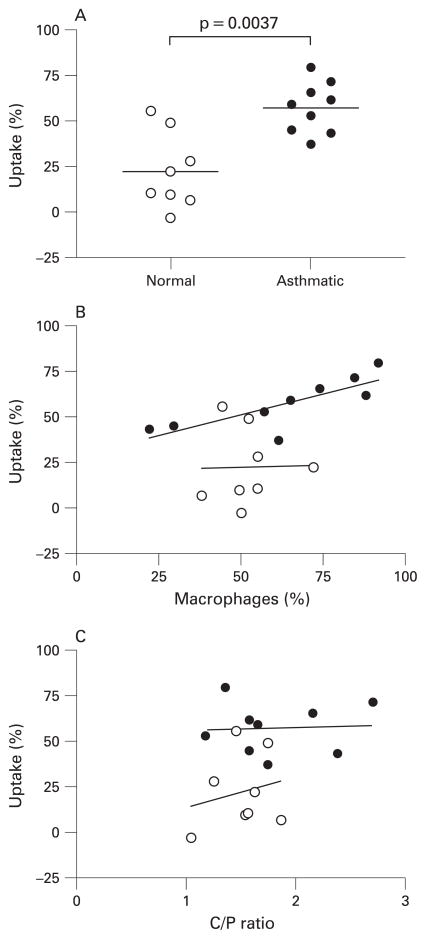
Figure 3.
(A) Corrected in vivo percentage uptake of radiolabelled sulfur colloid particles was significantly greater in subjects with asthma than in healthy subjects (57.2% (95% CI 46.5% to 67.9%) vs 22.3% (4.9% to 39.6%), p<0.01). (B) Uptake of sulfur colloid particles was significantly correlated with the percentage of mononuclear phagocytes in induced sputum for subjects with asthma (r = 0.8500, p<0.01) but not for normal healthy subjects. (C) In vivo particle uptake was not a function of the site of deposition as assessed by the lack of significant correlation with the central to peripheral (C/P) ratios for either normal subjects or those with asthma. Normal subjects (open circles, n = 8); subjects with asthma (closed circles, n = 9).