Figure 4.
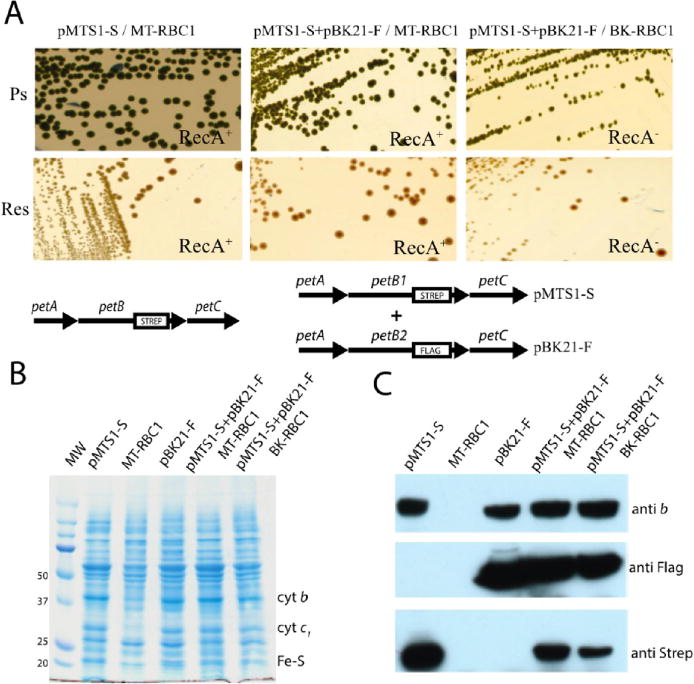
Growth and biochemical properties of strains carrying the two-plasmid system. (A) Photosynthetic (Ps) and respiration (Res) growth on enriched medium of wild-type R. capsulatus strain pMTS1/MT-RBC1 compared to that on MT-RBC1 (RecA+) and BK-RBC1 (RecA−) strains harboring the two-plasmid system (pMTS1-S + pBK21/MT-RBC1 and pMTS1-S + pBK21/BK-RBC1). In each case, the plasmids carrying the petABC operon are shown below the colony pictures. (B) SDS-PAGE and (C) immunoblot analyses of cytochrome bc1 subunits in a strain carrying the two-plasmid system. Chromatophore membranes (40 μg of total proteins per lane, from left to right) from pMTS1-S/MT-RBC1, MT-RBC1, pBK21-F/MT-RBC1, (pMTS1-S + pBK21)/MT-RBC1, and (pMTS1-S + pBK21)/BK-RBC1 were probed with polyclonal anti-cytochrome b and monoclonal anti-Flag and anti-Strep antibodies (see Materials and Methods).
