Abstract
Background
This systematic review aimed to present and critically appraise the available information on the efficacy of platelet rich plasma (PRP) in equine and human orthopedic therapeutics and to verify the influence of study design and methodology on the assumption of PRP’s efficacy. We searched Medline, PubMed, Embase, Bireme and Google Scholar without restrictions until July 2013. Randomized trials, human cohort clinical studies or case series with a control group on the use of PRP in tendons, ligaments or articular lesions were included. Equine clinical studies on the same topics were included independently of their design. Experimental studies relevant to the clarification of PRP’s effects and mechanisms of action in tissues of interest, conducted in any animal species, were selected.
Results
This review included 123 studies. PRP’s beneficial effects were observed in 46.7% of the clinical studies, while the absence of positive effects was observed in 43.3%. Among experimental studies, 73% yielded positive results, and 7.9% yielded negative results. The most frequent flaws in the clinical trials’ designs were the lack of a true placebo group, poor product characterization, insufficient blinding, small sampling, short follow-up periods, and adoption of poor outcome measures. The methods employed for PRP preparation and administration and the selected outcome measures varied greatly. Poor study design was a common feature of equine clinical trials. From studies in which PRP had beneficial effects, 67.8% had an overall high risk of bias. From the studies in which PRP failed to exhibit beneficial effects, 67.8% had an overall low risk of bias.
Conclusions
Most experimental studies revealed positive effects of PRP. Although the majority of equine clinical studies yielded positive results, the human clinical trials’ results failed to corroborate these findings. In both species, beneficial results were more frequently observed in studies with a high risk of bias. The use of PRP in musculoskeletal lesions, although safe and promising, has still not shown strong evidence in clinical scenarios.
Electronic supplementary material
The online version of this article (doi:10.1186/s12917-015-0403-z) contains supplementary material, which is available to authorized users.
Keywords: Platelet-rich plasma, Systematic review, Horse, Tendon, Ligament, Joint
Background
Musculoskeletal lesions are a common consequence of physical overstrain, which negatively impacts quality of life and athletic performance. Specifically among both, equine and human athletes, treating persistent or slow healing injuries poses a challenge for clinicians. These lesions, which frequently result in inadequate tissue reorganization and thus in a high re-injury rate, are often related to a long period of incapacity or to an unsatisfactory return to performance [1].
Hemoderivatives have been reported to be beneficial in scenarios in which efficient, cost-effective and safe forms of orthopedic interventions are necessary to restore the normal function and structure of musculoskeletal components and in which health care professionals are tempted to explore promising forms of therapy. The use of patients’ own biological materials for tissue healing and therapeutic purposes offers a safe and interesting alternative to conventional treatments, and such materials often lack side effects. Presently, several blood-derived products are available for intra-lesional injection, such as platelet-rich plasma (PRP) or plasma rich in growth factors, autologous conditioned serum, autologous blood preparations and autologous protein concentrate [1-6].
The rationale behind the injection of autologous blood preparations lies in the exploitation of advantageous mechanisms of the body’s natural response to injury, whether the platelets’ ability to induce hemostasis and to release growth factors [7,8] or the production of anti-inflammatory cytokines by blood components [5,9]. Blood is an important and unique source of cellular and protein products that has been explored more intensively over the last three decades for the production of biomaterials for clinical use [4]. A considerable number of data have suggested beneficial effects associated with their use, but these findings have not been unanimous when experimental and clinical trial’ results have been compared.
Platelet-rich products, in particular, have gained popularity for their increased concentrations of growth factors, but their compositions encompass much more than these factors. A myriad of other blood-derived substances such as fibrin and leukocytes are contained within these products, characterizing PRP as a complex and unique mixture, with donor-related properties and a yet unrevealed spectrum of active blood components [10]. Platelet concentrates with distinct compositions, and therefore distinct applications, are referred to as PRP. Some authors have proposed a more accurate terminology, along with a thorough description of the platelet concentrate. Using this terminology four different products can be recognized according to their fibrin architecture and leukocyte content: pure platelet-rich plasma, leukocyte and platelet-rich plasma, pure platelet-rich fibrin and leukocyte- and platelet-rich fibrin [11].
The cellular and molecular content of platelet concentrates also depend on the method or kit used for their preparation. Until now, there has been no consensus on which processing method yields the best platelet- related product for a particular purpose, and patented and non-patented technologies and procedures have been used in clinical and experimental scenarios [12].
During athletics, both horses and humans are subjected to escalating stresses to their appendicular systems, to compete successfully. These increasing demands are accompanied by a multitude of orthopedic lesions, for which conventional therapies have proven partially helpful.
The objectives of this systematic review were to assess the effectiveness of PRP in the healing of tendon, ligament and articular lesions in equine and human patients, to compare the results from clinical and experimental studies in both species, and to verify the existence of a relationship between the study designs and results of clinical trials. This review also aimed to evaluate critically the existing evidence to provide clinicians with high-quality information and a more thorough appreciation of the effects of the diversity of PRP’ processing techniques.
Methods
This systematic review was performed in accordance with the PRISMA (Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses) statement, an evidence-based, established guideline for systematic reviews published by the CONSORT group [13,14].
A comprehensive literature search addressing the use of hemoderivatives in orthopedic lesions was conducted in July 2013 for all relevant articles in English, French, German, Spanish and Portuguese without publication or date restrictions, and all of the authors (PMB, JJM, TSLM, RYAB) were involved. The Embase, Bireme, Medline, PubMed and Google Scholar databases were used, with the search terms “platelet rich plasma”, “PRP”, “tendon”, “joint”, “articular”, “ligament”, “musculoskeletal injuries”, “human” and “equine”. Additional studies were identified by searching the reference lists of eligible articles. Studies that used PRP in conjunction with stem cells or other biomaterials, as regenerative/anti-inflammatory therapies for other target tissues (e.g., bone) or in other medical fields (such as ophthalmology, craniomaxillofacial or plastic surgery) were excluded.
Equine clinical studies, because of their scarcity, were included independently of their design or level of evidence if they described the effects of PRP on tendon, ligament or articular injuries. Human clinical studies were included if they reported the use of PRP in tendon, ligament or articular lesions and were either double-blind RCTs or prospective/retrospective cohort studies or if they were case series with a control group.
Experimental studies with PRP conducted in several species, both in vivo and in vitro, were selected if they were controlled and relevant to the clarification of the effects and mechanisms of action of PRP in tissues of interest. Studies that used products not derived from blood processing, despite an analogous function or a similar composition to PRP, were not included [15-17].
Preliminarily, the abstracts and titles were reviewed to select manuscripts for full-text review. Relevant data were then extracted from the selected articles based on predefined data fields and were sorted in tables corresponding to clinical and experimental studies, independently, by all of the authors. The tables were intended to (1) facilitate the identification of the lesion/tissue/population studied; (2) characterize the control and intervention groups; (3) state the outcome measures and methods employed for the evaluation of effects; (4) describe in detail the method of preparation, composition and protocol of administration of PRP; and (5) present the results and rate them as positive or beneficial (+), partially positive (±) or negative (impartial) (−). This assessment was not made by the review’s authors and is in accordance to the results presented, when confronted with the selected outcome measures. This overall view of the studies’ design and contents was followed by annotation of weak points that could have negatively affected the generation of quality evidence or that could have biased the studies’ results. Experimental studies with in vivo and in vitro ramifications had their results presented on separate lines to allow for a thorough analysis.
The risk of bias of the selected clinical trials was presented in tables according to PRISMA guidelines, and the studies were assigned as having a high or a low risk of bias if they exhibited, respectively, more or fewer bias criteria. This information, together with the analysis of the clinical trials’ results, was used to verify a possible association between these two variables and was also presented in tables.
Results
Our search parameters yielded 7415 results: 3563 from Embase, 2817 from Bireme, 101 from Medline, 122 from PubMed and 812 from Google Scholar. Fifteen studies were identified in reference lists from the selected articles. The titles and abstracts of the retrieved records were screened for eligibility, and 5926 studies were thus excluded. One thousand five hundred four articles were fully assessed. One hundred twenty-three (123) articles were selected after the exclusion criteria (i.e., the exclusion of duplicates, review articles, non-controlled human trials, studies in which other tissues were examined and experimental studies investigating PRP preparation particularities) were applied (Figure 1).
Figure 1.
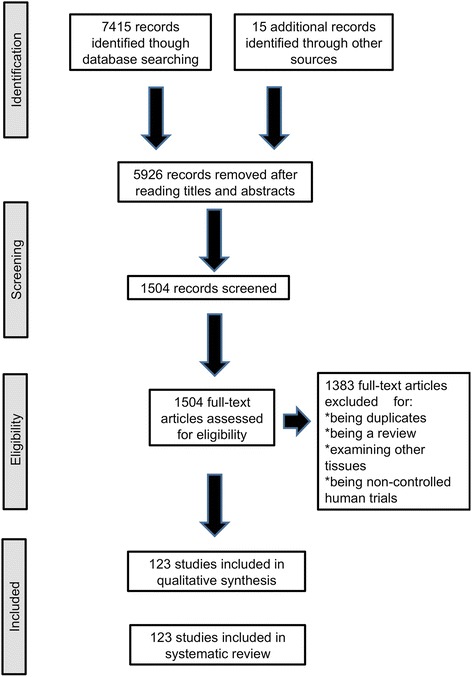
Flow diagram for identification of published studies. PRISMA 2009.
Among these 123 studies, a relatively homogeneous distribution between clinical trials (60 studies or 48.8%) and experimental studies (63 studies or 51.2%) was observed. These 123 articles yielded 126 results because two experimental studies comprised both in vivo and in vitro experiments, which were considered separately.
Clinical trials with PRP
From the 60 clinical studies included in this review, 11 (18.3%) [18-28] were conducted in horses, and 49 (81.7%) [29-77] were conducted in humans. Considering both species together, the results of the clinical trials were evenly distributed, that is, beneficial effects were observed in 28 studies (46.7%) [19,21-23,25,26,28,29,32,34-36,38,39,41,49,55,57,58,62,64,69,70,72-76], and negative effects were observed in 26 studies (43.3%) [18,30,31,33,37,42-45,47,48,50-54,56,59,60,63,65-68,71,77] after PRP application (Additional file 1: Table S1).
Analyzing the species separately, we observed that the distribution of results was not homogeneous and that positive results were more frequent than negative results in the equine species. Seven [19,21-23,25,26,28] of 11 equine clinical trials yielded positive results (63.6%), three [20,24,27] resulted in partially positive results (27.3%), and one (9.1%) [18] yielded a negative result. In contrast, of the 49 human clinical studies, 21 yielded positive results (42.8%) [29,32,34-36,38,39,41,49,55,57,58,62,64,69,70,72-76], while 25 studies (51%) [30,31,33,37,42-45,47,48,50-54,56,59,60,63,65-68,71,77] yielded negative results, and 3 (6.1%) [40,46,61] resulted in partially positive results.
Although the percentages of negative and positive results in the human clinical trials were fairly even, the study design distribution among the positively and negatively evaluated studies was not homogeneous. This distribution revealed a negative correlation between a rigorous study design and the finding of beneficial results associated with the clinical use of PRP. Thirty-five studies were classified as RCTs: 34 [29,30,32-40,43,44,46,47,49-54,56,57,59,61-63,66-68,70,71,75,77] from the human medical literature and one [18] from the equine medicine literature. Among them, 12 trials (34.3%) [29,32,34-36,38,39,49,57,62,70,75] yielded positive results, while 20 RCTs (57.1%) [18,30,33,37,43,44,47,50-54,56,59,63,66-68,71,77] yielded negative results, and 3 RCTs (8.6%) had [40,46,61] mixed results.
Among the remaining 10 equine clinical trials that were not RCTs, seven studies [19,21-23,25,26,28] that yielded positive results were uncontrolled trials. Overall, 2 studies (18.2%) [18,24] had control groups, and eight [19,21-23,25-28] uncontrolled case series accounted for 72.7% of the equine studies. The remaining 15 human studies [31,41,42,45,48,55,58,60,64,65,69,72-74,76] that were not RCTs were controlled retrospective or prospective cohorts, comparative studies, case control series and observational controlled studies.
Additionally, while 76.9% (20/26) of the studies [18,30,33,37,43,44,47,50-54,56,59,63,66-68,71,77] with negative results were classified as RCTs, 42.8% (12/28) of the studies [29,32,34-36,38,39,49,57,62,70,75] with positive results were RCTs.
Regarding study design, the lack of a true placebo control group was the most frequently assigned flaw. Forty-three studies (71.7%) [24,29-32,35,38-44,46-55,57-76] had control groups that differed from placebo, such as hyaluronic acid and corticosteroids, and/or that included physiotherapy, excentric exercises, peppering techniques, dry needling (or combinations of these techniques) or merely lack of PRP application. Nine studies (15%) [19-23,25-28] lacked a control group, and all of these studies were conducted in horses.
Poor PRP characterization was a feature of 35 clinical studies (58.3%) [20,24,29-33,35-38,42-47,49,50,53,55-60,62-64,67,68,71,73,76,77] and was the second most frequent flaw. Information regarding PRP preparation, activation and composition was not always provided in a complete manner, and in one clinical trial [60], this information was not provided at all. The product name, a description of the processing method in detail and a description of PRP activation when used (or stated otherwise) defined adequate hemoderivative characterization. Platelet and leukocyte concentrations, together with their concentration factors from baseline levels and an analysis of growth factor contents, should ideally have been stated. Of 60 clinical trials, eight (13.3%) [21,22,25,27,28,51,69,72] provided this standard of information. Seventeen studies (28.3%) [18,19,23,26,34,39-41,48,52,54,61,65,66,70,74,75] provided only average-quality information on the employed hemoderivative; no data on growth factor content were provided.
The methods employed for PRP preparation have been the object of controversy [1,7]. Of the 60 clinical studies, 30 (50%) [18,19,23,29,31-36,38,39,46,51,53,54,56,57,62-64,67-70,72,73,75-77] employed only one centrifugation, 19 (31.7%) [21,24,25,27,28,42-45,47,49,50,52,55,58,59,65,66,71] employed two centrifugations, and one [41] employed three centrifugations. Filtration was the method of choice for obtaining PRP in one study [22], and nine studies [20,26,30,37,40,48,60,61,74] did not state how many centrifugations were employed for PRP preparation. Of the 30 studies that employed one centrifugation, 18 yielded positive results (60%) [19,23,29,32,34-36,38,39,57,62,64,69,70,72,73,75,76]. Of the 19 studies that employed 2 centrifugations, 6 yielded positive results (31.6%) [21,25,28,49,55,58].
Regarding PRP activation, 23 studies [18,23,24,29-33,35,37,38,41,47,51,53,54,56,57,60,62,63,76,77] did not stipulate whether their product was activated or not. Overall, 35 studies (58.3%) [19-21,25-28,33,36,39,40,42-46,48-50,52,55,58,59,61,65-75] used activators together with PRP. Calcium was used in 23 studies [19,21,25,27,28,33,36,39,42-45,48-50,52,55,58,59,65,66,69,72] thrombin in five [20,61,67,73,74], and calcium and thrombin in combination in six [40,46,68,71,73,74]. In two studies [22,64], the PRP was not activated.
Insufficient blinding was the third most common flaw in design and was found in 33 studies (55%) [18-31,35,37-41,45,48,55,58,60,65,67,69,72-76]. Adequate blinding was defined as the outcome assessors, patients and treating physicians being blinded to the treatment or intervention that was applied. Among the 33 non-blinded studies encountered in this review, 19 (57.6%) [19,21-23,25,26,28,29,35,38,39,41,55,58,69,72-74,76] had favorable results associated with PRP intervention, and ten (30.3%) [18,30,31,37,45,48,60,65,67,77] yielded negative results.
The fourth most frequent flaw, occurring in 32 studies [18-28,30,35,37,40,43,45,46,51,52,56,58,59,61,64,65,67,70,72,75-77] (53.3%), was the enrollment of a smaller-than-desired number of subjects. A study was considered to have a small sample when this information was provided by the respective authors, based on power calculations of the selected population. Among the 28 studies in which PRP had positive effects, 14 (50%) [19,21-23,25,26,28,35,58,64,70,72,75,76] had a small sample, and among the 26 studies in which PRP intervention resulted in negative outcomes, 12 (46.1%) [18,30,37,43,45,51,52,56,59,65,67,77] enrolled a smaller-than-desired sample.
The adoption of a short follow-up period, that is, an observation period of less than 12 months, also occurred in 32 studies (53.3%) [20,23,29,32-42,51,53-55,59-61,63,65,67-71,73-75,77]. Among the 26 clinical trials with negative results, 12 (46.1%) [18,30,31,43-45,47,48,50,52,56,66] were considered to have sufficient duration. Among the 28 studies with positive results, 13 (46.4%) [19,21,22,25,26,28,49,57,58,62,64,72,76] were considered to have an appropriate follow-up period.
Inadequacy of the parameters for outcome evaluation was a feature of 29 studies (48.3%) [18,24-26,28,29,31,32,34,36-39,41,42,51,54,55,57,61-64,67,69,70,74-76]. Among the 26 studies with negative results, 8 [18,31,37,42,51,54,63,67] adopted inadequate outcome measures (30.8%). Among the 28 studies with favorable results, 19 [25,26,28,29,32,34,36,38,39,41,55,57,62,64,69,70,74-76] had inadequate outcome measures (67.8%), and nine studies [19,21-23,35,49,58,72,73] were classified as having adequate outcome measures.
Not only study design but also the evaluation of the risk of bias of individual studies showed relationships between studies with a higher risk of bias and positive (beneficial) results observed after PRP interventions, with 67.8% (19/28) [19,21-23,25,26,28,29,34,38,39,41,55,58,69,72-74,76] of high-risk studies having positive outcomes. Of the studies rated a low risk, 28.6% had favorable outcomes. Among all of the studies in which PRP did not positively affect the selected outcomes, 73.1% (19/26) [18,30,33,37,43,44,47,50-54,56,59,63,66,68,71,77] were attributed a low risk of bias (Table 1 and Figure 2).
Table 1.
Risk of bias of selected clinical studies
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) (patient-reported outcomes) | Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) (all-cause mortality) | Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) (short-term [2-6 weeks]) | Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) (long-term[> 6 weeks]) | Selective repoorting (reporting bias) | Risk of bias | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Garret 2013 | + | + | - | + | - | + | + | - | ↓ |
| Zuffova 2013 | - | - | - | - | - | + | + | + | ↑ |
| Edinger 2012 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | ↑ |
| Torricelli 2011 | - | - | - | - | - | + | + | + | ↑ |
| Castelijns 2011 | - | - | - | - | - | + | + | + | ↑ |
| Georg 2010 | - | - | - | - | - | + | ? | - | ↑ |
| Abelanet 2009 | - | - | - | - | - | + | + | - | ↑ |
| Carmona 2009 | - | - | - | - | - | + | + | + | ↑ |
| Waselau 2008 | - | - | - | - | - | + | + | + | ↑ |
| Arguelles 2008 | - | - | - | - | - | + | + | + | ↑ |
| Carmona 2007 | - | - | - | - | - | + | + | + | ↑ |
| Tiwari 2013 | ? | - | - | - | ? | + | + | - | ↑ |
| Antuna 2013 | + | + | - | + | + | + | + | + | ↓ |
| Magnussen 2013 | - | - | - | - | - | + | + | + | ↑ |
| Mishra 2014 | + | + | - | + | + | + | + | + | ↓ |
| Krogh 2013 | + | + | - | + | + | + | + | + | ↓ |
| Patel 2013 | + | ? | ? | ? | ? | + | + | - | ↑ |
| Wasterlain 2012 | + | + | - | + | + | + | + | + | ↓ |
| Jain 2012 | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | ↓ |
| Mardones 2012 | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | ↓ |
| Cerza 2012 | - | - | - | - | - | + | + | + | ↑ |
| Mei-Dan 2012 | + | - | - | - | + | + | + | + | ↑ |
| Almeida 2012 | + | - | - | - | + | + | + | + | ↓ |
| Spaková 2012 | - | - | - | - | - | + | + | + | ↑ |
| Aksahin 2012 | - | - | - | + | - | + | + | + | ? |
| Rodeo 2012 | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | ↓ |
| Weber 2012 | + | - | + | + | + | + | + | + | ↓ |
| Bergeson 2012 | - | - | - | - | + | + | + | + | ? |
| Cervelin 2012 | + | + | ? | - | + | + | + | - | ↓ |
| Filardo 2012 | + | + | + | + | + | + | - | + | ↓ |
| Jo 2011 | - | - | - | - | - | + | + | + | ↑ |
| Randelli 2011 | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | ↓ |
| Castricini 2011 | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | ↓ |
| Thanasas 2011 | + | + | - | + | + | + | + | + | ↓ |
| Schepul 2011 | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | ↓ |
| De Vos 2011 | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | ↓ |
| Creaney 2011 | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | ↓ |
| Kon 2011 | - | - | - | - | - | + | + | + | ↑ |
| Jonge 2011 | + | + | + | + | + | + | - | + | ↓ |
| Gosens 2011 | ? | ? | + | + | + | + | + | + | ↓ |
| Barber 2011 | - | - | - | - | - | + | + | + | ↑ |
| Horstman 2011 | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | ↓ |
| Buford 2011 | - | - | - | - | - | + | + | + | ↑ |
| Vogrin 2010 | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | ↓ |
| Peerboms 2010 | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | ↓ |
| De Vos 2010 | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | ↓ |
| Radice 2010 | - | - | - | - | + | + | + | + | ? |
| Filardo 2010 | - | - | - | - | - | + | + | - | ↑ |
| Nin 2009 | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | ↓ |
| Silva 2009 | - | - | - | - | - | + | + | + | ↑ |
| Peerboms 2009 | ? | + | + | + | + | + | - | + | ↓ |
| Sanchez 2008 | - | - | - | - | - | - | ? | + | ↑ |
| Everts 2008 | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | ↓ |
| Orrego 2008 | + | + | - | + | + | + | + | + | ↓ |
| Sanchez 2007 | - | - | - | - | - | + | + | + | ↑ |
| Everts 2007 | - | - | - | - | - | + | + | + | ↑ |
| Gardner 2007 | - | - | - | - | - | + | + | + | ↑ |
| Zavadil 2007 | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | ↓ |
| Mishra 2006 | - | - | - | - | - | + | - | + | ↑ |
| Ventura 2005 | + | + | - | - | - | + | + | + | ↓ |
Figure 2.
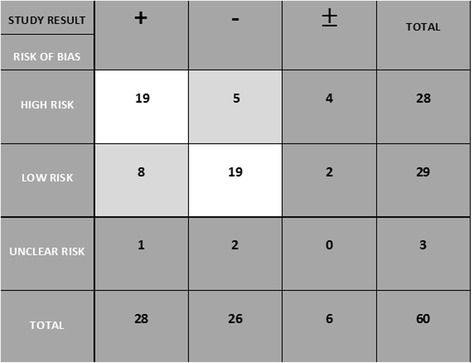
Association between risk of bias and clinical studies’ results.
Side effects associated with PRP use in the clinical setting were observed in two studies (3.3%); in one study [18] they referred to swelling at the injection site and in another [45] they related to infection after platelet-rich fibrin matrix application.
The majority of in vivo trials were devoted to observing the effects of PRP on tendinopathies (29 studies or 46%) [19-21,24,27,30,32,33,35,40,43-45,48-54,56-58,60,62,-63,65,72,76], followed by articular disorders (18 studies or 28.6%) [24,25,28,34,36-39,41,47,55,59,68-70,73-75] and ligament disorders (16 studies or 25.4%) [18,21-23,26,27,29,31,42,46,61,64,66,67,71,77]. The sum of recorded lesion locations (63 injury sites) exceeded the total number of clinical articles selected because a few studies observed the effects of PRP on both tendons and ligaments [21,23,27]. Considering 63 observation points, the injured tissues that were more positively affected by PRP treatment in in vivo trials were cartilage (20.6%) [25,28,34,36,38,39,41,55,69,70,73-75] and tendons (17.5%) [19,21,23,32,35,49,57,58,62,72,76] followed by ligaments (9.5%) [21-23,26,29,64]. Among the studies of arthropathies, 72.2% yielded positive results. In addition, 37.9% of the studies of tendinopathies yielded positive results, and 37.5% of the studies of desmopathies yielded positive results.
Experimental studies with PRP
In total, 63 experimental studies were included in this review: 13 (20.6%) [78-90] were conducted in horses, 16 (25.4%) [91-106] were conducted in humans and 34 (54%) [107-140] were conducted in other species.
Overall, their results contrasted with those of the clinical trials. Regarding outcomes, the homogeneity of the distribution between beneficial and negative results observed in the clinical trials was not mirrored in the experimental scenario. Among the 63 experimental studies, 46 (73%) [81-86,88,90-95,97-103,105-110,112,115,118-122,124-129,131,134-137,139,140] yielded positive results, 12 (19%) [78,79,87,89,96,104,111,113,116,123,130,133] yielded mixed results, and five (7.9%) [80,114,117,132,138] yielded negative results. Among the five experimental studies with negative results, all of them were conducted in vivo; four of them included mechanical evaluations among their outcome measures [80,117,132,138]. Two studies [114,132] exhibited side effects associated with PRP administration, and one study [114] failed to show improvements during the histological evaluation of experimentally induced tendon lesions treated with PRP.
From the 63 experimental studies, 35 (55.5%) [79,80,82-85,90,107,109-114,116-121,123-128,130-133,135-139] originated from in vivo experiments, 23 (36,5%) [81,86-89,91-103,105,108,115,133,139] originated from in vitro work, and five (7.9%) [78,96,104,106,122] originated from both in vivo and in vitro experiments (Additional file 2: Table S2). Considering separately the results of the five experiments conducted both in vivo and in vitro there are 67 experimental results. From the 41 in vivo trials, 27 (65.8%) [82-85,90,96,106,107,109,110,112,118-122,124-130,134,136,137,139] yielded positive results, while 23 of the 26 (88.5%) [81,86,88,91-103,105,106,108,115,122,134,140] in vitro experiments had positive results.
Considering only equine and human studies, there were 23 (79.3%) [81-86,88,90-103,105,106] positive results, 5 (17.2%) [78,79,87,89,104] mixed results and one (3.4%) [80] negative result.
Among the 12 experiments with partially positive results, nine (75%) [78,79,96,111,113,116,123,130,133] were conducted in vivo. Different reasons for adverse outcomes were observed. In one experiment [78], the PRP preparation resulted in an insufficient increase in growth factor content. In two experiments [78,79], side effects related to PRP administration were observed. In another two experiments [111,130], PRP treatment did not result in hyaline cartilage formation. In four studies [113,116,123,133], the treated tissues did not satisfactorily withstood mechanical challenges and in one trial [96], gene expression was not affected by PRP. In two in vitro trials with partially positive results [87,89], equine suspensory ligament explants cultured with PRP had increased gene expression, but this rate was greater when acellular bone marrow was added to the cultures, and in one [78] PRP preparation resulted in an insufficient increase in growth factor content.
In total, side effects were observed in five experiments [78,79,114,117,132]. One study [114] observed local reactions at different injection sites and concluded that PRP was capable of initiating an inflammatory response in the absence of an injury. In a second trial [117], a cellular response around grafts for anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) reconstruction was noted. In two studies [78,79], thrombin-activated PRP elicited both a local and a systemic inflammatory response after intra-articular injections in horses. Others (132) noticed cellular infiltration and fibroid necrosis 7 days after PRP application in a rotator cuff repair model.
Regarding PRP characterization, 16/63 (25.4%) experiments [78,79,81,87,88,90,98,100-103,105,113,125,135,140] exhibited good product characterization; in 26 studies (41.3%) [82,85,86,92-94,96,97,99,104,106-108,111,112,114,116,117,122,126,128-130,134,136,137] the hemoderivative was satisfactorily described, and in 21 (33.3%) [80,83,84,89,91,95,109,110,115,118-121,123,124,127,131-133,138, 139] experiments, the characterization was considered unsatisfactory.
Activation was employed in 39 experiments (61.9%) [78,79,82,85,92,94,96-108,110,112-114,116,117,119-122,125-127,129,130,132,134,136,137,140], and PRP activation was not mentioned in 23 experiments (36.5%) [80,81,83,84,86-91,93,95,109,111,115,118,123,124,130,133,135,138,139]. One study [128] stated that the hemoderivative was not activated.
For the preparation of PRP in experimental studies a single centrifugation was the method chosen for PRP preparation in 29 experiments (46%) [81,83,84,86-91,94,97,98,100,103-105,109-111,113,118-121,124,125,128,133,139]. Two centrifugations were used in 29 (46%) [80,82,92,95,96,99,101,106-108,112,114-117,122,123,126,127,129-132,134-138,140] experiments, one and two centrifugations were used in one experiment [93] and 3 centrifugations were employed in two experiments [85,102]. Filtration was used to obtain PRP in two trials [78,79]. Among the 29 experiments that employed one centrifugation, 25 yielded positive results (86.2%) [81,83,84,86,88,90,91,94,97,98,100,102,103,105,109,110,118-121,124,125,127,139,140]. Of the 29 experiments that employed two centrifugations, 20 yielded positive results (75%) [82,92,94-96,99,101,106-108,112,115,122,127,131,134-137,140].
Among the 67 experimental results, 17 were conducted in humans [91-106], 15 in rabbits [113-127], 13 in horses [78-90], ten in rats [128-137], five in sheep [96,104,110-112], three in pigs [138-140], three in dogs [107-109] and one in mice [96]. The number of species exceeds the number of experiments because, in a few cases, in vivo and in vitro trials of a same experiment yield two results in the species count down.
Thirty-five experiments (55.5%) [80,81,83-85,88,90-97,102,104-106,108,110,116,119-121,124,125,128,129,131-137] were related to tendon disorders, 16 (25.4%) [78,79,82,98-101,103,111,112,115,123,126,127,130,140] to cartilage, ten (15.9%) [87,89,107,109,113,117,118,122,138,139] to ligament lesions, one (1.6%) [86] to both ligament and tendon disorders, and one (1.6%) [114] to several potential injury tissues. PRP yielded positive results in 85.7% of the experiments with tendons (30 trials) [81,83-85,88,90-95,97,102,104-106,108,110,119-121,123,124,128,129,131,134-137], 68.7% (11 trials) of those with cartilage [82,98-101,103,112,115,126,127,140], and 50% of those with ligaments (five trials) [107,109,118,122,139].
Discussion
The use of hemoderivatives for tissue healing has gained increasing popularity for the treatment of musculoskeletal lesions. Among these derivatives, PRP has already been established as a part of the repertoire of possibilities for the treatment of orthopedic conditions [4,6,10,141-147].
Despite widespread acceptance of its ambulatory use, research continues for the purpose of providing convincing evidence of clinical benefits associated with this hemoderivative’s administration. Uncontrolled or biased reports of PRP’s efficacy have been excessive and have not strengthened the existing evidence, suggesting (but not definitively demonstrating) the beneficial effects of PRP.
The overall quality of the study design was less than ideal in the majority of the selected studies and the quality was inversely correlated with the performance of PRP in clinical trials. Rigorous study design and a low risk of bias were associated with negative outcomes in PRP clinical trials. Because a high-quality study design was a much more common feature of human studies and a rare feature of equine studies, it was not surprising to find more negatively affected outcomes in human clinical trials and positive outcomes in equine clinical trials. Other authors have emphasized the importance of well-designed clinical studies for the evaluation of PRP’s efficacy and limitations and these authors have warned about their scarcity [141,146,148-156], but the present review presented a quantitative link between study design and outcome.
Accordingly, 76.9% of the studies with negative results were classified as RCTs, while RCTs comprised only 42.8% of the studies with positive results. While the inclusion of studies with different designs can be a subject to debate if, in one hand, the inclusion of RCTs, cohorts and controlled case series caused heterogeneity of our study sample, on the other, the diversity and the large number of studies included allowed for comparisons and for the establishment of a quantitative relationship between study design and outcome after PRP intervention. This relationship was more consistent in the human clinical trials, given the scarcity of RCTs and controlled studies in the equine species. As expected, the majority of less than ideally- designed equine studies yielded positive results, and the only negative result among equine clinical trials originated from the only equine RCT. The same was true for including data of clinical and experimental studies, but, again, the comparison between results of PRP´s efficacy with these different methodologies revealed important results.
Another purpose of the current review was to analyze and summarize the most common flaws in study design and to evaluate their implications in the results of PRP interventions. The most striking feature contributing to the debatable quality of the clinical trials included in this review was the lack of a true placebo control group. This observation referred mainly to the human clinical trials because the majority of the equine clinical trials lacked a control group, thereby preventing comparison.
Because several of the selected studies adopted subjective outcome measures and lacked a true placebo control group, their results could have been impacted. However, a gold standard treatment, if one exists, can be assigned to the control group for comparison with a new proposed treatment. Then, researchers would be comparing two active treatment groups, without a placebo group [157]. This comparison was frequently observed in this review, and PRP’s effectiveness was often compared with that of hyaluronic acid, corticosteroids, autologous blood injections, no treatment, dry needling, physiotherapy or combinations of these therapies. Nevertheless, treatment controls, such as sham acupuncture and intra-articular hyaluronic acid, have a greater effect size than the average placebo effect [158]. Although control groups were often assigned to some sort of treatment in the selected articles, we could not identify relationships between positive or negative results and the lack of a true placebo group. In addition, as other authors [159] have mentioned, the use of PRP combined with other biological therapies could pose a challenge to the evaluation of PRP’s individual effects and confound interpretation of the results. Therefore, studies that chose to do so were not included in this review.
Poor hemoderivative characterization was the second most common flaw contributing to the assignment of study design as not ideal. Inconsistencies associated with PRP preparation and administration have contributed to the lack of strength and to the disparities of the generated evidence regarding PRP’s efficacy, in both clinical and experimental studies [160]. The most important consequence of the confounding diversity of the methods employed for PRP processing was the difference in resulting final products, which precluded a comparison of the treatment’s results [143,149,156]. Similar to any autologous blood-derived product, PRP has unique, non-reproducible and donor-related features that can jeopardize a comparison of the results [161,162]. Therefore, the hemoderivate composition should be verified and clearly presented [81,163] to minimize these effects.
This review confirmed the existing diversity of preparation methods, commercial or laboratorial, for obtaining PRP, as already indicated by other researchers [12,81,149,156,164-166]. These methods might include single, double or triple centrifugations, filtration and plateletpheresis, with and without the aid of activating agents. Most of the selected clinical studies employed one centrifugation step, and more positive results were observed with this method. Previous studies have demonstrated that a double centrifugation method resulted in higher platelet concentrations [167,168], but caused more alterations in platelet morphology and was more sensitive to small errors during preparation [168,169] compared with the single centrifugation method. This trend toward more positive outcomes with PRP prepared with one centrifugation step must be confirmed with further research. Overall, PRP characterization was more adequate in the experimental studies than in the clinical trials.
Another controversial topic in PRP preparation has been the need for activation – or the lack of it [163,170-172]. Until a consensus is reached, comparing activated to non-activated products is inevitable. Most of the clinical and experimental studies activated PRP before injection, and clinically more positive outcomes were observed without PRP activation. The percentages of clinical and experimental studies that employed activation were similar. Experimentally, there was no relationship between the use of activation before PRP administration and favorable or unfavorable outcomes.
The administration protocols also varied greatly among the studies - clinical and experimental - regarding injection or application techniques, volume of hemoderivative employed and timing and frequency of administration. Again, all of these variables limited our ability to compare the results from different articles [148,166].
Poor blinding was the third most frequent negative feature of the studies designs. Blinding limits bias in outcome evaluation, and whenever feasible, outcome assessors should not be aware of the treatment allocations of the patients in a clinical study [173]. Blinding of outcome assessors is one of the safeguards to assure the internal validity of a trial, and there has been strong evidence that their unblinding exaggerated treatment effects. Particularly when scoring subjective outcomes, for instance pain scores, biased findings can result from inadequate blinding [157,174]. Blinding becomes less important in reducing observer bias, as the outcome measure becomes less subjective [157]. In addition to the blinding of outcome assessors, trial participants and investigators should be unaware of an assigned intervention for similar reasons.
The adoption of a short follow-up period and the enrollment of a small sample were the fourth most commonly encountered weaknesses in study design, particularly in horses. Inadequate duration of follow-up or treatment compromises the external validity of an RCT. Clinicians treating patients with a variety of conditions have called attention to the contrast between the beneficial effects of treatments in short-term RCTs and the less encouraging experiences with long-term treatment in clinical practice [175]. Long-term follow-up evaluations should be a priority [81]. In this review, the classification of short study duration was evenly distributed between studies with positive and negative results and did not particularly affect outcomes, although a few clinical trials showed the short-term efficacy of PRP in improving knee function and quality of life [55,176].
The detrimental effects of enrolling a small sample on the power of a study have been well documented. When a sample is too small, a study is particularly susceptible to a type II errors; that is, the study could be insufficiently powerful to detect real differences between observed groups. Calculations of explicit sample size or power to anticipate this error have rarely been performed before the start of a research study [177]. However, in the selected articles, smaller samples were not particularly associated with positive or negative outcomes. Nevertheless, we encourage authors to enroll sufficient numbers of subjects in their studies to assure adequate power and significance to their findings.
The adoption of inadequate outcome measures was the fifth most frequently encountered weakness in study construction in this review. As already mentioned subjective outcomes present great opportunities for bias [174] and frequently were the only type of employed outcome measure in the selected studies.
In orthopedic research, health status can be assessed by a number of methods, which are classified either as objective (e.g., radiological changes, range of motion) or as subjective (those relying on responses obtained directly from patients about their perceptions of health and illness) and as either generic or disease-specific [174]. Most authors have accepted that a combination of objective and subjective measures is desirable for conducting a complete assessment. Often, a single given parameter employed for outcome evaluation suits certain circumstances but not others, and there has rarely been a single most appropriate rating system or outcome measure [173,178,179]. Employing different outcome measures allows for the capture of diverse aspects of overall function, and lack of agreement between patient-reported and objective measures reflects this diversity, rather than indicating a weakness in one method or the other [180].
In this review, 48.3% of the selected studies only evaluated PRP treatment’s efficacy with a few questionnaire-reported or subjective measures, as opposed to the ideal multifaceted evaluation; therefore, they were classified as having poor outcome measures. It is important to choose the most adequate measures for a particular task, condition and setting; otherwise, the results of clinical research can be misleading. In particular, the inclusion of mechanical tests resulted in more outcomes that were negative in the experimental studies. This association might help to explain why the consistently positive responses induced by PRP in vitro, particularly in cell cultures, were not correlated with similar improvements in outcomes in vivo. Another aspect that added confusion to the comparison of results of PRP treatments among the studies was the variety of lesions treated. PRP’s performance was compared in acute and chronic; experimentally induced and naturally occurring; tendon, ligament and articular disorders without due distinction for the particular tissues’ characteristics. Biomechanical particularities, such as those of the flexor and extensor tendons; lesion localization, such as insertional versus body tears in ligaments; and staging of lesions, such as advanced osteoarthritis versus mild cartilage injuries, were not considered when evaluating PRP’s treatment efficacy [166,177].
The localization of lesions in the clinical trials was associated with both positive and negative outcomes. PRP intervention yielded more positive results in tendinopathies than in arthropathies and desmopathies in humans. In a large survey of PRP’s effects in the equine species in which 191 subjects were treated for desmopathies, tendinopathies and arthropathies, good results after intralesional injection were obtained, but in tendinopathies results were more impressive [181]. The reasons for these findings are unknown, and given the heterogeneity of tissues and stage of diseases, these results should be interpreted with care. Other researchers failed to provide definite recommendations for PRP intervention on a tissue-related basis [164]. Clinical and experimental scenarios, as well as interventions in distinct phases of lesion progression, different species and particularly-affected structures do affect performance of a treatment modality and must be considered.
This review demonstrated that scientific evidence of the beneficial effects of PRP in clinical settings remains lacking. While the vast majority of experimental in vitro studies yielded positive results, the same promising outcomes were not verified in the clinical trials after intervention with PRP, particularly in humans. Corroborating these observations, we found that all of the negative results from experimental works came from in vivo studies. Other authors have made similar remarks when comparing in vivo and in vitro studies of PRP [78,182-184], but the present review furnished numeric data for making comparisons and drawing conclusions. Altogether, these numbers demonstrated that the high expectations created by PRP’s outstanding performance when tested in vitro have not been fulfilled when studies have been performed in living subjects. Given the small number of experimental studies with negative results, factors that could have adversely affected the outcomes were searched. Among the experimental in vivo studies that yielded negative results, four included mechanical evaluations in their outcome measures. Two studies exhibited side effects associated with PRP administration, and one study failed to show improvements during the histological evaluation of experimentally induced tendon lesions treated with PRP. The trend toward failure when mechanical tests were applied in PRP-treated tissues was already noted in in vivo studies with mixed results and was more evident when the follow-up period lasted longer after the PRP intervention. Mechanical tests should be considered when testing PRP’s effects in experimental models.
Why in vitro positive results outpaced the positive results observed in clinical and in vivo PRP studies by such a large margin remains to be determined. The particular characteristics of these distinct environments may provide clues about this discrepancy. The in vivo environment presents several variables that are absent outside of a living organism and that could interfere with PRP’s effectiveness. However, the primary advantage of in vitro research is that it allows for an enormous level of simplification of the system under study and of the effects of a compound on a system. As a drawback, in vitro experiments fail to replicate the precise cellular conditions of a living organism. They are conducted in a closed system that tend to allow for higher and longer exposure of cells or explants to a given molecule than the exposure found in body tissues, which are half open systems. In vivo, substances cannot easily reach target cells and are subject to biokinetics, which can result in underestimation of their effects [185].
Another relevant aspect that could harm the extrapolation of in vitro results to the in vivo scenario was the lack of consideration of interspecies differences. Numerous experimental in vivo studies have enrolled different animal models, and this finding could further affect the interpretation of the results of the efficacy of PRP in horses and humans.
Overall, PRP has proved to be a safe therapeutic tool, with few adverse effects observed in the selected articles. This finding was similar to reports by other authors [55,164,177,181,186]. Although the in vitro antibacterial effect of human PRP against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus has been demonstrated [187], as well as those of equine platelet concentrates and platelet-poor plasma [188] the potential risk for bacterial contamination during PRP processing must be considered.
Conclusion
PRP has demonstrated the potential to exert beneficial effects in the healing of tendons, ligaments and cartilage, but definitive clinical evidence of its efficacy remains lacking. A great amount of literature has been dedicated to the topic, and well-constructed clinical trials, with sufficient power and duration to detect differences between treatments, as well as standardization of products, procedures and conditions to be treated, are as important as they are scarce.
Our results confirmed that biased, poorly designed studies, that are not properly controlled or blinded and that adopt inadequate outcome measures, favored the observation of positive results. As a consequence of this finding, the majority of equine clinical studies, which lacked randomization; blinding; and adequate power, outcome measures and control groups, yielded positive results. Similarly, human clinical trials with analogous undesirable features tended toward positive outcomes. Although the human clinical trials were better constructed than the equine studies, some aspects of their design must nevertheless be improved to generate strong evidence regarding the use of PRP in clinical scenarios.
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by Fundação Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior (CAPES), Brasília, SP, Brazil; and Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de São Paulo (FAPESP), São Paulo, SP, Brazil. These sponsors did not have any influence on the study design, on the collection, analysis and interpretation of data, or on the writing of the manuscript and decision to submit for publication.
Abbreviations
- ABI
Autologous Blood Injection
- ABM
Acellular Bone Marrow
- ACL
Anterior cruciate ligament
- ACP
Autologous Conditioned Plasma, ADAMTS, A desintegrin and metalloproteinase with thrombospondin motifs
- AHFS
Ankle Hindfoot Scale
- AOFAS
American Orthopaedic Foot and Ankle Society
- ASES
American Shoulder and Elbow Surgeons
- ATRS
Achilles Tendon Total Rupture Score
- bFGF
basic fibroblast growth factor
- BMA
Bone marrow aspirate
- BMMC
Bone marrow mononucleated cell
- BMP
Bone morphogenetic protein
- BMS
Betamethasone
- Centrif.
Centrifugation
- Ca
Calcium
- ChM-I
Chondromodulin-I
- COL
Collagen
- COMP
Cartilage oligomeric matrix protein
- COX-2
Ciclo oxigenase- 2
- CSA
Cross sectional area
- CT
Computed tomography
- CXCR4
C-X-C chemokine receptor type 4
- DASH
Disabilities of the Arm, Shoulder and Hand
- DDFT
Deep Digital Flexor Tendon
- DMEM
Dulbecco’s modified eagle medium
- DS
Double spin
- EA
Extraarticular
- EGF
Endothelial growth factor
- ES
Echogenicity score
- Ex
Examination
- FAS
Fiber alignement score
- FBS
Foetal bovine serum
- FCS
Foetal calf serum
- FGF
Fibroblast growth factor
- GAG
Glycosaminoglycan
- GAPDH
Glyceraldehyde 3- phosphate dehydrogenase
- GF
Growth factor
- HA
Hyaluronic acid
- Hb
Haemoglobin
- HDGF
Hepatocyte-derived Growth Factor
- hGH
human growth hormone
- HMW
High molecular weight
- HS
Human serum
- IA
Intraarticular
- ICL
Inferior Check Ligament
- ICRS
International Cartilage Repair Society
- IGF-1
Insulin growth factor-1
- IKDC
International Knee Documentation Committee
- IL-1
Interleukin-1
- IL-6
Interleukin-6
- Inj
injection
- KOA
Knee osteoarthritis
- KOOS
Knee Injury and Osteoarthritis Outcome Score
- KSS
Knee society score
- KT-1000
KT-1000 arthrometer
- Le
Leukocyte
- LMW
Low molecular weight
- MFx
Microfractures
- MIZ
Maximum injury zone
- MMP
Metalloproteinase
- MPC
Mean platelet count
- MPD
Methylprednisolone
- MRI
Magnetic resonance imaging
- NFκB
Nuclear factor kappa B
- NRS
Numeric Rating Scale
- OA
Osteoarthritis
- OA*
Outcome acessors
- OC
Osteochondrosis
- P
Patient
- PBS
Phosphate buffered saline
- PC
Platelet concentrate
- PCR
Polimerase chain reaction
- PDGF
Platelet-derived growth factor
- Pl
Platelet
- PP
Platelet-poor
- PPACD
Platelet product acid citrate dextrose
- PPCPD
Platelet product citrate phosphate dextrose
- PPCR
Platelet-poor clot releasate
- PRCR
Platelet-rich clot releasate
- PPPR
Platelet-poor plasma releasate
- PRF
Platelet-rich fibrin
- PRFM
Platelet-rich fibrin matrix
- PRGF
Platelet-rich growth factor
- PRP
Platelet-rich plasma
- PRPR
Platelet-rich plasma releasate
- PRTEE
Patient-rated Tennis Elbow Evaluation
- PSD
Proximal suspensory desmitis
- PTGE
Prostaglandin endoperoxide synthase 2
- RBC
Red blood cell
- RCT
Randomized clinical trial
- ROM
Range of motion
- RTPCR
Reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction
- SANE
Single Assessment Numeric Evaluation
- SDFT
Superficial Digital Flexor Tendon
- SER
Strength in External Rotation
- SC
Subcutaneous
- SF
Synovial fluid
- Signif
Significant
- SOX-9
Transcription factor SOX 9
- SPADI
Shoulder Pain and Disability Index
- SS
Single spin
- SST
Simple Shoulder Test
- T
Thrombin
- TA
Triamcinolone
- TGFβ-1
Transforming Growth Factor Beta-1
- TIMP
Tissue inhibitor metalloproteinase
- TNF-α
Tumor necrosis factor alpha
- TP
Treating physician
- UCLA
University of California - Los Angeles
- US
Ultrasound
- UTC
Ultrasonographic tissue characterization
- VAS
Visual Analogue Score
- VCAM
Vascular cell adhesion protein 1
- VEGF
Vascular endothelial growth factor
- VISA
Victorian Institute of Sports Assessment
- WBC
White blood cells
- WOMAC
Western Ontario and McMaster Universities Arthritis Index
- WORC
Western Ontario Rotator Cuff
Additional file
Characteristics of 60 clinical studies that provided evidence regarding PRP intervention.
Characteristics of 63 experimental studies that provided evidence regarding PRP intervention.
Footnotes
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Authors’ contributions
PMB designed the study and wrote the manuscript. Abstracts and titles were reviewed by PMB, JJM and TSLM in order to select manuscripts for full-text review. RYAB supervised the studies and participated in the writing and revision of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Contributor Information
Patrícia M Brossi, Email: ptbrossi@uol.com.br.
Juliana J Moreira, Email: ju_veterinaria@yahoo.com.br.
Thaís SL Machado, Email: tsodrelima@gmail.com.
Raquel YA Baccarin, Email: baccarin@usp.br.
References
- 1.Ziltener JL, Allet L, Sclison P, Grosclaude M. How effective are injections of platelet-rich plasma (PRP) for the treatment of sports injuries: a critical review of the literature. J Sports Med Doping Studie 2012;doi:10.4172/2161-0673.S2-003.
- 2.Brossi PM, Baccarin RY, Massoco CO. Do blood components affect the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) by equine synovial fluid cells? Pesq Vet Bras. 2012;32:1355–60. [Google Scholar]
- 3.Moreira JJ, Moraes APL, Brossi PM, Machado TSL, Michelacci YM, Massoco CO, et al. Autologous processed plasma: cytokine profile and effects upon injection in healthy equine joints. J Vet Sci. 2015;16:47–55. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 4.Burnouf T, Goubran HA, Chen TM, Ou KL, El E, et al. Blood-derived biomaterials and platelet growth factors in regenerative medicine. Blood Rev. 2013;27:77–89. doi: 10.1016/j.blre.2013.02.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Textor J. Autologous biologic treatment for equine musculoskeletal injuries: platelet-rich plasma and IL-1 receptor antagonist protein. Vet Clin North Am Equine Pract. 2011;27:275–98. doi: 10.1016/j.cveq.2011.05.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Chevalier X. Intraarticular treatments for osteoarthritis: new perspectives. Curr Drug Targets. 2010;11:546–60. doi: 10.2174/138945010791011866. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Alsousou J, Thompson M, Hulley P, Noble A, Willett K. The biology of platelet-rich plasma and its application in trauma and orthopaedic surgery: a review of the literature. J Bone Joint Surg (Br) 2009;91:987–96. doi: 10.1302/0301-620X.91B8.22546. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Fortier LA, Barker JU, Strauss EJ, McCarrel TM, Cole BJ. The role of growth factors in cartilage repair. Clin Orthop. 2011;469:2706–15. doi: 10.1007/s11999-011-1857-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Gobbi G, Vitale M. Platelet-rich plasma preparations for biological therapy: applications and limits. Oper Tech Orthop. 2012;22:10–5. [Google Scholar]
- 10.Boswell SG, Cole BJ, Sundman EA, Karas V, Fortier LA. Platelet-rich plasma: a milieu of bioactive factors. Arthroscopy. 2012;28:429–39. doi: 10.1016/j.arthro.2011.10.018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Ehrenfest DMD, Bielecki T, Mishra A, Borzini P, Inchingolo F, Sammartino G, et al. In search of a consensus terminology in the field of platelet concentrates for surgical use: platelet-rich plasma (PRP), platelet-rich fibrin (PRF), fibrin gel polymerization and leukocytes. Cur Pharm Biotechnol. 2012;13(7):1131–7. doi: 10.2174/138920112800624328. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Carmona JU, López C, Sandoval JA. Review of the current available systems to obtain platelet related products to treat equine musculoskeletal injuries. Rec Pat Reg Med. 2013;3(2):148–59. [Google Scholar]
- 13.Moher D, Cook DJ, Eastwood S, Olkin I, Rennie D, et al. Improving the quality of reports of meta-analyses of randomized controlled trials: the QUOROM statement. Quality of reporting of meta-analyses. Lancet 354. 1999;9193:1896–900. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(99)04149-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG, PRISMA Group Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. Ann Intern Med. 2009;151:264–9. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-151-4-200908180-00135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Kanematsu A, Yamamoto S, Ozeki M, Noguchi T, Kanatani I, Ogawa O, et al. Collagenous matrices as release carriers of exogenous growth factors. Biomaterials. 2004;2S:4S13–20. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2003.11.035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Fleishmann RM, Schechtman J, Bennet R, Handel ML, Burmester G-R, Tesser J, et al. Anakinra, a Recombinant human interleukin-1 receptor antagonist (r-metHuIL-1ra), in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2003;48(4):927–34. doi: 10.1002/art.10870. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Nixon AJ, Saxer RA, Brower-Toland BD. Exogenous insulin-like growth factor-I stimulates an autoinductive IGF-I autocrine/paracrine response in chondrocytes. J Orhtop Res. 2001;19:26–32. doi: 10.1016/S0736-0266(00)00013-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Garrett KS, Bramlage LR, Spike-Pierce DL, Cohen ND. Injection of platelet- and leukocyte-rich plasma at the junction of the proximal sesamoid bone and the suspensory ligament branch for treatment of yearling thoroughbreds with proximal sesamoid bone inflammation and associated suspensory ligament branch desmitis. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 2013;243:120–5. doi: 10.2460/javma.243.1.120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Zuffova K, Krisova S, Zert Z. Platelet-rich plasma treatment of superficial digital flexor tendon lesions in racing thoroughbreds. Vet Med. 2013;58:230–9. [Google Scholar]
- 20.Edinger J, Rittler W, Banerjee A, Ferguson J, Pieber K, et al. Effective treatment of a traumatic tendon lesion within the tarsal sheath of a horse with PRP in combination with isolated bone marrow mononucleated cells. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2012;6(suppl 1):156. [Google Scholar]
- 21.Torricelli P, Fini M, Filardo G, Tschon M, Pischedda M, et al. Regenerative medicine for the treatment of musculoskeletal overuse injuries in competition horses. Int Orthop. 2011;35:1569–76. doi: 10.1007/s00264-011-1237-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Castelijns G, Crawford A, Schaffer J, Ortolano GA, Beauregard T, et al. Evaluation of a filter-prepared platelet concentrate for the treatment of suspensory branch injuries horses. Vet Comp Orthop Traumatol. 2011;24:363–9. doi: 10.3415/VCOT-11-01-0001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Georg R, Maria C, Gisela A, Bianca C. Autologous conditioned plasma as therapy of tendon and ligament lesions in seven horses. J Vet Sci. 2010;11:172–5. doi: 10.4142/jvs.2010.11.2.173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Abellanet I, Prades M. Intraarticular platelet rich plasma (PRP) therapy: evaluation in 42 sport horse with OA. In: Proceedings of the International Congress of World Equine Veterinary Association: September 2009; Guarujá, Brazil; 2009 (http://www.ivis.org/proceedings/weva/2009/72.pdf?LA=1). Accessed 01 Apr 2015.
- 25.Carmona JU, López C, Prades M. Uso de concentrados autólogos de plaquetas obtenidos mediante el método del tubo como tratamento de artropatía em caballos. Arch Med Vet. 2009;41:175–9. [Google Scholar]
- 26.Waselau M, Sutter WW, Genovese RL, Bertone AL. Intralesional injection of platelet-rich plasma followed by controlled exercise for treatment of midbody suspensory ligament desmitis in standardbred racehorses. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 2008;232:1515–20. doi: 10.2460/javma.232.10.1515. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Argüelles D, Carmona JU, Climent F, Muñoz E, Prades M. Autologous platelet concentrates as a treatment for musculoskeletal lesions in five horses. Vet Rec. 2008;162:208–11. doi: 10.1136/vr.162.7.208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Carmona JU, Argüelles D, Climent F, Prades M. Autologous platelet concentrates as a treatment of horses with osteoarthritis: a preliminary pilot clinical study. J Eq Vet Sci. 2007;27:167–70. [Google Scholar]
- 29.Tiwari M, Bhargava R. Platelet rich plasma therapy: a comparative effective therapy with promising results in plantar fasciitis. J Clin Orthop Trauma. 2013;4:31–5. doi: 10.1016/j.jcot.2013.01.008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Antuña S, Barco R, Díez JMM, Sánchez Máquez JM. Platelet- rich fibrin in arthroscopic repair of massive rotator cuff tears: a prospective randomized pilot clinical trial. Acta Orthop Belg. 2013;79:125–30. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Magnussen RA, Flanigan DC, Pedroza AD, Kaeding CC. Platelet rich plasma use in allograft ACL reconstructions: two-year clinical results of a MOON cohort study. Knee. 2013;20:277–80. doi: 10.1016/j.knee.2012.12.001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Mishra AK, Skrepnik NV, Edwards SG, Jones GL, Sampson S, et al. Efficacy of platelet-rich plasma for chronic tennis elbow: a double-blind, prospective, multicenter, controlled trial of 230 patients. Am J Sports Med. 2014;42:463–71. doi: 10.1177/0363546513494359. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Krogh TP, Fredberg U, Stengaard-Pedersen K, Christensen R, Jensen P, et al. Treatment of lateral epicondylitis with platelet-rich plasma, glucocorticoid, or saline: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Am J Sports Med. 2013;41:625–35. doi: 10.1177/0363546512472975. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Patel S, Dhillon MS, Aggarwal S, Marwaha N, Jain A. Treatment with platelet-rich plasma is more effective than placebo for knee osteoarthritis. Am J Sports Med. 2013;41:356–64. doi: 10.1177/0363546512471299. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Wasterlain AS, Braun HJ, Dragoo JL, Nead KT. Platelet-rich plasma as a treatment for patellar tendinopathy: a double-blind randomized controlled trial. Arthroscopy. 2012;28(suppl 1):e31–2. doi: 10.1177/0363546513518416. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Jain A, Patel S, Aggarwal S, Marwaha N, Dhillon MS. Autologous platelet derived growth factors as a treatment modality in early osteoarthritis knee – a prospective randomized control trial. Vox Sang. 2012;103(suppl 1):61. [Google Scholar]
- 37.Mardones R, Larrain C, Gerrero MA, Volpato GP, Tomic A, et al. Paper 45: Effects of platelet-rich plasma (PRP) on the management of early postoperative pain and inflammation following hip arthroscopy in patients with femoroacetabular impingement: a prospective, double-blinded, randomized, placebo controlled, clinical trial. Arthroscopy. 2012;28(suppl 2):e69–70. [Google Scholar]
- 38.Cerza F, Carnì S, Carcangiu A, Di Vavo I, Schiavilla V, et al. Comparison between hyaluronic acid and platelet-rich plasma, intra-articular infiltration in the treatment of gonarthrosis. Am J Sports Med. 2012;40:2822–7. doi: 10.1177/0363546512461902. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Mei-Dan O, Carmont MR, Laver L, Mann G, Maffulli N, et al. Platelet-rich plasma or hyaluronate in the management of osteochondral lesions of the talus. Am J Sports Med. 2012;40:534–41. doi: 10.1177/0363546511431238. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Almeida AM, Demange MK, Sobrado MF, Rodrigues MB, Pedrinelli A, et al. Pattelar tendo healing with platelet-rich plasma: a prospective randomized controlled trial. Am J Sports Med. 2012;40:1282–8. doi: 10.1177/0363546512441344. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Spaková T, Rosocha J, Lacko M, Harvanová D, Gharaibeh A. Treatment of knee joint osteoarthritis with autologous platelet-rich plasma in comparison with hyaluronic acid. Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 2012;91:411–7. doi: 10.1097/PHM.0b013e3182aab72. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Aksahin E, Dogruyol D, Yüksel HY, Hapa O, Doğan O, et al. The comparison of the effect of corticosteroids and platelet-rich plasma (PRP) for the treatment of plantar fasciitis. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2012;132:781–5. doi: 10.1007/s00402-012-1488-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Rodeo SA, Delos D, Williams RJ, Adler RS, Pearle A, et al. The effect of platelet-rich fibrin matrix on rotator cuff tendon healing: a prospective, randomized clinical study. Am J Sports Med. 2012;40:1234–41. doi: 10.1177/0363546512442924. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Weber SC, Kauffman JI, Parise C, Weber SJ, Katz SD. Platelet-rich fibrin matrix in the management of arthroscopic repair of rotator cuff: a prospective, randomized, double-blinded study. Am J Sports Med. 2012;41:263–70. doi: 10.1177/0363546512467621. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Bergeson AG, Tashjian RZ, Greis PE, Crim J, Stoddard GJ, et al. Effects of platelet-rich fibrin matrix on repair integrity of at-risk rotator cuff tears. Am J Sports Med. 2012;40:286–93. doi: 10.1177/0363546511424402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Cervellin M, Girolamo L, Bait C, Denti M, Volpi P. Autologous platelet-rich plasma gel to reduce donor-site morbidity after patellar tendon graft harvesting for anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction: a randomized, controlled clinical study. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2012;20:114–20. doi: 10.1007/s00167-011-1570-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Filardo G, Kon E, Di Martino A, Di Matteo B, Merli ML, et al. Platelet-rich plasma vs hyaluronic acid to treat knee degenerative pathology: study design and preliminar results of a randomized controlled trial. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2012;13:229. doi: 10.1186/1471-2474-13-229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Jo CH, Kim JE, Yoon KS, Lee JH, Kang SB, et al. Does platelet-rich plasma accelerate recovery after rotator curff repair? Am J Sports Med. 2011;39:2082–90. doi: 10.1177/0363546511413454. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Randelli P, Arrigoni P, Ragone V, Aliprandi A, Cabitza P. Platelet-rich plasma in arthroscopy rotator cuff repair: a prospective RCT study, 2-year follow-up. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2011;20:518–28. doi: 10.1016/j.jse.2011.02.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Castricini R, Longo UG, De Benetto M, Panfoli N, Pirani P, et al. Platelet-rich plasma augmentation for arthroscopic rotator cuff repair. Am J Sports Med. 2011;39:258–65. doi: 10.1177/0363546510390780. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Thanasas C, Papadimitriou G, Charalambidis C, Paraskevopoulos I, Papanikolaou A. Platelet-rich plasma versus autologous whole blood for the treatment of chronic lateral elbow epicondylitis: a randomized controlled clinical trial. Am J Sports Med. 2011;39:2130–4. doi: 10.1177/0363546511417113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Schepull T, Kvist J, Norrman H, Trinks M, Berlin G, et al. Autologous platelets have no effect on the healing of human Achilles tendon ruptures: a randomized single-blind study. Am J Sports Med. 2011;39:38–47. doi: 10.1177/0363546510383515. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.de Vos RJ, Weir A, Tol JL, Verhaar JA, Weinans H, et al. No effects of PRP on ultrasonographic structure and neovascularisation in chronic midportion achilles tendinopathy. Br J Sports Med. 2011;45:387–92. doi: 10.1136/bjsm.2010.076398. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Creaney L, Wallace A, Curtis M, Connell D. Growth factor-based therapies provides additional benefit beyond physical therapy in resistant elbow tendinopathy: a prospective, single-blind, randomized trial of autologous blood injections versus platelet-rich plasma injections. Br J Sports Med. 2011;45:966–71. doi: 10.1136/bjsm.2010.082503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Kon E, Mandelbaum B, Buda R, Filardo G, Delcogliano M, et al. Platelet-rich plasma intra-articular injection versus hyaluronic acid viscosupplementation as treatments for cartilage pathology: from early degeneration to osteoarthritis. Arthroscopy. 2011;27:1490–501. doi: 10.1016/j.arthro.2011.05.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Jonge S, de Vos R, Weir A, van Schie HT, Bierma-Zeinstra SM, et al. One-year follow-up of platelet-rich plasma treatment in chronic achilles tendinopathy. Am J Sports Med. 2011;39:1623–9. doi: 10.1177/0363546511404877. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Gosens T, Peerbooms JC, Van Laar W, den Oudsten BL. Ongoing positive effect of platelet-rich plasma versus corticosteroid injection in lateral epicondylitis. Am J Sports Med. 2011;39:1200–8. doi: 10.1177/0363546510397173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Barber FA, Hrnack SA, Snyder SJ, Hapa O. Rotator cuff repair healing influence by platelet-rich plasma construct augmentation. Arthroscopy. 2011;27:1029–35. doi: 10.1016/j.arthro.2011.06.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Horstmann WG, Slappendel R, van Hellemondt GG, Wymenga AW, Jack N, et al. Autologous platelet gel in total knee arthroplasty: a prospective randomized study. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2011;19:115–21. doi: 10.1007/s00167-010-1207-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Buford DA. Rotator cuff healing with and without platelet rich plasma application. Arthroscopy. 2011;27:e37–8. [Google Scholar]
- 61.Vogrin M, Rupreth M, Dinevski D, Hašpl M, Kuhta M, et al. Effects of a platelet gel on early graft revascularization after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction: a prospective, randomized, double-blind, clinical trial. Eur Surg Res. 2010;45:77–85. doi: 10.1159/000318597. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Peerbooms JC, Sluimer J, Bruijn DJ, Gosens T. Positive effect of an autologous platelet concentrate in lateral epicondilytis in a double-blind randomized controlled trial. Am J Sports Med. 2010;38:255–62. doi: 10.1177/0363546509355445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.de Vos R, Weir A, van Schie HTM, Bierma-Zeinstra SMA, Verhaar JAN, et al. Platelet-rich plasma injection for chronic achilles tendinopathy. J Am Med Assoc. 2010;303:144–9. doi: 10.1001/jama.2009.1986. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Radice F, Yánez R, Gutiérrez V, Rosales J, Pinedo M, et al. Comparison of magnetic resonance imaging findings in anterior cruciate ligament grafts with and without autologous platelet-derived growth factors. Arthroscopy. 2010;26:50–7. doi: 10.1016/j.arthro.2009.06.030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Filardo G, Kon E, Della Villa S, Vincentelli F, Fornasari PM, et al. Use of platelet-rich plasma for the treatment of refractory jumper’s knee. Int Orthop. 2010;34:909–15. doi: 10.1007/s00264-009-0845-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Nin JRV, Gasque GM, Azcárate AV, Beola JD, Gonzalez MH. Has platelet-rich plasma any role in anterior cruciate ligament allograft healing? Arthroscopy. 2009;25:1205–13. doi: 10.1016/j.arthro.2009.06.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Silva A, Sampaio R. Anatomic ACL reconstruction: does the platelet-rich plasma accelerate tendon healing? Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2009;17:676–82. doi: 10.1007/s00167-009-0762-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Peerbooms JC, de Wolf GS, Colaris JW, Bruijn DJ, Verhaar JA. No positive effect of autologous platelet gel after total knee arthroplasty. Acta Orthop. 2009;80:557–62. doi: 10.3109/17453670903350081. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Sánchez M, Anitua E, Azofra J, Aguirre JJ, Andia I. Intra-artiuclar injection of an autologous preparation rich in growth factors for the treatment of knee OA: a restrospective cohort study. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2008;26:910–3. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Everts PA, Devilee RJJ, Mahoney CB, van Erp A, Oosterbos CJ, et al. Exogenous application of platelet-leukocyte gel during open subacromial decompression contributes to improved patient outcome. Eur Surg Res. 2008;40:203–10. doi: 10.1159/000110862. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Orrego M, Larrain C, Rosales J, Valenzuela L, Matas J, et al. Effects of platelet concentrate and a bone plug on the healing of hamstring tendons in a bone tunnel. Arthroscopy. 2008;24:1373–80. doi: 10.1016/j.arthro.2008.07.016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Sánchez M, Anitua E, Azofra J, Andía I, Padilla S, et al. Comparison of surgically repaired achilles tendo tears using platelet-rich fibrina matrices. Am J Sports Med. 2007;35:245–51. doi: 10.1177/0363546506294078. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Everts PAM, Devilee RJJ, Oosterbos JM, Mahoney CB, Schattenkerk ME, et al. Autologous platelet gel and fibrin sealant enhance the efficacy of total knee arthroplasty: improved range of motion, decreased legth of stay and a reduce incidence of arthrofibrosis. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2007;15:888–94. doi: 10.1007/s00167-007-0296-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Gardner MJ, Demetrakopoulos D, Klepchick PR, Mooar PA. The efficacy of autologous platelet gel in pain control and blood loss in total knee arthroplasty. Int Orthop. 2007;31:309–13. doi: 10.1007/s00264-006-0174-z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Zavadil DP, Satterlee CC, Costigan JM, Holt DW, Shostrom VK. Autologous platelet gel and platelet-poor plasma reduce pain with total shoulder arthroplasty. J Extra Corpor Technol. 2007;39:177–82. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Mishra A, Pavelko T. Treatment of chronic elbow tendinosis with buffered platelet-rich plasma. Am J Sports Med. 2006;34:1774–8. doi: 10.1177/0363546506288850. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Ventura A, Terzaghi C, Borgo E, Verdoia C, Gallazzi M, et al. Use of growth factors in ACL surgery: preliminar study. J Orthopaed Traumatol. 2005;6:76–9. [Google Scholar]
- 78.Textor JA, Willits NH, Tablin F. Synovial fluid growth factor and cytokine concentrations after intra-articular injection of a platelet-rich product in horses. Vet J. 2013;198:217–23. doi: 10.1016/j.tvjl.2013.07.020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Textor JA, Tablin F. Intra-articular use of a platelet-rich product in normal horses: clinical signs and cytologic responses. Vet Surg. 2013;42:499–510. doi: 10.1111/j.1532-950X.2013.12015.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Zandim BM, Souza MV, Frassy LN, Vilória MIV, Maia L, et al. Immunohistochemistry of factor VIII, histology and morphometry in equine tendon treated with platelet-rich plasma. Rev Bras Med Vet. 2013;35:169–84. [Google Scholar]
- 81.McCarrel TM, Minas T, Fortier LA. Optimization of leukocyte concentration in platelet-rich plasma for the treatment of tendinopathy. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2012;94:e143. doi: 10.2106/JBJS.L.00019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Yamada ALM, Carvalho AM, Oliveira PGG, Felisbino SL, Queiroz DL, et al. Plasma rico em plaquetas no tratamento de lesões condrais articulares induzidas experimentalmente em equinos: avaliação clinica, macroscópica, histológica e histoquímica. Arq Bras Med Vet Zootec. 2012;64:323–32. [Google Scholar]
- 83.Bosch G, Moleman M, Barneveld A, van Weeren PR, van Schie HT. The effect of platelet-rich plasma on the neovascularization of surgically created equine superficial digital flexor tendon lesions. Scand J Med Sci Sports. 2011;21:554–61. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0838.2009.01070.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Bosch G, van Weeren PR, Barneveld A, van Schie HT. Computerised analysis of standardized ultrasonographic images to monitor the repair of surgically created core lesions in equine superficial digital flexor tendons following treatment with intratendinous platelet rich plasma or placebo. Vet J. 2011;187:92–8. doi: 10.1016/j.tvjl.2009.10.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Maia L, Souza MV, Ribeiro Junior JI, Oliveira AC, Alves GES, et al. Platelet-rich plasma in the treatment of induced tendinopathy in horses: histologic evaluation. J Eq Vet Sci. 2009;29:618–26. [Google Scholar]
- 86.McCarrel T, Fortier L. Temporal growth factor release grom platelet-rich plasma, trehalose lyophilized platelets, and bone marrow aspirate and their effect on tendon and ligament gene expression. J Orthopaed Res. 2009;27:1033–42. doi: 10.1002/jor.20853. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Schnabel LV, Mohammed HO, Jacobson MS, Fortier LA. Effects of platelet rich plasma and acellular bone marrow on gene expression patterns and DNA content of equine suspensory ligament explant cultures. Eq Vet J. 2008;40:260–5. doi: 10.2746/042516408X278030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Schnabel LV, Mohammed HO, Miller BJ, McDermott WG, Jacobson MS, et al. Platelet rich plasma (PRP) enhances anabolic gene expressions patterns in flexor digitorum superficialis tendons. J Orthopaed Res. 2007;25:230–40. doi: 10.1002/jor.20278. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Smith JJ, Ross MW, Smith RKW. Anabolic effects of acellular bone marrow, platelet rich plasma, and serum on equine suspensory ligament fibroblasts in vitro. Vet Comp Orthop Traumatol. 2006;19:43–7. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Bosch G, van Schie HTM, Groot MW, Cadby JA, van de Lest CH, et al. Effects of platelet-rich plasma on the quality of repair of mechanically induced core lesions in equine superficial digital flexor tendons: a placebo-controlled experimental study. J Orthopaed Res. 2010;28:211–7. doi: 10.1002/jor.20980. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Sadoghi P, Lohberger B, Aigner B, Kaltenegger H, Friesenbichler J, et al. Effect of platelet-rich plasma on the biologic activity of the human rotator-cuff fibroblasts: A controlled in vitro study. J Orthopaed Res. 2013;31:1249–53. doi: 10.1002/jor.22360. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Muto T, Kokubu T, Mifune Y, Sakata R, Nagura I, et al. Platelet-rich plasma protects rotator cuff-derived cells from deleterious effects of triamcinolone acetonide. J Orthopaed Res. 2013;31:976–82. doi: 10.1002/jor.22301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Carofino B, Chowaniec DM, McCarthy MB, Bradley JP, Delaronde S, et al. Corticosteroids and local anesthetics decrease positive effects of platelet-rich plasma: an in vitro study on human tendon cells. Arthroscopy. 2012;28:711–9. doi: 10.1016/j.arthro.2011.09.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94.Jo CH, Kim JE, Yoon KS, Shin S. Platelet-rich plasma stimulates cell proliferation and enhances matrix gene expression and synthesis in tenocytes from human rotator cuff tendons with degenerative tears. Am J Sports Med. 2012;40:1035–45. doi: 10.1177/0363546512437525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 95.Zhai W, Wang N, Qi Z, Gao Q, Yi L. Platelet-rich plasma reverses the inhibition of tenocytes and osteoblasts in tendon-bone healing. Orthopedics. 2012;35:e520–5. doi: 10.3928/01477447-20120327-22. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 96.Wang X, Qiu Y, Triffitt J, Carr A, Xia Z, et al. Proliferation and differentiation of human tenocytes in response to platelet rich plasma: an in vitro and in vivo study. J Orthopaed Res. 2012;30:982–90. doi: 10.1002/jor.22016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 97.Baboldashti NZ, Poulsen RC, Franklin SL, Thompson MS, Hulley PA. Platelet-rich plasma protects tenocytes from adverse side effects of dexamethasone and ciprofloxacin. Am J Sports Med. 2012;39:1929–35. doi: 10.1177/0363546511407283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 98.Van Buul GM, Koevoet WLM, Kops N, Bos PK, Verhaar JA, et al. Platelet-rich plasma releasate inhibits inflammatory processes in osteoarthritic chondrocytes. Am J Sports Med. 2011;39:2362–70. doi: 10.1177/0363546511419278. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 99.Wu C-C, Chen W-H, Zao B, Lai PL, Lin TC, et al. Regenerative potentials os platelet-rich plasma enhanced by collagen in retrieving pro-inflammatory cytokine-inhibited chondrogenesis. Biomaterials. 2011;32:5847–54. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2011.05.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 100.Bendinelli P, Matteucci E, Dogliotti G, Corsi MM, Banfi G, et al. Molecular basis of anti-inflammatory action of platelet-rich plasma on human chondrocytes: mechanisms of NF-kβ inhibition via HGF. J Cell Physiol. 2010;225:757–66. doi: 10.1002/jcp.22274. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 101.Spreafico A, Chellini F, Frediani B, Bernardini G, Niccolini S, et al. Biochemical investigation of the effects of human platelet releasates on human articular chondrocytes. J Cell Biochem. 2009;108:1153–65. doi: 10.1002/jcb.22344. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 102.de Mos M, van der Windt A, Jahr H, van Schie HT, Weinans H, et al. Can platelet-rich plasma enhance tendon repair? Am J Sports Med. 2008;36:1171–8. doi: 10.1177/0363546508314430. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 103.Anitua E, Sánchez M, Nurden AT, Zalduendo MM, de la Fuente M, et al. Platelet-released growth factors enhance the secretion of hyaluronic acid and induce hepatocyte growth factor production by synovial fibroblast from arthritic patients. Rheumatol. 2007;46:1769–72. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/kem234. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 104.Anitua E, Sanchez M, Nurden AT, Zalduendo M, de la Fuente M, et al. Autologous fibrin matrices: a potential source of biological mediators that modulate tendon cell activities. J Biomed Mater Res. 2006;77:285–93. doi: 10.1002/jbm.a.30585. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 105.Anitua E, Andia I, Sanchez M, Azofra J, del Mar ZM, et al. Autologous preparations rich in growth factors promote proliferation and induce VEGF and HGF production by human tendon cells in culture. J Orthop Res. 2005;23:281–6. doi: 10.1016/j.orthres.2004.08.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 106.de Mos M, Koevoet W, van Schie HTM, Kops N, Jahr H, et al. In vitro model to study chondrogenic differentiation in tendinopathy. Am J Sports Med. 2009;37:1214–22. doi: 10.1177/0363546508331137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 107.Xie X, Wu H, Zhao S, Xie G, Huangfu X, et al. The effect of platelet-rich plasma on patterns of gene expression in a dog model of anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction. J Surg Res. 2013;180:80–8. doi: 10.1016/j.jss.2012.10.036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 108.Visser LC, Arnoczky SP, Caballero O, Egerbacher M. Platelet-rich fibrin constructos elute higher concentrations of transforming growth fator-β1 and increase tendon cell proliferation over time when compared to blood clots: a comparative in vitro analysis. Vet Surg. 2010;39:811–7. doi: 10.1111/j.1532-950X.2010.00739.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 109.Murray MM, Spindler KP, Ballard P, Welch TP, Zurakowski D, et al. Enhanced histologic repair in a central wound in the anterior cruciate ligament with a collagen-platelet-rich plasma scaffold. J Orthopaed Res. 2007;25:1007–17. doi: 10.1002/jor.20367. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 110.Fernández-Sarmiento JA, Dominguez JM, Granados MM, Morgaz J, Navarrete R, et al. Histological study of the influence of plasma rich in growth factors (PRGF) on the healing of divided Achilles tendons in sheep. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2013;95:246–55. doi: 10.2106/JBJS.K.01659. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 111.Milano G, Deriu L, Passino ES, Masala G, Manunta A, et al. Repeated platelet concentrate injections enhance reparative response of microfractures in the treatment of chondral defects of the knee: an experimental study in an animal model. Arthroscopy. 2012;28:688–701. doi: 10.1016/j.arthro.2011.09.016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 112.Milano G, Sanna Passino E, Deriu L, Careddu G, Manunta L, et al. The effect of platelet rich plasma combined with microfractures on the treatment of chondral defects: na experimental sutyd in a sheep model. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2010;10:971–80. doi: 10.1016/j.joca.2010.03.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 113.Yoshioka T, Kanamori A, Washio T, Aoto K, Uemura K, et al. The effects of plasma rich in growth factors (PRGF-Endoret) on healing of medial collateral ligament of the knee. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2013;21:1763–9. doi: 10.1007/s00167-012-2002-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 114.Harris L, Huffer WE, von Stade E, Larson AI, Phinney S, et al. The effect of platelet-rich plasma on normal soft tissues in the rabbit. J Bone Joint Surg. 2012;94:786–93. doi: 10.2106/JBJS.J.00984. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 115.Park S-I, Lee H-R, Kim S, Ahn MW, Do SH. Time-sequential modulation in expression. Of growth factors from platelet-rich plasma (PRP) on the chondrocyte cultures. Mol Cell Biochem. 2012;361:9–17. doi: 10.1007/s11010-011-1081-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 116.Sato D, Takahara M, Narita A, Yamakawa J, Hashimoto J, et al. Effect of platelet-rich plasma withi fibrin matrix on healing of intrasynovial flexor tendons. J Hand Surg [Am] 2012;37:1356–63. doi: 10.1016/j.jhsa.2012.04.020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 117.Lee A-J, Chung W-H, Kim D-H, Lee KP, Chung DJ, et al. Anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction in a rabbit model using canine small intestinal submucosa and autologous platelet-rich plasma. J Surg Res. 2012;178:206–15. doi: 10.1016/j.jss.2012.01.052. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 118.Lyras DN, Kazakos K, Georgiadis G, Mazis G, Middleton R, et al. Does a single application of PRP alter the expression of IGF-I in the early phase of tendon healing? J Foot Ankle Surg. 2011;50:276–82. doi: 10.1053/j.jfas.2011.02.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 119.Lyras DN, Kazakos K, Agrogiannis G, Verettas D, Kokka A, et al. Experimental study of tendon healing early phase: is IGF-1 expression influenced by platelet rich plasma gel? Orthopaed Traumatol Surg Res. 2010;96:381–7. doi: 10.1016/j.otsr.2010.03.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 120.Lyras DN, Kazakos K, Verettas D, Polychronidis A, Simopoulos C, et al. Immunohistochemical study of angiogenesis after local administration of platelet-rich plasma in a pattelar tendon defect. Int Orthopaed. 2010;34:143–8. doi: 10.1007/s00264-009-0728-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 121.Lyras DN, Kazakos K, Tryfonidis M, Agrogiannis G, Botaitis S, et al. Temporal and spatial expression of TGF-β1 in an Achilles tendon section model after application of platelet-rich plasma. Foot Ankle Surg. 2010;16:137–41. doi: 10.1016/j.fas.2009.09.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 122.Saito M, Takahashi KA, Arai Y, Inoue A, Sakao K, et al. Intraarticular administration of platelet-rich plasma with biodegradable gelatin hydrogel microspheres prevents osteoarthritis progression in the rabbit knee. Cli Exp Rheumatol. 2009;27:201–7. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 123.Qi YY, Chen X, Jiang YZ, Cai HX, Wang LL, et al. Local Delivery of autologous platelet in collagen matrix simulated in situ articular cartilage repair. Cell Transplant. 2009;18:1161–9. doi: 10.3727/096368909X12483162197169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 124.Lyras DN, Kazakos K, Verettas D, Polychronidis A, Tryfonidis M, et al. The influence of platelet-rich plasma on angiogenesis during the early phase of tendon healing. Foot Ankle Int. 2009;30:1101–6. doi: 10.3113/FAI.2009.1101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 125.Lyras DN, Kazakos K, Verettas D, Botaitis S, Agrogiannis G, et al. The effect of platelet-rich plasma gel in the early phase of patellar tendon healing. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2009;129:1577–82. doi: 10.1007/s00402-009-0935-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 126.Sun Y, Feng Y, Zhan CQ, Chen SB, Cheng XG. The regenerative effect of platelet-rich plasma on healing in large ostochondral defects. Int Orthop. 2010;34:589–97. doi: 10.1007/s00264-009-0793-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 127.Wu W, Chen F, Liu Y, Ma Q, Mao T. Autologous injectable tissue-engineered cartilage by using platelet-rich plasma: experimental study in a rabbit model. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2007;65:1951–7. doi: 10.1016/j.joms.2006.11.044. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 128.Dallaudière B, Lempicki M, Pesquer L, Louedec L, Preux PM, et al. Efficacy of intra-tendinous injection of platelet-rich plasma in treating tendinosis: comprehensive assessment of a rat model. Eur Radiol. 2013;23:2830–7. doi: 10.1007/s00330-013-2926-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 129.Kaux J-F, Drion PV, Colige A, Pascon F, Libertiaux V, et al. Effects of platelet-rich plasma (PRP) on the healing of Achilles tendon of rats. Wound Rep Reg. 2012;20:748–56. doi: 10.1111/j.1524-475X.2012.00826.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 130.Vaisman A, Figueroa D, Calvo R, Espinosa M, Melean P, et al. Steroids and platelet-rich plasma as coadjuvants to microfracture for the treatment of chondral lesions in animal model: can the healing be enhanced? Cartilage. 2012;3:118–27. doi: 10.1177/1947603511422053. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 131.Hapa O, Çakici H, Kükner A, Aygün H, Sarkalkan N, Baysal G. Effect of platelet-rich plasma on tendon-to-bone healing after rotator cuff repair in rats: an in vivo experimental study. Acta Orthop Traumatol Turc. 2012;46(4):301–7. doi: 10.3944/aott.2012.2664. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 132.Beck J, Evans D, Tonino PM, Yong S, Callaci JJ. The biomechanical and histologic effects of platelet-rich plasma on rat rotator cuff repais. The AM J Sports Med. 2012;40(9):2037–44. doi: 10.1177/0363546512453300. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 133.Spang JT, Tischer T, Salzmann GM, Winkler T, Burgkart R, et al. Platelet concentrate vs. saline in a rat tendon healing model. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2011;19:495–502. doi: 10.1007/s00167-010-1291-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 134.Tohidnezhad M, Varoga D, Wruck CJ, Brandenburg LO, Seekamp A, et al. Platelet-released growth factors can accelerate tenocyte proliferation and activate the anti-oxidant response element. Histochem Cell Biol. 2011;135:453–60. doi: 10.1007/s00418-011-0808-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 135.Kajikawa Y, Morihara T, Sakamoto H, Matsuda K, Oshima Y, et al. Platelet rich-plasma enhances the initial mobilization of circulation-derived cells for tendon healing. J Cell Physiol. 2008;215:837–45. doi: 10.1002/jcp.21368. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 136.Virchenko O, Aspenberg P. How can one platelet injection after tendon injury lead to a stronger tendon after 4 weeks? Interplay between early regeneration and mechanical stimulation. Acta Orthop. 2006;77:806–12. doi: 10.1080/17453670610013033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 137.Aspenberg P, Virchenko O. Platelet concentrate injection improves Achilles tendon repair in rats. Acta Orthop Scand. 2004;75:93–9. doi: 10.1080/00016470410001708190. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 138.Murray MM, Palmer M, Abreu E, Spindler KP, Zurakowski D, et al. Platelet-rich plasma alone is not sufficient to enhance suture repair of the ACL in skeletally immature animals: an in vivo study. J Orthopaed Res. 2009;27:639–45. doi: 10.1002/jor.20796. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 139.Murray MM, Spindler KP, Abreu E, Muller JA, Nedder A, et al. Collagen-platelet rich plasma hydrogel enhances primary repair of the porcine anterior cruciate ligament. J Orthopaed Res. 2007;25:81–91. doi: 10.1002/jor.20282. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 140.Akeda K, Okuma M, Attawia M, Attawia M, Miyamoto K, et al. Platelet-rich plasma stimulates porcine articular chondrocyte proliferation and matrix biosynthesis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2006;14:1272–80. doi: 10.1016/j.joca.2006.05.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 141.Lee KS, Wilson JJ, Rabago DP, Baer GS, Jacobson JA, et al. Musculoskeletal applications of platelet-rich plasma: fad or future? Am J Roentgenol. 2011;196:628–36. doi: 10.2214/AJR.10.5975. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 142.Ahmad Z, Howard D, Brooks RA, Wardale J, Henson FM, et al. The role of platelet rich plasma in musculoskeletal science. JRSM Short Rep. 2012;3:40. doi: 10.1258/shorts.2011.011148. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 143.Middleton KK, Barro V, Muller B, Terada S, Fu FH. Evaluation of the effects of platelet-rich plasma (PRP) therapy involved in the healing of sports-related soft tissue injuries. Iowa Orthop J. 2012;32:150–63. [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 144.Gross G, Hoffmann A. Therapeutic strategies for tendon healing based on novel biomaterials, factors and cells. Pathobiology. 2013;80:203–10. doi: 10.1159/000347059. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 145.Santo VE, Gomes ME, Mano JF, Reis RL. Controlled release strategies for bone, cartilage, and osteochondral engineering – Part II: challenges on the evolution from single to multiple bioactive factor delivery. Tissue Eng Part B Rev. 2013;19:327–52. doi: 10.1089/ten.teb.2012.0727. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 146.Smyth NA, Murawski CD, Fortier LA, Cole BJ, Kennedy JG. Platelet-rich plasma in the pathologic processes of cartilage: review of basic science evidence. Arthroscopy. 2013;29:1399–13409. doi: 10.1016/j.arthro.2013.03.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 147.Pichereau F, Décory M, Cuevas RG. Autologous platelet concentrate as a treatment for horses with refractory fetlock osteoarthritis. J Equine Vet Sci. 2014;2014:489–93. [Google Scholar]
- 148.Kon E, Filardo G, Di Martino A, Marcacci M. Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) to treat sports injuries: evidence to support its use. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2011;19:516–27. doi: 10.1007/s00167-010-1306-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 149.Nguyen RT, Borg-Stein J, McInnis K. Applications of platelet-rich plasma in musculoskeletal and sports medicine: an evidence-based approach. PM R. 2011;3:226–50. doi: 10.1016/j.pmrj.2010.11.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 150.Paoloni J, De Vos RJ, Hamilton B, Murrell GA, Orchard J. Platelet-rich plasma treatment for ligament and tendon injuries. Clin J Sport Med. 2011;21:37–45. doi: 10.1097/JSM.0b013e31820758c7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 151.Taylor D, Petrera M, Hendry M, Theodoropoulos JS. A systematic review of the use of platelet-rich plasma in sports medicine as a new treatment for tendon and ligament injuries. Clin J Sport Med. 2011;21:344–52. doi: 10.1097/JSM.0b013e31821d0f65. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 152.Kon E, Filardo G, Di Matteo B, Di Martino A, Marcacci M. Platelet-rich plasma in sports medicine: new treatment for tendon and cartilage lesions. Oper Tech Orthop. 2012;22:78–85. [Google Scholar]
- 153.Papalia R, Vasta S, Zampogna B, Tecame A, Maffulli N, et al. Platelet-rich plasma injections and surgery: short-term outcomes and long-term prognosis. Oper Tech Orthop. 2012;22:71–7. [Google Scholar]
- 154.Sánchez M, Albillos J, Angulo F, Santisteban J, Andia I. Platelet-rich plasma in muscle and tendon healing. Oper Tech Orthop. 2012;22:16–24. [Google Scholar]
- 155.Sheth U, Simunovic N, Klein G, Fu F, Einhorn TA, et al. Efficacy of autologous platelet-rich plasma use for orthopaedic indications: a meta-analysis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2012;94:298–307. doi: 10.2106/JBJS.K.00154. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 156.Steinert AF, Middleton KK, Araujo PH, Fu FH. Platelet-rich plasma in orthopaedic surgery and sports medicine: pearls, pitfalls, and new trends in research. Oper Tech Orthop. 2012;22:91–103. [Google Scholar]
- 157.Schulz KF, Grimes DA. Blinding in randomized trials: hiding who got what. Lancet. 2002;359:696–700. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(02)07816-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 158.Zhang W, Robertson J, Jones AC, Dieppe PA, Doherty M. The placebo effect and its determinants in osteoarthritis: meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Ann Rheum Dis. 2008;67:1716–23. doi: 10.1136/ard.2008.092015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 159.Carmona JU, López C. Comments on Torricelli et al.: Regenerative medicine for the treatment of musculoskeletal overuse injuries in competition horses. Letter to the editor. Int Orthop. 2011;35(11):1745. doi: 10.1007/s00264-011-1311-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 160.Baksh N, Hannon CP, Murawisk CD, Smyth NA, Kennedy JG. Platelet-rich plasma in tendon models: a systematic review of basic science literature. Arthroscopy. 2013;29:596–607. doi: 10.1016/j.arthro.2012.10.025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 161.Giraldo CE, López C, Álvarez ME, Samudio IJ, Prades M, et al. Effects of the breed, sex and age on cellular content and growth factor release from equine pure-platelet rich plasma and pure-platelet rich gel. BMC Vet Res. 2013;9:29. doi: 10.1186/1746-6148-9-29. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 162.Woodell-May J, Matuska A, Oyster M, Welch Z, O’Shaughnessey K, Hoeppner J. Autologous protein solution inhibits MMP-13 production by IL-1β and TNF-α- stimulated human articular chondrocytes. J Orthop Res. 2011;29:1320–26. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 163.DeLong JM, Russell RP, Mazzocca AD. Platelet-rich plasma: the PAW classification system. Arthroscopy. 2012;28:998–1009. doi: 10.1016/j.arthro.2012.04.148. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 164.Engebretsen L, Steffen K, Alsousou J, Anitua E, Bachi N. IOC consensus paper on the use of platelet-rich plasma in sports medicine. Br J Sports Med. 2010;44:1072–81. doi: 10.1136/bjsm.2010.079822. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 165.Kaux JF, Le Goff C, Seidel L, Peters P, Gothot A, et al. Étude comparative de cinq techniques de préparation plaquettaire (platelet-rich plasma) Pathol Biol. 2011;59:157–60. doi: 10.1016/j.patbio.2009.04.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 166.Filardo G, Kon E. PRP: more words than facts… Knee Surg Sports Traumatol. Arthroscop. 2012;20:1655–6. doi: 10.1007/s00167-012-2136-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 167.Arguelles D, Carmona JU, Pastor J, Iborra A, Viñals L, et al. Evaluation of single and double centrifugation tube methods for concentrating equine platelets. Res Vet Sci. 2006;81:237–45. doi: 10.1016/j.rvsc.2005.12.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 168.Tamimi MJH, Messora MR, Furlaneto FA, Fucini SE, Bosco AF, et al. Effectiveness of two methods for preparation of autologous platelet-rich plasma: an experimental study in rabbits. Eur J Dent. 2010;4:395–402. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 169.Tamimi FM, Montalvo S, Tresguerres I, Blanco JL. A comparative study of 2 methods for obtaining platelet-rich plasma. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2007;65:1084–93. doi: 10.1016/j.joms.2006.09.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 170.Harrison S, Vavken P, Kevy S, Jacobson M, Zurakowski D, et al. Platelet activation by collagen provides sustained release of anabolic cytokines. Am J Sports Med. 2011;39:729–34. doi: 10.1177/0363546511401576. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 171.Textor JA, Norris JW, Tablin F. Effects of preparation method, shear force, and exposure to collagen on release of growth factors from equine platelet-rich plasma. Am J Vet Res. 2011;72:271–8. doi: 10.2460/ajvr.72.2.271. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 172.Textor JA, Tablin F. Activation of equine platelet-rich plasma: comparison of methods and characterization of equine autologous thrombin. Vet Surg. 2012;41:784–94. doi: 10.1111/j.1532-950X.2012.01016.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 173.Bhandari M, Petrisor B, Schemitsch E. Outcome measurements in orthopedic. Indian J Orthop. 2007;41:32–6. doi: 10.4103/0019-5413.30523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 174.Karanicolas PJ, Farrokhyar F, Bhandari M. Blinding: who, what, when, why, how? Can J Surg. 2010;53:345–8. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 175.Rothwell P. External validity of randomized controlled trials: “to whom do the results of this trial apply?”. Lancet. 2005;365:82–93. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(04)17670-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 176.Filardo G, Kon E, Buda R, Timoncini A, Di Martino A, et al. Platelet-rich plasma intra-articular knee injections for the treatment of degenerative cartilage lesions and osteoarthritis. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2011;19:528–35. doi: 10.1007/s00167-010-1238-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 177.Freedman KB, Back S, Bernstein J. Sample size and statistical power of randomized, controlled trials in orthopaedics. J Bone Joint Surg (Br) 2001;83:397–402. doi: 10.1302/0301-620x.83b3.10582. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 178.Dawson J, Carr A. Outcomes evaluation in orthopaedics. J Bone Joint Surg (Br) 2001;83:313–5. doi: 10.1302/0301-620x.83b3.12148. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 179.Smith MV, Klein SE, Clohisy JC, Baca GR, Brophy RH, et al. Lower extremity-specific measures of disability and outcomes in orthopaedic surgery. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2012;94:468–77. doi: 10.2106/JBJS.J.01822. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 180.Harreld K, Clark R, Downes K, Virani N, Frankle M. Correlation of subjective and objective measures before and after shoulder arthroplasty. Orthopedics. 2013;36:808–14. doi: 10.3928/01477447-20130523-29. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 181.Oleza IA. La terapia de lesiones de tejidos blandos y articulaciones con plasma rico en plaquetas en caballos de deporte: evidencias clínicas y bioquímicas que validan su utilización. 2009. http://www.itrt.es/que-es-itrt/presentacion-del-equipo-itrt. Accessed 13 feb 2015.
- 182.Halpern BC, Chaudhury S, Rodeo SA. The role of platelet-rich plasma in inducing musculoskeletal tissue healing. HSS J. 2012;8:137–45. doi: 10.1007/s11420-011-9239-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 183.Kaux JF, Crielaard JM. Tendinopathies et plasma riche en plaquettes (PRP): applications cliniques. Revue de la littérature. J Traumatol Sport. 2012;29:174–8. [Google Scholar]
- 184.Smets F, Croisier JL, Forthomme B, Crielaard JM, Kaux JF. Applications cliniques du plasma riche en plaquettes (PRP) dans les lésions tendineuses: revue de la littérature. Sci Sports. 2012;27:141–53. [Google Scholar]
- 185.Blaauboer BJ. In vitro and other non-animal experiments in the biomedical sciences. ANZCCART News. 1996;9:1–4. [Google Scholar]
- 186.Wang-Saegusa A, Cugat R, Ares O, Seijas R, Cuscó X, Garcia-Balletbó M. Infiltration of plasma rich in growth factors for osteoarthritis of the knee short-term effects on function and quality of life. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2011;131:311–7. doi: 10.1007/s00402-010-1167-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 187.Bielecki TM, Gazdzik TS, Arendt J, Szczepanski T, Krol W, Wielkoszynski T. Antibacterial effect of autologous platelet gel enriched with growth factors and other active substances –An in vitro study. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2007;89B:417–20. doi: 10.1302/0301-620X.89B3.18491. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 188.Alvarez ME, López C, Giraldo CE, Samudio I, Carmona JU. In vitro bactericidal activity of equine platelet concentrates, platelet poor plasma, and plasma agains methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Arch Med Vet. 2011;43:155–61. [Google Scholar]


