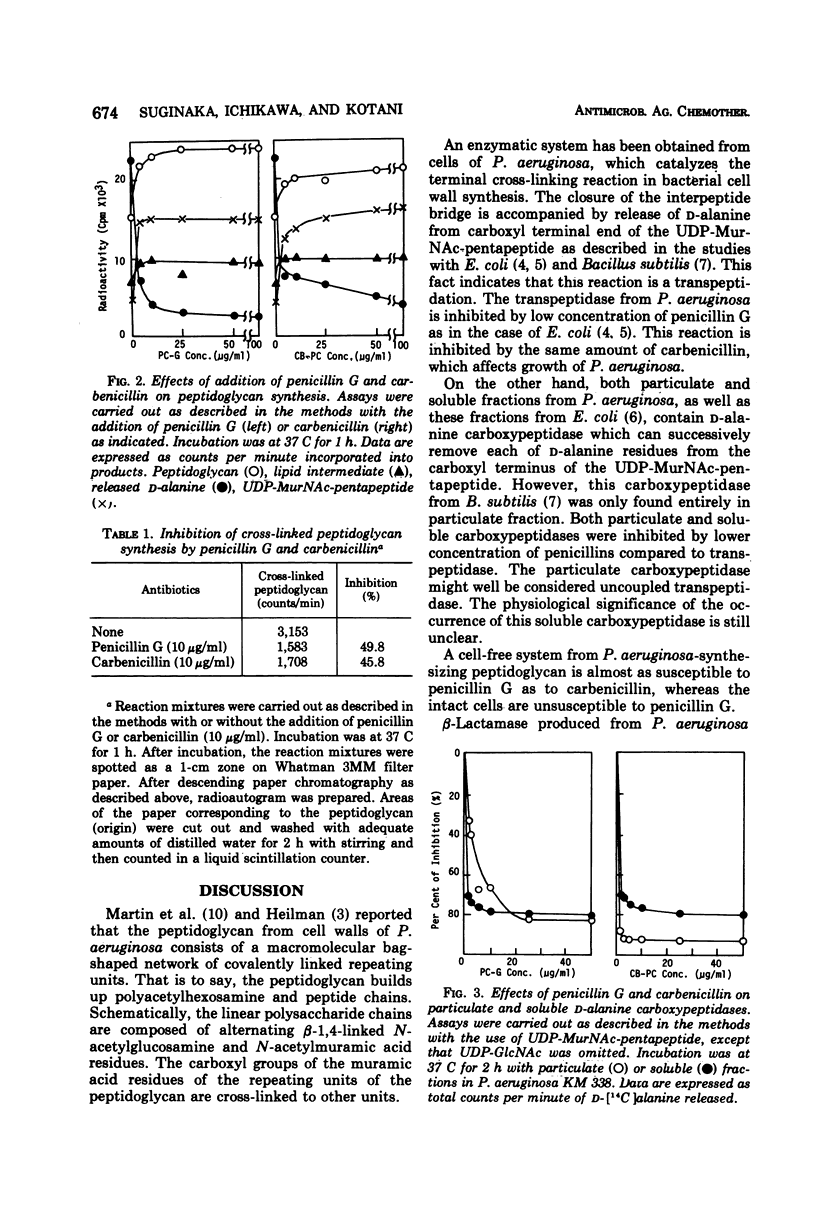
A membrane fraction from Pseudomonas aeruginosa KM 338 was shown to catalyze in vitro peptidoglycan synthesis from uridine 5′-diphosphate-N-acetylmuramyl-l-alanyl-d- glutamyl-meso-diaminopimelyl-d-alanyl-d-alanine and uridine 5′-diphosphate-N-acetylglucosamine. Synthesized peptidoglycan was partially cross-linked by transpeptidation, which was accompanied by the release of d-alanine. This reaction was strongly inhibited by 25 and 50 μg of penicillin G and carbenicillin per ml respectively, whereas the intact cells were relatively resistant to penicillins (minimal inhibitory concentration of penicillin G and carbenicillin, 30 and 0.125 mg/ml, respectively). Soluble d-alanine carboxypeptidase present in P. aeruginosa KM 338 was studied as well, which was found almost completely inhibited by penicillin G and carbenicillin (10 μg/ml).
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Araki Y., Shimada A., Ito E. Effect of penicillin on cell wall mucopeptide synthesis in a Escherichia coli particulate system. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1966 May 25;23(4):518–525. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(66)90760-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heilmann H. D. On the peptidoglycan of the cell walls of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Eur J Biochem. 1972 Dec 18;31(3):456–463. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1972.tb02552.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Izaki K., Matsuhashi M., Strominger J. L. Biosynthesis of the peptidoglycan of bacterial cell walls. 8. Peptidoglycan transpeptidase and D-alanine carboxypeptidase: penicillin-sensitive enzymatic reaction in strains of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1968 Jun 10;243(11):3180–3192. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Izaki K., Matsuhashi M., Strominger J. L. Glycopeptide transpeptidase and D-alanine carboxypeptidase: penicillin-sensitive enzymatic reactions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Mar;55(3):656–663. doi: 10.1073/pnas.55.3.656. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Izaki K., Strominger J. L. Biosynthesis of the peptidoglycan of bacterial cell walls. XIV. Purification and properties of two D-alanine carboxypeptidases from Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1968 Jun 10;243(11):3193–3201. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEDERBERG J. Mechanism of action of penicillin. J Bacteriol. 1957 Jan;73(1):144–144. doi: 10.1128/jb.73.1.144-144.1957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawrence P. J., Strominger J. L. Biosynthesis of the peptidoglycan of bacterial cell walls. XVI. The reversible fixation of radioactive penicillin G to the D-alanine carboxypeptidase of Bacillus subtilis. J Biol Chem. 1970 Jul 25;245(14):3660–3666. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lederberg J. BACTERIAL PROTOPLASTS INDUCED BY PENICILLIN. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1956 Sep;42(9):574–577. doi: 10.1073/pnas.42.9.574. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin H. H., Heilmann H. D., Preusser H. J. State of the rigid-layer in celll walls of some gram-negative Bacteria. Arch Mikrobiol. 1972;83(4):332–346. doi: 10.1007/BF00425246. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mirelman D., Sharon N. Biosynthesis of peptidoglycan by a cell wall preparation of Staphylococcus aureus and its inhibition by penicillin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Mar 10;46(5):1909–1917. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90069-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PARK J. T., STROMINGER J. L. Mode of action of penicillin. Science. 1957 Jan 18;125(3238):99–101. doi: 10.1126/science.125.3238.99. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PARK J. T. Uridine-5'-pyrophosphate derivatives. II. Isolation from Staphylococcus aureus. J Biol Chem. 1952 Feb;194(2):877–884. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STROMINGER J. L., PARK J. T., THOMPSON R. E. Composition of the cell wall of Staphylococcus aureus: its relation to the mechanism of action of penicillin. J Biol Chem. 1959 Dec;234:3263–3268. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schleifer K. H., Kandler O. Peptidoglycan types of bacterial cell walls and their taxonomic implications. Bacteriol Rev. 1972 Dec;36(4):407–477. doi: 10.1128/br.36.4.407-477.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strominger J. L., Blumberg P. M., Suginaka H., Umbreit J., Wickus G. G. How penicillin kills bacteria: progress and problems. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1971 Dec 31;179(1057):369–383. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1971.0103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suginaka H., Blumberg P. M., Strominger J. L. Multiple penicillin-binding components in Bacillus subtilis, Bacillus cereus, Staphylococcus aureus, and Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1972 Sep 10;247(17):5279–5288. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tipper D. J., Strominger J. L. Biosynthesis of the peptidoglycan of bacterial cell walls. XII. Inhibition of cross-linking by penicillins and cephalosporins: studies in Staphylococcus aureus in vivo. J Biol Chem. 1968 Jun 10;243(11):3169–3179. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tipper D. J., Strominger J. L. Mechanism of action of penicillins: a proposal based on their structural similarity to acyl-D-alanyl-D-alanine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Oct;54(4):1133–1141. doi: 10.1073/pnas.54.4.1133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wise E. M., Jr, Park J. T. Penicillin: its basic site of action as an inhibitor of a peptide cross-linking reaction in cell wall mucopeptide synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Jul;54(1):75–81. doi: 10.1073/pnas.54.1.75. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



