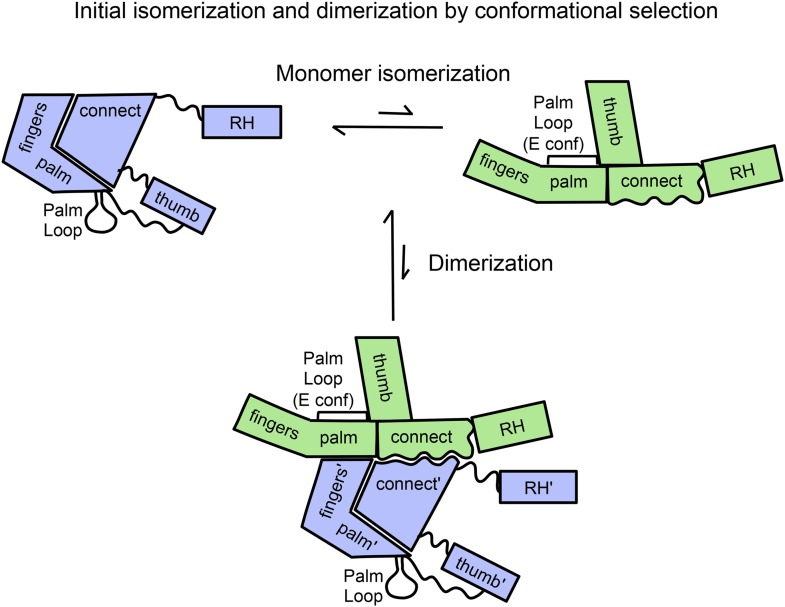
(
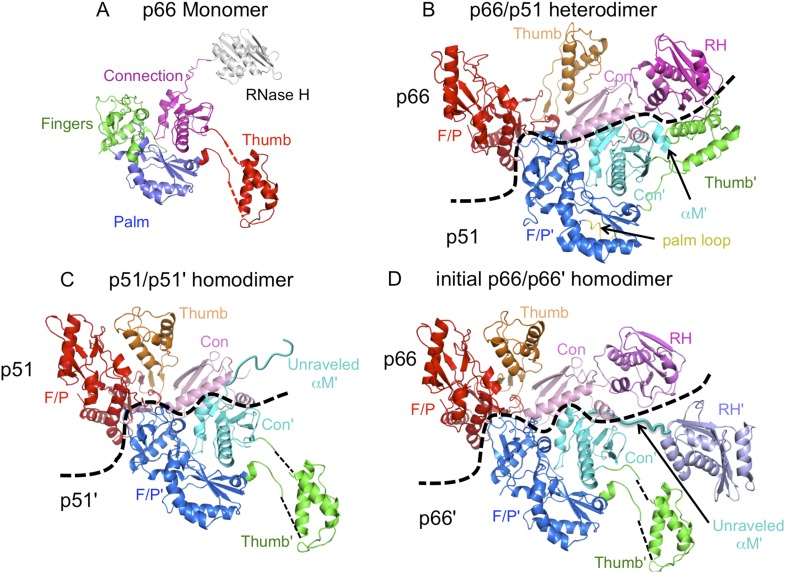
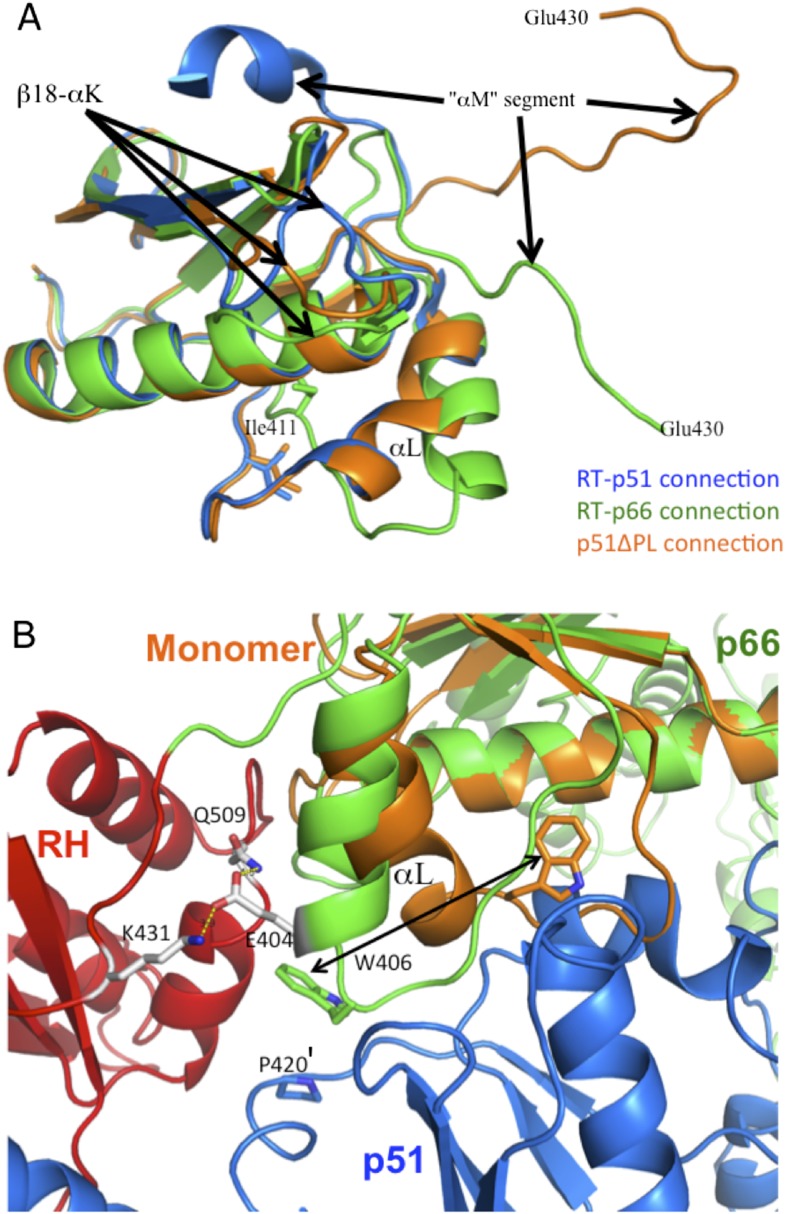
A) The monomer structure of p66 is based on the crystal structure of p51∆PL (pdb: 4KSE) and NMR data showing that it also contains a folded ribonuclease H (RH) domain linked by residues derived from an unfolded α-helix M. Domains are identified as fingers (green), palm (blue), thumb (red), connection (magenta), and RH (gray). (
B) Ribbon diagram of the RT heterodimer structure (pdb: 1S9E,
Das et al., 2004). For this panel, we used an NNRTI complex containing the palm loop, so the position of the p66 thumb domain differs from that in panels
C and
D. Color coding: p66 subunit: fingers/palm (red), thumb (orange), connection (pink), RH (magenta); p51 subunit: fingers/palm (blue), thumb (green), connection (cyan), palm loop (yellow). (
C) Ribbon representation of the p51/p51' homodimer derived from the p66/p51 heterodimer structure (pdb: 1DLO) by deletion of the p66 RH domain and replacement of the p51 subunit with the p51∆PL monomer. Color coding: p51 subunit: fingers/palm (red), thumb (orange), connection (pink); p51' subunit: fingers/palm (blue), thumb (green), connection (cyan). Note that α-helix M' is unfolded in the p51' subunit of the homodimer, as it is in the monomer. (
D) Initial p66/p66' homodimer structure based on NMR results and modeled from the p66/p51 heterodimer by replacing the p51 subunit with the p51∆PL monomer, and adding an additional, folded RH' domain. The disordered helix M' residues (418'–430') observed in the crystal structure of p51∆PL have been moved to avoid structural conflict with the p66 subunit and are linked to the supernumerary RH' domain (purple).