Abstract
Polycystic kidney diseases (PKDs) are inherited disorders characterized by the formation of fluid filled renal cysts. Elevated cAMP levels in PKDs stimulate progressive cyst enlargement involving cell proliferation and transepithelial fluid secretion often leading to end stage renal disease. The glycogen synthase kinase-3 (GSK3) family of protein kinases consists of GSK3α and GSK3β isoforms and plays a crucial role in multiple cellular signaling pathways. We previously found that GSK3β, a regulator of cell proliferation, is also crucial for cAMP generation and vasopressin mediated urine concentration by the kidneys. However, the role of GSK3β in the pathogenesis of PKDs is not known. Here we found that GSK3β expression and activity were markedly up-regulated and associated with cyst-lining epithelia in the kidneys of mice and humans with PKD. Renal collecting duct specific gene knockout of GSK3β or pharmacological inhibition of GSK3 effectively slowed the progression of PKD in mouse models of autosomal recessive or autosomal dominant PKD. GSK3 inactivation inhibited cAMP generation and cell proliferation resulting in reduced cyst expansion, improved renal function and extended lifespan. GSK3β inhibition also reduced pERK, c-Myc and Cyclin-D1, known mitogens in proliferation of cystic epithelial cells. Thus, GSK3β plays a novel functional role in PKD pathophysiology and its inhibition may be therapeutically useful to slow cyst expansion and progression of PKD.
Keywords: ADPKD, vasopressin, chronic kidney disease, cell signaling
INTRODUCTION
Progressive cyst enlargement in PKD is associated with abnormal cell proliferation, loss of cell differentiation and polarity, and increased luminal fluid secretion that obliterates the renal architecture, often leading to renal failure 1. Understanding the molecular basis of PKD is important for the identification of targets for diagnosis and treatment of this disease. Cyclic AMP, a ubiquitous and versatile second messenger is elevated in PKD and stimulates proliferation and fluid secretion by the cyst lining epithelial cells 2-8. In a normal kidney, extracellular ligand binding leads to G protein–coupled receptor (GPCR)-mediated activation of adenylate cyclase, and thereby cAMP generation. In PKD, renal cAMP levels are elevated due to a) activation of calcium-inhibitable adenylate cyclase and inhibition of calcium-activated phosphodiestrases, b) loss of polycystin-1 mediated suppression of adenylate cyclase activity and c) enhanced vasopressin (AVP) signaling through its type-2 receptor (V2R) which activates adenylate cyclase 5. The importance of cAMP in PKD is further supported by studies in which reducing cAMP levels by inhibition of V2R or lack of AVP reduces cystogenesis in rodent models of PKD 9, 10.
The GSK3α and GSK3β isoforms regulate multiple fundamental cellular processes by modulating cell-signaling pathways and are targets for drug development in cancer, Alzheimer's disease and diabetes 11, 12. In certain forms of cancer, GSK3 plays a tumor promoter role mainly by increasing cell proliferation 13, but its role in renal cyst expansion in PKD has not been examined. Importantly in the kidney, GSK3β is crucial for AVP sensitive adenylate cyclase activity and cAMP generation. Lithium, a common treatment for bipolar disorders has been for long thought to inhibit adenylate cyclase activity and reduce cAMP 14-17, though it had no effect on cAMP levels in dDAVP treated Brattleboro rats 18. Lithium is also a non-specific inhibitor of GSK3. In previous studies we demonstrated that pharmacological inhibition using a highly specific GSK3 inhibitor or renal collecting duct specific knockout of GSK3β can significantly reduce adenylate cyclase activity and cAMP accumulation 19. Hence we hypothesized that inactivation of GSK3 could reduce renal cAMP levels and cyst expansion in PKD.
To test the pathophysiological role of GSK3 in renal cyst development in PKD, we used the Cys1cpk mouse, a well-characterized mouse model of autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease (ARPKD) that carries a gene mutation for Cys1. Though non-orthologous, this mouse model closely mimics human ARPKD 20-22. Postnatal renal cyst enlargement in Cys1cpkmice is rapid, resulting in death at approximately 3 weeks of age. Importantly, Cys1cpk mice are known to exhibit increased vasopressin receptor expression, proto-oncogenes and cell proliferation 20, 23, 24. We also used the PKD1f/f:PKHD1cre mouse, an orthologous model for autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD) which is also characterized by increased renal cell proliferation 25-27. Systemic GSK3 inhibition or collecting duct specific GSK3β gene deletion was carried out in these mouse models of PKD were employed to analyze mechanism. The results of these studies are presented.
RESULTS
Abnormal renal GSK3 expression in PKD
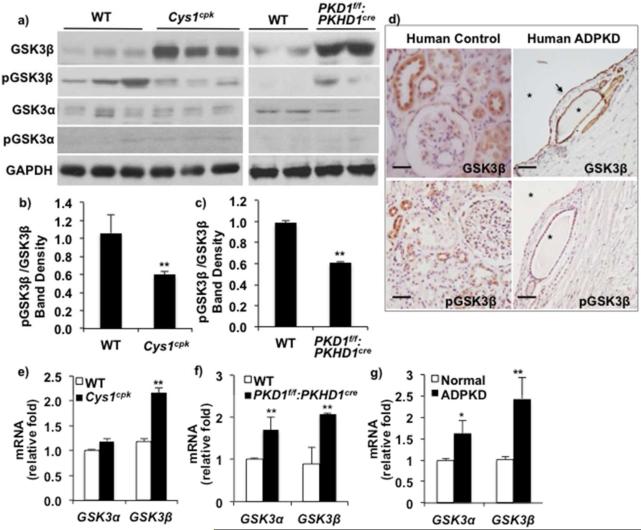
To determine the role of GSK3 in PKD, we examined GSK3α and GSK3β expression in cystic mouse and human kidneys. In Cys1cpk mice, cysts develop during late embryogenesis and expand rapidly resulting in death around postnatal day-21 (P21) while in PKD1f/f:PKHD1cremice, renal cysts appear by P12-P14 and death occurs by P40. Renal GSK3β protein levels were significantly high in Cys1cpk mice by P14 and in PKD1f/f:PKHD1cre mice by P21, compared to their wild type mice (WT) littermates (Fig-1a). Unlike GSK3β, GSK3α and pGSK3α levels showed no significant change in both PKD models compared to WT mice (Fig-1a). Renal GSK3β protein levels in Cys1cpk mice were unchanged at P7 (data not shown). GSK3β activity was also increased in Cys1cpk and PKD1f/f:PKHD1cre mice, indicated by the reduced inactive pGSK3β (phospho-GSK3β-serine 9) to total GSK3β ratio (Fig-1a,b,c). Similarly in human ADPKD kidneys, immunostaining for pGSK3β was low or absent in cyst lining epithelia in spite of high GSK3β expression in cyst lining epithelium (Fig-1d). In Cys1cpk mice, GSK3β mRNA levels were significantly higher while GSK3α mRNA levels were unchanged compared to WTmice (Fig-1e). In PKD1f/f:PKHD1cre mouse and human ADPKD kidneys, mRNA levels of GSK3β and to a lesser extent, GSK3α were increased compared to WT mouse or control human kidneys respectively (Fig-1f, g). Since GSK3 isoforms are known to be regulated at the level of their activity rather than total protein 28, this aberrant renal GSK3 expression in PKD is a novel finding in renal pathophysiology.
Fig 1. Renal GSK3β expression is upregulated in PKD.
(a) Western blot analysis shows increased renal GSK3β in Cys1cpk (P14) and PKD1f/f:PKHD1cre mice (P21) compared to WT littermates. (b) Ratio of inactive pGSK3β-Serine 9 to total GSK3β is decreased in Cys1cpk and (c) PKD1f/f:PKHD1cre mice. (d) Immunostaining shows high GSK3β levels (arrow) and low pGSKβ levels in cyst-lining epithelium in human ADPKD kidney. (Star indicates cyst, scale bar=25μm) (e) qRT-PCR shows increased GSK3β mRNA relative to 18S mRNA in Cys1cpk mice, (f) PKD1f/f:PKHD1cre mice and (g) human ADPKD kidney. *P<0.05, **P<0.01 compared to WT mice, n=6 mice/group.
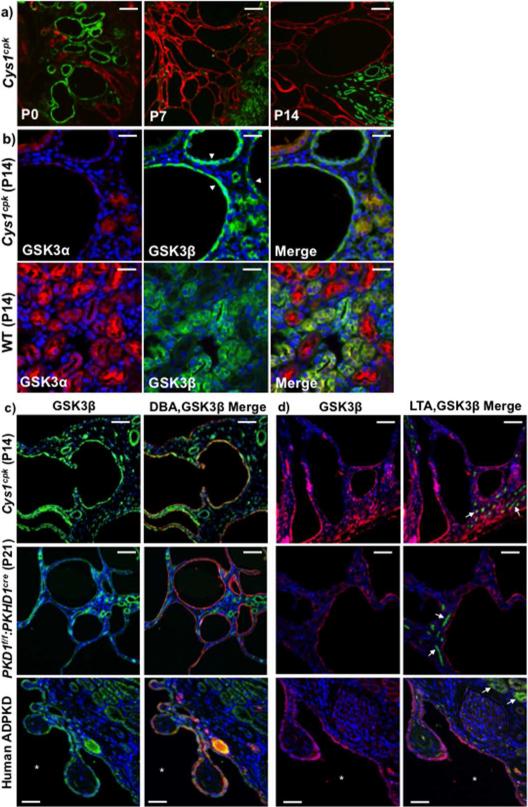
In Cys1cpk mice, renal cysts at P0 were mostly of proximal tubule origin (identified by Lotus tetragonolobus agglutinin, green staining), while the enlarged cysts at P7 and P14 were of collecting duct origin (identified by Dolichos biflorous, red staining) (Fig-2a). At P14, intense staining for GSK3β was observed in the cyst-lining cells in Cys1cpk mice, while GSK3α expression was restricted mostly to smaller cysts or non-cystic tubules (Fig-2b). In WT littermates, ubiquitous staining for GSK3α and GSK3β was observed in renal tubules (Fig-2b). GSK3β staining was observed in all cyst lining epithelia in Cys1cpk, PKD1f/f:PKHD1cre and human ADPKD kidneys and most of the enlarged cysts were of collecting duct origin and not proximal tubular (Fig-2c,d). The location of GSK3β in cyst-lining epithelium and its higher expression levels in cystic kidneys of both ADPKD and ARPKD mouse models as well as humans suggest that GSK3β could be mechanistically involved in abnormal cell signaling and cyst enlargement in PKD.
Fig 2. GSK3β is expressed in cyst lining epithelium.
(a) Cys1cpk kidneys show LTA (green) staining cysts at P0 and DBA (red) staining cysts at P7 and P14. Scale bar=50μm. (b) At P14, Cys1cpk kidneys show GSK3β (green) staining in cyst-lining epithelium (white arrow heads) and GSK3α (red) in non-cystic tubules. In wild type mice show ubiquitous staining for GSK3α and GSK3β in renal tubules. Scale bar=25μm (c) Immunofluorescence staining for GSK3β (green) and DBA (red, representing collecting ducts) and (d) GSK3β (red) and LTA (green, representing proximal tubules-white arrows) in Cys1cpk, PKD1f/f:PKHD1cre mice and human PKD kidneys. DAPI (blue) staining indicates nucleus in all figures. Scale bar=50μm.
Systemic GSK3 inhibition reduced cysts and preserved renal function in PKD
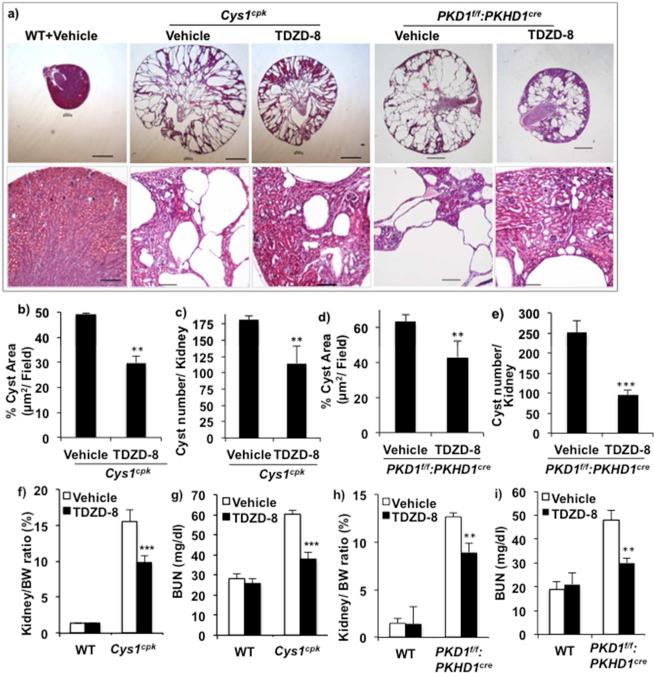
To determine the pathophysiological role of GSK3 in PKD, we tested the effect of pharmacological inhibition of GSK3 on cyst development in Cys1cpk and PKD1f/f:PKHD1cre mice. TDZD-8 29, 30, is a highly selective, ATP non-competitive inhibitor of GSK3 that others and we have effectively used in mice 29, 31. TDZD-8 was administered to Cys1cpk and WTlittermates from P3 until P14 and to PKD1f/f:PKHD1cre and WT littermates from P10 until P21. TDZD-8 treatment in both Cys1cpk and PKD1f/f:PKHD1cre mice significantly reduced overall kidney size and preserved more intact parenchyma (Fig-3a). TDZD-8 treatment also reduced renal cyst area and cyst number in Cys1cpk mice (Fig-3b,c) as well as in PKD1f/f:PKHD1cre mice (Fig-3d,e) compared to vehicle treatment.
Fig 3.
Systemic inhibition of GSK3 slows cyst expansion and progression of PKD in Cys1cpk and PKD1f/f:PKHD1cre mice. Cys1cpk mice, PKD1f/f:PKHD1cre mice and their WT littermates were treated with vehicle or TDZD-8. Analysis of P14 tissue in Cys1cpk mice and P21 tissue in PKD1f/f:PKHD1cre mice are shown. (a) TDZD-8 treated Cys1cpk and PKD1f/f:PKHD1cre mice had smaller kidneys with more intact parenchyma. Scale bar=1mm, Magnified images, Scale bar=100μm (b) cyst area and (c) cyst number in Cys1cpk mice (n=6/group). (d) cyst area and (e) cyst number in PKD1f/f:PKHD1cre mice (n=6/group). (f) Kidney to body weight ratio and (g) blood urea nitrogen levels in Cys1cpk mice (n=10/ group). (h) Kidney to body weight ratio and (i) blood urea nitrogen levels in PKD1f/f:PKHD1cre mice (n=10/ group). **P<0.01, ***P<0.001, compared to vehicle treated mice.
TDZD-8 treatment reduced kidney to body weight ratio by 37% and blood urea nitrogen (BUN) levels by 36% (Fig-3f,g) in Cys1cpk mice. Similarly in PKD1f/f:PKHD1cre mice, TDZD-8 treatment reduced kidney to body weight ratio by 28% (Fig-3h) and BUN by 37% (Fig-3i), compared to vehicle treatment. TDZD-8 treated Cys1cpk and WT mice did not show a significant difference in body weight (Supplemental-1). These results suggest that GSK3 inhibition could reduce cyst development and expansion in Cys1cpk and PKD1f/f:PKHD1cre mice.
Collecting duct specific gene knockout of GSK3β slowed PKD and increased life span
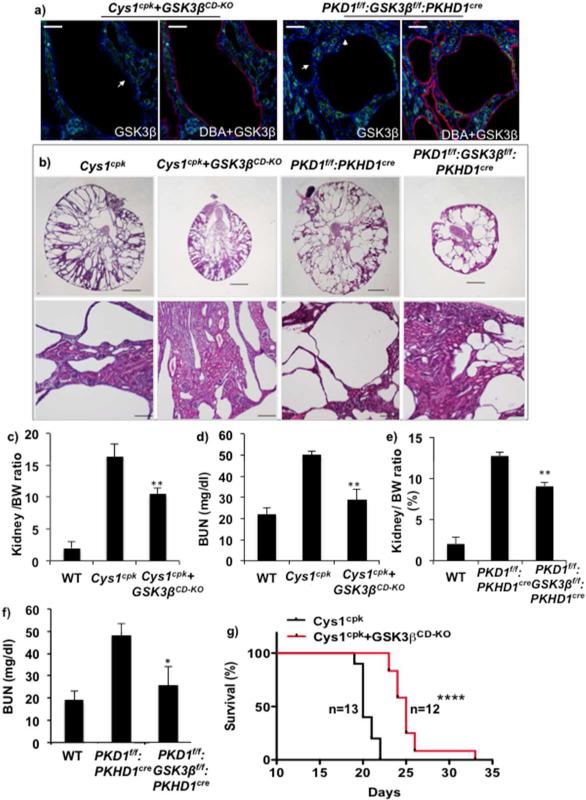
To evaluate further the isoform-selective and tissue specific role of GSK3β on cyst expansion, we generated Cys1cpk and PKD1f/f:PKHD1cre mice lacking GSK3β in renal collecting ducts (Cys1cpk+GSK3βCD-KO and PKD1f/f:GSK3:PKHD1cre). Collecting duct specific gene deletion of GSK3β was achieved using HoxB7cre in Cys1cpk+GSK3βCD-KO mice and PKHD1cre inPKD1f/f:GSK3:PKHD1cre mice. Immunostaining of kidney sections showed no staining for GSKβ in collecting duct cysts of Cys1cpk+GSK3βCD-KO and PKD1f/f:GSK3:PKHD1cre mice (Fig-4a), while GSK3β staining was observed in other tubule segments (Supplemental-2). Proximal tubular cysts were observed in Cys1cpk+GSK3βCD-KO and not PKD1f/f:GSK3:PKHD1cre mice (Supplemental-2). In comparison to Cys1cpk kidneys, the Cys1cpk+GSK3βCD-KO kidneys had more intact parenchyma and were less cystic (Fig-4b). The kidney to body weight ratio and BUN levels were also lower in Cys1cpk+GSK3βCD-KO mice compared to Cys1cpk mice (Fig-4c,d). Similarly in PKD1f/f:PKHD1cre mice, collecting duct specific gene knockout of GSK3β also significantly reduced overall kidney size (Fig-4b), kidney to body weight ratio and BUN (Fig-4e,f). Consistent with their slower cyst progression, the life span of the Cys1cpk+GSK3βCD-KO mice increased by 25% compared to Cys1cpk mice (Fig-4g). This suggests that GSK3β in collecting ducts play an important role in cyst development in the Cys1cpk and PKD1f/f:PKHD1cre mice.
Fig 4.
Renal collecting duct specific GSK3β gene knockout reduces PKD in Cys1cpk and PKD1f/f:PKHD1cre mice. (a) Cys1cpk+GSK3βCD-KO and PKD1f/f:GSK3βf/f:PKHD1cre mice lack GSK3β (green) in DBA (red) staining collecting duct cells (white arrows). DAPI (blue) staining indicates nucleus. Scale bar=50μm (b) Cys1cpk+GSK3βCD-KO and PKD1f/f:GSK3βf/f:PKHD1cre have smaller kidneys with more intact parenchyma. Scale bar=1mm, Magnified images, Scale bar=100μm (c) Kidney to body weight ratio and (d) blood urea nitrogen levels in Cys1cpk mice (n=8/ group). (e) Kidney to body weight ratio and (f) blood urea nitrogen levels in PKD1f/f:PKHD1cre mice (n=8/ group). (g) Survival curve shows median survival to be 25 days for Cys1cpk+GSK3βCD-KO mice and 20 days for Cys1cpk mice. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ****P<0.0001, compared to Cys1cpk or PKD1f/f:PKHD1cre mice.
GSK3 inhibition reduced proliferation of cyst lining epithelial cells
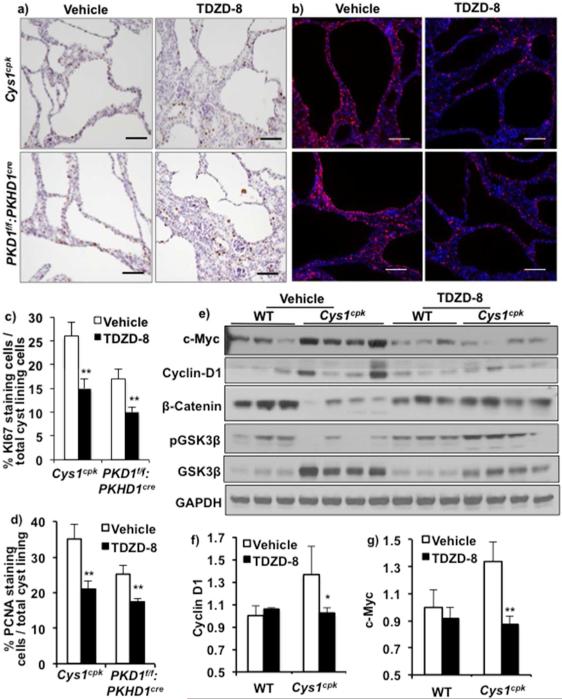
In order to examine the mechanism by which GSK3 regulates renal cyst expansion, we determined the effect of GSK3β inhibition on cell proliferation, a central contributor to cyst enlargement in PKD, and a cellular process regulated by GSK3. In vehicle treated Cys1cpk and PKD1f/f:PKHD1cre mice, immunostaining for KI-67 and PCNA revealed a large number of dividing cells (Fig-5a,b). TDZD-8 treatment significantly reduced the number of dividing cells in both Cys1cpk and PKD1f/f:PKHD1cre mouse kidneys (Fig-5a,b,c,d).
Fig 5.
GSK3 inhibition reduced cell proliferation. (a) Cell proliferation measured by KI67 (brown) or (b) PCNA (pink) staining shows less proliferating cells in the cyst-lining epithelium of TDZD-8 treated Cys1cpk (P14) and PKD1f/f:PKHD1cre (P21) mice. DAPI (blue) staining indicates nucleus. (Scale bar=50μm). (c) Quantification of cyst-lining cells that stain for KI67 or (d) PCNA (n=6 mice/group). Data expressed as % dividing cells / total cyst lining cells. (e) Western blot analysis shows increase in c-Myc and Cyclin-D1 levels in Cys1cpk compared to WT. TDZD-8 treatment reduces c-Myc and Cyclin-D1 in Cys1cpk kidneys. (f) relative band density measurement for c-Myc and (g) Cyclin D1. *P<0.05, **P<0.01.
A variety of pro-proliferative transcription factors/co-activators and cell cycle regulators such as β-catenin, c-Myc and Cyclin-D1 are important for cyst enlargement in PKD 23, 32-35. c-Myc and Cyclin-D1 levels were significantly increased in Cys1cpk mice when compared to WT mice (Fig-5 e,f,g, Supplemental-3). Beta-catenin level on the other hand was significantly reduced in Cys1cpk kidneys compared to WT kidney and β-catenin immunostaining was not associated with cystic epithelium (Fig-5c, Supplemental-3). The protein and mRNA levels of β-catenin was also found to be reduced by 40-50% in the Cys1cpk and PKD1f/f:PKHD1cre mice respectively (Supplemental-4,5,6,7), suggesting that β-catenin may not be critical for proliferation of the cyst lining epithelium in these mice.TDZD-8 treatment reduced Cyclin-D1 and (Fig-5e,f, Supplemental-8) c-Myc (Fig-5e,g) levels in Cys1cpk mice, while β-catenin levels increased (Fig-5e). The reduced c-Myc and Cyclin-D1 levels in Cys1cpk mice support the reduced cell proliferation indicated by PCNA staining observed in these mice. Thus, GSK3 inhibition could reduce proliferation of cyst lining epithelial cells and thereby cyst expansion.
GSK3 inhibition reduced renal cAMP and activation of ERK1/2
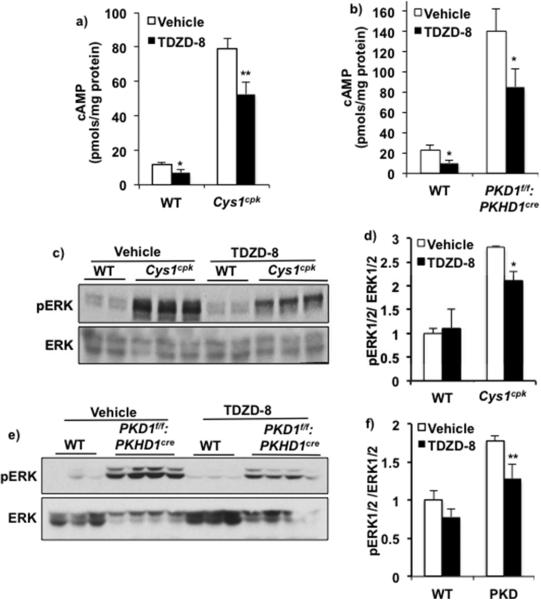
Since cAMP stimulates proliferation of cyst-lining epithelial cells 36, we determined the effect of GSK3 inhibition on renal cAMP. In Cys1cpk and PKD1f/f:PKHD1cre mice, renal cAMP levels were 7 and 6-folds higher compared to their respective WT littermates. TDZD-8 treatment reduced renal cAMP by 33% in Cys1cpk mice and 39% in PKD1f/f:PKHD1cre mice when compared to their vehicle treated controls (Fig-6a,b).
Fig 6.
GSK3 inhibition reduced renal cAMP. TDZD-8 treatment reduced renal cAMP concentration in (a) Cys1cpk and (b) PKD1f/f:PKHD1cre mice compared to vehicle treated mice. n=7 mouse kidneys/group. TDZD-8 treatment also reduced pERK to ERK ratio in (c,d) Cys1cpk and (e,f) PKD1f/f:PKHD1cre mice compared to vehicle treated mice. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, TDZD-8 vs Vehicle treated.
Cyclic AMP mediated activation of B-Raf/ERK/MAPK pathway is known to increase cell proliferation in cultured PKD cells 37 and regulate c-Myc and Cyclin-D1 expression levels 38. In Cys1cpk and PKD1f/f:PKHD1cre mouse kidneys, the pERK levels were significantly higher than in WT littermates (Fig-6c,d,e,f). Treatment with TDZD-8 significantly reduced pERK/ERK ratio in both models (Fig-6c,d,e,f). The reduced cAMP and ERK activation in the TDZD-8 treated PKD mice are consistent with their reduced c-Myc and Cyclin-D1 levels and support the reduced cell proliferation indicated by PCNA staining observed in these mice. Thus, GSK3 is important for cAMP-mediated proliferation by cyst lining epithelial cells in PKD and its inactivation can slow cAMP induced cyst expansion in mouse models of PKD.
DISCUSSION
The current studies demonstrate a novel functional role of GSK3β in renal cyst development and progression of PKD. Our conclusions are based on the key observations that, 1) GSK3β expression is increased and associated with cyst lining epithelium in ARPKD and ADPKD mouse models and human ADPKD kidney, and 2) pharmacological inhibition or collecting duct specific gene deletion of GSK3β protects renal structure and function and slows cyst expansion in Cys1cpk and PKD1f/f:PKHD1cre mice. Examination of mechanism demonstrated that GSK3β inactivation was associated with reduced intracellular cAMP generation and cell proliferation. GSK3 inhibition suppressed ERK pathway activation, and reduced c-Myc and Cyclin-D1 levels, resulting in reduced cell proliferation. Overall, these studies revealed a previously undescribed role of GSK3 in the pathogenesis of cyst expansion.
GSK3 is an important regulatory component of fundamental processes including epithelial cell differentiation, polarity and proliferation 39. It is known to be ubiquitously expressed and constitutively active in the absence of external stimuli 11, 12. Since WNT and growth factor mediated signaling which inhibit GSK3 12 are active in PKD 32, 40, it could be assumed that GSK3β activity is suppressed in PKD. On the contrary, the current studies not only found an increase in GSK3β activity in cystic kidneys, but also a significant increase in its expression. It is also significant that GSK3β expression was found to be especially high in collecting ducts, which respond to AVP, undergo proliferation, secrete fluid and are the primary source of cysts in PKD 9, 41, 42. Thus GSK3β could have a pathological role in renal cyst expansion.
Evidence implicating GSK3β in the pathogenesis of PKD was provided by our studies in which treatment with a highly specific inhibitor of GSK3 or collecting duct specific gene deletion of GSK3β slowed the progression of cyst expansion. This observation can be said to be unexpected, because lithium treatment is thought to be associated with renal cyst development. Renal cysts have been observed in patients on long-term lithium therapy with known or unknown familial history of PKD 43-45. Similarly, postnatal exposure to LiCl through mother's milk produced renal collecting duct microcysts in male rats 46, although adult rats treated with LiCl for over 40 days showed increased cell proliferation but no cysts 47, 48. Hence it is not clear if inhibition of GSK3, one among the many activities of lithium, is the mechanism for cyst formation. Moreover, the renal collecting duct specific GSK3ß knockout mice used in the current studies and described earlier 19 do not show any renal cysts for up to two years of age. In the current study, the reduction in kidney weight / body weight ratio in TDZD-8 treated Cys1cpk mice (37%) and PKD1f/f:PKHD1cre mice (28%) are comparable to other recent preclinical studies using PP242 (mTOR kinase inhibitor) 49, R-roscovitin (Cyclin Dependent Kinase inhibitor) 50, STA-2842 (Heat shock protein 90 inhibitor) 51, Tolvaptan+Rapamycin 52 or Tolvaptan+Pasireotide 53, to name a few.
Inhibition or gene deletion of GSK3 slowed the progression of cyst expansion by reducing proliferation of cyst lining epithelial cells. Proliferation of the cystic epithelium is critical for the development and enlargement of renal cysts 25, 54, 55 and progressive cyst enlargement in both ADPKD and ARPKD involve increased proliferation of cyst-lining epithelial cells 36. Hence various growth factors and their receptors, oncogenes and cell cycle regulatory proteins that regulate cell proliferation have been studied as possible targets for the treatment of PKD 56. β-catenin, a crucial component of canonical WNT-signaling is thought to be important in PKD 35, 57, although no increase in β-catenin/TCF/Lef1 activity has been detected in renal cyst lining epithelial cells 35, 58-61. In the current study, β-catenin was significantly reduced in both Cys1cpk and PKD1f/f:PKHD1cre mice, compared to wild type mice (Supplemental data 3-7). β-catenin is a substrate of GSK3β, which negatively regulates its cytoplasmic accumulation 39. Hence the decreased β-catenin level in Cys1cpk mice is consistent with their increased GSK3β activity and increased β-catenin after TDZD-8 treatment corresponds to the reduced GSK3β activity. Alternately, it is also possible that β-catenin expression is independent of GSK3β in the PKD kidney, because in GSK3β global knock out mice, β-catenin levels did not increase 62. Similarly in colon cancer, both β-catenin as well as GSK3β are up regulated and involved in pathogenesis 63.
Regulation of cell proliferation is a basic function of GSK3, although its role is context dependent. GSK3 inhibition enhances proliferation of embryonic and hematopoietic stem cells 64, 65, embryonic cardiomyocytes 66, cancer cells 13 and accelerates regeneration of proximal tubular cells following acute kidney injury 29. However, GSK3 inhibition can also reduce cell proliferation and tumor progression in ovarian, myeloma, leukemia, pancreatic, colorectal and hepatic cancers by inducing cell cycle arrest and reducing mitogenic factors 67-72.
Our results demonstrate that GSK3 could regulate cell proliferation in PKD by a cAMP-dependent mechanism. GSK3 inhibition by TDZD-8 reduced cAMP levels in both Cys1cpk and PKD1f/f:PKHD1cre mouse models. Cyclic AMP mediated activation of B-Raf/ERK pathway increases cell proliferation in cultured PKD cells 37. In-vivo, activation of the B-Raf/ERK pathway has been observed in rodent models of PKD, but its role in proliferation of cyst lining epithelial cells has been inconclusive 26, 73. ERK/MAPK activity can induce expression of c-Myc and Cyclin-D1 38, which are important factors for proliferation in PKD 23, 32-35. In the current studies, renal ERK activity, Cyclin D1 and c-Myc levels were high in the Cys1cpk mice and TDZD-8 treatment significantly reduced their levels. C-Myc and Cyclin-D1 are primary molecular targets of GSK3β for phosphorylation-dependent protein degradation in the ubiquitin–proteasome system 39. However, in normal WT mice, TDZD-8 treatment did not increase C-Myc and Cyclin-D1 levels (fig-5). Hence, the reduced c-Myc and Cyclin-D1 levels in Cys1cpk+TDZD-8 mice are more consistent with observations in cancer cells in which inhibition of GSK3 can reduce c-Myc and Cyclin-D1 levels and suppress cell proliferation 68, 70, 71.
In summary, renal GSK3β expression is up-regulated in PKD and plays an important role in cAMP-mediated proliferation and anion secretion by cyst lining epithelial cells. Pharmacological inhibition of GSK3 or collecting duct specific gene deletion of GSK3β reduced cyst volume and delayed cyst progression. The results thus demonstrate a novel pathological role of GSK3β in promoting renal cyst expansion. Use of a GSK3 inhibitor may be therapeutically useful to reduce cyst expansion and preserve renal function in PKD.
METHODS
Mouse Studies
The Cys1cpk/+ mice were originally purchased from the Jackson Laboratory (Bar Harbor, ME). Mouse pups were genotyped on postnatal day 2 (P2). For TDZD-8 treatment, WT and Cys1cpk mouse littermates were treated with TDZD-8 (5mg/kg body weight) or vehicle (5% DMSO in saline) from P3 until P14 by single, daily, intra-peritoneal injections. This dose of TDZD-8 was selected based on results from our pilot study and was found to be better than a dose of 1mg/Kg bodyweight in reducing kidney to bodyweight ratio in Cys1cpk mice. Similarly, PKD1f/f:PKHDcre 26 mice were injected with TDZD-8 from P10 until P21.
To generate Cys1cpk mice lacking GSK3β in renal collecting ducts, the Cys1cpk mice were bred with GSK3βf/f,HoxB7cre mice19. Mouse pups of the following genotypes-GSK3βf/f (WT), Cys1cpk+GSK3βf/f,HoxB7cre (Cys1cpk+GSK3βCD-KO), and Cys1cpk were mice were used for the studies. Similarly, PKD1f/f:PKHD1cre mice were bred with GSK3βf/f mice to generate PKD1f/f:PKHD1cre mice lacking GSK3β in the collecting duct. PKD1f/f (WT), PKD1f/f:GSK3βf/f:PKHD1cre and PKD1f/f:PKHD1cre mice were used for the studies. Body weight was measured daily. At sacrifice, blood and urine samples were collected, and kidneys were weighed and flash frozen for protein and RNA analysis or fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde for histological examination. All mouse study protocols were approved by the University of Kansas Medical Center Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee.
Quantification of Cysts and Cell Proliferation
The kidney (left and right kidneys) / body weight % and cyst area were used as indicators of cyst progression. Cyst surface area was measured from 10 random fields (x100 magnification) from hematoxylin and eosin stained tissue sections (5μLm) of paraffin-embedded kidneys. Images were obtained with a dissection microscope connected to a digital camera (Leica Microsystems, Buffalo Grove, IL). A blinded observer determined cyst number and cystic cross-sectional SA per kidney section using LUZEX FS software (Kideko CO. LTD, Tokyo, Japan).
For quantification of cell proliferation, tissue sections were immunostained for KI-67 and PCNA, and the cells stained for KI-67 or PCNA and total number of cells in each cyst-lining epithelium were counted from 10 random fields (x200 magnification). A reviewer, blinded to the identity of the mouse kidney, performed measurements.
Blood Urea Nitrogen (BUN) Levels
Blood was collected at sacrifice and immediately centrifuged at 2,000xg for serum collection. BUN levels were measured using a QuantiChrom Urea Assay Kit from BioAssay Systems (Hayward, CA, USA).
Western Blot
Mouse kidneys were homogenized in RIPA buffer and loaded onto 12% SDS-PAGE gels and transferred to nitrocellulose membranes and blocked with 5% milk in TBST. Membranes were probed with primary antibody followed by TBST washes and horseradish peroxidase secondary antibody application. The following antibodies were used, GSK3α, GSK3β, pGSK3α, pGSK3β, β-Catenin, Cyclin-D1 (Cell Signaling Technology, Inc., MA, USA), c-Myc, GAPDH, pERK and ERK (Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Inc. TX, USA). Secondary antibodies were purchased from Dako (CA, USA) and ECL reagent from PerkinElmer (Netherlands).
Immunohistochemistry/Immunofluorescence (IHC/IF)
Fixed kidney tissues were embedded in paraffin. For both IHC and IF, sections were deparaffinized, rehydrated, washed in PBS containing 0.1% Tween 20 (PBST) and blocked in 10% normal goat serum. The following primary antibodies were applied to sections and incubated at 4°C overnight: β-Catenin, cyclin D1, KI-67 and pGSK3β (Cell Signaling Technology, Inc., MA, USA), GSKα (Sigma Aldrich, MO, USA), GSK3β (Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Inc. TX, USA), PCNA (Dako, CA, USA), DBA and LTA (Vector Laboratories, CA, USA). For IHC, slides were blocked with Avidin/Biotin (Invitrogen), and then biotinylated goat anti-rabbit IgG or anti-mouse IgG (Invitrogen, NY, USA) secondary antibodies were applied, followed by incubation with Streptavidin HRP conjugate (Invitrogen, NY, USA). Finally slides were developed with DAB (Vector Laboratories) and counterstained with Harris Haematoxylin, dehydrated, and mounted with Permount (Fisher Scientific). For IF, after incubation with primary antibody, goat anti-Rabbit IgG fluor, Goat anti-mouse IgG Texas red (Invitrogen, NY, USA), or Goat anti-chicken IgG Alexa 555 (Sigma Aldrich, MO,USA) secondary antibodies were applied, and following incubation, washed, stained with DAPI and mounted with Flour-G (Invitrogen, NY, USA). All images were captured using a Nikon 80i microscope in KUMC imaging center.
Quantitative Real-Time PCR
Quantitative real-time PCR on RNA isolated from whole kidney samples were carried out as described before 19. The 18S, GSK3α and GSK3β probes were obtained from Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA, USA.
Measurement of cAMP
A cAMP Enzyme Immunoassay Kit (Direct) from Sigma-Aldrich (MO,USA) was used. The kidneys were ground to a fine powder under liquid nitrogen and homogenized in 10 volumes of ice cold 0.1% HCl, centrifuged at 600xg and cAMP levels measured following the manufacturer's protocols.
Human Tissue
Human control and ADPKD kidney tissues were obtained from the National disease research interchange and were approved by the institutional review board.
Statistics
Values are expressed as mean ± standard error for all bar charts, except for band density measurements of western blots, which is expressed as mean ± standard deviation. Data was analyzed by two-tailed unpaired t-test with Welch's correction and F test to compare variances or One-Way Analysis of Variance followed by Tukey's multiple comparison test and Bartlett's test for equal variance using Graphpad Prism software (Version 5.0d). A probability level of 0.05 (P ≤ 0.05) was considered significant. To compare survival curves, Log-rank (Mantel-cox) Test and Gehan-Breslow-Wilcoxon Test were used.
Supplementary Material
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
We thank Drs. Alan Yu, James Calvet, Robin Masser and Jared Grantham for helpful discussions, Dr. Peter Igarashi for PKHD1CRE mice, Dr. Stefan Somlo and the Yale PKD Center (P30 DK090744) for PKD1f/f mice. This study was supported by NIH R01-DK083525 to Rao.
Footnotes
Disclosures: The authors declare that no conflict of interest exists.
REFERENCES
- 1.Grantham JJ, Mulamalla S, Swenson-Fields KI. Why kidneys fail in autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2011;7:556–566. doi: 10.1038/nrneph.2011.109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Choi YH, Suzuki A, Hajarnis S, et al. Polycystin-2 and phosphodiesterase 4C are components of a ciliary A-kinase anchoring protein complex that is disrupted in cystic kidney diseases. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2011;108:10679–10684. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1016214108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Fonseca JM, Bastos AP, Amaral AG, et al. Renal cyst growth is the main determinant for hypertension and concentrating deficit in Pkd1-deficient mice. Kidney Intl. 2014;85:1137–1150. doi: 10.1038/ki.2013.501. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Gattone VH, 2nd, Wang X, Harris PC, et al. Inhibition of renal cystic disease development and progression by a vasopressin V2 receptor antagonist. Nat Med. 2003;9:1323–1326. doi: 10.1038/nm935. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Torres VE. Cyclic AMP, at the hub of the cystic cycle. Kidney Intl. 2004;66:1283–1285. doi: 10.1111/j.1523-1755.2004.00945.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Torres VE, Harris PC. Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease: the last 3 years. Kidney Intl. 2009;76:149–168. doi: 10.1038/ki.2009.128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Wallace DP. Cyclic AMP-mediated cyst expansion. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2011;1812:1291–1300. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2010.11.005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Yamaguchi T, Nagao S, Kasahara M, et al. Renal accumulation and excretion of cyclic adenosine monophosphate in a murine model of slowly progressive polycystic kidney disease. Am J Kidney Dis. 1997;30:703–709. doi: 10.1016/s0272-6386(97)90496-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Torres VE, Wang X, Qian Q, et al. Effective treatment of an orthologous model of autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. Nat Med. 2004;10:363–364. doi: 10.1038/nm1004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Wang X, Wu Y, Ward CJ, et al. Vasopressin directly regulates cyst growth in polycystic kidney disease. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2008;19:102–108. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2007060688. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Harwood AJ. Regulation of GSK-3: a cellular multiprocessor. Cell. 2001;105:821–824. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(01)00412-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Kaidanovich-Beilin O, Woodgett JR. GSK-3: Functional Insights from cell biology and animal models. Front Mol Neurosci. 2011;4:40. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2011.00040. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Mishra R. Glycogen synthase kinase 3 beta: can it be a target for oral cancer. Mol Cancer. 2010;9:144. doi: 10.1186/1476-4598-9-144. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Goldberg H, Clayman P, Skorecki K. Mechanism of Li inhibition of vasopressin-sensitive adenylate cyclase in cultured renal epithelial cells. Am J Physiol. 1988;255:F995–1002. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1988.255.5.F995. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Jackson BA, Edwards RM, Dousa TP. Lithium-induced polyuria: effect of lithium on adenylate cyclase and adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate phosphodiesterase in medullary ascending limb of Henle's loop and in medullary collecting tubules. Endocrinol. 1980;107:1693–1698. doi: 10.1210/endo-107-6-1693. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Mann L, Heldman E, Shaltiel G, et al. Lithium preferentially inhibits adenylyl cyclase V and VII isoforms. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2008;11:533–539. doi: 10.1017/S1461145707008395. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Yamaki M, Kusano E, Tetsuka T, et al. Cellular mechanism of lithium-induced nephrogenic diabetes insipidus in rats. Am J Physiol. 1991;261:F505–511. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1991.261.3.F505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Li Y, Shaw S, Kamsteeg EJ, et al. Development of lithium-induced nephrogenic diabetes insipidus is dissociated from adenylyl cyclase activity. JASN. 2006;17:1063–1072. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2005080884. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Rao R, Patel S, Hao C, et al. GSK3beta mediates renal response to vasopressin by modulating adenylate cyclase activity. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2010;21:428–437. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2009060672. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Alcalay NI, Sharma M, Vassmer D, et al. Acceleration of polycystic kidney disease progression in cpk mice carrying a deletion in the homeodomain protein Cux1. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2008;295:F1725–1734. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.90420.2008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Gattone VH, 2nd, MacNaughton KA, Kraybill AL. Murine autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease with multiorgan involvement induced by the cpk gene. Anat Rec. 1996;245:488–499. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-0185(199607)245:3<488::AID-AR5>3.0.CO;2-O. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Hou X, Mrug M, Yoder BK, et al. Cystin, a novel cilia-associated protein, is disrupted in the cpk mouse model of polycystic kidney disease. J Clin Invest. 2002;109:533–540. doi: 10.1172/JCI14099. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Cowley BD, Jr., Chadwick LJ, Grantham JJ, et al. Elevated proto-oncogene expression in polycystic kidneys of the C57BL/6J (cpk) mouse. J Am Soc Nephrol. 1991;1:1048–1053. doi: 10.1681/ASN.V181048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Gattone VH, 2nd, Maser RL, Tian C, et al. Developmental expression of urine concentration-associated genes and their altered expression in murine infantile-type polycystic kidney disease. Dev Genet. 1999;24:309–318. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1520-6408(1999)24:3/4<309::AID-DVG14>3.0.CO;2-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Karihaloo A, Koraishy F, Huen SC, et al. Macrophages promote cyst growth in polycystic kidney disease. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2011;22:1809–1814. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2011010084. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Shibazaki S, Yu Z, Nishio S, et al. Cyst formation and activation of the extracellular regulated kinase pathway after kidney specific inactivation of Pkd1. Hum Mol Genet. 2008;17:1505–1516. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddn039. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Zhou X, Fan LX, Sweeney WE, Jr., et al. Sirtuin 1 inhibition delays cyst formation in autosomal-dominant polycystic kidney disease. J Clin Invest. 2013;123:3084–3098. doi: 10.1172/JCI64401. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Medina M, Wandosell F. Deconstructing GSK-3: The fine regulation of its activity. Int J Alzheimers Dis. 2011;2011:479249. doi: 10.4061/2011/479249. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Howard C, Tao S, Yang HC, et al. Specific deletion of glycogen synthase kinase-3beta in the renal proximal tubule protects against acute nephrotoxic injury in mice. Kidney Intl. 2012;82:1000–1009. doi: 10.1038/ki.2012.239. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Martinez A, Alonso M, Castro A, et al. First non-ATP competitive glycogen synthase kinase 3 beta (GSK-3beta) inhibitors: thiadiazolidinones (TDZD) as potential drugs for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease. J Med Chem. 2002;45:1292–1299. doi: 10.1021/jm011020u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Beurel E, Kaidanovich-Beilin O, Yeh WI, et al. Regulation of Th1 cells and experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis by glycogen synthase kinase-3. J Immunol. 2013;190:5000–5011. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1203057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Gallagher AR, Germino GG, Somlo S. Molecular advances in autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. Adv Chronic Kidney Dis. 2010;17:118–130. doi: 10.1053/j.ackd.2010.01.002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Ricker JL, Mata JE, Iversen PL, et al. c-myc antisense oligonucleotide treatment ameliorates murine ARPKD. Kidney intl. 2002;61:S125–131. doi: 10.1046/j.1523-1755.2002.0610s1125.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Schwensen KG, Burgess JS, Graf NS, et al. Early cyst growth is associated with the increased nuclear expression of cyclin D1/Rb protein in an autosomal-recessive polycystic kidney disease rat model. Nephron Exp Nephrol. 2011;117:e93–103. doi: 10.1159/000320149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Wuebken A, Schmidt-Ott KM. WNT/beta-catenin signaling in polycystic kidney disease. Kidney intl. 2011;80:135–138. doi: 10.1038/ki.2011.87. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Grantham JJ. Regulation of cell proliferation and fluid secretion in theprogressive enlargement of renal cysts. Contrib Nephrol. 1992;97:15–22. doi: 10.1159/000421641. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Yamaguchi T, Wallace DP, Magenheimer BS, et al. Calcium restriction allows cAMP activation of the B-Raf/ERK pathway, switching cells to a cAMP-dependent growth-stimulated phenotype. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:40419–40430. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M405079200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Chang F, Steelman LS, Shelton JG, et al. Regulation of cell cycle progression and apoptosis by the Ras/Raf/MEK/ERK pathway (Review). Int J Oncol. 2003;22:469–480. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Woodgett JR, Force T. Unique and overlapping functions of GSK-3 isoforms in cellular differentiation, proliferation, and cardiovascular development. J Biol Chem. 2008;15:9643–7. doi: 10.1074/jbc.R800077200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Torres VE, Harris PC. Mechanisms of Disease: autosomal dominant and recessive polycystic kidney diseases. Nat Clin Pract Nephrol. 2006;2:40–55. doi: 10.1038/ncpneph0070. quiz 55. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Verani RR, Silva FG. Histogenesis of the renal cysts in adult (autosomal dominant) polycystic kidney disease: a histochemical study. Mod Pathol. 1988;1:457–463. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Wu G, D'Agati V, Cai Y, et al. Somatic inactivation of Pkd2 results in polycystic kidney disease. Cell. 1998;93:177–188. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)81570-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Atagun MI, Oral ET, Sevinc C. [Polycystic kidney disease in a patient using lithium chronically]. Turk Psikiyatri Derg. 2013;24:213–216. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Farres MT, Ronco P, Saadoun D, et al. Chronic lithium nephropathy: MR imaging for diagnosis. Radiology. 2003;229:570–574. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2292020758. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Shah S, Watnick T, Atta MG. Not all renal cysts are created equal. Lancet. 2010;376:1024. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(10)60956-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Kjaersgaard G, Madsen K, Marcussen N, et al. Tissue injury after lithium treatment in human and rat postnatal kidney involves glycogen synthase kinase-3beta-positive epithelium. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2012;302:F455–465. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00144.2011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Christensen BM, Kim YH, Kwon TH, et al. Lithium treatment induces a marked proliferation of primarily principal cells in rat kidney inner medullary collecting duct. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2006;291:F39–48. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00383.2005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Christensen BM, Marples D, Kim YH, et al. Changes in cellular composition of kidney collecting duct cells in rats with lithium-induced NDI. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2004;286:C952–964. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00266.2003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Ravichandran K, Zafar I, Ozkok A, et al. An mTOR kinase inhibitor slows disease progression in a rat model of polycystic kidney disease. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2014 doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfu296. [Epub ahead of print] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Bukanov NO, Moreno SE, Natoli TA, et al. CDK inhibitors R-roscovitine and S-CR8 effectively block renal and hepatic cystogenesis in an orthologous model of ADPKD. Cell Cycle. 2012;11:4040–4046. doi: 10.4161/cc.22375. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Seeger-Nukpezah T, Proia DA, Egleston BL, et al. Inhibiting the HSP90 chaperone slows cyst growth in a mouse model of autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2013;110:12786–12791. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1301904110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Sabbatini M, Russo L, Cappellaio F, et al. Effects of combined administration of rapamycin, tolvaptan, and AEZ-131 on the progression of polycystic disease in PCK rats. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2014;306:F1243–1250. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00694.2013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Hopp K, Hommerding CJ, Wang X, et al. Tolvaptan plus pasireotide shows enhanced efficacy in a PKD1 Model. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2014;11:4257–73. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2013121312. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Harris PC, Torres VE. Polycystic kidney disease. Annu Rev Med. 2009;60:321–337. doi: 10.1146/annurev.med.60.101707.125712. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Hopp K, Ward CJ, Hommerding CJ, et al. Functional polycystin-1 dosage governs autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease severity. J Clin Invest. 2012;122:4257–4273. doi: 10.1172/JCI64313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Chang MY, Ong AC. New treatments for autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2013;76:524–535. doi: 10.1111/bcp.12136. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Song X, Di Giovanni V, He N, et al. Systems biology of autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD): computational identification of gene expression pathways and integrated regulatory networks. Hum Mol Genet. 2009;18:2328–2343. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddp165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Iglesias DM, Hueber PA, Chu L, et al. Canonical WNT signaling during kidney development. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2007;293:F494–500. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00416.2006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Miller MM, Iglesias DM, Zhang Z, et al. T-cell factor/beta-catenin activity is suppressed in two different models of autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. Kidney intl. 2011;80:146–153. doi: 10.1038/ki.2011.56. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Schmidt-Ott KM, Masckauchan TN, Chen X, et al. beta-catenin/TCF/Lef controls a differentiation-associated transcriptional program in renal epithelial progenitors. Development. 2007;134:3177–3190. doi: 10.1242/dev.006544. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Sugiyama N, Tsukiyama T, Yamaguchi TP, et al. The canonical Wnt signaling pathway is not involved in renal cyst development in the kidneys of inv mutant mice. Kidney intl. 2011;79:957–965. doi: 10.1038/ki.2010.534. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Hoeflich KP, Luo J, Rubie EA, et al. Requirement for glycogen synthase kinase-3beta in cell survival and NF-kappaB activation. Nature. 2000;406:86–90. doi: 10.1038/35017574. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Ougolkov AV, Billadeau DD. Targeting GSK-3: a promising approach for cancer therapy? Future Oncol. 2006;2:91–100. doi: 10.2217/14796694.2.1.91. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Sato N, Meijer L, Skaltsounis L, et al. Maintenance of pluripotency in human and mouse embryonic stem cells through activation of Wnt signaling by a pharmacological GSK-3-specific inhibitor. Nat Med. 2004;10:55–63. doi: 10.1038/nm979. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Trowbridge JJ, Xenocostas A, Moon RT, et al. Glycogen synthase kinase-3 is an in vivo regulator of hematopoietic stem cell repopulation. Nat Med. 2006;12:89–98. doi: 10.1038/nm1339. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Kerkela R, Kockeritz L, Macaulay K, et al. Deletion of GSK-3beta in mice leads to hypertrophic cardiomyopathy secondary to cardiomyoblast hyperproliferation. J Clin Invest. 2008;118:3609–3618. doi: 10.1172/JCI36245. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Shakoori A, Mai W, Miyashita K, et al. Inhibition of GSK-3 beta activity attenuates proliferation of human colon cancer cells in rodents. Cancer Sci. 2007;98:1388–1393. doi: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2007.00545.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Ougolkov AV, Fernandez-Zapico ME, Savoy DN, et al. Glycogen synthase kinase-3beta participates in nuclear factor kappaB-mediated gene transcription and cell survival in pancreatic cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2005;65:2076–2081. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-04-3642. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Kunnimalaiyaan M, Vaccaro AM, Ndiaye MA, et al. Inactivation of glycogen synthase kinase-3beta, a downstream target of the raf-1 pathway, is associated with growth suppression in medullary thyroid cancer cells. Mol Cancer Ther. 2007;6:1151–1158. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-06-0665. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Kim HM, Kim CS, Lee JH, et al. CG0009, a novel glycogen synthase kinase 3 inhibitor, induces cell death through cyclin D1 depletion in breast cancer cells. PloS one. 2013;8:e60383. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0060383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Cao Q, Lu X, Feng YJ. Glycogen synthase kinase-3beta positively regulates the proliferation of human ovarian cancer cells. Cell Res. 2006;16:671–677. doi: 10.1038/sj.cr.7310078. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Bilim V, Ougolkov A, Yuuki K, et al. Glycogen synthase kinase-3: a new therapeutic target in renal cell carcinoma. Br J Cancer. 2009;101:2005–2014. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6605437. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Omori S, Hida M, Fujita H, et al. Extracellular signal-regulated kinase inhibition slows disease progression in mice with polycystic kidney disease. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2006;17:1604–1614. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2004090800. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.