Abstract
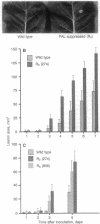
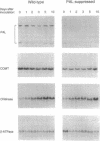
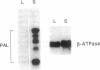
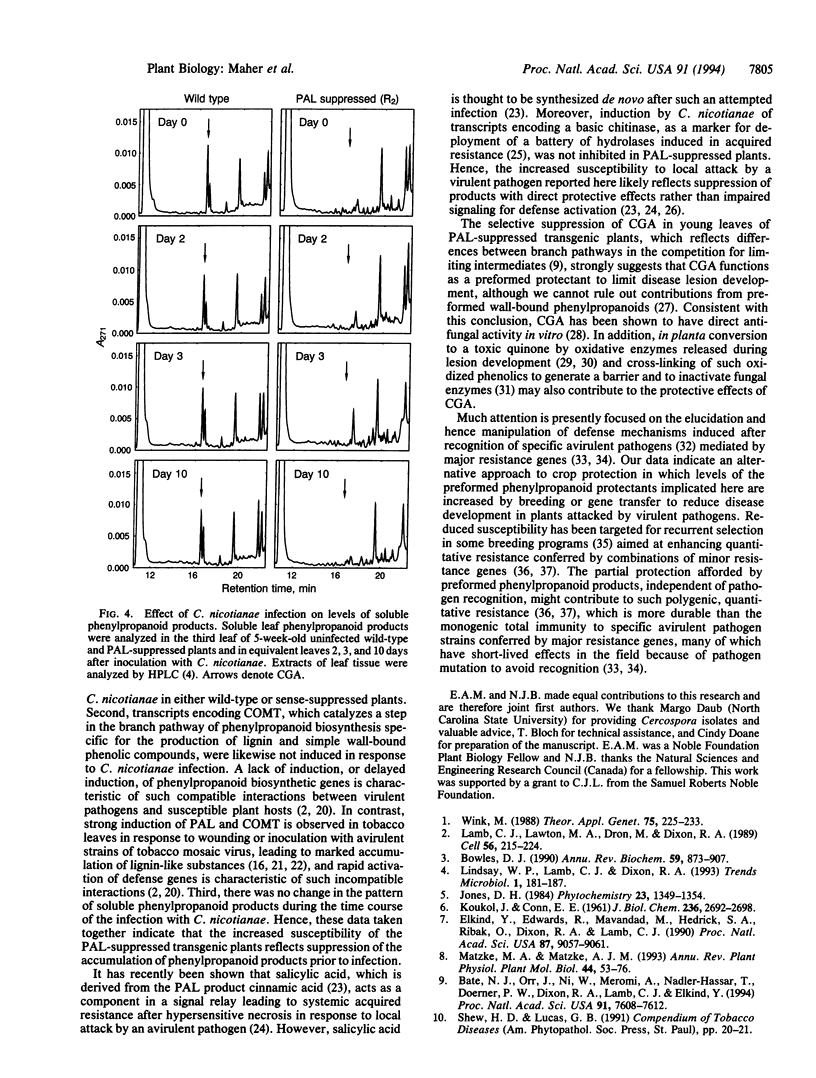
It has been proposed that natural products synthesized by plants contribute to their resistance to pests and pathogens. We show here that transgenic tobacco plants with suppressed levels of the phenylpropanoid biosynthetic enzyme phenylalanine ammonia-lyase (L-phenylalanine ammonia-lyase, EC 4.3.1.5) and correspondingly low levels of chlorogenic acid, the major soluble leaf phenylpropanoid product, exhibit more rapid and extensive lesion development than wild-type plants after infection by the virulent fungal pathogen Cercospora nicotianae. These observations provide direct evidence that phenylpropanoid products contribute to disease limitation. No induction of transcripts encoding phenylalanine ammonia-lyase or the lignin branch pathway enzyme caffeic acid O-methyltransferase was observed during the infection and there was no perturbation in the pattern of soluble phenylpropanoids. Hence, increased disease susceptibility does not involve inhibition of a pathogen-induced response but likely reflects inhibition of the developmental accumulation of chlorogenic acid. Demonstration of the contribution of such preformed protectants to plant health identifies attractive targets for manipulation by breeding or gene transfer to reduce the quantitative impact of disease.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bate N. J., Orr J., Ni W., Meromi A., Nadler-Hassar T., Doerner P. W., Dixon R. A., Lamb C. J., Elkind Y. Quantitative relationship between phenylalanine ammonia-lyase levels and phenylpropanoid accumulation in transgenic tobacco identifies a rate-determining step in natural product synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Aug 2;91(16):7608–7612. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.16.7608. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boutry M., Chua N. H. A nuclear gene encoding the beta subunit of the mitochondrial ATP synthase in Nicotiana plumbaginifolia. EMBO J. 1985 Sep;4(9):2159–2165. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03910.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowles D. J. Defense-related proteins in higher plants. Annu Rev Biochem. 1990;59:873–907. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.59.070190.004301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duchesne M., Fritig B., Hirth L. Phenylalanine ammonia-lyase in tobacco mosaic virus-infected hypersensitive tobacco. Density-labelling evidence of de novo synthesis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Dec 8;485(2):465–481. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(77)90182-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elkind Y., Edwards R., Mavandad M., Hedrick S. A., Ribak O., Dixon R. A., Lamb C. J. Abnormal plant development and down-regulation of phenylpropanoid biosynthesis in transgenic tobacco containing a heterologous phenylalanine ammonia-lyase gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Nov;87(22):9057–9061. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.22.9057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enyedi A. J., Yalpani N., Silverman P., Raskin I. Signal molecules in systemic plant resistance to pathogens and pests. Cell. 1992 Sep 18;70(6):879–886. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90239-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaffney T., Friedrich L., Vernooij B., Negrotto D., Nye G., Uknes S., Ward E., Kessmann H., Ryals J. Requirement of salicylic Acid for the induction of systemic acquired resistance. Science. 1993 Aug 6;261(5122):754–756. doi: 10.1126/science.261.5122.754. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gowri G., Bugos R. C., Campbell W. H., Maxwell C. A., Dixon R. A. Stress Responses in Alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.): X. Molecular Cloning and Expression of S-Adenosyl-l-Methionine:Caffeic Acid 3-O-Methyltransferase, a Key Enzyme of Lignin Biosynthesis. Plant Physiol. 1991 Sep;97(1):7–14. doi: 10.1104/pp.97.1.7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOUKOL J., CONN E. E. The metabolism of aromatic compounds in higher plants. IV. Purification and properties of the phenylalanine deaminase of Hordeum vulgare. J Biol Chem. 1961 Oct;236:2692–2698. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keen N. T. Gene-for-gene complementarity in plant-pathogen interactions. Annu Rev Genet. 1990;24:447–463. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.24.120190.002311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiedrowski S., Kawalleck P., Hahlbrock K., Somssich I. E., Dangl J. L. Rapid activation of a novel plant defense gene is strictly dependent on the Arabidopsis RPM1 disease resistance locus. EMBO J. 1992 Dec;11(13):4677–4684. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05572.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamb C. J., Lawton M. A., Dron M., Dixon R. A. Signals and transduction mechanisms for activation of plant defenses against microbial attack. Cell. 1989 Jan 27;56(2):215–224. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90894-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamb C. J., Ryals J. A., Ward E. R., Dixon R. A. Emerging strategies for enhancing crop resistance to microbial pathogens. Biotechnology (N Y) 1992 Nov;10(11):1436–1445. doi: 10.1038/nbt1192-1436. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liang X. W., Dron M., Cramer C. L., Dixon R. A., Lamb C. J. Differential regulation of phenylalanine ammonia-lyase genes during plant development and by environmental cues. J Biol Chem. 1989 Aug 25;264(24):14486–14492. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liang X. W., Dron M., Schmid J., Dixon R. A., Lamb C. J. Developmental and environmental regulation of a phenylalanine ammonia-lyase-beta-glucuronidase gene fusion in transgenic tobacco plants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(23):9284–9288. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.23.9284. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindsay W. P., Lamb C. J., Dixon R. A. Microbial recognition and activation of plant defense systems. Trends Microbiol. 1993 Aug;1(5):181–187. doi: 10.1016/0966-842x(93)90088-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linthorst H. J., van Loon L. C., van Rossum C. M., Mayer A., Bol J. F., van Roekel J. S., Meulenhoff E. J., Cornelissen B. J. Analysis of acidic and basic chitinases from tobacco and petunia and their constitutive expression in transgenic tobacco. Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 1990 Jul-Aug;3(4):252–258. doi: 10.1094/mpmi-3-252. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loake G. J., Faktor O., Lamb C. J., Dixon R. A. Combination of H-box [CCTACC(N)7CT] and G-box (CACGTG) cis elements is necessary for feed-forward stimulation of a chalcone synthase promoter by the phenylpropanoid-pathway intermediate p-coumaric acid. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Oct 1;89(19):9230–9234. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.19.9230. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pellegrini L., Geoffroy P., Fritig B., Legrand M. Molecular cloning and expression of a new class of ortho-diphenol-O-methyltransferases induced in tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum L.) leaves by infection or elicitor treatment. Plant Physiol. 1993 Oct;103(2):509–517. doi: 10.1104/pp.103.2.509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmid J., Doerner P. W., Clouse S. D., Dixon R. A., Lamb C. J. Developmental and environmental regulation of a bean chalcone synthase promoter in transgenic tobacco. Plant Cell. 1990 Jul;2(7):619–631. doi: 10.1105/tpc.2.7.619. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]