Abstract
Reactive oxygen species (ROS) are key intermediates in cellular signal transduction pathways whose function may be counterbalanced by antioxidants. Acting as an antioxidant, ascorbic acid (AA) donates two electrons and becomes oxidized to dehydroascorbic acid (DHA). We discovered that DHA directly inhibits IκBα kinase β (IKKβ) and IKKα enzymatic activity in vitro, whereas AA did not have this effect. When cells were loaded with AA and induced to generate DHA by oxidative stress in cells expressing a constitutive active IKKβ, NF-κB activation was inhibited. Our results identify a dual molecular action of vitamin C in signal transduction and provide a direct linkage between the redox state of vitamin C and NF-κB signaling events. AA quenches ROS intermediates involved in the activation of NF-κB and is oxidized to DHA, which directly inhibits IKKβ and IKKα enzymatic activity. These findings define a function for vitamin C in signal transduction other than as an antioxidant and mechanistically illuminate how vitamin C down-modulates NF-κB signaling.
Dietary vitamin C is essential for humans, primates, guinea pigs, and several other animals and insects that lack l-gulono-γ-lactone oxidase, the final enzyme in its biosynthetic pathway from glucose (25). Under physiological conditions, vitamin C predominantly exists in its reduced form, ascorbic acid (AA); it also exists in trace quantities in the oxidized form, dehydroascorbic acid (DHA). There are two known mechanisms for transporting vitamin C (21). A universal system, present in all cells, transports vitamin C as DHA via facilitative glucose transporters (34). Once inside the cell, DHA is rapidly reduced and accumulates as AA (34, 35). The second transport system is functional in specialized cells where AA is directly transported into cells via sodium-dependent AA cotransporters (SVCT1 and/or SVCT2) (33).
AA functions as a cofactor for enzymes involved in the biosynthesis of collagen (26), carnitine (28), and norepinephrine (18) and in the amidation of hormones (8). In plasma and cells, AA is a powerful antioxidant, quenching reactive oxygen species (ROS) and reactive nitrogen species (10, 14). Intracellular vitamin C can prevent cell death and inhibit mutations induced by oxidative stress (12, 22, 37). During the process of quenching free radicals, ascorbate donates an electron, becoming the unstable intermediate ascorbyl radical that can be reversibly reduced back to ascorbate. Ascorbyl radical can donate a second electron and be converted to DHA (13, 14). DHA may be reduced back to AA or be irreversibly hydrolyzed to 2,3-diketo-gulonic acid, which then is metabolized to threonic and oxalic acid (14). In cells loaded with AA and exposed to hydrogen peroxide, AA is converted to DHA, some of which effluxes from the cells via the glucose transporters, thereby providing a mechanism for recycling vitamin C to the extracellular medium (12). Alternatively, intracellular DHA can be transported to intracellular compartments and organelles (2, 20). DHA functions primarily as a readily transportable form of vitamin C (36).
ROS play a key role in cellular responses as chemical second messenger molecules, and conversely, antioxidants modulate selected signaling responses (24). For example, ROS activate transcription factors, such as NF-κB, that are important in host defense, inflammation, and apoptosis (1, 11, 32). Pro-inflammatory cytokines, such as tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α), hydrogen peroxide, and ceramide, activate NF-κB by inducing the phosphorylation of IκB proteins (11, 19). Phosphorylated IκBα releases NF-κB and is itself degraded via proteasomal pathways (17), while unphosphorylated IκB associates with NF-κB in the cytosol, preventing its nuclear migration. It was initially reported that AA inhibits TNF-α-induced NF-κB activation in endothelial cells via activation of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) (4); however, we recently showed that AA suppresses TNF-α-dependent activation of NF-κB by inhibiting the activation of kinases involved in the phosphorylation of IκBα (6).
We investigated the modulation of NF-κB activation by vitamin C and found that DHA directly inhibited the kinase activity of IKKβ and IKKα in vitro and in cellular assays. Thus, our data suggest a dual mechanisms of action of vitamin C in regulating NF-κB function. First, as an antioxidant quenching ROS, AA inhibits ROS-mediated signaling events. Second, after oxidization to DHA, vitamin C directly inhibits IKK kinase activity.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Vitamin C loading.
HeLa cells were loaded with vitamin C as previously described (6). Briefly, cells were incubated for 30 min with incubation buffer (15 mM HEPES [pH 7.4], 135 mM NaCl, 5 mM KCl, 1.8 mM CaCl2, 0.8 mM MgCl2) (pH 7.4) and then treated with different concentrations of DHA for 30 min at 37°C in the same buffer. DHA was obtained from Sigma (St. Louis, Mo.) or enzymatically generated by incubating AA with ascorbate oxidase (Sigma).
Immunoblotting analysis.
Cell extracts were prepared as previously described (6). Immunoblot analysis was performed with the following rabbit polyclonal antibodies: anti-phospho-IκBα, anti-IκBα, anti-p38 MAPK, anti-phospho-p38 MAPK, anti-phosphorylated p44/42 MAPKs (Cell Signaling Technology, Beverly, Mass.) anti-p44/42 MAPKs (Upstate Biotech, Lake Placid, N.Y.) and anti-FLAG antibody (Sigma). Membranes were incubated with horseradish peroxidase-conjugated anti-rabbit immunoglobulin G antibody, and the proteins were revealed using enhanced chemiluminescence assay (Amersham Pharmacia Biotech, Piscataway, N.J.).
Transfection and luciferase assays.
HeLa cells were transiently transfected with pNFκB-luc (Clontech, Palo Alto, Calif.) or cotransfected with plasmids containing IKKβ(SS/EE) (a constitutively active IKKβ in which serines 177 and 181 had been replaced by glutamic acid) or its mutants by the calcium phosphate method or Superfect (QIAGEN, Valencia, Calif.). Cells were incubated with 30 ng of TNF-α per ml in triplicate for the time indicated in the figures. Luciferase activity was determined using the luciferase reporter assay system (Promega).
Kinase assays.
Endogenous IKKβ was isolated from TNF-α-treated cellular extracts by immunoprecipitation with anti-IKKβ antibody (Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Santa Cruz, Calif.). IKKβ(SS/EE) and its mutants were isolated from transfected HeLa cell extracts with anti-FLAG antibody beads (Sigma). Recombinant IKKα and IKKβ were isolated from transfected 293T cells. Cells were transiently transfected using Genejammer transfection reagent (Stratagene, La Jolla, Calif.) with plasmids containing IKKα or IKKβ. After 48 h, the cells were harvested, and the kinases were isolated by immunoprecipitation. The kinase activity of endogenous IKKβ, recombinant IKKα and IKKβ, and IKKβ(SS/EE) was determined after 15 min at 30°C in buffer containing 10 μM ATP, 1 μCi of [γ-32P]ATP and 1 μg of substrate (glutathione S-transferase [GST]-IκBα). The phosphorylated substrate was detected by autoradiography (6). MAPK (p38) activity in vitro was analyzed using a purified GST fusion enzyme and phosphorylated heat- and acid-stable protein 1 (PHAS-1) as the substrate (Calbiochem), and the kinase reaction was performed as indicated by the manufacturer (Calbiochem).
DHA binding assay in vitro.
IKKβ(SS/EE) and its mutants were isolated from transfected HeLa cells by immunoprecipitation with anti-FLAG beads. The beads carrying IKKβ were incubated in kinase buffer for 15 min at 30°C with 6 mM [14C]DHA or 6 mM [14C]AA. [14C]DHA was generated in incubation buffer (pH 5.5) by incubating [14C]AA with ascorbate oxidase. The kinase was eluted from the beads with FLAG peptide, and the associated radioactivity was counted with a Beckman LS 6000LL counter.
Detection of ROS.
HeLa cells were kept for 16 h in serum-free medium containing 0.2% bovine serum albumin. The cells were then loaded with vitamin C, washed, and treated for 10 min with 50 ng of TNF-α per ml. Cells were then incubated with 20 μM 2′,7′-dichlorodihydrofluorescein diacetate (DCF) for 10 min at 37°C, and ROS were visualized with fluorescence using an Olympus BX60 microscope (40×, DP40, WIBA) equipped with a Qimaging digital charge-coupled device camera (Retiga 1300C) and QCapture software.
Site-directed mutagenesis.
Site-directed mutagenesis was performed using the QuikChange XL site-directed mutagenesis kit from Stratagene per the manufacturer's instructions.
RESULTS
Intracellular vitamin C inhibits TNF-α-induced activation of NF-κB.
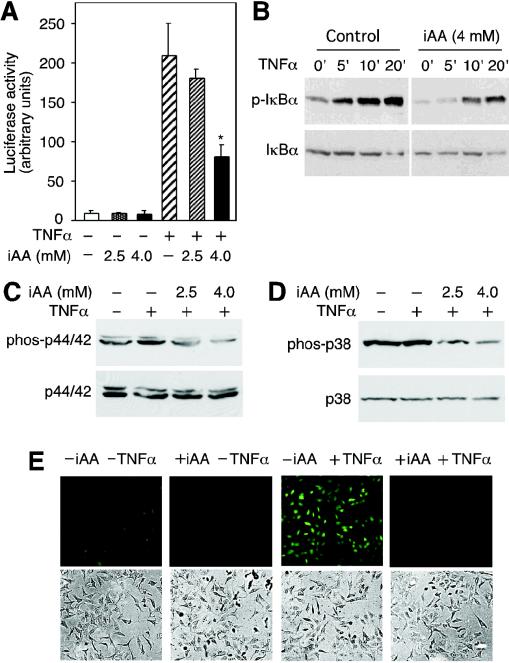
We used HeLa cells as a model system to investigate the molecular mechanisms of inhibition of NF-κB activation by vitamin C. Cells were loaded with vitamin C by exposing them to DHA (6). This procedure circumvents artifacts associated with the pro-oxidant effects of AA in tissue culture medium (7). Consistent with our previous findings, HeLa cells transfected with the NF-κB-dependent luciferase reporter construct (pNFκB-luc) induced a 20-fold increase in luciferase activity after treatment with TNF-α (Fig. 1A). Cells loaded with 4.0 mM AA showed a weaker induction of luciferase activity of approximately eightfold, corresponding to a 60% inhibition of luciferase activity. Intracellular concentrations of 2.5 mM AA had no significant effect on TNF-α-induced luciferase activity (P = 0.21, n = 3, one-tailed t test) (Fig. 1A). TNF-α induced phosphorylation of IκBα and cells loaded with 4 mM AA showed decreased phosphorylation of IκBα (Fig. 1B). These results suggested that intracellular vitamin C inhibits TNF-α-induced NF-κB transcriptional responses by preventing the phosphorylation of IκBα.
FIG. 1.
Intracellular vitamin C (iAA) inhibits TNF-α-induced signaling. (A) HeLa cells transfected with pNFκB-luc reporter construct loaded with vitamin C were incubated for 6 h with TNF-α (+), and luciferase activity was determined. Data are expressed as the means ± standard deviations of three samples, and the asterisk indicates a statistically significant difference between cells loaded with vitamin C and cells not loaded with vitamin C (P = 0.001, n = 3; one-tailed student t test). (B) Cells loaded with 4 mM AA or not loaded with AA were incubated with TNF-α for the times (in minutes) indicated above the blots. Cell extracts were prepared, and phosphorylated IκBα (p-IκBα) was visualized by immunoblotting with an anti-phospho-IκBα antibody. Nonphosphorylated IκBα is shown in the lower blot. (C) HeLa cells loaded with vitamin C (iAA) were treated with TNF-α for 10 min, and phosphorylated (phos-p44/42) and nonphosphorylated p44/42 MAPK (p44/42) were detected by immunoblotting. (D) Cells loaded with AA were treated with TNF-α, and immunoblots of phosphorylated (phos-p38) and nonphosphorylated p38 MAPK (p38) are shown. (E) HeLa cells loaded with 4 mM intracellular vitamin C (+iAA) or not loaded with 4 mM intracellular vitamin C (−iAA) were treated with TNF-α (+TNFα), and ROS were determined with DCF by fluorescence microscopy (top panels). Cells visualized with light microscopy are shown (bottom panels).
TNF-α induces the MAPK pathway activating p44/42 MAPKs and p38 MAPK (16). Therefore, we investigated whether intracellular AA could also inhibit the activation of these kinases. TNF-α induced the phosphorylation of p44/42 MAPK in HeLa cells as assayed by immunoblotting (Fig. 1C). Loading cells with AA inhibited TNF-α-induced phosphorylation of p44/42 MAPK (Fig. 1C). Cells treated with TNF-α showed a modest increase in phosphorylated p38 MAPK, but loading cells with AA resulted in a substantial decrease in p38 MAPK phosphorylation (Fig. 1D). Since the activation of NF-κB by TNF-α involves ROS (11), we measured the relative levels of ROS induced by TNF-α in cells loaded with vitamin C. Intracellular ROS was detected using DCF and fluorescence microscopy. TNF-α treatment induced an increase in intracellular ROS; however, the levels of ROS in cells loaded with 4 mM vitamin C were barely detected (Fig. 1D). These results suggest that vitamin C prevents TNF-α-dependent activation of NF-κB via inhibition of the phosphorylation of IκBα by quenching ROS involved in the activation of IKK and also decreases the accumulation of ROS that is a result of signaling.
Intracellular vitamin C inhibits a constitutively active IKKβ.
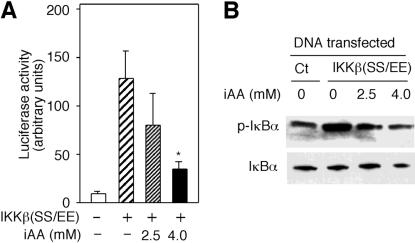
IKKβ is activated by phosphorylation at serines 177 and 181 and phosphorylates IκBα. The replacement of these serines with glutamic acids yields a constitutively active IKKβ, IKKβ(SS/EE) (38). To investigate the possibility that vitamin C has another mode of action beyond inhibiting the activation of IKKβ, we analyzed the activity of IKKβ(SS/EE) in cells loaded with vitamin C. Cotransfection of pNFκB-luc and a plasmid expressing IKKβ(SS/EE) induced a 12-fold increase in luciferase activity (Fig. 2A). However, cells loaded with 4 mM vitamin C inhibited IKKβ(SS/EE)-dependent luciferase activity. Lower concentrations of AA (2.5 mM) had no significant effect (P = 0.11, n = 3, one-tailed t test) (Fig. 2A). To determine whether vitamin C inhibits the activity of IKKβ(SS/EE), we measured the levels of phosphorylated IκBα in cells transfected with IKKβ(SS/EE). IKKβ(SS/EE)-dependent phosphorylation of IκBα was inhibited in cells loaded with vitamin C (Fig. 2B). Analysis of IKKβ(SS/EE) showed that intracellular vitamin C had no effect on its expression (data not shown). Thus, the inhibition of IκBα phosphorylation induced by the expression of IKKβ(SS/EE) in cells loaded with the vitamin points to direct inhibition of IKKβ(SS/EE) activity by vitamin C.
FIG. 2.
Intracellular vitamin C (iAA) inhibits a constitutively active IKKβ. (A) HeLa cells cotransfected with pNFκB-luc and plasmid encoding the constitutive active IKKβ [IKKβ(SS/EE)] were loaded with the indicated concentrations of AA. Luciferase activity was measured in arbitrary units and expressed as the mean ± standard deviation of three samples. The asterisk indicates a statistically significant difference between cells loaded with vitamin C and cells not loaded with vitamin C (P = 0.006, n = 3; one-tailed student t test). (B) HeLa cells transfected with IKKβ(SS/EE) expression vector or control vector (Ct) were loaded with 2.5 or 4 mM AA. Immunoblots of phosphorylated (p-IκBα) and total IκBα are shown.
DHA, the oxidized form of vitamin C, inhibits the activity of IKKβ and IKKα in vitro.
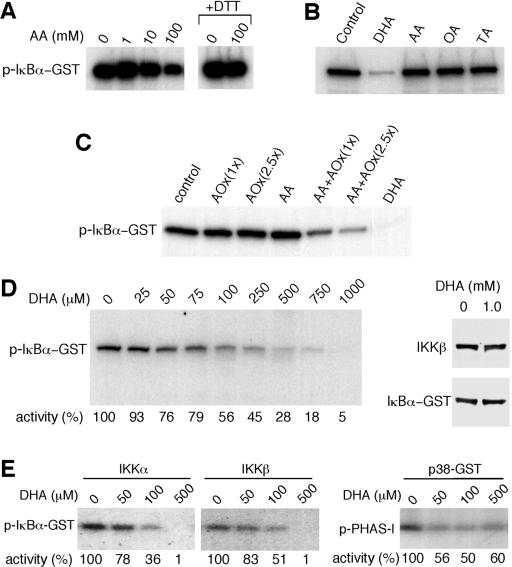
Since intracellular vitamin C inhibited IKKβ(SS/EE)-induced phosphorylation of IκBα, we examined whether AA would directly inhibit the kinase activity of IKKβ in a cell-free system. Activated IKKβ isolated by immunoprecipitation from TNF-α-treated HeLa cells was immobilized on protein G-agarose beads and then assayed for in vitro kinase activity (6). The addition of 1 or 10 mM AA to the kinase reaction mixture had no effect on IKKβ activity (Fig. 3A). Under similar assay conditions, 100 mM AA inhibited IKKβ activity, but this inhibition was abolished when the kinase reaction mixture included dithiothreitol (DTT), suggesting that the inhibitory activity was associated with oxidation of AA (Fig. 3A). Under nonreducing conditions, AA oxidizes to DHA, which can then be hydrolyzed to oxalic and threonic acid (13, 14).
FIG. 3.
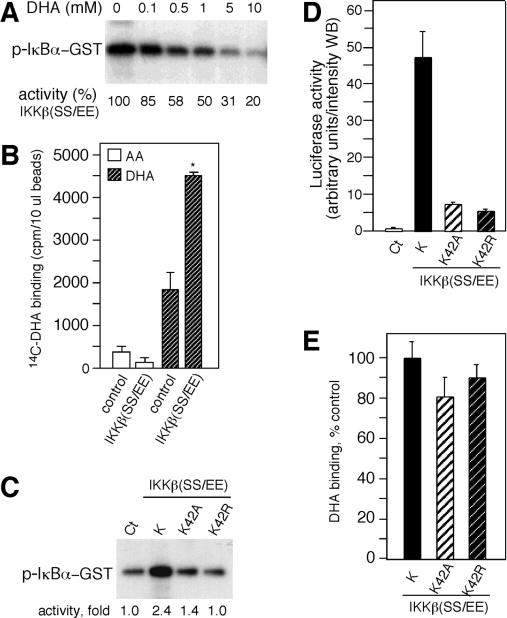
The oxidized form of vitamin C (DHA) inhibits IKKβ and IKKα in vitro. (A) IKKβ immunoprecipitated from TNF-α-treated HeLa cell extracts with an anti-IKKβ antibody was assayed for IKKβ activity. The kinase reaction mixture was incubated with AA as indicated. DTT was added to the kinase reaction mixture in some cases (+DTT). The phosphorylated GST-IkBα (p-IκBα-GST) was visualized by autoradiography. (B) IKKβ activity was assayed in the presence of buffer (control) or with 1 mM DHA, AA, oxalic acid (OA), or threonic acid (TA). (C) IKKβ activity was assayed in the presence of buffer, ascorbate oxidase (AOx), AA, DHA generated enzymatically (AA+AOx), or DHA. One hundred or 250 U of ascorbate oxidase was used [AOx(1x) or AOx(2.5x), respectively. (D) IKKβ activity was assayed in the presence of different concentrations of DHA as indicated above the blot, and the relative kinase activity is shown as a percentage of control below the blot. GST-IκBα and IKKβ from a kinase reaction mixture incubated for 30 min with buffer or 1 mM DHA were visualized by immunoblotting with anti-IκBα antibody or with an anti-IKKβ antibody. (E) Activated IKKα and IKKβ immunoprecipitated from transfected cells were assayed in vitro for kinase activity. The kinase activity of p38 MAPK (p38-GST) was assayed in vitro in the presence of DHA. PHAS-1 was used as a substrate (p-PHAS-1). The phosphorylated proteins were determined by autoradiography, and the relative kinase activity is shown as a percentage below the blots.
To determine whether any of these derivatives of AA could inhibit the activity of IKKβ, we incubated the kinase reaction mixture with either 1 mM AA, DHA, oxalic acid, or threonic acid. Incubation with 1 mM DHA inhibited the in vitro kinase activity of IKKβ (Fig. 3B). In contrast, no effect on IKKβ activity was detected when the kinase reaction mixture was incubated with 1 mM AA, oxalic acid, or threonic acid (Fig. 3B). To exclude the possibility of kinase-inhibitory contaminants in the DHA preparations, DHA was enzymatically produced from AA using ascorbate oxidase, and its inhibitory activity was assayed. DHA enzymatically derived from AA also inhibited IKKβ activity. AA and ascorbate oxidase alone had no inhibitory effect, verifying the activity of DHA (Fig. 3C). We found that approximately 100 μM DHA was required to inhibit about 50% of the kinase activity of IKKβ (Fig. 3D). The inhibitory activity of DHA was not affected by DTT (data not shown). Incubation for 30 min with 1 mM DHA did not induce degradation of the substrate or IKKβ (Fig. 3D), confirming that DHA directly inhibits the enzymatic activity of IKKβ in vitro. We also investigated whether DHA inhibits the activity of IKKα and p38 MAPK. The kinase activities of IKKα and IKKβ isolated from transfected cells were inhibited by DHA. At 500 μM, DHA inhibited almost all kinase activity (Fig. 3E). p38 MAPK was also inhibited by DHA, but 500 μM DHA inhibited approximately 50% of the kinase activity (Fig. 3E).
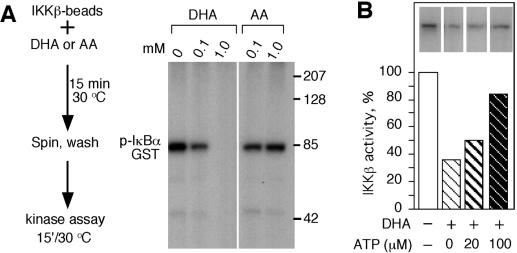
To further investigate the mechanism of kinase inhibition by DHA, endogenous IKKβ immobilized to protein G was incubated with DHA or AA, and beads were washed to remove AA and DHA prior to the kinase reaction (Fig. 4A). IKKβ preincubated with 1 mM DHA was completely inhibited, whereas preincubation with 0.1 mM DHA caused retention of approximately 40% activity. Preincubation with AA resulted in no decrease in IKKβ activity (Fig. 4A). These findings suggest that DHA inhibits IKKβ by altering its enzymatic properties, likely by binding directly to the kinase and interfering with ATP or substrate binding or catalysis. DHA inhibition was maintained after the beads were washed, indicating that DHA did not bind to ATP or the substrate. Interference with ATP binding was investigated by analyzing whether DHA would inhibit IKKβ activity when incubated in the presence of ATP. ATP partially competed the inhibitory activity of DHA (Fig. 4B), implying that DHA could be interfering with ATP binding to IKKβ.
FIG. 4.
ATP competed the inhibitory activity of DHA. (A, left) A schematic representation of the procedure. 15′, 15 min. (Right) The kinase activity of IKKβ was determined by autoradiography as described in the legend to Fig. 3, and an immunoblot of phosphorylated IκBα-GST is shown. (B) IKKβ beads were incubated with DHA in the presence of buffer or 20 or 100 μM ATP. The kinase activity is showed as a percentage of the control. The inserts show the phosphorylated GST-IκBα (pIκBα-GST).
DHA inhibits and binds to the constitutively active IKKβ(SS/EE) in vitro.
To investigate whether DHA binds to IKKβ, we used IKKβ(SS/EE) isolated from transfected cells. Prior to the binding studies, we determined whether DHA inhibits IKKβ(SS/EE) activity in vitro. A dose-response inhibitory assay showed that 1 mM DHA inhibited the activity of IKKβ(SS/EE) by 40% (Fig. 5A). Next we investigated whether vitamin C bound to IKKβ(SS/EE). Beads containing IKKβ(SS/EE) were incubated with [14C]DHA or [14C]AA. AA showed low binding to beads preincubated with control extracts or beads containing IKKβ(SS/EE) compared to DHA binding activity (Fig. 5B). The binding of DHA to IKKβ beads was twofold greater than the binding to beads preincubated with control extracts (Fig. 5B). Since ATP decreases the inhibitory activity of DHA, we determined whether DHA could bind to a mutated ATP binding site on IKKβ(SS/EE). Mutation of the invariant lysine found in the ATP binding site of all kinases results in loss of ATP binding and consequently kinase activity (15). Substitution mutants with lysine 42 in IKKβ(SS/EE) changed to alanine (K42A) or arginine (K42R) were generated and assayed for kinase activity in vitro. Both mutants were defective in kinase activity (Fig. 5C). Consistent with these results, transfection of the IKKβ(SS/EE) mutants showed decreased luciferase activity (Fig. 5D). DHA bound to IKKβ(SS/EE)K42R and K42A at levels identical to those of IKKβ(SS/EE) (P = 0.14, n = 3 one-tailed t test) (Fig. 3E). These results indicate that DHA binding to IKKβ was independent of a functional ATP binding site and suggested a discrete binding site distinct from the ATP binding pocket.
FIG. 5.
DHA binds to IKKβ. (A) The constitutively active IKKβ, IKKβ(SS/EE), immunoprecipitated from transfected cells was assayed in vitro for kinase activity. Kinase activity was determined by autoradiography. (B) IKKβ(SS/EE) bound to anti-FLAG beads was incubated with [14C]DHA and [14C]AA and eluted with FLAG peptide, and the radioactivity associated with IKKβ(SS/EE) was determined by scintillation spectrometry. The radioactivity nonspecifically associated with the anti-FLAG beads was estimated using beads incubated with extracts from nontransfected cells (control). (C) IKKβ(SS/EE) and the ATP binding site mutants IKKβ(SS/EE)K42A and K42R were assayed for kinase activity in vitro. A digitalized image was quantified, and the kinase activity is shown as fold increase below the blot. (D) HeLa cells cotransfected with pNFκB-luc reporter construct and IKKβ(SS/EE) (K), K42A, and K42R were assayed for luciferase activity. Luciferase activity is shown in arbitrary units per intensity of the Western blot (WB). Control extracts (Ct) were obtained from cells cotransfected with an empty vector. (E) Beads containing IKKβ(SS/EE) (K), K42A, and K42R were incubated with [14C]DHA, and its binding activity is shown as a percentage of control binding with IKKβ(SS/EE).
Conversion of AA to DHA by oxidative stress inhibits luciferase activity induced by IKKβ(SS/EE).
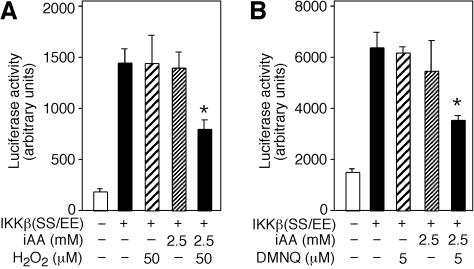
To generate intracellular DHA from AA by an oxidative stressor, such as H2O2, we first determined the concentration of H2O2 that had no effect on cell viability or luciferase activity. Cells transfected with IKKβ(SS/EE) and treated with 50 μM H2O2 or not treated with H2O2 showed identical luciferase activity. However, cells loaded with 2.5 mM AA and incubated with 50 μM H2O2 showed an approximately 50% reduction in the luciferase activity (P = 0.004, n = 3, one-tailed t test) (Fig. 6A). Intracellular AA (2.5 mM) alone had no significant effect (P = 0.5, n = 3, one-tailed t test).
FIG. 6.
Intracellular DHA inhibits IKKβ(SS/EE)-induced luciferase activity. (A) Cells cotransfected with pNFκB-luc reporter construct and IKKβ(SS/EE) (+) were loaded with 2.5 mM iAA (intracellular vitamin C) or not loaded with iAA (−) and treated with 50 μM H2O2 or not treated with H2O2 (−). Cell extracts were prepared, and luciferase activity was determined and expressed in arbitrary units. (B) Cells cotransfected with pNFκB-luc and IKKβ(SS/EE) (+) loaded with 2.5 mM iAA or not loaded with iAA (−) were treated with 5 μM DMNQ or not treated with DMNQ (−). After 4 h, cell extracts were prepared, and luciferase activity is expressed as arbitrary units.
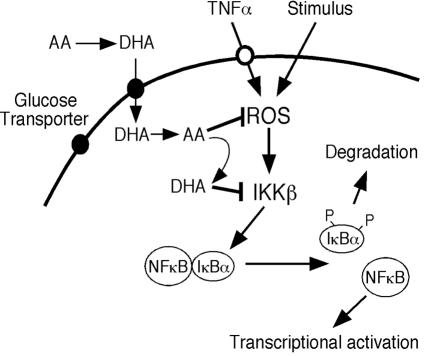
We investigated whether an intracellular generator of ROS, such as dimethoxinaphthoquinine (DMNQ), would also inhibit IKKβ(SS/EE)-dependent luciferase activity in cells preloaded with 2.5 mM vitamin C. The concentration of DMNQ that had no effect on luciferase activity or viability in cells transfected with IKKβ(SS/EE) was found to be 5 μM. Cells loaded with 2.5 mM vitamin C and incubated with 5 μM DMNQ showed significantly reduced luciferase activity (P = 0.003, n = 3, one-tailed t test) (Fig. 6B). These results indicate that intracellular conversion of AA to DHA inhibits kinase activity of IKKβ(SS/EE), suggesting that DHA functions as a kinase inhibitor in vivo. We propose that in cells loaded with vitamin C and placed under oxidative conditions, AA quenches ROS and transforms into DHA. The DHA generated can leave the cell via facilitative glucose transporters or function as a direct kinase inhibitor as shown here for IKKα and IKKβ (Fig. 7). These processes link oxidative stress to kinase inhibition via the antioxidant, vitamin C.
FIG. 7.
Schematic representation of the regulation of signaling responses by vitamin C. Vitamin C enters the cell through the glucose transporters as DHA and is rapidly reduced to AA. ROS induces NF-κB signaling responses by activating IKKβ, and AA quenches ROS, inhibiting the activation of IKKβ. Throughout these processes, AA becomes oxidized to DHA, and DHA inhibits IKKβ.
DISCUSSION
ROS are produced during cellular metabolism and also participate as important mediators of signal transduction pathways. Therefore, antioxidants could play key roles in modulating cellular responses to external stimuli (24). A distinction between metabolic accumulation of ROS and localized receptor activation-induced ROS is defining a particular role for intracellular vitamin C in signal transduction (5, 27). For example, granulocyte-macrophage colony stimulating factor (GM-CSF) and interleukin-3 signaling is known to involve ROS (5, 30), and vitamin C inhibited GM-CSF responses at the level of Jak2 activation, inhibiting phosphorylation of the beta GM-CSF receptor (5). NF-κB responses are also known to utilize ROS in signaling, and it has been shown that activation of NF-κB is inhibited by overexpression of antioxidant enzymes and antioxidants, such as pyrrolidine dithiocarbamate, N-acetyl-l-cysteine, thioredoxin, glutathione, and vitamin C (4, 6, 9, 11, 23). In this study, we sought to define the role of vitamin C in inhibiting the phosphorylation of IκBα in a mechanistic manner.
The importance of vitamin C as an intracellular antioxidant is well documented and inhibits cell death induced by hydrogen peroxide (12, 37), apoptosis induced by FAS binding to CD95 (27), and DNA damage induced by oxidative stress (22). In addition to these functions, vitamin C is a cofactor for various enzymatic hydroxylation reactions (13, 14). All of these functions of vitamin C, including its role as a cofactor, rely on its ability to donate electrons, becoming oxidized to DHA in the process. DHA functions mainly in the transport of vitamin C (36) but has also been reported to inhibit hexokinase activity (8a).
We discovered that DHA can function as a kinase inhibitor and directly inhibit the activity of IKKβ, IKKα, and p38 MAPK, expanding our knowledge of how vitamin C modulates ROS-dependent NF-κB signaling (4, 6). The initial evidence pointing to vitamin C inhibition of IKKβ enzymatic activity was the down-modulation of responses induced by the constitutively active IKKβ [IKKβ(SS/EE)]. Studies in vitro indicated that the oxidized form of vitamin C inhibited immunopurified IKKβ and IKKβ(SS/EE). Using radioactively labeled [14C]DHA, we found that DHA binds to IKKβ, whereas AA showed neither inhibitory activity nor binding activity to IKKβ in vitro.
The inhibitory effect of DHA on IKKα and β enzymatic activities defines two mechanisms for the negative regulation of NF-κB responses by vitamin C. First, AA quenches signaling ROS induced by the cytokine-receptor interaction, preventing the activation of ROS-mediated responses, and also quenches ROS that result from signaling. Second, as a consequence of AA oxidation, DHA is generated and inhibits the kinase(s) activated by ROS. This point was experimentally demonstrated in cells loaded with AA and induced to generate DHA by stressing them with H2O2 or DMNQ. These findings suggest an anti-inflammatory role for vitamin C in inhibiting TNF-α signal initiation and transduction via IKKβ.
The precise mechanism of kinase inhibition by DHA is not certain, but we propose that DHA binds to a pocket near the active site of the kinase. The results of the initial competition experiments with ATP suggested that it could interact with the ATP binding site, but the results of binding assays indicated that an intact ATP site was not required for DHA binding. These apparent conflicting results can be reconciled by the presence of an independent binding site for DHA. Docking simulation and computer modeling indicated that DHA could bind near the catalytic site and not in the ATP binding site (data not shown).
It has been reported that vitamin C inhibits the enzymatic activity of rabbit muscle adenylyl kinase; however, the inhibition was overcome by first incubating AA with DTT (29). These results suggest that AA was converted to DHA and that DHA could be the molecule inhibiting adenylyl kinase. The soluble guanylyl cyclase was also reported to be repressed by AA (31). Cells loaded with vitamin C and under oxidative stress induced a transient cell cycle arrest at the G2/M checkpoint, and it was postulated that DHA induced cell cycle arrest by delaying the activation of cyclin B-cdc2 (3). These results can be rationalized by hypothesizing that DHA may be affecting kinase reaction(s) important in cell cycle control. Our data indicate that DHA can inhibit IKKβ, IKKα, and p38 MAPK, while T4 polynucleotide kinase was resistant to DHA inhibition (data not shown).
Inhibitors of NF-κB activation, such as salicylate and aspirin, play important roles in decreasing inflammation and perhaps oncogenesis. These agents inhibit the kinase activity of IKKβ by competing with ATP binding (38). Our findings with vitamin C as an NF-κB inhibitor point to a role for the vitamin in inflammation and apoptosis. Vitamin C can inhibit the activation of NF-κB by two distinct but related mechanisms: down-regulating ROS induced activation and directly inhibiting IKKα and IKKβ.
Acknowledgments
We thank Richard Gaynor for providing the pFLAG-CMV2-IKK2, pRcBactin3xHA-IKK1κ, and pFLAG-CMV2-IKK2(SS/EE) plasmids.
This work was supported in part by grants from the National Institutes of Health (CA30388), New York State Department of Health, and Lebensfeld Foundation.
REFERENCES
- 1.Baeuerle, P. A., and T. Henkel. 1994. Function and activation of NF-κB in the immune system. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 12:141-179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Banhegyi, G., P. Marcolongo, F. Puskas, R. Fulceri, J. Mandl, and A. Benedetti. 1998. Dehydroascorbate and ascorbate transport in rat liver microsomal vesicles. J. Biol. Chem. 273:2758-2762. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Bijur, G. N., B. Briggs, C. L. Hitchcock, and M. V. Williams. 1999. Ascorbic acid-dehydroascorbate induces cell cycle arrest at G2/M DNA damage checkpoint during oxidative stress. Environ. Mol. Mutagen. 33:144-152. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Bowie, A. G., and L. A. O'Neill. 2000. Vitamin C inhibits NF-κB activation by TNF via the activation of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase. J. Immunol. 165:7180-7188. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Cárcamo, J. M., O. Bórquez-Ojeda, and D. W. Golde. 2002. Vitamin C inhibits granulocyte macrophage-colony-stimulating factor-induced signaling pathways. Blood 99:3205-3212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Cárcamo, J. M., A. Pedraza, O. Bórquez-Ojeda, and D. W. Golde. 2002. Vitamin C suppresses TNFα-induced NFκB activation by inhibiting IκBα phosphorylation. Biochemistry 41:12995-13002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Clement, M. V., J. Ramalingam, L. H. Long, and B. Halliwell. 2001. The in vitro cytotoxicity of ascorbate depends on the culture medium used to perform the assay and involves hydrogen peroxide. Antioxid. Redox. Signal. 3:157-163. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Englard, S., and S. Seifter. 1986. The biochemical functions of ascorbic acid. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 6:365-406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8a.Fiorani, M., R. DeSanctis, F. Scarlatti, L. Vallorani, R. DeBellis, G. Serafini, M. Bianchi, and V. Stocchi. 2000. Dehydroascorbic acid irreversibly inhibits hexokinase activity. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 209:145-153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Flohe, L., R. Brigelius-Flohe, C. Saliou, M. G. Traber, and L. Packer. 1997. Redox regulation of NF-κB activation. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 22:1115-1126. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Frei, B., L. England, and B. N. Ames. 1989. Ascorbate is an outstanding antioxidant in human blood plasma. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 86:6377-6381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Garg, A. K., and B. B. Aggarwal. 2002. Reactive oxygen intermediates in TNF signaling. Mol. Immunol. 39:509-517. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Guaiquil, V. H., J. C. Vera, and D. W. Golde. 2001. Mechanism of vitamin C inhibition of cell death induced by oxidative stress in glutathione-depleted HL-60 cells. J. Biol. Chem. 276:40955-40961. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Halliwell, B. 1999. Vitamin C: poison, prophylactic or panacea? Trends Biochem. Sci. 24:255-259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Halliwell, B., and J. M. C. Gutteridge. 1999. Free radicals in biology and medicine, 3rd ed. Oxford University Press, Oxford, N.Y.
- 15.Hanks, S. K., A. M. Quinn, and T. Hunter. 1988. The protein kinase family: conserved features and deduced phylogeny of the catalytic domains. Science 241:42-52. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Jupp, O. J., S. M. McFarlane, H. M. Anderson, A. F. Littlejohn, A. A. Mohamed, R. H. MacKay, P. Vandenabeele, and D. J. MacEwan. 2001. Type II tumour necrosis factor-alpha receptor (TNFR2) activates c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) but not mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) or p38 MAPK pathways. Biochem. J. 359:525-535. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Karin, M., and Y. Ben-Neriah. 2000. Phosphorylation meets ubiquitination: the control of NF-κB activity. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 18:621-663. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Levine, M., K. Morita, E. Heldman, and H. B. Pollard. 1985. Ascorbic acid regulation of norepinephrine biosynthesis in isolated chromaffin granules from bovine adrenal medulla. J. Biol. Chem. 260:15598-15603. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Li, Q., and I. M. Verma. 2002. NF-κB regulation in the immune system. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2:725-734. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Li, X., C. E. Cobb, K. E. Hill, R. F. Burk, and J. M. May. 2001. Mitochondrial uptake and recycling of ascorbic acid. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 387:143-153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Liang, W. J., D. Johnson, and S. M. Jarvis. 2001. Vitamin C transport systems of mammalian cells. Mol. Membrane Biol. 18:87-95. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Lutsenko, E. A., J. M. Carcamo, and D. W. Golde. 2002. Vitamin C prevents DNA mutation induced by oxidative stress. J. Biol. Chem. 277:16895-16899. (Erratum, 277:27576.) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Mercurio, F., and A. M. Manning. 1999. NF-κB as a primary regulator of the stress response. Oncogene 18:6163-6171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Nathan, C. 2003. Specificity of a third kind: reactive oxygen and nitrogen intermediates in cell signaling. J. Clin. Investig. 111:769-778. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Nishikimi, M., R. Fukuyama, S. Minoshima, N. Shimizu, and K. Yagi. 1994. Cloning and chromosomal mapping of the human nonfunctional gene for L-gulono-gamma-lactone oxidase, the enzyme for L-ascorbic acid biosynthesis missing in man. J. Biol. Chem. 269:16895-16898. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Padh, H. 1991. Vitamin C: newer insights into its biochemical functions. Nutr. Rev. 49:65-70. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 27.Perez-Cruz, I., J. M. Cárcamo, and D. W. Golde. 2003. Vitamin C inhibits FAS-induced apoptosis in monocytes and U937 cells. Blood 102:336-343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Rebouche, C. J. 1991. Ascorbic acid and carnitine biosynthesis. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 54:1147S-1152S. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Russell, P. J., A. Williams, and T. A. Austin. 2000. Inhibition of rabbit muscle isozymes by vitamin C. J. Enzyme Inhib. Med. Chem. 15:283-296. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Sattler, M., T. Winkler, S. Verma, C. H. Byrne, G. Shrikhande, R. Salgia, and J. D. Griffin. 1999. Hematopoietic growth factors signal through the formation of reactive oxygen species. Blood 93:2928-2935. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Schrammel, A., D. Koesling, K. Schmidt, and B. Mayer. 2000. Inhibition of purified soluble guanylyl cyclase by L-ascorbic acid. Cardiovasc. Res. 47:602-608. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Schreck, R., K. Albermann, and P. A. Baeuerle. 1992. Nuclear factor κB: an oxidative stress-responsive transcription factor of eukaryotic cells (a review). Free Radic. Res. Commun. 17:221-237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Tsukaguchi, H., T. Tokui, B. Mackenzie, U. V. Berger, X. Z. Chen, Y. Wang, R. F. Brubaker, and M. A. Hediger. 1999. A family of mammalian Na+-dependent L-ascorbic acid transporters. Nature 399:70-75. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Vera, J. C., C. I. Rivas, J. Fischbarg, and D. W. Golde. 1993. Mammalian facilitative hexose transporters mediate the transport of dehydroascorbic acid. Nature 364:79-82. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Vera, J. C., C. I. Rivas, F. V. Velasquez, R. H. Zhang, I. I. Concha, and D. W. Golde. 1995. Resolution of the facilitated transport of dehydroascorbic acid from its intracellular accumulation as ascorbic acid. J. Biol. Chem. 270:23706-23712. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Wilson, J. X. 2002. The physiological role of dehydroascorbic acid. FEBS Lett. 527:5-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Witenberg, B., H. H. Kalir, Z. Raviv, Y. Kletter, V. Kravtsov, and I. Fabian. 1999. Inhibition by ascorbic acid of apoptosis induced by oxidative stress in HL-60 myeloid leukemia cells. Biochem. Pharmacol. 57:823-832. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Yin, M. J., Y. Yamamoto, and R. B. Gaynor. 1998. The anti-inflammatory agents aspirin and salicylate inhibit the activity of IκB kinase-β. Nature 396:77-80. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]