Abstract
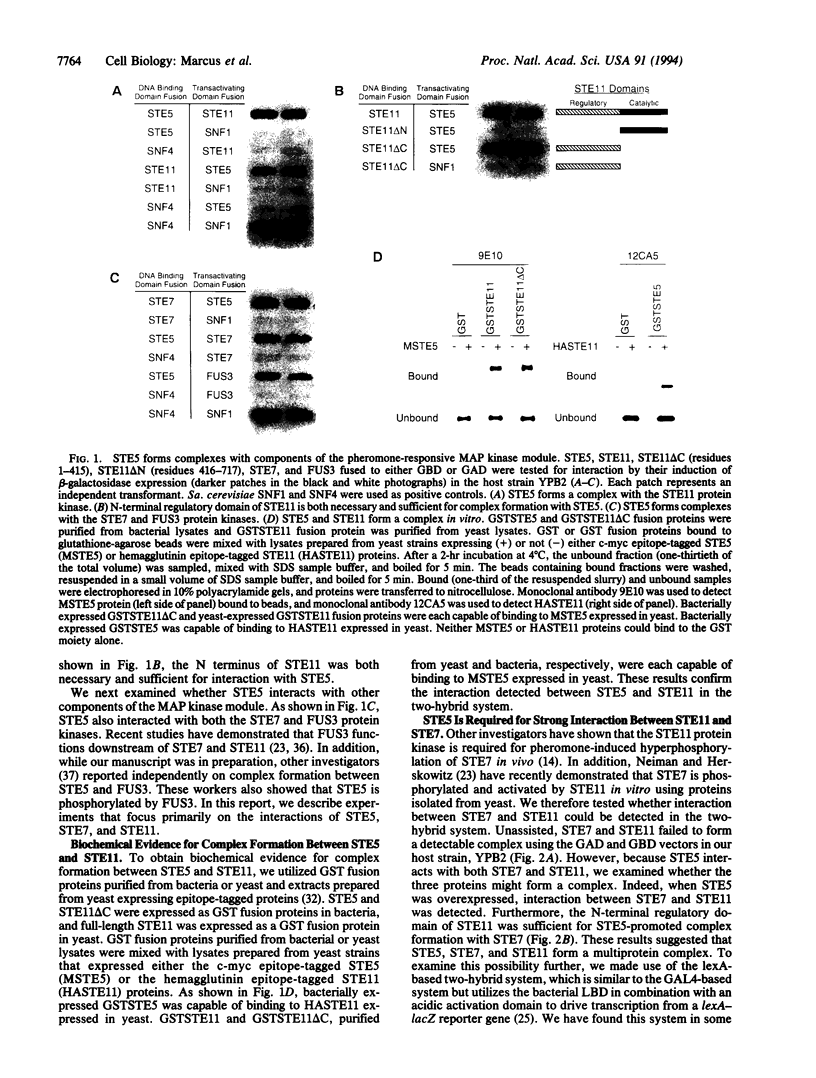
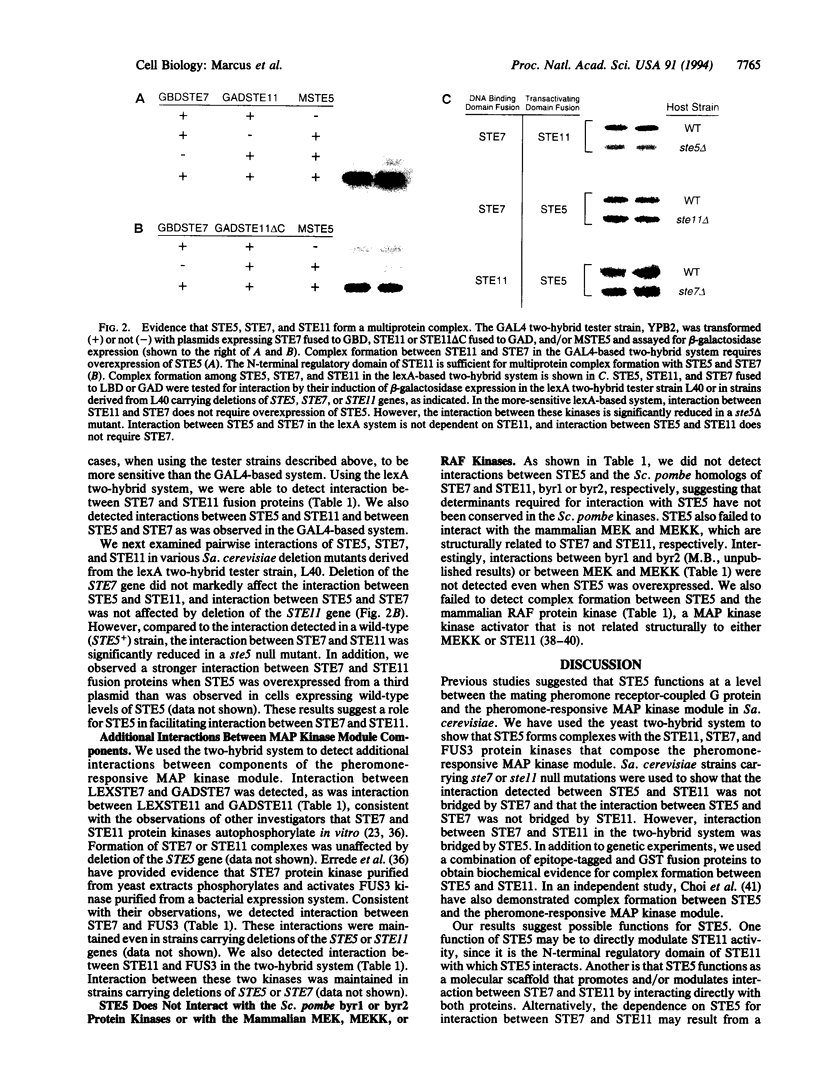
We present genetic evidence for complex formation of STE5 and the STE11, STE7, and FUS3 protein kinases, the pheromone-responsive mitogen-activated protein kinase module of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Interaction between STE5 and STE11 is not dependent on STE7, and interaction between STE5 and STE7 does not require STE11. The N-terminal regulatory domain of STE11 is both necessary and sufficient for interaction with STE5. Interaction between STE7 and STE11 is bridged by STE5, suggesting the formation of a multiprotein complex. We also demonstrate biochemical interaction between STE5 and STE11 by using a combination of bacterially expressed fusion proteins and extracts prepared from yeast. Our results suggest that STE5 is a scaffolding protein that facilitates interactions between components of the pheromone-responsive mitogen-activated protein kinase module. We further propose that such scaffolding proteins serve to inhibit cross-talk between functionally unrelated mitogen-activated protein kinase modules within the same cell.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blenis J. Signal transduction via the MAP kinases: proceed at your own RSK. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jul 1;90(13):5889–5892. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.13.5889. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boulton T. G., Nye S. H., Robbins D. J., Ip N. Y., Radziejewska E., Morgenbesser S. D., DePinho R. A., Panayotatos N., Cobb M. H., Yancopoulos G. D. ERKs: a family of protein-serine/threonine kinases that are activated and tyrosine phosphorylated in response to insulin and NGF. Cell. 1991 May 17;65(4):663–675. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90098-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burkholder A. C., Hartwell L. H. The yeast alpha-factor receptor: structural properties deduced from the sequence of the STE2 gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Dec 9;13(23):8463–8475. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.23.8463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cairns B. R., Ramer S. W., Kornberg R. D. Order of action of components in the yeast pheromone response pathway revealed with a dominant allele of the STE11 kinase and the multiple phosphorylation of the STE7 kinase. Genes Dev. 1992 Jul;6(7):1305–1318. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.7.1305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Celenza J. L., Eng F. J., Carlson M. Molecular analysis of the SNF4 gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae: evidence for physical association of the SNF4 protein with the SNF1 protein kinase. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Nov;9(11):5045–5054. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.11.5045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crews C. M., Alessandrini A., Erikson R. L. The primary structure of MEK, a protein kinase that phosphorylates the ERK gene product. Science. 1992 Oct 16;258(5081):478–480. doi: 10.1126/science.1411546. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crews C. M., Erikson R. L. Extracellular signals and reversible protein phosphorylation: what to Mek of it all. Cell. 1993 Jul 30;74(2):215–217. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90411-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dent P., Haser W., Haystead T. A., Vincent L. A., Roberts T. M., Sturgill T. W. Activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase by v-Raf in NIH 3T3 cells and in vitro. Science. 1992 Sep 4;257(5075):1404–1407. doi: 10.1126/science.1326789. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dietzel C., Kurjan J. The yeast SCG1 gene: a G alpha-like protein implicated in the a- and alpha-factor response pathway. Cell. 1987 Sep 25;50(7):1001–1010. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90166-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Errede B., Gartner A., Zhou Z., Nasmyth K., Ammerer G. MAP kinase-related FUS3 from S. cerevisiae is activated by STE7 in vitro. Nature. 1993 Mar 18;362(6417):261–264. doi: 10.1038/362261a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Errede B., Levin D. E. A conserved kinase cascade for MAP kinase activation in yeast. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1993 Apr;5(2):254–260. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(93)90112-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evan G. I., Lewis G. K., Ramsay G., Bishop J. M. Isolation of monoclonal antibodies specific for human c-myc proto-oncogene product. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Dec;5(12):3610–3616. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.12.3610. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Field J., Nikawa J., Broek D., MacDonald B., Rodgers L., Wilson I. A., Lerner R. A., Wigler M. Purification of a RAS-responsive adenylyl cyclase complex from Saccharomyces cerevisiae by use of an epitope addition method. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 May;8(5):2159–2165. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.5.2159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fields S., Song O. A novel genetic system to detect protein-protein interactions. Nature. 1989 Jul 20;340(6230):245–246. doi: 10.1038/340245a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gartner A., Nasmyth K., Ammerer G. Signal transduction in Saccharomyces cerevisiae requires tyrosine and threonine phosphorylation of FUS3 and KSS1. Genes Dev. 1992 Jul;6(7):1280–1292. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.7.1280. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagen D. C., McCaffrey G., Sprague G. F., Jr Evidence the yeast STE3 gene encodes a receptor for the peptide pheromone a factor: gene sequence and implications for the structure of the presumed receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(5):1418–1422. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.5.1418. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasson M. S., Blinder D., Thorner J., Jenness D. D. Mutational activation of the STE5 gene product bypasses the requirement for G protein beta and gamma subunits in the yeast pheromone response pathway. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Feb;14(2):1054–1065. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.2.1054. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howe L. R., Leevers S. J., Gómez N., Nakielny S., Cohen P., Marshall C. J. Activation of the MAP kinase pathway by the protein kinase raf. Cell. 1992 Oct 16;71(2):335–342. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90361-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kosako H., Nishida E., Gotoh Y. cDNA cloning of MAP kinase kinase reveals kinase cascade pathways in yeasts to vertebrates. EMBO J. 1993 Feb;12(2):787–794. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05713.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kranz J. E., Satterberg B., Elion E. A. The MAP kinase Fus3 associates with and phosphorylates the upstream signaling component Ste5. Genes Dev. 1994 Feb 1;8(3):313–327. doi: 10.1101/gad.8.3.313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurjan J. Pheromone response in yeast. Annu Rev Biochem. 1992;61:1097–1129. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.61.070192.005313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyriakis J. M., App H., Zhang X. F., Banerjee P., Brautigan D. L., Rapp U. R., Avruch J. Raf-1 activates MAP kinase-kinase. Nature. 1992 Jul 30;358(6385):417–421. doi: 10.1038/358417a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lange-Carter C. A., Pleiman C. M., Gardner A. M., Blumer K. J., Johnson G. L. A divergence in the MAP kinase regulatory network defined by MEK kinase and Raf. Science. 1993 Apr 16;260(5106):315–319. doi: 10.1126/science.8385802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leberer E., Dignard D., Harcus D., Thomas D. Y., Whiteway M. The protein kinase homologue Ste20p is required to link the yeast pheromone response G-protein beta gamma subunits to downstream signalling components. EMBO J. 1992 Dec;11(13):4815–4824. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05587.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee K. S., Levin D. E. Dominant mutations in a gene encoding a putative protein kinase (BCK1) bypass the requirement for a Saccharomyces cerevisiae protein kinase C homolog. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Jan;12(1):172–182. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.1.172. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcus S., Wigler M., Xu H. P., Ballester R., Kawamukai M., Polverino A. RAS function and protein kinase cascades. Ciba Found Symp. 1993;176:53–66. doi: 10.1002/9780470514450.ch4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsh L., Neiman A. M., Herskowitz I. Signal transduction during pheromone response in yeast. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1991;7:699–728. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.07.110191.003411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyajima I., Nakafuku M., Nakayama N., Brenner C., Miyajima A., Kaibuchi K., Arai K., Kaziro Y., Matsumoto K. GPA1, a haploid-specific essential gene, encodes a yeast homolog of mammalian G protein which may be involved in mating factor signal transduction. Cell. 1987 Sep 25;50(7):1011–1019. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90167-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mukai Y., Harashima S., Oshima Y. Function of the ste signal transduction pathway for mating pheromones sustains MAT alpha 1 transcription in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Apr;13(4):2050–2060. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.4.2050. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakayama N., Miyajima A., Arai K. Nucleotide sequences of STE2 and STE3, cell type-specific sterile genes from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. EMBO J. 1985 Oct;4(10):2643–2648. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03982.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neiman A. M., Herskowitz I. Reconstitution of a yeast protein kinase cascade in vitro: activation of the yeast MEK homologue STE7 by STE11. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Apr 12;91(8):3398–3402. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.8.3398. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neiman A. M., Stevenson B. J., Xu H. P., Sprague G. F., Jr, Herskowitz I., Wigler M., Marcus S. Functional homology of protein kinases required for sexual differentiation in Schizosaccharomyces pombe and Saccharomyces cerevisiae suggests a conserved signal transduction module in eukaryotic organisms. Mol Biol Cell. 1993 Jan;4(1):107–120. doi: 10.1091/mbc.4.1.107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park H. O., Chant J., Herskowitz I. BUD2 encodes a GTPase-activating protein for Bud1/Rsr1 necessary for proper bud-site selection in yeast. Nature. 1993 Sep 16;365(6443):269–274. doi: 10.1038/365269a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perlman R., Yablonski D., Simchen G., Levitzki A. Cloning of the STE5 gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae as a suppressor of the mating defect of cdc25 temperature-sensitive mutants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jun 15;90(12):5474–5478. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.12.5474. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peter M., Gartner A., Horecka J., Ammerer G., Herskowitz I. FAR1 links the signal transduction pathway to the cell cycle machinery in yeast. Cell. 1993 May 21;73(4):747–760. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90254-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins D. J., Cheng M., Zhen E., Vanderbilt C. A., Feig L. A., Cobb M. H. Evidence for a Ras-dependent extracellular signal-regulated protein kinase (ERK) cascade. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Aug 1;89(15):6924–6928. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.15.6924. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothstein R. J. One-step gene disruption in yeast. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:202–211. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01015-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sikorski R. S., Hieter P. A system of shuttle vectors and yeast host strains designed for efficient manipulation of DNA in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics. 1989 May;122(1):19–27. doi: 10.1093/genetics/122.1.19. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. B., Johnson K. S. Single-step purification of polypeptides expressed in Escherichia coli as fusions with glutathione S-transferase. Gene. 1988 Jul 15;67(1):31–40. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90005-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevenson B. J., Rhodes N., Errede B., Sprague G. F., Jr Constitutive mutants of the protein kinase STE11 activate the yeast pheromone response pathway in the absence of the G protein. Genes Dev. 1992 Jul;6(7):1293–1304. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.7.1293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stotz A., Linder P. The ADE2 gene from Saccharomyces cerevisiae: sequence and new vectors. Gene. 1990 Oct 30;95(1):91–98. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(90)90418-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Aelst L., Barr M., Marcus S., Polverino A., Wigler M. Complex formation between RAS and RAF and other protein kinases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jul 1;90(13):6213–6217. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.13.6213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vojtek A. B., Hollenberg S. M., Cooper J. A. Mammalian Ras interacts directly with the serine/threonine kinase Raf. Cell. 1993 Jul 16;74(1):205–214. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90307-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whiteway M., Hougan L., Dignard D., Thomas D. Y., Bell L., Saari G. C., Grant F. J., O'Hara P., MacKay V. L. The STE4 and STE18 genes of yeast encode potential beta and gamma subunits of the mating factor receptor-coupled G protein. Cell. 1989 Feb 10;56(3):467–477. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90249-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zheng C. F., Guan K. L. Cloning and characterization of two distinct human extracellular signal-regulated kinase activator kinases, MEK1 and MEK2. J Biol Chem. 1993 May 25;268(15):11435–11439. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zheng C. F., Guan K. L. Properties of MEKs, the kinases that phosphorylate and activate the extracellular signal-regulated kinases. J Biol Chem. 1993 Nov 15;268(32):23933–23939. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou Z., Gartner A., Cade R., Ammerer G., Errede B. Pheromone-induced signal transduction in Saccharomyces cerevisiae requires the sequential function of three protein kinases. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Apr;13(4):2069–2080. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.4.2069. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





