Figure 8.
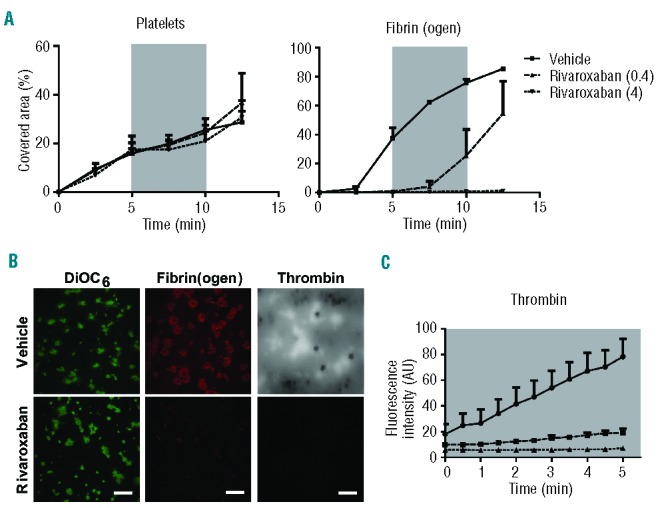
Effect of the FXa inhibitor rivaroxaban on the formation of platelet-fibrin thrombi. Human blood was pre-incubated with (A, B) OG488-fibrinogen or (B, C) thrombin substrate peptide Z-GGR-AMC and indicated concentrations of rivaroxaban (μg/mL), and then perfused under coagulant conditions over a collagen/tissue factor surface at a shear rate of 1000 s−1. After 5 min of flow, the shear rate was reduced to 150 s−1, as indicated by the gray areas. Flow was continued at 1000 s−1 after 5 min. (A) Microscopic images taken at indicated times were quantified for platelet deposition and fibrin(ogen) staining. (B) Representative fluorescence images of DiOC6-labeled thrombi, and fibrin(ogen) and accumulated AMC staining. (C) Fluorescence images of AMC fluorescence due to thrombin activity were quantified during 5 min of stasis after an initial 5 min of thrombus formation. Mean ± SEM; n = 3.
