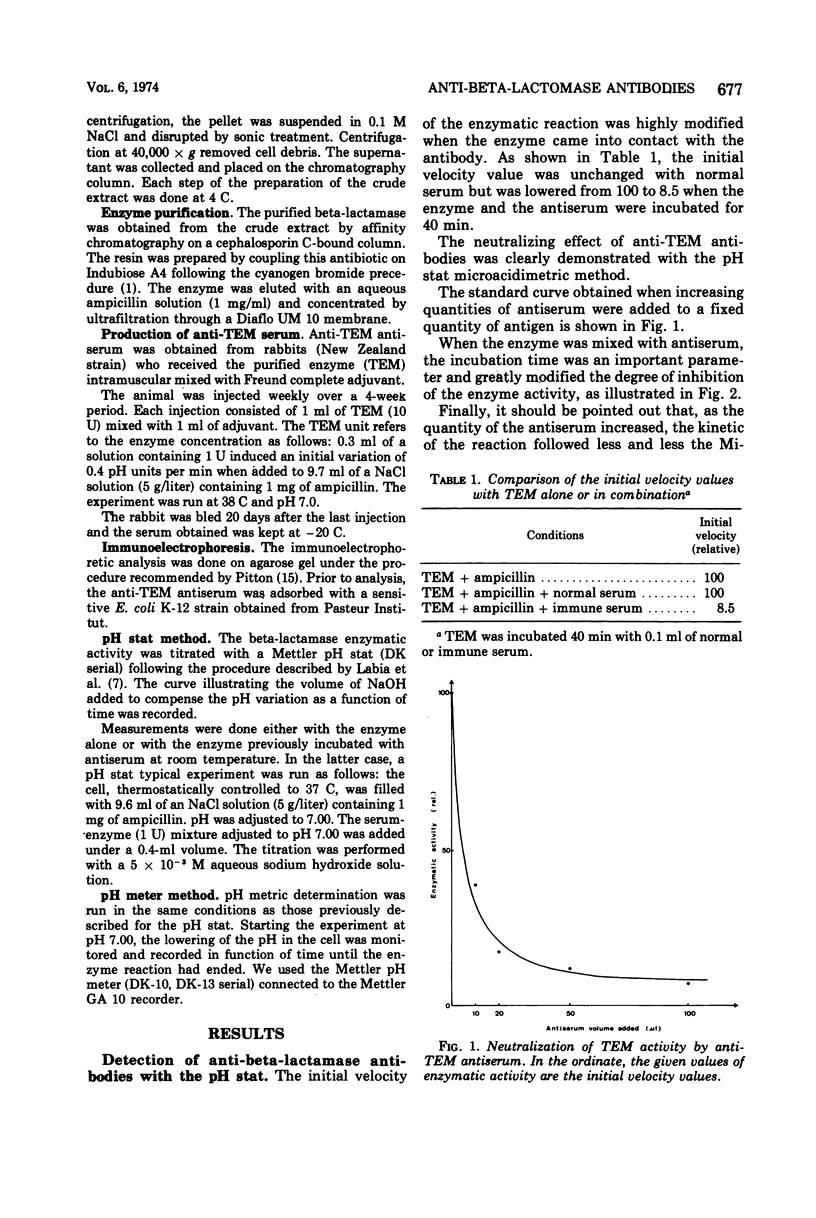
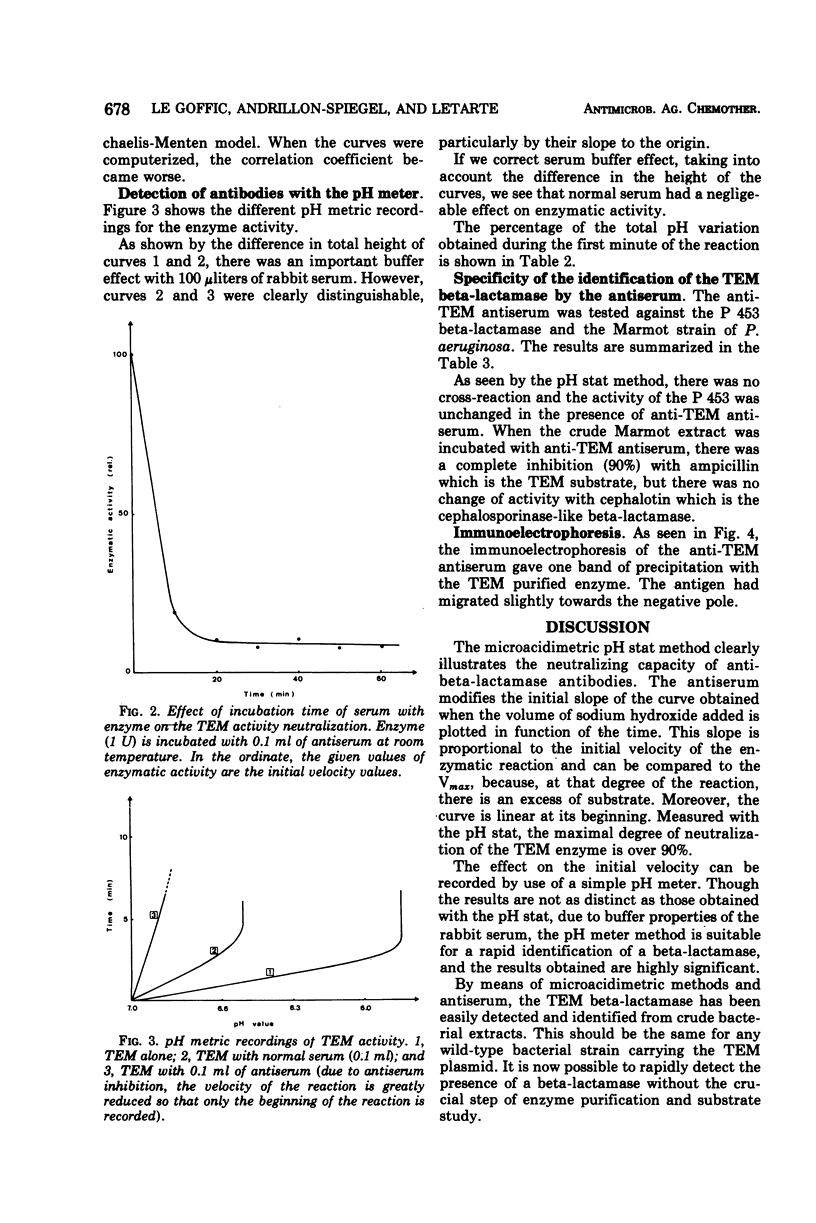
Abstract
A beta-lactamase was extracted from an Escherichia coli K-12 strain carrying the R-TEM plasmid and has been purified by affinity chromatography. Antisera to this enzyme were prepared in the rabbit, and the enzyme-antibody neutralization reaction has been evaluated with acidimetric methods (pH stat or pH meter). Under defined experimental conditions, it is now possible to clearly illustrate the enzyme-antibody reaction by means of accurate, rapid, and simple-to-perform methods. These methods are in accord with the specificity of the two reactive partners and allow the detection of the enzyme in a crude bacterial extract which would eventually contain more than one beta-lactamase.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Dale J. W., Smith J. T. A direct comparison of two unusual R-factor-mediated -lactamases. Biochem J. 1972 Jun;128(1):173–174. doi: 10.1042/bj1280173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dale J. W., Smith J. T. Some relationships between R-factor and chromosomal -lactamase in Gram-negative bacteria. Biochem J. 1971 Jul;123(4):507–512. doi: 10.1042/bj1230507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Datta N., Richmond M. H. The purification and properties of a penicillinase whose synthesis is mediated by an R-factor in Escherichia coli. Biochem J. 1966 Jan;98(1):204–209. doi: 10.1042/bj0980204. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jack G. W., Richmond M. H. A comparative study of eight distinct beta-lactamases synthesized by gram-negative bacteria. J Gen Microbiol. 1970 Apr;61(1):43–61. doi: 10.1099/00221287-61-1-43. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kazmierczak A., Philippon A., Chardon H., Labia R., Le Goffic F. Constantes enzymatiques (Km et Vmax) des beta-lactamases mesurées par une méthode micro-acidimétrique couplée a l'ordinateur. Ann Microbiol (Paris) 1973 Oct;124(3):259–268. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labia R., Andrillon J., Le Goffic F. Computerized microacidimetric determination of beta lactamase Michaelis-Menten constants. FEBS Lett. 1973 Jun 15;33(1):42–44. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(73)80154-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linström E. B., Boman H. G., Steele B. B. Resistance of Escherichia coli to penicillins. VI. Purification and characterization of the chromosomally mediated penicillinase present in ampA-containing strains. J Bacteriol. 1970 Jan;101(1):218–231. doi: 10.1128/jb.101.1.218-231.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogawara H., Maeda K., Umezawa H. A -lactamase of Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Nov 10;289(1):203–211. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(72)90123-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POLLOCK M. R. An immunological study of the constitutive and the penicillin-induced penicillinases of Bacillus cereus, based on specific enzyme neutralization by antibody. J Gen Microbiol. 1956 Feb;14(1):90–108. doi: 10.1099/00221287-14-1-90. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POLLOCK M. R. The cell-bound penicillinase of Bacillus cereus. J Gen Microbiol. 1956 Aug;15(1):154–169. doi: 10.1099/00221287-15-1-154. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pitton J. S. Mechanisms of bacterial resistance to antibiotics. Ergeb Physiol. 1972;65:15–93. doi: 10.1007/3-540-05814-1_2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RICHMOND M. H. Immunological properties of exopenicillinase synthesized by Bacillus cereus 569/H in the presence of amino acid analogues. Biochem J. 1960 Oct;77:112–121. doi: 10.1042/bj0770112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richmond M. H., Sykes R. B. The beta-lactamases of gram-negative bacteria and their possible physiological role. Adv Microb Physiol. 1973;9:31–88. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2911(08)60376-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roupas A., Pitton J. S. R factor-mediated and chromosomal resistance to ampicillin in Escherichia coli. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1974 Feb;5(2):186–191. doi: 10.1128/aac.5.2.186. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamagishi S., O'Hara K., Sawai T., Mitsuhashi S. The purification and properties of penicillin beta-lactamases mediated by transmissible R factors in Escherichia coli. J Biochem. 1969 Jul;66(1):11–20. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a129111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




